Pipes for heating boilers: which pipes are best for piping the boiler + installation tips
An autonomous source of heat energy used in individual buildings is often a heating boiler running on one of the types of fuel: coal, gas or electricity.An important role in organizing heating is played by pipes for heating boilers, with the help of which piping is carried out - the assembly of all elements into a single system.
The labor intensity of installation, the cost of arrangement and the efficiency of the heating complex largely depend on the type of pipe products. Therefore, the issue of choosing pipes should be considered carefully, don’t you agree?
We will tell you what characteristics pipelines made of different materials have, outline the parameters of the heating system that must be taken into account when designing the pipeline, and also provide practical advice on installing utilities.
The content of the article:
What types of pipes can be used?
When carrying out installation work on a heating boiler, elements made of metals and polymers can be used. When choosing, you should pay attention to such characteristics as thermal insulation properties, ease of installation and operation, durability, and cost of products.
Based on the sum of these criteria, the following types of pipes are used to perform piping.
High-quality but expensive copper products
Copper piping is relatively rare, since such pipes are quite expensive and also require special skill during installation.
At the same time, structures made from this metal have a number of significant advantages, namely:
- good heat dissipation;
- resistance to corrosion and aggressive substances;
- resistance to freezing;
- high heat resistance.
Copper heats up quickly and well with a minimum amount of thermal energy, so parts made of this material will constantly generate heat during the transportation of the coolant.

Pipes made of this metal can withstand environmental influences. Over time, they can only become covered with a thin layer of oxide, which does not affect the performance characteristics at all.
Unlike pipes made of steel or polymers, ductile copper structures do not burst when the coolant in them freezes.
To the disadvantages copper pipes for heating, include the impossibility of using them to create closed structures in grooves, as well as the already mentioned high cost.
Budget steel products
Another common option is products made of steel.
Their advantages include:
- High strength, allowing you to easily tolerate mechanical loads.
- Low thermal coefficient of linear expansion, due to which the length of the parts remains unchanged even at high temperatures.
- High thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient heat transfer.
The disadvantages, first of all, include the tendency to corrosion, which destroys the metal, which is why such elements need to be painted or coated with an anti-corrosion compound.

When choosing, it is better to give preference steel pipes made of stainless steel: they are more expensive, but demonstrate greater resistance to environmental influences and better performance.
Durable and lightweight polypropylene pipelines
Such products, made from modern types of plastics, have become widespread due to many positive aspects.
Main advantages:
- Affordable price: prices for such products are significantly lower than for metal analogues.
- A light weight. Such elements weigh very little, thanks to which you can save effort and money on their storage, transportation and installation.
- Easy to install. Plastic pipes are easily assembled into finished structures. By using special soldering iron even a non-specialist can quickly arrange the harness.
- Coolant circulation speed. Polypropylene pipes, even if they have a complex shape, practically do not form blockages. This facilitates the flow of water, the speed of which remains unchanged throughout the entire service life (20-50 years).
- Good resistance to high pressure. This allows the use of plastic elements even under difficult operating conditions.
Main disadvantage PPR pipes – a high coefficient of thermal expansion, due to which these products slightly increase in length when heated. To counteract this phenomenon, measures must be taken by installing compensators.

