Calculation of the area of air ducts and fittings: rules for performing calculations + examples of calculations using formulas
The key to flawless and efficient ventilation operation is a competent calculation of the area of air ducts and fittings, on which the selection of both individual elements and equipment depends. The purpose of the calculation is to ensure the optimal frequency of air changes in rooms in accordance with their purpose.
In the article, we examined in detail each of the required stages of calculations: determining the cross-section and actual area of ducts, calculating air speed and selecting the parameters of shaped products. In addition, we outlined the main requirements for the size of ventilation ducts, and also gave an example of calculating air ducts for a private house.
The content of the article:
Purpose of performing calculations
Features of calculation and selection of air ducts depend on their type and the material from which they are made. The latter characteristic determines the nuances that arise during air movement and the peculiarities of the interaction of an air avalanche with the walls.
Air ducts are:
- metal - it can be black steel, galvanized, stainless steel;
- aluminum flexible corrugated;
- plastic ventilation ducts - flexible and rigid;
- fabric.
According to the cross-section geometry, air ducts are made round, rectangular, or oval. The latter are not as popular as the first two.
Even if there is the most correct design of the ventilation system, an error in the selection of air duct sections can lead to disruption of air circulation.

This parameter depends on:
- the speed of flow of the air mass and its volume;
- degree of tightness of connections;
- noisy ventilation system;
- power consumption
Calculations done correctly will make it possible to save money, since the amount of material will be determined accurately. But besides economic issues, the main thing is the ventilation parameters, which ensure comfortable living conditions for people.
General information for calculating cross-sectional area
The area of pipes for an air duct is calculated using different values:
- For compliance with sanitary and hygienic parameters (SanPiN).
- By the number of residents.
- By the area of the rooms.
The result can be obtained both for a separate room and for the house as a whole. For calculations there are special programs with embedded algorithms. Another calculation option is to use formulas.
During their design, the cross-sectional area of the air ducts is selected so that the air moves along all lengths at approximately the same speed. Along the entire length of the system, the amount of air is different, so the cross-sectional area of the air duct should change upward as the volume of the air mass increases.

As the circular cross-section increases, the air flow speed decreases. At the same time, aerodynamic noise will also be reduced. The disadvantage of such air ducts is the bulkiness of the design, which makes it impossible to install them in the space between the draft and suspended ceilings, as well as the increased cost.
If this is not possible, you can give preference to rectangular geometry, since the height of the rectangular section is smaller. On the other hand, round products are easier to install, and they also have their own operational advantages.

The choice of one option or another depends on the user's priorities. If energy savings, minimal noise are at the forefront and there are all the possibilities for installing a large network, the best choice is the round shape of the air duct.
Calculation steps
Calculation work consists of several stages:
- Drawing up a general ventilation system diagrams. Here the lengths of straight sections, rotating parts and their type, and places where the section changes should be noted.
- Selecting an air exchange rate identical to sanitary and hygienic requirements.
- Calculation of the speed of movement of air masses through the pipeline. This parameter depends on type of ventilation, and it can be natural or forced.
- Calculation of air duct area and other parameters.
There are many programs for performing such calculations.

