Water heating in a private house: rules, regulations and organization options
The climatic conditions of central and northern Eurasia require thermal insulation of houses, but insulation alone is not enough. Heat losses must be compensated using a heating system.Water heating in a private home is a common and most effective method.
The quality of operation of the heating circuit directly depends on the design features, choice of heating device and type of wiring. You will learn how to decide on the equipment and the most suitable scheme by reading the article we propose. The information presented is based on the requirements of building regulations.
We described in detail the design principle of a water heating system and examined typical device options. To optimize the perception of a difficult topic, we included diagrams, photo selections and videos.
The content of the article:
Structure and operating principle
Heating structures with liquid coolant have a similar set of component parts, these are:
- heating equipment – boiler (gas, liquid or solid fuel), stove, fireplace.
- Closed loop in the form of a pipeline, ensuring continuous circulation of heated and cooled coolant (antifreeze).
- Heating devices – metal finned, panel or smooth-tube radiators, convectors, pipelines for water-heated floors.
- Shut-off valvesnecessary to disconnect individual devices or lines of the system for repair and maintenance;
- devices for adjusting and monitoring the operation of the system (expansion tank, pressure gauge, relief valves, etc.).
- Circulation pumps, used to create a forced supply of coolant, sometimes a booster pump is installed to ensure stable pressure in the system.
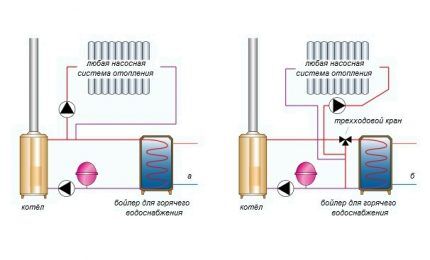
If there is a centralized gas main nearby, the most economical solution is to install a gas boiler.
In the absence of central networks for an independent gas supply system, a gas holder will have to be installed. However, this option is applicable only in the case of arranging an estate of a sufficiently large area.
In cottages built on small plots in non-gas-free areas, an ordinary cylinder will ensure autonomous operation of gas heating equipment. As an alternative solution, you can use liquid or solid fuel stoves, and only as a last resort - expensive electrical devices.
Preference water heating in country houses give back thanks to a simple operating principle. Heating in the boiler to a certain temperature, water is supplied under pressure into pipes leading to radiators or convectors.
Based on the type of coolant movement through heating circuits, they are divided into:
- Natural (gravity). The circulation of coolant in them is stimulated by natural phenomena, according to which heated water rushes upward, and after transferring heat to the radiators and cooling, it returns downward. There it again falls into the cauldron to resume its cyclic movement.
- Artificial (aka pumping or forced). A circulation pump is responsible for the circulation of the coolant in forced circuits, which pumps hot coolant on one side of the circuit and sucks in cooled water on the other.
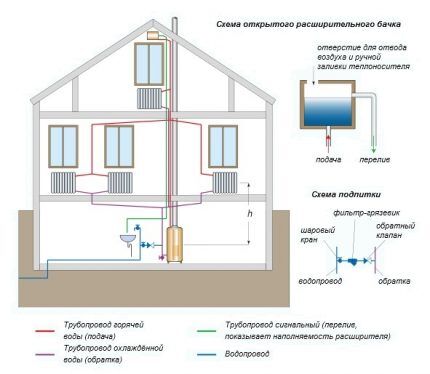
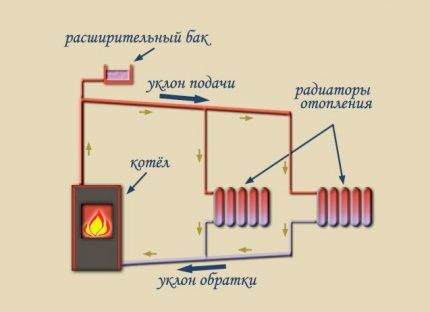
The gravity scheme is the simplest and most accessible option for independent implementation. It contains a minimum of equipment. These are return and supply lines, a boiler, an open expansion tank, and radiators. Becausethe movement of the coolant does not require pump stimulation, the systems are completely energy independent.
