Polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes: comparative review and selection of the best option
Often, for the installation of heating systems, hot water supply and hot water supply, domestic plumbers prefer to choose pipes made of metal-plastic or polypropylene. Each of these products has its own advantages. Both are characterized by high strength, corrosion resistance and flexibility. But which option is better?
In this article we will try to figure out what is better to take for independent installation of pipelines for various purposes - polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes, having examined their technical characteristics and features.
The information we provide is supplemented with visual photos and detailed videos with an overview of the differences and features of installing a pipeline made of metal-plastic and polypropylene.
The content of the article:
Features of metal-plastic pipes
Products made from aluminum-polyethylene metal-plastic combine the best aspects of plastic and metal. When comparing them with a polypropylene competitor, you should understand that the price per linear meter in both cases is approximately the same.
However fittings for metal-plastic much more expensive than those used when installing PPR pipelines.
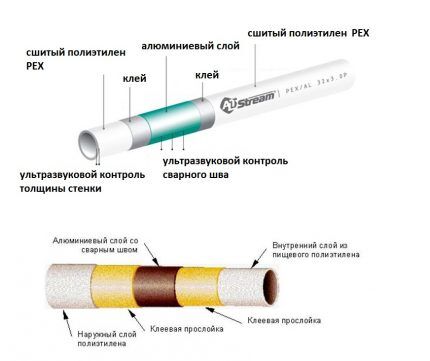
“Crosslinking” of polyethylene occurs during its production at the molecular level. There are no traces of seams or thread stitches there.There are three main technologies for manufacturing this plastic, designated PEX-A, PEX-B and PEX-C in the marking of pipe products.
These production nuances do not make a significant difference to the final characteristics of the pipe. What is more important here is compliance with the PEX technology itself on the part of the manufacturer.
And the buyer on the label needs to pay more attention to the indicated nominal pressure (PN) and wall thickness. The purpose of the product and its operating parameters largely depend on these two numbers. We spoke in more detail about the range and technical characteristics of metal-plastic pipes In this article.
A thin layer of aluminum between the inner and outer layers of PEX serves to:
- partial compensation of thermal expansion of the pipe;
- formation of a diffusion barrier.
Cross-linked polyethylene is initially designed for high operating temperatures up to +95 °C. However, when heated, it begins to expand slightly. To compensate for this expansion, an aluminum insert is made between two polyethylene layers. The metal absorbs most of the stress arising in the polyethylene through the adhesive layer, preventing the plastic from expanding too much and deforming.
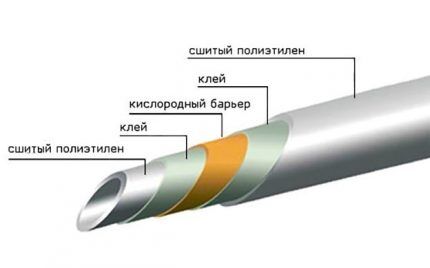
Among the advantages of metal-plastic pipelines it is worth highlighting:
- absence of stray currents;
- constant flow area;
- less noise compared to metal analogues;
- no expansion of plastic (sagging pipes) as a result of heating the water in them;
- ease of installation of the pipeline system.
The symbiosis of metal and plastic is able to withstand a short-term increase in the temperature of the water inside up to +115 °C. And plus 95 degrees Celsius is the norm for him.
Metal-plastic pipes are ideal for hot water supply systems, “warm floors” and heating. It is thanks to them that the aggressive effect of oxygen on various hydraulic pumps, as well as heating boilers and radiators can be minimized.
Among the negative aspects of metal-plastic pipes are:
- aging of polyethylene under direct sunlight;
- the need for a grounding device for plumbing fixtures with a metal body, because plastic is a dielectric;
- the need to tighten fittings a year after putting the pipeline system into operation.
Metal-plastic pipes must be covered behind the finish from direct sunlight, otherwise their service life will be sharply reduced. Fittings require tightening due to thermal deformations of the pipeline, which are simply impossible to completely get rid of.
And the main disadvantage is that metal-plastic cannot be frozen. Due to such sudden changes in temperature, it can simply come apart at the seams.
Characteristics of polypropylene products
If the internal structure of metal-plastic is a composite of several layers, then the polypropylene pipe is completely plastic.
The only exceptions are products with reinforcement in the form of perforated aluminum foil. And even then the foil layer is not glued to the plastic, like the competitor discussed above, but is soldered into the plastic.
Polypropylene pipes in stores are found in four versions:
- PN10 (1 MPa) – for cold water with water temperatures up to +20 °C and “warm floors” with operating temperatures up to +45 °C.
- PN16 (1.6 MPa) – for cold water and hot water with temperatures up to +60 °C.
- PN20 (2 MPa) – for DHW (up to +80 °C).
- PN25 (2.5 MPa) – for hot water supply and central heating pipelines with coolant temperatures up to +95 °C.
The absence of glue and the solidity of the plastic (even in the case of reinforcement) make the polypropylene pipe product more durable. Here this option wins over metal-plastic.
PPR pipes are available in grey, green, white and black. In the first three cases, this is just a color to simplify the wiring. And the black color means that the product contains additives that protect it from ultraviolet radiation.
In a metal-plastic pipe, the aluminum layer in the thickness of the polyethylene wall is located approximately in the middle. And in a product made of PN25 polypropylene, aluminum is shifted to its outer side. In this case, this layer performs exclusively reinforcing functions. Aluminum is often replaced with fiberglass, which copes with the task of strengthening no worse.
To read in more detail about the characteristics, range, types and features of polypropylene pipes and fittings used for their installation, go to via this link.
Polypropylene pipes are connected by soldering using a special soldering iron. Even with a little practice it is not difficult to work with. However, there is one caveat - if the temperature of the polypropylene at the joint is too low or too high, the connection will turn out to be fragile.
At the same time, the likelihood of underheating of the plastic and associated leaks increases sharply when working in the cold. At sub-zero temperatures, installation of PPR pipes is generally prohibited. Manufacturers recommend that polypropylene pipelines be assembled only in rooms where the air is heated above +10 °C.

