What should the air speed in the ventilation duct be according to technical standards?
The microclimate provided by ventilation systems in residential or industrial premises affects the well-being and performance of people.To create comfortable living conditions, standards have been developed that determine the composition of air. Agree, regular air exchange is vital.
We will tell you what the air speed in the duct should be. We will advise you on what needs to be done to ensure that the air flow always remains fresh and meets hygienic standards. Here you will find a detailed description of calculation methods and a list of rules for selecting the optimal air duct.
The information offered for review is based on data from regulatory reference books. Examples are given for the practical development of calculation methods. The text material is supplemented with visual illustrations and videos that make the difficult topic easier to understand.
The content of the article:
The importance of air exchange for humans
According to construction and hygiene standards, every residential or industrial facility must be provided with ventilation system.
Its main purpose is to maintain air balance and create a microclimate favorable for work and rest. This means that in the atmosphere that people breathe, there should not be an excess of heat, moisture, or pollution of various kinds.
Violations in the organization of the ventilation system lead to the development of infectious diseases and diseases of the respiratory system, decreased immunity, and premature spoilage of food.
In an excessively humid and warm environment, pathogenic microorganisms quickly develop, and pockets of mold and mildew appear on walls, ceilings and even furniture.
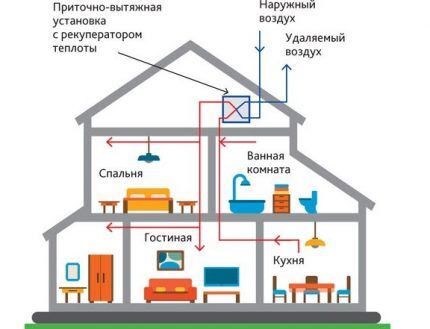
One of the conditions for maintaining a healthy air balance is the correct design of the ventilation system. Each part of the air exchange network must be selected based on the volume of the room and the characteristics of the air in it.
Let’s assume that in a small apartment there is sufficiently well-established supply and exhaust ventilation, while in production workshops it is mandatory to install equipment for forced air exchange.
When constructing houses, public institutions, and workshops of enterprises, they are guided by the following principles:
- each room must be provided with a ventilation system;
- it is necessary to observe hygienic air parameters;
- enterprises should install devices that increase and regulate the air exchange rate; in residential premises - air conditioners or fans if there is insufficient ventilation;
- in rooms for different purposes (for example, in patient rooms and an operating room, or in an office and a smoking room), it is necessary to equip different systems.
In order for ventilation to meet the listed conditions, you need to make calculations and select equipment - air supply devices and air ducts.
Also when ventilation system design It is necessary to choose the correct air intake locations to prevent contaminated flows from flowing back into the premises.
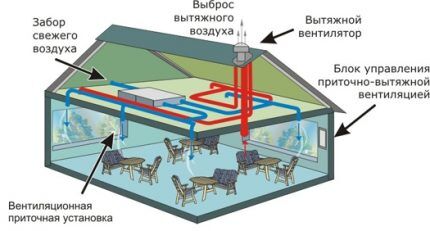
The efficiency of air exchange depends on the size of the air ducts (including house shafts). Let's find out what the standards for air flow speed in ventilation are, specified in the sanitary documentation.
Rules for determining air speed
The speed of air movement is closely related to concepts such as noise level and vibration level in the ventilation system. The air passing through the channels creates a certain noise and pressure, which increases with the number of turns and bends.
The greater the resistance in the pipes, the lower the air speed and the higher the fan performance. Let's consider the norms of associated factors.
No. 1 - sanitary standards for noise levels
The standards specified in SNiP apply to residential (private and apartment buildings), public and industrial premises.
In the table below, you can compare standards for different types of premises, as well as areas adjacent to buildings.
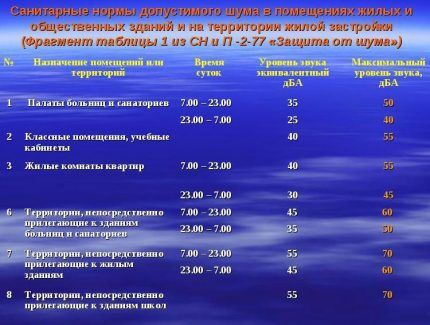
One of the reasons for the increase in accepted standards may just be incorrectly designed air duct system.
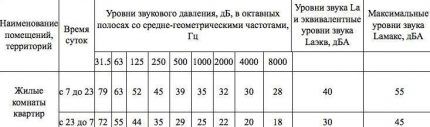
Sound pressure levels are presented in another table:
No. 2 - vibration level
The power of the fans is directly related to the level of vibration.
The maximum vibration threshold depends on several factors:
- duct sizes;
- quality of gaskets that reduce vibration levels;
- pipe manufacturing material;
- speed of air flow passing through the channels.