On to the pros natural heating It is worth considering that the construction costs are insignificant compared to the pump analogue. They do not need to be equipped with complex technical devices that are not cheap. There are no energy costs during operation.
A significant disadvantage of gravity systems is their extremely limited range. They can work at full capacity over a horizontal length of up to 30 m. Such heating takes a long time to “accelerate” after inactivity. There is a risk of the coolant freezing in an open tank during frosty periods.
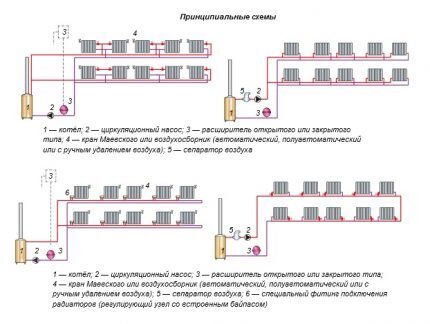
Forced circulation is good because it easily handles multi-story buildings with an extensive and extensive heating network. The scheme is more effective than the previous type, but more expensive and more difficult to construct. Before its construction, it is necessary to make competent calculations and develop a project.
Heating with artificial circulation it is equipped not only with pumps, but also with all kinds of technical devices for adjusting heat transfer and monitoring the operation of the system. These include automatic and mechanical air ducts, thermostats, pressure gauges, safety valves for discharging excess coolant into the sewer system, etc.

Forced heating equipment must be selected based on calculations. For example, to move the coolant along every 10 m of the heating circuit, 0.6 m of pressure generated by the pump is required. In order to select the necessary device, you need to know exactly the length of the pipeline and the hydraulic resistance in all sections.
It often happens that one pump is not enough to equip artificial water heating in a country house. Then an additional circulation analog or booster pump is installed.
The main disadvantage of forced heating is its dependence on a continuous supply of electricity. In case of interruptions, it is recommended to stock up on a generator, which is also not low in price.
Standards and requirements for autonomous heating
Before designing a heating structure, you need to look into SNiP 2.04.05-91, which sets out the basic requirements for pipes, heating devices and shut-off valves.
General standards boil down to ensuring a comfortable microclimate in the house for the people living in it, properly equipping the heating system, having previously drawn up and approved the project.
Many requirements are formulated in the form of recommendations in SNiP 31-02, which regulates the rules for the construction of single-family houses and their provision with communications.
Temperature-related provisions are specified separately:
- the parameters of the coolant in the pipes should not exceed +90ºС;
- optimal indicators are within +60-80ºС;
- the temperature of the outer surface of heating devices located in the direct access zone should not exceed 70ºС.
It is recommended to make pipelines for heating systems from brass, copper, and steel pipes. In the private sector, polymer and metal-plastic pipe products approved for use in construction are predominantly used.

The method of laying the heating pipeline can be:
- Open. Involves laying on building structures with fastening with clips and clamps. Allowed when constructing circuits made of metal pipes. The use of polymer analogues is permitted if their damage from thermal or mechanical influence is excluded.
- Hidden. It involves laying pipelines in grooves or channels selected in building structures, in baseboards or behind protective and decorative screens. Embedding of the circuit is allowed in buildings designed for at least 20 years of operation and with a pipe service life of at least 40 years.
The open method of laying is a priority, because the design of the pipeline route must provide for free access to any element of the system for repair or replacement.
Pipes are hidden in rare cases, only when such a decision is dictated by technological, hygienic or structural necessity, for example, when installing “warm floors” in a concrete screed.
At open gasket highways, sections crossing unheated premises must be provided with thermal insulation that corresponds to the climatic data of the construction region.
Autonomous heating pipelines with a natural type of circulation must be installed in the direction of the coolant flow, so that the heated water reaches the radiators by gravity, and after cooling in the same way, moves along the return line to the boiler. The mains of pumping systems are constructed without a slope, because there is no need for it.
The use of different types is stipulated expansion tanks:
- open, used for both pumping and natural forced systems, should be installed above the main riser;
- closed membrane devices, used exclusively in forced systems, are installed on the return line in front of the boiler.
Expansion tanks are designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the liquid when heated. They are needed to dump excess into the sewer or simply onto the street, as is the case with the simplest open options. Closed capsules are more practical because they do not require human participation in adjusting the pressure of the system, but they are more expensive.
