Open heating system: schematic diagrams and design features
Due to its ease of installation, low cost and sufficient efficiency, the open heating system continues to be in demand.Once you understand the principle of operation, equipment and installation rules, you will be able to organize the heat supply to your home yourself.
We will tell you how to create a workable open-type heating circuit. We will show you how to build a system, strictly following technological requirements and standards when selecting and connecting elements. Taking into account our recommendations, you will build a trouble-free, efficient circuit.
We offer independent craftsmen to familiarize themselves with practice-tested assembly options. The information presented for consideration is supplemented with useful diagrams, photo collections, and video instructions.
The content of the article:
Equipment and principle of operation of the system
IN water heating system Liquid acts as an intermediary in the transfer of thermal energy from the boiler plant to the radiators. Coolant circulation can be carried out over long distances, providing heating for houses and rooms of different sizes. This explains the widespread introduction of water heating.
The operation of an open type heating system is possible without the use of a pump. Coolant circulation is based on the principles of thermodynamics.The movement of water through pipes occurs due to the difference in density of hot and cold liquids, as well as due to the slope of the laid pipes.
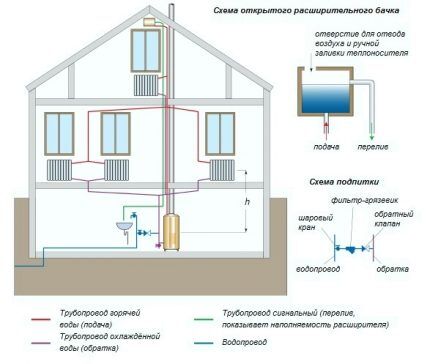
An indispensable element of the system is an open expansion tank into which excess heated coolant flows. Thanks to the reservoir, the liquid pressure is automatically stabilized. The container is installed above all system components.
The entire process of functioning of “open heating” is conventionally divided into two stages:
- Innings. The heated coolant moves from the boiler to the radiators.
- Return. Excess warm water enters the expansion tank, cools and returns to the boiler.
In one-pipe systems, the function of supply and return is performed by one line; in two-pipe systems, the supply and return pipes are independent of each other.
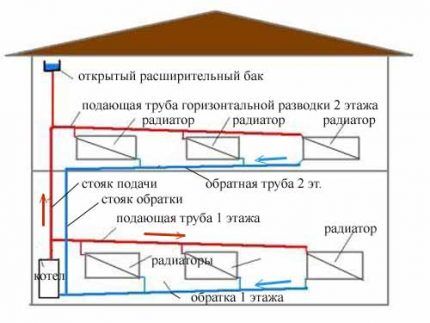
It is considered the simplest and most accessible for self-installation single pipe system. The design of the system is elementary.
The basic package of one-pipe heat supply includes:
- boiler;
- radiators;
- expansion tank;
- pipes.
Some people refuse to install radiators and place a pipe with a diameter of 8-10 cm around the perimeter of the house. However, experts note that the efficiency of the system and ease of use with this solution are reduced.
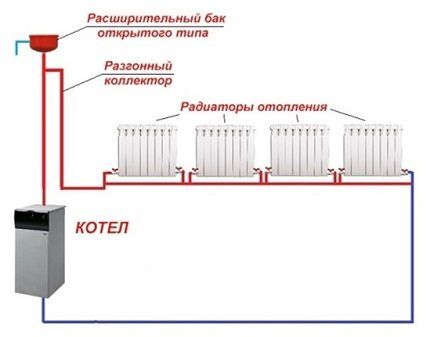
More complex to design and more expensive to implement two-pipe heating option. However, the costs and complexity of the construction are fully offset by the elimination of the standard disadvantages of single-pipe systems.
A coolant with an equal temperature is supplied almost simultaneously to all devices; the cooled water is collected by the return line and does not flow into the next battery.
Requirements for arrangement and operation
When installing heat supply to a home, it is important to take into account a number of features of an open heating system:
- To ensure normal circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point in the line, and the expansion tank at the highest point.
- The optimal place to place the expansion tank is the attic. During the cold season, the container and supply riser within the unheated attic must be insulated.
- The laying of the main line is carried out with a minimum number of turns, connecting and fitting parts.
- In a gravity heating system, water circulates slowly (0.1-0.3 m/s), so heating should occur gradually. Do not allow it to boil - this accelerates the wear of radiators and pipes.
