How to install air ducts: installation of flexible and rigid ventilation ducts
Modern offices, residential buildings, industrial buildings need to ensure normal air exchange and proper ventilation. To build an organized system, air ducts are installed.They are installed both inside and outside buildings. But a complete ventilation system is also needed at home, do you agree with this?
Knowing the principles of system design and the nuances of connecting air ducts in a certain sequence, it will be possible to create a functional ventilation network. But how to do it correctly? Let's figure it out together - this material discusses the types of air ducts used to create ventilation systems.
The features of installing flexible and rigid channels are also discussed in detail. For clarity, the article is supplemented with thematic photos, diagrams, and detailed video instructions for installing and fastening air ducts.
The content of the article:
Principle of air duct classification
Air ducts are a system of pipes adapted for the movement of air flow through it and arranged in a certain way.
They are used for installation of ventilation systems in houses, air duct networks form ventilation systems and air conditioning, with their help they connect industrial and kitchen hoods‚ used in air heating systems.
Based on their design, they are divided into round and rectangular. Round air ducts are ergonomic, air moves through them almost silently, vibration during operation is insignificant.
They connect air duct elements with a circular cross-section without the use of additional elements.
A rectangular duct section is preferable when the system needs to be made invisible by hiding it under the trim.
This and a satisfactory level of throughput determine their choice when installing a ventilation system in residential buildings. In addition, air ducts are rigid and flexible.

The former have a cross-section that can be either round or rectangular, while the latter have only a circle in cross-section. Their use is appropriate at branch points. Produce flexible air ducts (corrugated) mainly made of aluminum foil, polyester, although there are also products made of silicone, textiles, rubber, resistant to aggressive chemicals.
They are connected directly to fans, supply and exhaust anemostats, grilles, but sometimes, in order to connect such an air duct with the main system, additional connecting and mounting parts are needed.
Inside, the surface of flexible air ducts is not particularly smooth, so increased aerodynamic resistance creates additional noise.

Flexible air ducts have a multilayer structure. For greater rigidity, steel wire is placed between the layers. Most often, ventilation ducts in residential buildings are laid from PVC pipes, which have high sound-absorbing and heat-insulating characteristics.
Corrugation is used in places where the speed of movement of the air mass does not exceed 30 m/s and the pressure does not exceed 5 tons. Pa.
According to their design, air ducts can be built-in, in the form of ventilation shafts, and external, laid along walls and ceilings. The first ones are located inside the walls.
In order for them to work effectively, the surface inside must be as smooth as possible, then the air will circulate freely without encountering any obstacles. At the bottom of the shaft there is a hole that allows you to clean the air duct.
Suspended and attached boxes are used to install external air ducts. They are an assembly consisting of pipes and connectors of various sizes and shapes. Based on such a feature as the presence of insulation, air ducts can be insulated or without insulation.
Based on the design of the premises and the design features of the building, they choose one specific in the form of air ducts.
The installation of the system must be preceded by a high-quality aerodynamic calculation. It will be necessary to determine the pressure in the system, the volume of air masses passing through the air duct, its cross-section, and the type of air exchange.
Aerodynamic calculation of the air duct
To determine the cross-sectional size of the air duct, you need a sketch of the air network. First, the cross-sectional area is calculated.
For a round pipe, the diameter is found from the formula:
D = √4S/π
If the cross-section is rectangular, its area is found by multiplying the length of the side by the width: S = A x B.
Having calculated the cross section and applied the formula S = L/3600V, find the volume of air replacement L in mᶾ/h.
The speed of air movement in the air duct in the area of the supply grille is recommended to be in the range from 2 to 2.5 m/s for offices and housing and from 2.5 to 6 m/s in production.
In main air ducts - from 3.5 to 6 in the first case, from 3.5 to 5 - in the second and from 6 to 11 m/s - in the third. If the speed exceeds these indicators, the noise level will increase above the standard value. The factor 3600 coordinates seconds and hours.
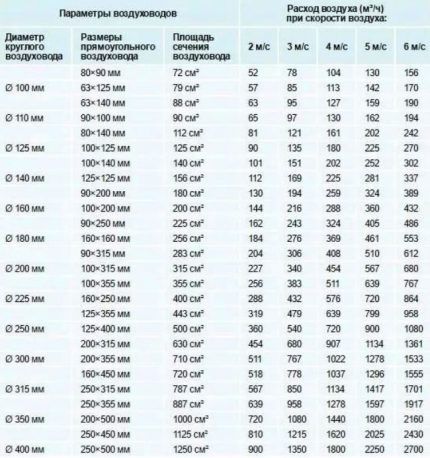
From the table, focusing on the air flow speed, you can also take the approximate air mass flow rate.
You may also find detailed information on calculating duct area with examples of calculations discussed in our other article.
Features of air duct installation
Regardless of the type and functions assigned to the ventilation system, the main task of transporting air is performed by channels for transporting air flow. Of all the system installation work, the most difficult part is the installation of air ducts.
Even with a well-performed calculation, violating the technology, it will never be possible to create a system that works without failures.
In addition to the main tasks, ventilation can also perform a number of additional functions:
- monitor the purity of the air supplied to the room;
- maintain a given percentage of humidity;
- free the air removed from the building from all impurities.
When installing exhaust ventilation Only one air duct is needed. IN supply and exhaust system It will be necessary to lay two independent air ducts so that clean air enters the room through one of them, and used air leaves through the other.