The standards that should be followed when choosing ventilation devices and when making calculations regarding air ducts are presented in the following table:
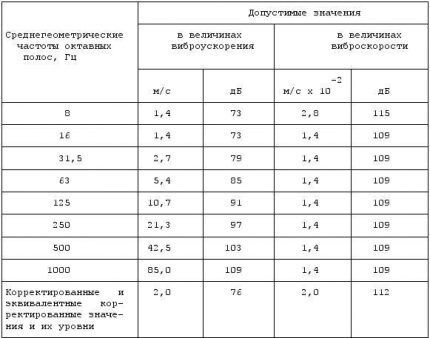
The air speed in shafts and channels should not affect the increase in vibration indicators, as well as the associated parameters of sound vibrations.
No. 3 - air exchange rate
Air purification occurs through the air exchange process, which is divided into natural or forced.
In the first case, it is carried out by opening doors, transoms, vents, windows (and is called aeration) or simply by infiltration through cracks at the joints of walls, doors and windows, in the second - with the help of air conditioners and ventilation equipment.
The air in a room, utility room or workshop must be changed several times an hour in order for the degree of air pollution to be acceptable. The number of shifts is a multiplicity, a value also necessary to determine the air speed in the ventilation ducts.
The multiplicity is calculated using the following formula:
N=V/W,
Where:
- N – frequency of air exchange, once every 1 hour;
- V – volume of clean air filling the room in 1 hour, m³/h;
- W – volume of the room, m³.
In order to avoid additional calculations, the average multiplicity indicators are collected in tables.
For example, the following air exchange rate table is suitable for residential premises:
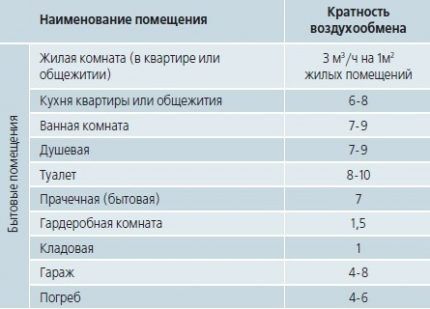
What happens if the air exchange rate standards are not met or are met, but to an insufficient extent?
One of two things will happen:
- The multiplicity is below normal. Fresh air stops replacing polluted air, as a result of which the concentration of harmful substances in the room increases: bacteria, pathogens, dangerous gases. The amount of oxygen, important for the human respiratory system, decreases, and carbon dioxide, on the contrary, increases. Humidity rises to a maximum, which is fraught with the appearance of mold.
- The multiplicity is higher than normal. Occurs if the speed of air movement in the channels exceeds the norm. This negatively affects the temperature: the room simply does not have time to heat up. Excessively dry air provokes diseases of the skin and respiratory system.
In order for the air exchange rate to comply with sanitary standards, ventilation devices should be installed, removed or adjusted, and, if necessary, air ducts should be replaced.
Algorithm for calculating air speed
Taking into account the above conditions and the technical parameters of a particular room, it is possible to determine the characteristics ventilation system, and also calculate the air speed in the pipes.
You should rely on the air exchange rate, which is the determining value for these calculations.
To clarify the flow parameters, the table is useful:
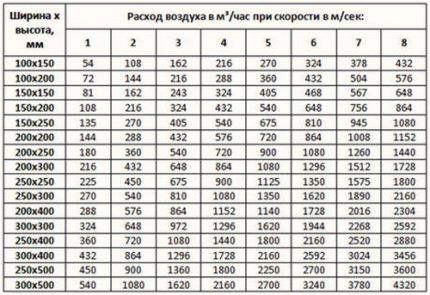
To make your own calculations, you need to know the volume of the room and the rate of air exchange for a room or hall of a given type.
For example, you need to know the parameters for a studio with a kitchen with a total volume of 20 m³. Let's take the minimum multiplicity value for the kitchen - 6.It turns out that within 1 hour the air channels must move about L = 20 m³ * 6 = 120 m³.
You also need to know cross-sectional area of air ductsinstalled in the ventilation system. It is calculated using the following formula:
S = πr2 = π/4*D2,
Where:
- S — cross-sectional area of the air duct;
- π — the number “pi”, a mathematical constant equal to 3.14;
- r — radius of the air duct section;
- D - cross-sectional diameter of the air duct.
Let's assume that the diameter of the round duct is 400 mm, substitute it into the formula and get:
S = (3.14*0.4²)/4 = 0.1256 m²
Knowing the cross-sectional area and flow rate, we can calculate the speed. Formula for calculating air flow speed:
V = L/3600*S,
Where:
- V — air flow speed, (m/s);
- L — air flow, (m³/h);
- S — cross-sectional area of air channels (air ducts), (m²).