- If the heating system is not used in winter, the liquid must be drained - this measure will keep the pipes, radiators and boiler intact.
- The coolant level in the expansion tank must be monitored and periodically replenished. Otherwise, air pockets will appear in the line, reducing the efficiency of the radiators.
- Water is the optimal coolant.Antifreeze is toxic and is not recommended for use in systems that have free contact with the atmosphere. Its use is advisable if it is not possible to drain the coolant during an unheated period.
Particular attention is paid to calculating the cross-section and slope of the pipeline. Design standards are regulated by SNiP number 2.04.01-85.
In circuits with gravitational movement of the coolant, the cross-sectional size of the pipe is larger than in pumping circuits, but the total length of the pipeline is almost two times less. The slope of the horizontal sections of the system, equal to 2 - 3 mm per linear meter, is suitable only when installing heat supply with natural movement of the coolant.
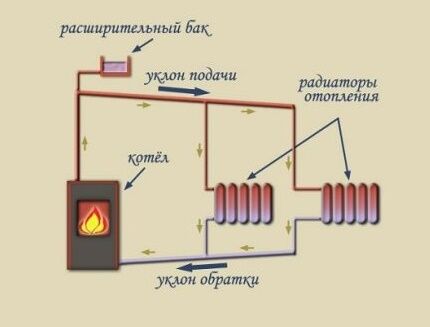
Types of open heating schemes
In an open heating system, the coolant moves in two different ways. The first option is natural or gravitational circulation, the second is forced or artificial stimulation from a pump.
The choice of scheme depends on the number of floors and area of the building, as well as on the expected thermal conditions.
Natural circulation in heating
IN gravitational system there is no mechanism to ensure the movement of the coolant. The process is carried out solely by the expansion of hot water. For the operation of the circuit, an accelerating riser is provided, the height of which is at least 3.5 m.
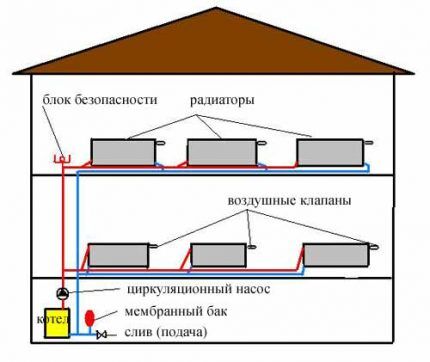
The natural circulation heating system is optimal for buildings with an area of up to 60 square meters. m. The maximum length of the circuit capable of providing heat is considered to be a 30 m mainline. An important factor is the height of the building and the number of storeys of the house, which allows the installation of an accelerating riser.
The natural circulation scheme is not suitable for low-temperature applications. Insufficient expansion of the coolant will not create the proper pressure in the system.
Possibilities of the gravity circuit:
- Connection to heated floors. A circulation pump is mounted on the water circuit leading to the floor. The rest of the system operates as usual. If the power goes out, the house will continue to be heated.
- Working with the boiler. The heating device is mounted at the top of the system - slightly below the expansion tank.
To ensure uninterrupted operation, a pump can be installed on the boiler. Then the heat supply and hot water production scheme automatically becomes a forced option. Additionally, a check valve is installed to prevent recirculation of the coolant.
Forced system with pump
In order to increase the speed of the coolant and reduce the time for heating the room, a pump is built in. The movement of water flow increases to 0.3-0.7 m/s. The intensity of heat transfer increases, and the branches of the main heat up evenly.
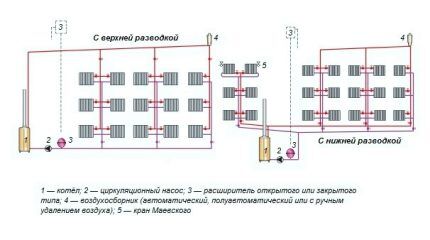
Important points of organization compulsory system:
- The circuit with a built-in pump is volatile. To ensure that the heating of the room does not stop during a power outage, the pumping equipment is placed on the bypass.
- The pump is installed in front of the boiler inlet on the return pipe. The distance to the boiler is 1.5 m.
- When installing the pump, the direction of water movement is taken into account.
Two shut-off valves and a bypass elbow with a circulation pump are mounted on the return line. If there is current in the network, the taps close - the coolant moves through the pump. If there is no voltage, then the valves must be opened - the system will switch to natural circulation.