General installation rules
There are documents that specify the requirements for the installation and operation of air ducts. These include SP 60.13330 And SP 73.13330.2012. The first is called “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning” and the second is called “Internal sanitary systems of buildings”.
In addition, manufacturers producing air ducts include their instructions with them.
Requirements subject to strict compliance include:
- Full stretching of flexible air ducts during their installation.
- No sagging to avoid pressure loss.
- Mandatory grounding because the highway tends to accumulate static electricity.
- Do not plan the installation of flexible and semi-rigid air ducts if the vertical section of the system is a route covering more than 2 floors.
- Install exclusively rigid pipes in basements, basements, concrete structures, and in places in contact with the ground.
- At the design stage and when installing flexible and other air ducts, one should take into account the fact that in an operating ventilation system the air path is a spiral.
- At turns, provide a radius equal to at least two pipe diameters.
- Route the air duct through the walls using special metal sleeves and adapters.
- An air duct damaged during installation must be replaced.
Most often, air ducts are attached to walls, ceilings, in the space between ceiling trusses. What remains unchanged is that the center of the air ducts and the plane of the structures must remain parallel to each other.
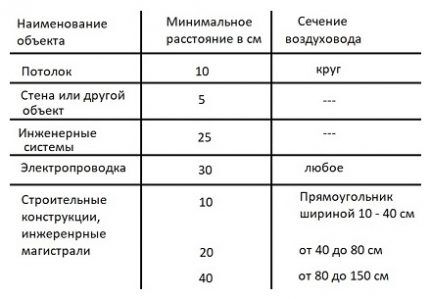
The standards also regulate the minimum distance from the air duct to other structures.
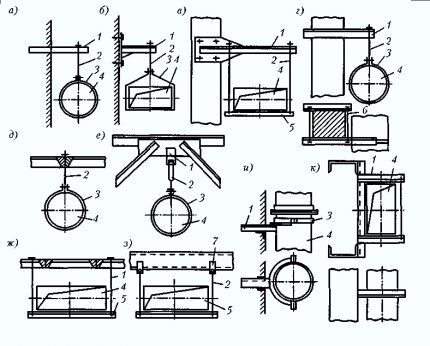
When laying air ducts, there are 2 options. The first is that the combined pipes form a system with a common outlet pipe. Second, each room has an individual air duct.
Types of rigid duct connections
When installing a ventilation system, it is recommended to make as few connections as possible. The air ducts are connected using flange and band fastening.
In the first case, the shaped elements and pipe ends are supplemented with flanges, then connected using self-tapping screws, using rivets, placing them every 200 mm, or using welding. Rubber gaskets are used as seals for flanges.
Manufacturing flanges is a complex process and not very profitable for the manufacturer.
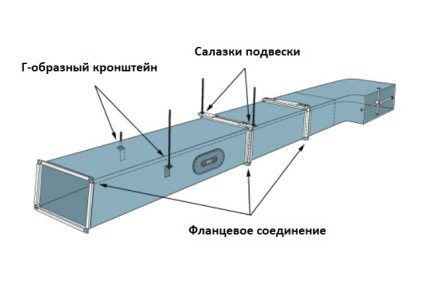
A bandage or wafer connection is more profitable both financially and in terms of time.It involves applying a bandage, which is thin metal strips or slats, to the joint. This type of connection also cannot be called perfect.
The main thing is that the tightness is low, which is why the joints become places for air leaks, and at sub-zero temperatures condensation accumulates here.

There is a third connection method when installing rigid air ducts - a tire and an angle. This is an invention of Metz engineers from Germany. Now it is successfully gaining ground over the first two methods. To cut tires, you do not need expensive equipment, and the corner is made by stamping.
Air duct fastening methods
There are 4 ways to attach air ducts:
- hairpin plus profile;
- pin and traverse;
- stud plus clamp;
- punched paper tape
The first of these methods is what professionals like to use. The profile used has L or Z-shaped form. The second one mainly fastens heavy air ducts. The corner installed under the lower corner reduces the load on the fasteners and provides additional rigid support for the box.
Rubber seals are placed in the place where the profile is attached. They are needed to reduce noise and dampen vibration.