In terms of advantages and disadvantages, polypropylene is generally similar to metal-plastic. The only exception is thermal expansion. As the temperature rises, the PPR pipe begins to deform. It is the plastic that expands due to heating, and in this case there is nothing to compensate for this expansion.
The pipes eventually sag. Moreover, they can not only sag, but also rest against the wall with a turn or end with a plug. And then the pipeline may be destroyed. When installing PPR, it is important to take this feature into account by providing compensating elements and sliding supports in the wiring diagram.
Comparison of metal-plastic and polypropylene
To determine whether a metal-plastic pipe is better or a polypropylene pipe, you need to carefully consider both options from all sides.In some cases, metal-plastic will be the best choice, and in others, polypropylene. It all depends on the specific conditions of installation and operation of the future pipeline.
Criterion #1 - pipe performance
In terms of plasticity, polypropylene is somewhat stiffer than metal-plastic. The second pipes are simpler bend, which simplifies their transportation and installation. This rigidity is related both to the hardness of the plastic itself and to the thickness of the pipe walls made from it. With the same performance characteristics, polypropylene products are thicker than metal-plastic ones.
Unlike polypropylene, metal-plastic pipes are bent. They are recommended to be used when installing a “warm floor” with its laying in a spiral without additional connections at the corners.
If you assemble such a heating system from polypropylene, you will have to make each bend using angle fittings. And these are additional points of potential breakthroughs.
In both cases, the internal coating of the pipes retains its smoothness, regardless of the hardness of the water or coolant inside and the temperature of the flow. Clogging due to deposits in plastic pipelines is virtually eliminated.

When comparing operating pressure, you need to look at the temperature of the water inside.If the latter is heated to +20 °C, then both types of pipes can withstand up to 25 atm. Here polyethylene is equal to metal-plastic. However, in the case of heating systems the situation changes somewhat.
As temperatures rise, a polyethylene pipe begins to lose out to a metal-plastic pipe. The first, when heated to 80–90 °C, can withstand no more than 7 atm, and the second will not break through even at 10 atm.
Criterion #2 - operating temperatures
In this parameter, metal-plastic has a slight advantage. At maximum it can withstand up to +115 °C. For polypropylene, the maximum temperature is only 95-100 °C. However, there is one caveat here.
A metal-plastic pipe can easily withstand high temperatures of hot coolant from the boiler for a long time. Its service life reaches 50 years. The polypropylene analogue will last under such loads for up to half a century, only if it is a PN25 product.
If too hot water at high pressure is introduced into a pipeline made of PPR PN10 or PN16 even once, its service life will be at most 3–4 years. These options for polypropylene pipes are not initially intended for heating systems with elevated coolant temperatures.