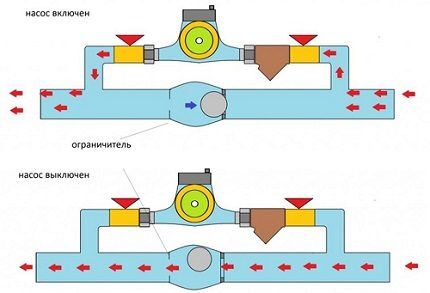
Options for piping in the system
From the layout heating devices and connecting pipes depend on the efficiency, economy and aesthetics of the heating system. The choice of wiring is determined based on the design features and area of the house.
Specifics of one-pipe and two-pipe schemes
Heated water flows to the radiators and back to the boiler in different ways. In a single-circuit system, the coolant is supplied through one large-diameter pipeline. The pipeline runs through all radiators.
Advantages of a single-pipe self-circulation system:
- minimal consumption of materials;
- ease of installation;
- limited number of pipes inside the living space.
The main disadvantage of a scheme with one pipe performing supply and return duties is the uneven heating of the heating radiators. The heating intensity and heat transfer of the batteries decreases as they move away from the boiler.
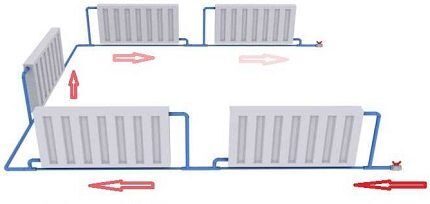
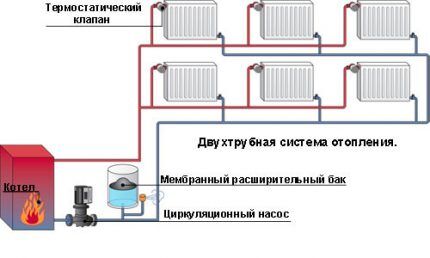
The two-pipe heating scheme is confidently gaining ground. Radiators connect the return and supply pipelines. Local rings form between the batteries and the heat source.
Main advantages of the system:
- all heating devices heat up evenly;
- the ability to adjust the heating of each radiator separately;
- reliability of operation of the circuit.
A dual-circuit system requires large investments and labor costs. It will be more difficult to install two lines of communications along building structures.
Upper and lower coolant supply
Depending on the location of the main line supplying hot coolant, a distinction is made between upper and lower connections.
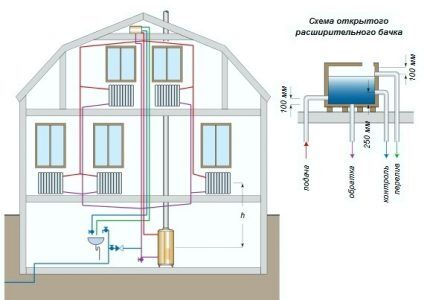
With overhead distribution, warm water rises through the main riser and is transferred through distribution pipelines to the radiators. The installation of such a heating system is advisable in one- and two-story cottages and private houses.
A heat supply system with bottom wiring is quite practical. The supply pipe is located at the bottom, next to the return pipe. Coolant movement in the direction from bottom to top. The water, having passed through the radiators, is directed through the return pipeline to the heating boiler. Batteries are equipped Mayevsky cranes to remove air from the line.
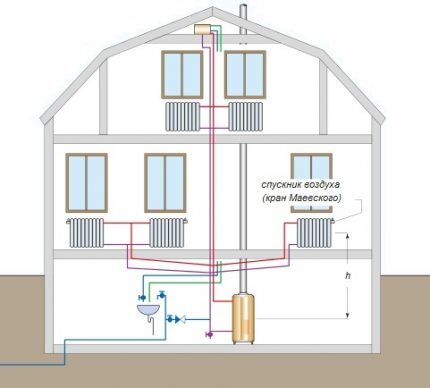
Vertical and horizontal risers
Based on the type of position of the main risers, a distinction is made between vertical and horizontal pipeline routing methods. In the first option, radiators on all floors are connected to vertical risers.
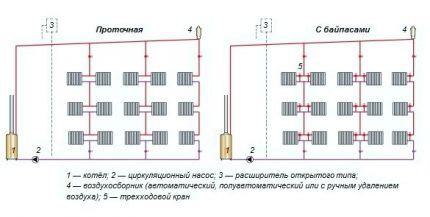
Features of “vertical” systems:
- no air pockets;
- suitable for heating high-rise buildings;
- floor connection to the riser;
- difficulties in installing apartment heat meters in multi-storey buildings.