In addition, there are special pipe options, which include aluminum foil-reinforced products marked PN 25 - they can be used in systems with pressures up to 2.5 mPa and temperatures of +95°C, as well as reinforced PN 20 elements that allow operation in conditions temperature +80°C and pressure 2 MPa.
One- and two-pipe heating systems
The choice of pipes is also influenced by the pipeline layout (single-pipe, two-pipe) through which the coolant moves.
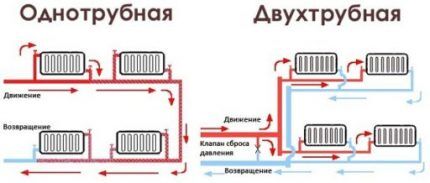
Let's look at the differences in the installation of both circuit solutions.
Option #1 - single pipe system
In this case, the “supply” departs from the boiler - the main line, which has a large diameter. It simultaneously serves both to transfer hot coolant and to collect cooled liquid.
Heating radiators are connected in series to the central artery. For this, two thin pipes are used, one of them receives the coolant, and the second - releases it.
IN single pipe heating system The liquid passes through all the radiators one by one, transferring some of the heat energy during its journey.
Two types of one-pipe circuits
Based on the design features, two system options can be distinguished: flow-through and with bypasses. The flow-through design does not provide for risers, limiting itself to the direct connection of radiators on the upper floor with their counterparts located below.
When using this scheme, you must not forget about the ban on the use of control valves, since they can prevent access to the coolant flowing to the devices.
Such a system is easy to implement, but it has a number of disadvantages. The coolant in the circuit cools down quite quickly; in addition, it is impossible to repair or adjust the system without completely shutting it down.
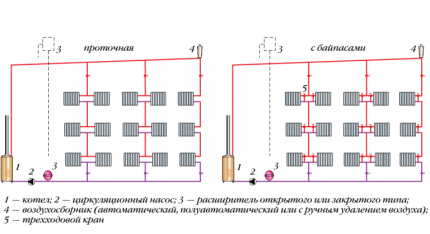
Heating system with bypasses also involves connecting radiators with risers, which are responsible for supplying the networks with coolant. At the same time, the batteries are separated from the circuit by closing links.
The coolant is distributed over all connected devices in portions at almost the same time, due to which the heated liquid cools down significantly less than in flow-through circuits.
With a heating circuit with bypasses, it is possible to adjust the temperature and repair the outgoing device without shutting down the system.
Selecting elements for a one-pipe system
The most popular option for implementing single-pipe heating schemes are steel products, which have reasonable prices and good technological characteristics. They are especially common in older apartment buildings.
When installing pipes, it is necessary to observe a slope, the value of which should exceed 5 millimeters per 1 linear meter. Such installation ensures free transfer of coolant, which will continue even in the event of a sudden or planned shutdown of the circulation pump.

For wiring the forward and return lines of a single-pipe system, elements of large diameter (<50 mm) are used, while for connecting heating radiators in an open system, structural elements with a diameter of 32 mm are sufficient.
Option #2 - effective two-pipe scheme
This version of the heating circuit provides two lines: along one of them - “supply” - the coolant is transported, which is heated in the boiler, and along the second - “return” - cooled liquid is collected, which is discharged to the heating unit.
This modification of the heating system provides for parallel connection of batteries. Since the intensity of liquid circulation depends on the difference in temperature between the supply and return connections, the coldest battery will warm up faster, and, consequently, the temperature in all connected devices will be equalized.
The advantages of two-pipe systems include:
- high coolant circulation rate;
- the ability to create hidden systems with pipelines hidden in walls or floors;
- air heating efficiency;
- hydrodynamic stability of the system;
- possibility of easy connection of a device used to regulate the supply of hot water.
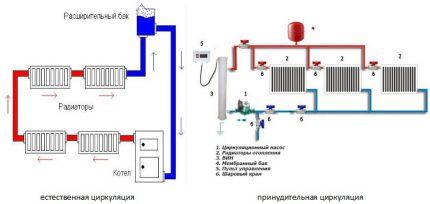
Two-pipe systems can be of different types:
- with bottom or top wiring;
- with associated or dead-end coolant transfer;
- natural and forced circulation (in the latter case, a circulation pump is used).
A two-pipe system is significantly more expensive than a single-pipe system, and is also more difficult to install than the latter. At the same time, this option guarantees more comfortable operating conditions.
Among the disadvantages of such a system are such factors as:
- double the number of pipes required to lay the structure, which significantly increases its cost and increases the time required for installation;
- the need to use various types of control and shut-off valves.
Despite the comments made above, it is two-pipe system is considered the preferred solution, especially when it comes to a network connected to autonomous boilers.
It works with greater efficiency and allows you to quickly achieve a comfortable microclimate. The compatibility of such structures with all types of boilers and various types of heating batteries also attracts attention.
Design elements for two-pipe systems
When choosing parts for the construction of two-pipe structures, it is better to give preference to polypropylene elements, although you can use other options (copper, metal-plastic) that can withstand high temperature and pressure.