In terms of frost resistance, both types of pipes are comparable. That is, you should never allow water to freeze in them. If polypropylene can still withstand a slight short-term expansion due to the formation of ice inside, and then return to its original state, then metal-plastic will certainly immediately collapse when the water supply freezes.
The main advantage and main problem of metal-plastic pipes is their multilayer structure. It makes these products more resistant to high temperatures. However, with sudden temperature changes it can lead to separation of the metal from the plastic.
Aluminum and polyethylene have different expansion rates. With a sharp jump in temperature, the adhesive layer simply does not have time to transfer stress from one material to another. As a result, the metal-plastic material delaminates and the pipe simply breaks. This can happen both when the water in the pipeline suddenly heats up, and when it suddenly freezes. Plus, in the latter case, there is also the danger of rupture of the aluminum layer along the weld.
Criterion #3 - installation methods
To assemble the pipeline you will need a pipe cutter for polypropylene or metal-plastic. According to the connection technology, both polypropylene and metal-plastic pipelines belong to one-piece systems.
To connect metal-plastic pipes, only fittings are used, for installation of which three technologies are used:
In the first case, polypropylene fittings for soldering are used, and in the second, crimp couplings and press fittings are used. It is impossible to disassemble a water supply system assembled using these elements and then reinstall it in the previous configuration.
We have it on our website detailed review methods for installing metal-plastic pipes, where special attention is paid to the rules for making reliable connections.
Polypropylene pipelines greatly outperform metal-plastic pipelines in terms of quality and connection reliability. After heating and cooling of polypropylene, a chemically homogeneous monolithic joint is formed between the fitting and the pipe, provided that welding rules. It is almost impossible to break such a connection with your hands or water pressure.
But this only applies to water pipelines that are connected in compliance with all technology standards. When polypropylene is overheated or underheated with a soldering iron, the joint inevitably becomes fragile and will not last long. The result is leaks and finishing repairs. That's why it's so important to choose correct soldering temperature.
Systems made of polypropylene pipes are more complex in structure and the number of connecting elements used. Like metal-plastic ones, they cannot be bent. Each turn of the pipeline must be made using angles and tees. However, such fittings are several times cheaper than analogues for connecting metal-plastic.

If a metal-plastic pipeline is planned to be laid under a screed on the floor or embedded in a wall, then it should be assembled exclusively using press fittings. They are more reliable than couplings with crimp nuts and do not require subsequent tightening.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
To make it easier for you to understand all the nuances of choosing between polypropylene and metal-plastic, we have selected several videos describing pipes made of various materials and the features of their installation.
Review - which is better metal plastic or polypropylene:
Comparison of different plastic pipes:
Features of installation of heating systems made of metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes:
When choosing between a metal-plastic and polypropylene pipe, you need to decide in advance on the further finishing and installation method.
If you are making a “warm floor”, then it is better to buy metal-plastic with reliable press fittings. And for the water supply in the bathroom of an apartment, polypropylene, which is cheaper in materials and assembly, is quite suitable.
Are you choosing between metal-plastic and polypropylene and want to clarify certain nuances? Perhaps we did not touch upon a question that concerns you in this article? Ask our experts for advice - write your comments in the block below.
Or maybe you would like to supplement our article with useful recommendations from practice or share your observations? Write your comments - many newbies will benefit from your experience.




The information is great. I didn’t even know that these metal-plastic pipes burst due to temperature changes.Does this mean that if the hot water was turned off in the apartment and then turned back on, then the pipe is at risk? And it’s not clear how to check when soldering: are the pipes and fittings connected at a sufficiently high temperature? Could you please share this moment as urgently as possible! We installed 2 risers made of metal-plastic for hot water - after turning on the hot water, the pipes bent, although they were placed next to cold water made of simple polypropylene - smooth. Pipe made in Turkey from a company store. The sizes were chosen accurately.
The temperature in your apartment is not sub-zero, so the difference will not be very sharp. Especially if, as usual, they are turned off for a short time. There is no risk of pipe rupture in this case.
Working with polypropylene is difficult and there are few workers who know how to work with it. You can install and connect everything beautifully, or you can make it ugly. In our village, on the first floor the pipes are hidden under the floor, and on the second floor, the attic, they are inside the room. On the second floor you can see that they all went in a wave, many came off their fastenings. So if we do heating in our house, we will hide the pipes.
Just remember polypropylene cannot be hidden