When choosing shut-off valves, preference is given to ball valves; when choosing a pumping unit, preference is given to equipment with a pressure of up to 30 kPa and a capacity of up to 3.0 m3/h.
The budget opening variety needs to be refilled periodically due to normal liquid evaporation. For their installation, it is necessary to significantly strengthen the attic floor and insulate the attic.

Types of water heating systems
The type of heating system is determined by a combination of several factors. These include the circulation of the coolant, the method of assembling the system, the lower or upper option for laying the supply pipe, etc.
Regardless of the type of heating device, be it a traditional radiator, a baseboard convector or a “warm floor” coil, the heated water reaches them and, after cooling, leaves in the standard way for all systems.
Double-pipe and single-pipe designs
The final object of heat transfer is devices located in all heated rooms of the house. In many ways, the efficiency of heating depends on the pipeline installation scheme, so we will dwell in more detail on one- and two-pipe wiring.
The most common classification consists of two points:
- Single-pipe option – serial connection of radiators. The bottom line is that the coolant entering the system sequentially flows from one device to another. On approaches to distant points, it has time to cool down significantly.
- Two-pipe version – a system with parallel connection of the supply and return pipes. Its principle is based on the fact that supply is carried out to all devices almost simultaneously. The cooled water does not flow into the next device, but is collected by the return line and moved to the boiler.
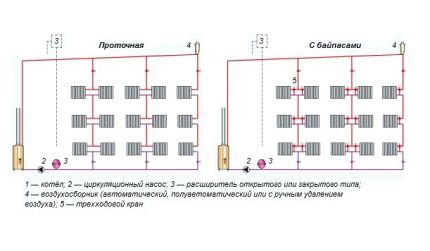
Single-pipe schemes come with both natural and forced water movement. Within their class, they are divided into two types: flow-through and with bypasses.
In flow-through circuits, the coolant, upon reaching the outermost radiator, has time to cool down greatly, so in distant rooms it is recommended to install devices with an increased number of sections.
Implementation in bypass system allows you to partially redirect the hot coolant to the following devices, due to which almost all batteries receive and give off almost equal amounts of heat. The movement of heated water is regulated either by two valves installed on the bypass and supply pipe, or by one three-way valve.
The main difference between two-pipe structures is the use of two branches: supply and return. The first serves to supply hot coolant to the radiators, the second - to drain water back to the boiler.
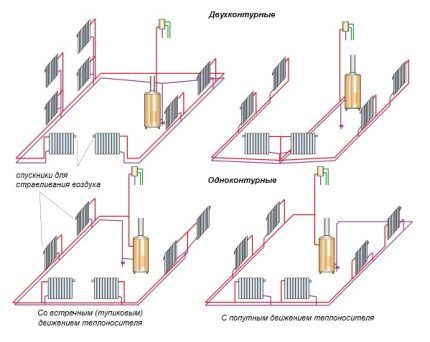
The two-pipe wiring diagram is used in systems with both types of coolant movement. Depending on the number of processed circuits, it can be single- or double-circuit.
In the first case boiler being installed at the beginning of the pipeline, and the pipes are routed to the left and right of the unit along the perimeter of the heated object.In the second case, the boiler is installed in the center, and the heating circuits are positioned so that their rings are on both sides of the unit.
The 2-pipe system is more functional and reliable, allowing heat to be evenly distributed throughout all rooms. Thanks to additional taps and adjustment devices, you can control the heat supply to each individual radiator. If one element fails, the performance of the remaining devices will not be affected.