We substitute the known values, we get: V = 120/(3600*0.1256) = 0.265 m/s
Therefore, in order to ensure the required air exchange rate (120 m3/h) when using a round duct with a diameter of 400 mm, you will need to install equipment that allows you to increase the air flow speed to 0.265 m/s.
It should be remembered that the previously described factors - parameters of the vibration level and noise level - directly depend on the speed of air movement.
If the noise exceeds the norm, you will have to reduce the speed, and therefore increase the cross-section of the air ducts. In some cases, it is enough to install pipes made of a different material or replace a curved channel fragment with a straight one.
Recommended air exchange rate standards
When drawing up a building project, calculations are made for each individual section.In production these are workshops, in residential buildings - apartments, in a private house - floor blocks or separate rooms.
Before installing a ventilation system, it is known what the routes and sizes of the main lines are, what geometry is needed ventilation ducts, what pipe size is optimal.

Calculations related to the movement of air flows inside residential and industrial buildings are considered to be the most complex, so experienced, qualified specialists must deal with them.
The recommended air speed in air ducts is indicated in SNiP - regulatory state documentation, and when designing or commissioning objects they are guided precisely by it.
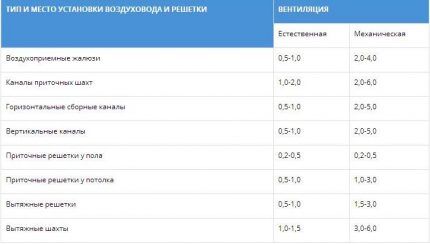
It is believed that indoor air speed should not exceed 0.3 m/s.
Exceptions are temporary technical circumstances (for example, repair work, installation of construction equipment, etc.), during which the parameters can exceed the standards by a maximum of 30%.
In large premises (garages, production workshops, warehouses, hangars), instead of one ventilation system there are often two.
The load is divided in half, therefore, the air speed is selected so that it provides 50% of the total calculated volume of air movement (removal of contaminated air or supply of clean air).
If force majeure occurs, there is a need for a sharp change in air speed or a complete suspension of the ventilation system.
For example, according to fire safety requirements, the speed of air movement is reduced to a minimum in order to prevent the spread of fire and smoke into adjacent rooms during a fire.
For this purpose, cut-off valves and valves are installed in air ducts and transition areas.
Subtleties of choosing an air duct
Knowing the results of aerodynamic calculations, you can correctly select the parameters of the air ducts, or more precisely, the diameter of the round sections and the dimensions of the rectangular sections. In addition, you can select a device in parallel forced air supply (fan) and determine the pressure loss during air movement through the channel.
Knowing the amount of air flow and the speed of its movement, you can determine what cross-section of air ducts will be required.
To do this, take the formula inverse to the formula for calculating air flow:
S = L/3600*V.
Using the result, you can calculate the diameter:
D = 1000*√(4*S/π),
Where:
- D — diameter of the air duct section;
- S — cross-sectional area of air channels (air ducts), (m²);
- π - the number “pi”, a mathematical constant equal to 3.14;.
The resulting number is compared with factory standards approved by GOST, and the products closest in diameter are selected.
If you need to choose rectangular rather than round air ducts, you should determine the length/width of the products instead of the diameter.
When choosing, focus on the approximate cross-section, using the principle a*b ≈ S and size tables provided by manufacturers. We remind you that according to the norms the ratio of width (b) and length (a) should not exceed 1 to 3.

Generally accepted standards for rectangular channels: minimum dimensions - 100 mm x 150 mm, maximum - 2000 mm x 2000 mm. Round air ducts are good because they have less resistance and, accordingly, have minimal noise levels.
Recently, convenient, safe and lightweight plastic boxes.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Useful videos will teach you how to work with physical quantities and help you better understand how the ventilation system works.
Video #1. Calculation of natural ventilation parameters using a computer program:
Video #2. Useful information about the design of the ventilation system in a private house under construction:
The information in this article can be used for informational purposes and to better understand the operation of the ventilation system.
For more accurate calculations of air speed when designing home communications, we recommend contacting engineers who know the nuances of ventilation devices and will help you choose the correct size of air ducts.
If you would like to share your personal experience gained when installing air ducts, interesting facts and specific information, please write comments in the block below. Ask questions about controversial issues. We or site visitors will be happy to participate in the discussion.




We started paying attention to this after having children. You should always monitor ventilation and air in your home. Therefore, I spared no expense in installing ventilation systems. I have one for now, and that’s enough for us. Maybe we'll install another one in the future. It’s very difficult without fresh air, especially since I work from home and I don’t need to go outside every day.
You amazed me with the uselessness of going out, Pasha. Be sure to read about “circadian rhythms,” which, of course, does not concern ventilation, but is a driver of life processes.
I remember that Soviet doctors always advised children to take daily walks for a total duration of at least two hours a day. Briefly about the benefits of natural light, it synchronizes life processes in the body, affecting the circadian cells located on the retina.