Calculation of duct cross-section
The expression used to calculate the quadrature of shaped elements and air ducts looks like this:
Sc = (L x 2.778) : V,
Where:
- Sc - area in cross section;
- L — flow rate of air circulating in the system;
- 2.778 — coefficient that reconciles different dimensions;
- V — the speed of an air avalanche in a specific place, measured in meters per second.
The result of the calculation will be a value measured in cm².
There is an alternative formula:
S = L : k × V,
The K coefficient in this case is 3600.
Determining the actual duct area
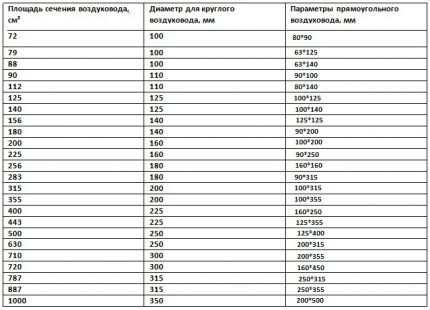
The regular ventilation area for round ventilation ducts is calculated using the formula:
S = (π x D2) : 400,
Where:
- S — actual area;
- D — diameter.
For rectangular pipelines:
S = (A x B) : 100,
Where:
- S — actual area;
- D — diameter;
- A — height of the air duct;
- IN - width of the structure.
The cross-sectional area for a pipe with an oval cross-section is calculated using the formula:
S = π × A × B: 4,
Where:
- A - larger diameter of the oval;
- IN - smaller diameter accordingly.
There are other formulas for calculating the area of the air duct.
Using a regulatory document such as SNiP, you can compare the cross-sectional dimensions of air ducts with the required indicators. This makes it even easier to determine the appropriate size of the air piping.
Some manufacturers provide nomograms in the description of air ducts. They are also in the normative literature.
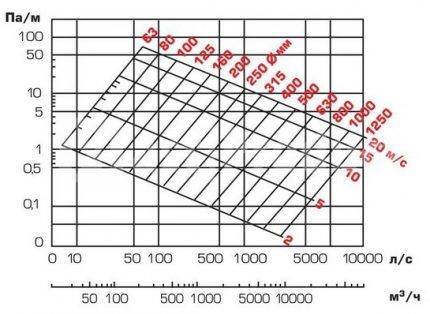
From the nomograms you can take the value of the cross-sectional area. It is approximate, but suitable for creating a system with minimal noise.
To find the duct dimensions for a specific branch pipe that transports a given volume of air, you need to do the following:
- Determine on the nomogram the point of intersection of the volume of air moved in 1 hour and the line of highest speed for the design section.
- Near this point, find the value of the most suitable diameter.
In addition, having a nomogram, you can not only facilitate the calculation of the cross-section of air ducts and fittings, but also specify the pressure loss along a section of the air line at a set speed.
It is not necessary to use a nomogram; you can determine the required cross-sectional area depending on the speed of the air mass.
Air speed calculation
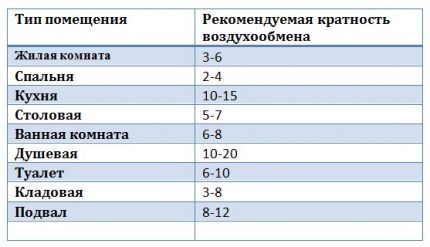
Using formulas or special tables, calculate the air duct speed. The key parameter here is the multiplicity index, which determines the volume of air at which a room with a volume of 1 m2 is fully ventilated.3 within 1 hour.
To determine the multiplicity index, experts recommend studying specific conditions at existing industrial facilities for which there is actual data on the release of gases, toxic vapors, etc. It is best to do an independent calculation using formulas.
The formula for calculating the multiplicity looks like this:
N=V:W,
Where:
- N — the required multiplicity;
- V - the volume of fresh air mass entering the room within an hour;
- W - volume of the room.
The unit of multiplicity is the number of times/hour, V is measured in mᶾ/h, volume is in mᶾ.
Let's consider a specific example of determining the required amount of air by multiplicity.
There is a living room with a volume of 22 mᶾ. It will require air: L = 22 x 6 = 132 m3, here 6 is the air exchange rate taken from the table.
The speed of mass movement (V) is measured in m/s and determined by the formula:
V=L : 3600 x S,
Where:
- L — air used (mᶾ/h);
- S — sectional area of the air duct (mᶾ).
Additionally, 2 more parameters affect air speed: noise level, vibration coefficient. They must be taken into account when designing the system.
Calculation example for a small cottage
For the calculation, we took a cottage with an internal area of 108.8 m2 and a height from floor to ceiling of 3 m. Inside there is a living room, bedroom, children's room, kitchen, bathroom. The multiplicity indicator is taken equal to 1.