Variations in connecting pipes and devices
All of the listed types of water heating for arranging a country cottage are divided into subtypes:
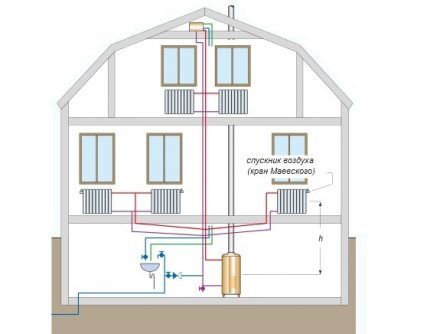
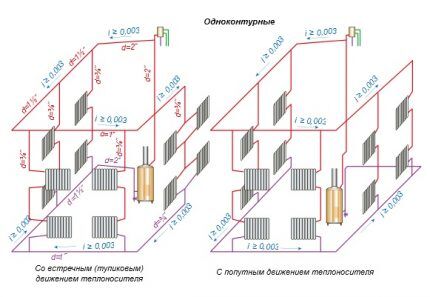
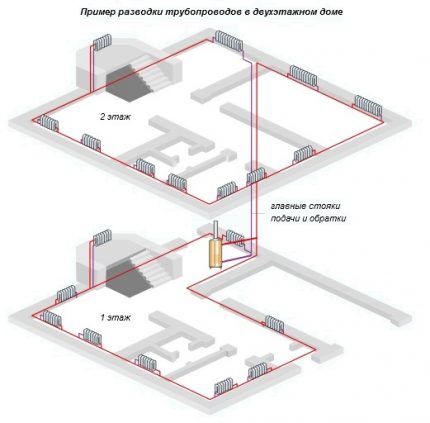
- By location of risers, combining heating devices. They are divided into horizontal and vertical. It is clear that the former are used in one-story buildings, the latter in multi-story buildings. Single-pipe systems with natural movement have only supply risers.
- According to the location of the supply and return pipes. They come with top or bottom wiring. The first provide for routing the supply at the highest points of the system, due to which the coolant enters the devices from above. According to the second situation, the return and supply lines are laid below the radiators.
Gravity systems with bottom wiring are used extremely rarely due to difficulties with air removal in long-distance devices. Bottom wiring is better combined with pump circulation, each device of which is still equipped with an air vent.
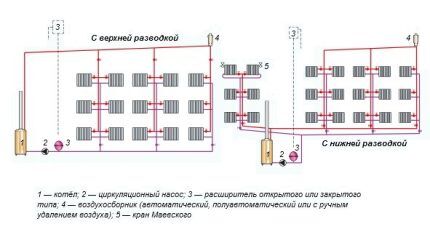
Heating with overhead wiring is installed in cottages without basements, but with an attic. Occasionally, in the absence of an attic, the supply is laid along the line where the ceiling meets the walls, which negatively affects the interior picture. Bottom wiring is suitable for houses with a flat roof without an attic, but with a basement.
Pipeline assembly method
Classification according to the method of pipeline construction divides heating systems into tee, manifold and combined.
Tee circuits can easily be considered a classic of the genre. They involve assembling pipelines and connecting devices to them using tees used in the nodes connecting pipes to risers, radiators to pipes, etc. In principle this is a sequential circuit.
Collector or otherwise beam design increases the possibilities of water heating of the cottage. This is a kind of modified system with separate pipeline branches (beams) extended to each device and with a distribution element in the center.
The distribution unit - the manifold is equipped with many outlets, thanks to which you can control the heat transfer of each device separately and turn it off for repairs. If desired and financially possible, each outlet can be equipped with its own pumping device.
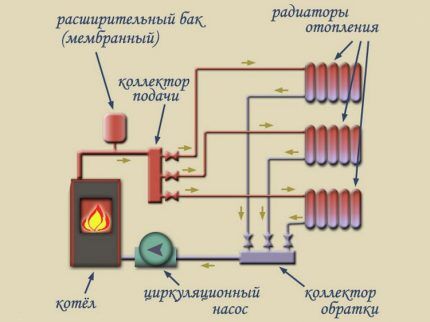
Manifold wiring is arranged mainly for horizontal circuits with a lower supply pipe. When installing in 2- and 3-story buildings, it is recommended to install a distribution manifold on each floor - this way you can regulate the air temperature in any corner of the building.
The control unit for cottages with several floors consists of two interconnected units: a supply manifold and an analogue for the return. The first is responsible for the delivery of hot coolant to the devices, the second stimulates the removal of cooled liquid.
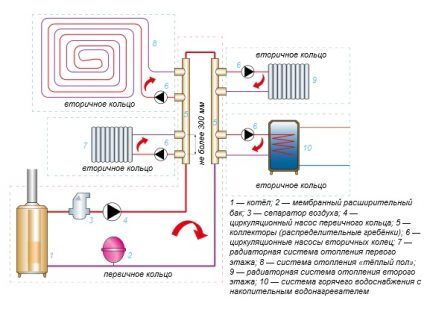
Manifold wiring is arranged on the basis of one- and two-pipe heating systems and is used in combination with a perimeter (tee).