Pipes with a diameter of 50 mm are optimally suited for the supply and collection lines that are connected to the boilers. Similar parts are also used to make risers to which radiators are attached.
Connection to the supply and return of batteries is made with pipes of various diameters, the choice of which is influenced by the number of sections:
- to connect 25-35-section radiators, pipes with a diameter of 1.5 inches are required;
- 10-25 section – 1 inch;
- less than 10 sections - three quarters of an inch.
To prevent heat loss, all pipes and connections must be thermally insulated.
Tips for installation work
When piping heating boilers, certain rules should be applied. For example, it is recommended to use polypropylene pipes, the markings of which indicate service class 5, operating pressure 4-6 atmospheres, nominal pressure (PN) - 25 atmospheres or higher.
To prevent changes in the dimensions of PPR pipelines during design, the installation of compensation loops should be considered.

At boiler piping polypropylene fittings can be connected to pipes into a single heating system by screwing a thread or by cold/hot welding. The threaded method is much more convenient, but it will cost much more due to the need to use a large number of adapters.
It is impossible to do without threaded fittings if there is a need to connect polypropylene pipes to metal parts or to arrange fasteners between elements of different diameters.

For convenient installation of linear systems and making node connections, a large assortment of fittings is designed: tees, couplings, adapters and others.
Cold welding means the use of a special adhesive composition that secures the parts of the system. Recently, this method has practically fallen out of use, since its results are not reliable enough.
The threaded connection allows the reuse of structural elements: if problems arise, they can be disassembled and then the elements can be screwed back on. Welding allows you to install more reliable systems, but they are disposable: if the structure has the slightest malfunction, it will need to be replaced.

For hot welding a special apparatus is used designed for soldering plastic elements. In this case, both parts of the structure are simultaneously heated on the nozzle to a melting temperature of 260°C, after which they are pressed against each other, forming a reliable connection.
When connecting reinforced pipes with foil, the metal layer must be cleaned so that it does not interfere with fastening, whereas with elements with fiberglass this operation can be safely avoided.
Plastic does not combine well with antifreeze, so in systems made of polymer elements, only heated water is suitable as a coolant.
When making heating systems, all threaded connections should be sealed using paronite or other high-temperature sealant, since the coolant circulating in them has a high temperature.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
In the video below you will hear a reasoned opinion from a specialist on the use of different types of pipes for installing a heating system.
To perform boiler piping, you can use different types of pipes, for the optimal selection of which you should take into account a whole range of factors: features of the boiler and heating system, material capabilities, personal preferences.
If you have some qualifications, you can install plastic elements yourself, strictly following the diagram, but for installing metal pipes it is better to seek help from specialists.
Are you looking for high-quality pipes for piping your boiler? Or do you have experience in installing and using a certain pipe product? Please leave comments on the article, ask questions and participate in discussions. The contact form is located below.




It seems to me that if a heating boiler is installed in a living space, then it is stupid to save on piping and install something other than copper. At the very least, you can make copper in the boiler room and risers, and the rest, for example, with metal-plastic.Estimate the cost of the boiler and consider whether the small savings are worth the reduced efficiency of the entire system. In my opinion, this is unreasonable.
I have a solid fuel boiler, I didn’t want metal, although of course it was necessary. You need a pipe bender, or bends, threads, in general, no. I installed ecoplastic pipes - this is a good quality PP pipe. True, a large diameter does not come cheap. It's been going on for eight years now, everything is fine.
It happened a couple of times, the boiler boiled, the temperature rose to 120C, but the pipe did nothing, it can withstand short-term high temperatures.