First, calculate the amount of removed and incoming air for the entire building.
The SNiP method is used for this:
- Since the bedroom and living room are the same in area, the amount of air removed from them is 21 x 3 x 1 = 63 mᶾ/h.
- For a child’s room - 24 x 3 x 1 = 72 mᶾ/h.
- For the kitchen - 22 x 3 x 1 + 100 = 166 mᶾ/h.
- For a bathroom - 10 x 3 x 1 = 30 mᶾ/h.
- As a result: 63 x 2 + 48 + 166 + 30 = 394 mᶾ/h.
The corridor and hallway were not taken into account. 100 mᶾ is the volume that goes through the hood in the kitchen.
Correct distribution of air flow in the house is also a very important point. In buildings of this type, a natural ventilation system is usually installed.There is still a coercive element here - kitchen hood.
Next, determine the diameters of the ventilation ducts. Since 100 m3 If the hood is removed forcibly, then all that remains is to distribute the remaining 294 m3. They will leave naturally through 2 shafts. For each it will be necessary: 294: 2 = 147 mᶾ.
Since air speed in natural ventilation shafts ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 m/s, the average value of 1 m/s is usually taken in calculations. Substituting the known values into the formula S = L: k × V, they find: S = 147: 3600 x 1 = 0.0408 m².
Now it is possible to determine the diameter of an air duct with a circle in cross-section using the formula: S = (π x D2) : 400 or 0.0408 = (3.14 x D2) : 400.
Having solved this equation with one unknown, through simple calculations, they find that the diameter of the air duct is 2.28 mm. The nearest larger standard pipe size is selected for this value.
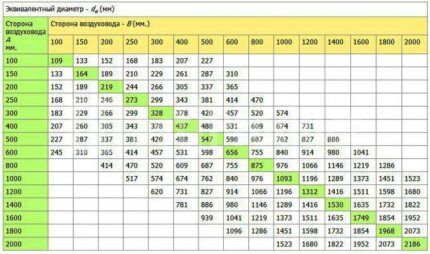
When installing a rectangular air duct, select its size according to the table, focusing on the area. The nearest larger value is 200 x 250 mm.
Using the same scheme, the cross-sectional area of the outlet for the kitchen hood is determined, with the difference that the air speed here is 3 m/s. S = 100: 3600 x 3 = 0.083 m² or diameter 107 mm.
A conversion table is needed when you need to calculate air ducts with a rectangular cross-section and apply the table for round products. Here are the diameters of air ducts with a circular cross-section, in which the pressure reduction due to friction is equal to the same value in a rectangular design.
There are three ways to determine the equivalent value:
- by speed;
- along the cross section;
- by consumption.
These values are associated with different parameters of the air duct. Each of them has an individual method of using tables. The main thing is that, regardless of the technique used, the amount of pressure loss due to friction is the same.
Finally, the speed is checked: V = 147: (3600 x 0.0408) = 1.0 m/s. This is within the acceptable limit.
Shaped products and their calculation
At installation of air ducts straight sections of various sizes are connected using shaped products.

Shaped products include:
- Bends. They are used to change the direction of the air pipeline at any angle. They come in both round, rectangular and oval.
- Transitions. They are used to connect air ducts of different sections. Any geometry - from round to combined.
- Couplings, nipples. Connect straight sections of the highway.
- Tees. The branches or two branches of the air duct are connected.
- Stubs. Blocking the air flow.
- Crosspieces. Separate or connect air flows.
- Ducks. Provide multi-level transition of the air duct.
To calculate the required parameters of shaped products, mathematical skills are required.

An error made in one indicator will lead to a deterioration in the operational characteristics of the system. There are no ready-made formulas for such calculations.
Many designers use special programs and online calculators. You only need to enter the primary values and get ready-made parameters at the output.
The programs allow you not only to determine the required sizes of all parts, but also to make their development. Such a development, printed on a 3D printer, allows for a perfect fit of the ventilation ducts.
Basic calculation requirements
When determining the final parameters of air ducts, it is necessary to take into account that determining the area of air ducts must ensure that:
- The temperature regime in the room is ensured. Where there is excess heat, its removal is provided, and where there is a deficiency, its losses are minimized.
- The speed of air movement does not in any way reduce the level of comfort of people in the room. Air purification is required in work areas.
- Harmful chemical compounds and suspended particles present in the air are present in a volume corresponding to GOST 12.1.005-88.
For individual rooms, a prerequisite for selecting the area of air ducts is to constantly maintain pressure and exclude air supply from outside.

The category of premises where backup is required includes basements, as well as premises in which harmful substances can accumulate.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Online program to help the design engineer:
Plot about the organization of ventilation of a private house as a whole:
The cross-sectional area, shape, and length of the air duct are some of the parameters that determine the performance of the ventilation system. Correct calculation is extremely important, because... the air throughput capacity, as well as the flow speed and efficient operation of the structure as a whole, depend on it.
When using an online calculator, the degree of accuracy of the calculation will be higher than when calculating manually. This result is explained by the fact that the program automatically rounds the values to more accurate values.
Do you have personal experience in designing, installing and calculating an air duct system? Do you want to share your accumulated knowledge or ask questions on the topic? Please leave comments and participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.




Hello, I have a garage length 6 x width 4 x height 3, please tell me what diameter of the round pipe is needed for natural ventilation?