When installing heat- and sound-insulated air ducts where the width of the main line is more than 60 cm, the second fastening method is used. The load from the air duct itself falls on the traverse, and the studs protect against horizontal movements.
For better noise insulation, a rubber profile is also required. It is placed between the body of the air duct and the traverse.
To install round air ducts - simple or insulated - use the third method - a pin and a clamp. In small sections of the air duct made of flexible pipes, you can get by with clamps alone. A simple and cheap way is to fix it using punched tape.
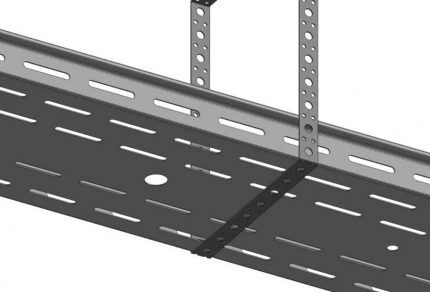
For a round air duct, a loop is made from punched paper tape, and for a rectangular duct, it is connected to the bolts. This method is used for systems with a diameter of no more than 20 cm, because the structure does not have sufficient rigidity.
From the rear side, the air duct is fixed directly to the ceiling structures using an anchor connection or using a clamp.
Installation of flexible pipes
Flexible air ducts are easier to install than rigid ones.
The technology consists of the following operations:
- Cutting. The air duct is stretched to improve aerodynamic characteristics, the length is measured and marked. Next, make a cut along the coil.
- Connections. The air duct is placed on the pipe with an overhang of at least 5 cm. In this case, be sure to take into account the direction of air movement, marked with a colored mark on the flexible pipe. Correct installation reduces noise levels in the system.
- Sealing. The joint is sealed using sealant or special aluminum tape. Secure the air duct using a hose clamp.
When installing heat-insulated hoses, the same technology is used, but when the air duct is cut off or its sections are connected, a layer of insulation is first wrapped.
The bare frame is joined or cut off, the connection is sealed and only then the insulation is returned to its place. After this, it needs to be fixed again and insulated.

The attachment points should be at a distance of 1.5 - 3 m from each other. A sag between them of no more than 5 cm per 1 m is allowed. If the air duct is placed parallel and above the ceiling structures, the distance between the axes of the clamps is 100 cm.
When the air duct is in a vertical position, the distance between the fasteners is increased to a maximum of 180 cm. The coverage of the air duct by the clamp cannot be less than ½ the diameter of the first one.
If you need to make turns, you need the largest possible radius. As this parameter decreases, the pressure drops. It is optimal when the radius at the bend is equal to 2 pipe diameters.

Unprotected from weather and UV rays, flexible ductwork will not last long if installed outdoors.
A flexible air duct made of metal polyester tape in contact with the heating system pipe will definitely sag and quickly age. Contact between air ducts made of different metals should not be allowed - this also negatively affects their service life.
Static electricity causes significant damage to synthetic air ducts.If there is a large accumulation of it and a discharge occurs, an explosion may even occur. This situation is possible when in the air moving with considerable speed‚ vapors of natural solvents are present.
Grounding will help in this case. To do this, the grounding wire is connected to the wire that forms the frame of the air duct. If this is an exhaust unit located above the equipment, the spiral wire is brought to its body.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Here you will see how specialists install air ducts:
Plastic air ducts and their installation:
It is important to initially have a competent design for laying air ducts. Having familiarized yourself with the types and features of installation of different types of air ducts, you can start constructing a simple system yourself.
Bulky and complex designs are best left to professionals.
Do you have not only theoretical knowledge, but also practical experience in installing ventilation ducts? Perhaps you noticed inconsistencies in information or technical errors in the material reviewed? Please write to us about this in the comments below the article.
If you have any questions or want to clarify some point regarding the installation of air ducts, ask for advice - we will try to help you.




Non-return dampers should be installed whenever possible. This will prevent dust and foreign odors from entering the room when ventilation is not working. Try to install fans in easily accessible places so that, if necessary, you can replace the device without additional work. Install filter elements in air intake areas, for example, made of caprolon. Change them at least once every six months.
“Whenever possible, non-return dampers should be installed.” “Non-return flaps”? 🙂 It’s obvious that this was written by a professional; they got caught in the ventilation today... :)
Let’s just say that “L or Z-shaped profile” seems to have been invented by Systemair. We don’t have this in our technological maps. And installing them takes longer and is more labor-intensive. It's faster on a traverse or belt.
Our installers put them on fleas and eat it all. And according to our rules, these profiles must be attached to the air duct with RIVETS or welded (which is unrealistic with thin sheet and galvanized steel).
It is also IMPOSSIBLE to install fasteners on the flanges of the air duct (this is for the photo with the slides on the flanges for hangers)!