Features of baseboard heating
Radiators or batteries in the traditional sense are not the only heating devices for creating a comfortable microclimate in individual rooms. Appeared not long ago "warm baseboards" — heating elements, in their shape and location reminiscent of construction analogues of the same name.

The operating principle of the device located around the perimeter helps maintain the set temperature constantly. First, the tubes inside the housing are heated, then the box, from which warm air rises, increasing the temperature of the walls.
Thus, the air in the room is heated directly from the baseboards and from all the walls along which they are located.

Advantages of baseboard heating:
- creating a comfortable microclimate that excludes active air circulation;
- the possibility of insulating risk zones at the junctions of floors and walls, where mold often appears;
- simple installation that can be performed without the involvement of specialists;
- selection of modules by type (single- and double-row) and power (for example, 310 W and 510 W);
- various designs that do not require camouflage;
- affordable price.
The disadvantages include special location conditions: furniture cannot be placed along horizontal elements, as this will harm the heat transfer process. Each circuit included in the system should not be longer than 15 meters, so for a large room it is necessary to install 2 or 3 circuits (combined heating is an option).

In addition to water baseboards, electric ones are used, but their maintenance is too expensive for a private home.
Equipment for the "Warm Floor" system
An effective and inexpensive design called heated floor, which heats the room from the floor side, has long proven itself only from the best side. It is actively used in city apartments to create a comfortable atmosphere in bathrooms, toilets, bedrooms, kitchens and loggias.
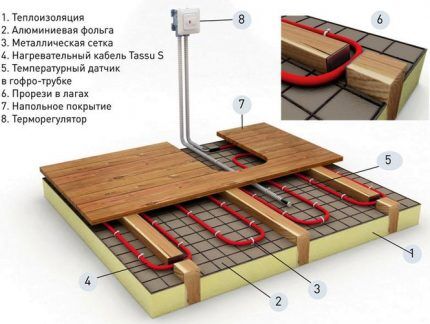
The pipeline must have high thermal conductivity, strength, elasticity, and minimal resistance, so metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene is used for its manufacture. The protective and stabilizing coating is a cement screed.
Advantages of heated floors:
- effective on any type of flooring (laminate, linoleum, carpet, ceramic tile);
- noticeable heat savings - from 30% to 50%;
- inexpensive cost and installation;
- possibility of DIY installation;
- use in combined heating systems (along with radiators and convectors).
Autonomous water heating does not depend on the supply of electrical energy, as it is powered by a gas (or other) boiler.
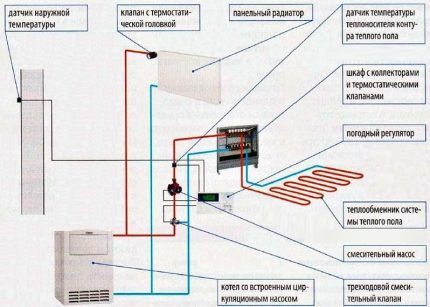
To the disadvantages water heated floors This may include imperfect regulation and the impossibility of installation in the city with centralized heating, but this does not apply to local suburban systems. If installation rules are violated, an emergency situation and flooding may occur, so you should carefully consider both the choice of equipment and installation.
More information about the coolant and its properties
There is no liquid that is ideal for any heating system.Each of the options presented on the coolant market has specific characteristics, for example, operating temperature range.
If you violate the boundaries of the specified range, the heating system will simply “stop”, and in the worst case scenario, pipes will burst and expensive equipment will fail.
In addition to temperature parameters, pipeline fluid has properties such as viscosity, anti-corrosion, and the ability to release toxic substances. An analysis of the required qualities showed that the best liquid coolants are purified water and a special chemical solution - antifreeze.