Horizontal wiring involves connecting radiators on one floor to a single riser. The advantage of the scheme is that the device uses fewer pipes and installation costs are lower.
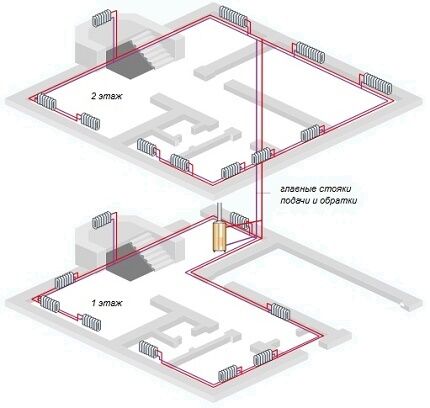
Arrangement of gravity type heating
It is better to entrust the development of a gravity system project to heating specialists. The document specifies the type of heating, method of connecting radiators and circulation of coolant, recommended equipment parameters, number of radiators and pipeline footage.
Heat supply system calculation
It is necessary to determine the hydraulic characteristics of the system, which will subsequently help to correctly select the optimal pipeline diameter.
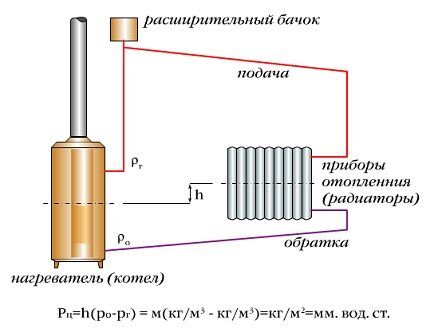
To calculate the value of the circulation pressure (RC) you must have the following data:
- Distance from the center of the heating boiler to the center of the radiator (h). The greater the distance between these devices, the more stable the circulation.
- Cooled down pressure (Ro) and heated (Pr) water.
The circulation pressure depends only on the temperature difference of the coolant. Exact indicators can be found in the tabular data.
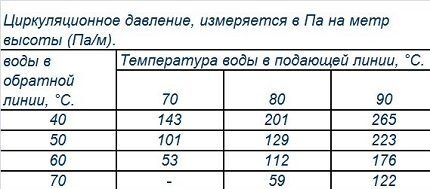
To width pipeline sections influenced by the type of material. The diameter of the steel pipe must be at least 50 mm. After branching, the cross-section of the highway narrows by one size. The return, on the contrary, is assembled with subsequent expansion.
Particular attention is paid to the volume of the expansion tank. The size of the reservoir should not be less than 5% of the total volume of coolant in the system. Failure to comply will result in water draining from the system or pipe rupture.
Selection of main components
For an open system, it is better to choose a boiler that runs on solid fuel or fuel oil. Installation of electric boilers and gas equipment is prohibited.Air jams sometimes form in the line - this can lead to an emergency.
The heater power is determined based on the calculation - 1 kW of heat energy per 10 sq.m of house. Depending on the quality of the room insulation, 10-30% is added to the obtained value.

The expansion tank for a gravity-type heating system must be made of steel. It is highly undesirable to use polymeric materials. For heating a small one-story house, a tank of 8-15 liters is suitable.
To construct the pipeline, pipes made of the following materials are used:
- Steel. They are characterized by high thermal conductivity and resistance to high pressure. The disadvantage is the complexity of installation and the need to use welding equipment.
- Polypropylene. Main advantages: resistance to temperature fluctuations, strength, tightness and ease of installation. Service life – 25 years.
- Metal-plastic. The material does not corrode and prevents clogging of the circuit. Disadvantages of the highway: limited service life (up to 15 years) and high cost.
- Copper. Pipes with maximum heat transfer and resistance to high temperatures - up to +500°C. The main disadvantage is the high cost of the material.
In an open heating circuit radiators are installedmade from high strength metals.
The most common are steel models. They have an optimal balance of key parameters: appearance, price and thermal power.

Open system installation steps
The entire process of organizing a gravity heating system can be divided into several stages:
- Boiler installation. The equipment is fixed on the floor surface or hung on the wall. The choice of method depends on the dimensions of the boiler.
- Pipeline layout according to the chosen scheme and developed project. It is important to observe the recommended slope angle of the pipe circuit.
- Radiator installation heating and connecting them to the system.