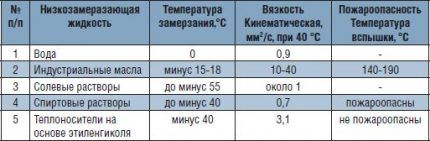
Filling with antifreeze is necessary in houses that are not a permanent place of residence. Usually, when leaving a building during the cold season, owners drain the water to avoid accidents and equipment breakdown. There is no need to remove antifreeze - upon return, you can immediately turn on the boiler without fear of leakage or rupture.
At extreme temperatures, the chemical coolant, having changed its structure, retains its original dimensions. Simply put, it turns into a gel that retains its properties unchanged. When the temperature reaches a comfortable level, the gel-like structure becomes liquid again, completely retaining its original volume.
Some more useful information about antifreeze:
- lasts at least 5 years, one fill can withstand 10 heating seasons;
- fluidity is 2 times higher than that of water, therefore, it is necessary to monitor the tightness of the connections;
- increased viscosity requires the installation of a more powerful circulation pump;
- the ability to expand when heated entails the installation of a volumetric expansion tank.
And you must always remember that the chemical solution is toxic and dangerous to human health.

Despite the outstanding characteristics of antifreeze, water is more popular as a coolant. It has the highest possible heat capacity, which is approximately 1 kcal. This means that the coolant heated to 75ºC, when cooled in the radiator to 60 ºC, will release about 15 kcal of heat to the room.
Water is available. If you equip your water supply system with reliable filters, you can use a free option - water from your own well. It does not contain hazardous chemical compounds and will not cause poisoning in the event of an accident.
The negative side of water is that it contains some mineral salts that cause corrosion. The problem can be solved by simply boiling it or using rain water (or melt water) instead of well water.
Water is not recommended for use in houses for periodic residence.
Selection of pipes for distribution
The final result, which consists in preserving and saving heat, depends on the quality of each system part, so the longest elements - pipes - must also be given some attention.
From a technological point of view pipes and fittings must have the following qualities:
- strength;
- ease;
- suitability for repair;
- tightness;
- low noise level.
Low cost is also an important component when choosing, because heating system equipment requires a large number of products for various purposes.

Nowadays, hardly anyone will undertake the installation of wiring from metal pipes. Steel, copper and galvanized products are becoming a thing of the past, giving way to cheaper and more functional analogues.
The best alternative is polymer products. which can be divided into three groups:
- polypropylene;
- metal-plastic.
pros polypropylene pipes – inexpensive, easy to weld, long service life. Disadvantage: lack of elasticity. When replacing a pipe, you will have to change the entire fragment from connection to connection.

Durable metal-plastic pipes resistant to sudden temperature changes. Capable of serving without major repairs for up to 30 years. The weak point is the connecting elements - fittings with an unreasonably narrowed cross-section. If the coolant freezes, a breakthrough is likely.
When choosing pipes, focus on the main technical indicators of the equipment and the type of coolant.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Interesting videos provide useful information about diagrams, components, installation of liquid heating systems, as well as personal installation experience.
Video #1. Features of a single-pipe heating system:
Video #2. Overview of two-pipe heating system diagrams:
Video #3.Practical application of the beam scheme:
Video #4. Detailed instructions for installing the heating system:
Advice to anyone who wants to independently equip a complex heating system in a country house: when drawing up a project, be sure to consult with a specialist so that after installation you do not encounter unforeseen circumstances. Plumbers will help you choose reliable equipment, suggest a more efficient wiring diagram, make accurate calculations, and the result will be comfort and warmth in the house.
Do you have any questions while reading the information we offer? Would you like to share useful information or your own experience in the design of a heating circuit? Please write comments in the block below.




We have a gas boiler in our house that heats the water and supplies heat to all rooms. Only the farthest rooms are the coldest there. You have to supply more gas to warm those rooms, which means more energy consumption. Now we are thinking about how to redo the heating in the house so that all rooms are heated evenly and the energy consumption is not too high.
My wife and I were thinking about installing water heating in our dacha. I personally didn’t know much about this topic. Following the link, I came across a topic that interested me. There was more than enough information, and it was presented in fairly understandable language. The video at the end was especially helpful. After studying the article, I found answers to many questions that interested me. Now I think we can begin to deal with this issue without fear of being a layman.
you made the short circuit on a single-pipe system smaller in diameter. And if you need to disconnect the battery and the passage through the short circuit pipe will be smaller