- Installation of expansion tank and its insulation.
- Connecting all the elements, checking the tightness of joints and starting the system.
After the boiler, on the supply pipe, it is advisable to install a temperature sensor to monitor the efficiency of the heating system.

Features of assembling a forced circuit
In order for the compulsory system to justify itself and function properly, it is necessary to choose the right circulation pump and correctly “embed” it into the heating main.
Selecting a circulation pump
The main parameters for choosing pumping equipment: device power and pressure. These characteristics are determined based on the area of the heated room.
Indicative indicators:
- for houses of 250 sq.m., a pump with a power of 3.5 cubic meters per hour and a pressure of 0.4 atm is suitable;
- in rooms measuring 250-350 sq.m, install the device at 4.5 cubic meters per hour with a pressure of 0.6 atm;
- if the area of the house is 350-800 sq.m, then it is advisable to purchase a pump with a capacity of 11 cubic meters per hour, the pressure of which is at least 0.8 atm.
In a more scrupulous selection, specialists take into account the length of the heating system, the type and number of radiators, the material of manufacture and the diameter of the pipes, as well as the type of boiler.
Installing the pump in the main
The pump is placed on the return line so that the coolant that is not too hot passes through the device. It is possible to install modern models made of high-temperature resistant materials on the supply line.
When inserting the pump, the water circulation should not be disrupted. It is important that at any point in the pipeline when the pumping unit is operating, the hydrostatic pressure remains excessive.
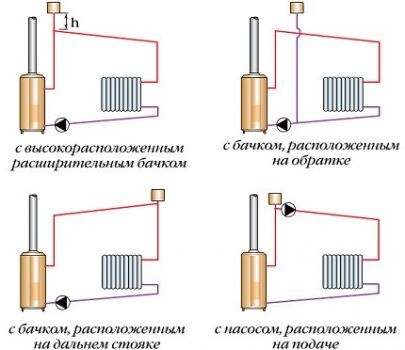
Option 1. Raising the expansion tank.A simple way to convert a natural circulation system to a forced one. To implement the project you will need a high attic space.
Option 2. Moving the tank to a distant riser. The labor-intensive process of reconstructing the old system and installing a new one is not justified. Simpler and more successful methods are possible.
Option 3. Expansion tank pipe near the pump nozzle. To change the type of circulation, it is necessary to cut off the tank from the supply line, and then connect it to the return line - behind the circulation pump.
Option 4. The pump is included in the supply line. The simplest way to reconstruct the system. The disadvantage of the method is unfavorable operating conditions for the pump. Not every device can withstand high temperatures.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Recommendations for assembling a heating system with natural circulation:
Video #2. Procedure for installing the circulation pump:
Important aspects of arranging an effective heating system are choosing a workable circuit, calculating the parameters of the main line, selecting components and following installation technology. Manual installation is possible if you have plumbing skills, but it is better to entrust the development of a detailed project to professionals.
Do you want to ask a question about the organization diagram and wiring of an open water supply circuit? Please leave comments in the block below. Here you have the opportunity to ask a question or report an interesting fact on the topic.




An open heating system is quite widespread in villages and suburbs because it is easy to operate and very cheap to install.But when you start using it, you realize that you need to know how it actually works, what the driving forces are in the heating process. If you are going to install such a system, do not be lazy and read about the principle of its operation, features, pros and cons of heating of this type. But don't forget to consult a specialist.
Ilya, there is nothing good about such a heating system, it is a relic of the past, now rarely anyone does it. It is not economical even in terms of fuel consumption. Judge for yourself how much water flows in all these thick-diameter pipes and radiators (only cast iron ones fit there).
Its only advantage is that it is electrically independent, that is, there is no light, but you have heat, there is no pump in the system.
But the view is, to put it mildly, depressing - pipes all over the house, this terrible slope, bulky expansion tank, constantly gurgling... No, I definitely wouldn’t want one like that.
I have an open system on a two-story house. Bimetallic radiators. The distribution pipe is copper 18 and 22, the slope is 5 mm per meter, not noticeable to the eye. The accelerating riser is 50 mm, structurally hidden. Expansion tank - 8 liters. Nothing gurgles :)
Hello, there is a problem: low pressure occurs in the pipe heating system (without radiators). This becomes clear when you try to bleed air through the pump and Mayevsky taps, but on the contrary, air is sucked into the system. The question is: why can the pressure in an open heating system decrease?