Do-it-yourself water heating: everything about water heating systems
If a country house is actively used not only during the summer season, but also during the cold season, the creation of a high-quality heating system in it is an urgent need.
Different coolants can be used in heat supply lines: air heated to 60°C, water steam at 130°C and water at a temperature of 95°C. Water heating is most often used.
One of the main advantages of this coolant is the ability to install various water heating systems depending on the design features of the house, personal preferences and other factors.
In the article, we described a detailed classification of water heat supply schemes, outlined the features of each option, and also provided recommendations for choosing the main components of the system. The information presented will help you design the heating of a private home.
The content of the article:
- Classification of water heating systems
- Requirements for the operation of the heating system
- Equipment power calculations
- Water heating systems
- Methods for installing water heating systems
- Open and closed heating systems
- Heating system elements
- Water system "Warm floor"
- Baseboard heating system
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Classification of water heating systems
Depending on the location of the place where heat is generated, water heating systems are divided into centralized and local. In a centralized manner, heat is supplied, for example, to apartment buildings, all kinds of institutions, enterprises and other objects.
In this case, heat is generated in CHP plants (combined heat and power plants) or boiler houses, and then delivered to consumers via pipelines.
Local (autonomous) systems provide heat, for example, to private homes. It is produced directly at the heat supply facilities themselves. For this purpose, furnaces or special units operating on electricity, natural gas, liquid or solid combustible materials are used.
Depending on the method by which the movement of water masses is ensured, heating can be with forced (pumping) or natural (gravitational) movement of the coolant. Systems with forced circulation can be with ring circuits and with primary-secondary ring circuits.
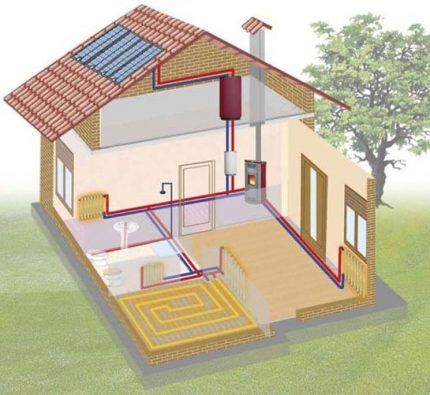
In accordance with the direction of movement of water in supply and return lines, heat supply can be with associated or dead-end movement of the coolant. In the first case, water moves in the mains in one direction, and in the second - in different directions.
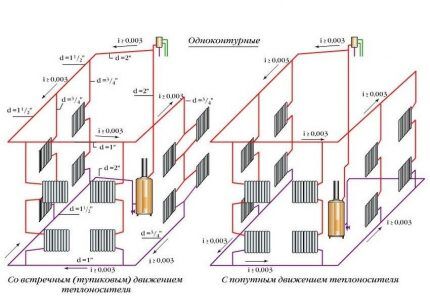
Heating pipes can be connected to heating devices in different patterns. If heating devices are connected in series, such a circuit is called one-pipe, if in parallel - two-pipe.
There is also a bifilar scheme, in which all the first halves of the devices are first connected in series, and then, to ensure reverse outflow of water, their second halves are connected.
The location of the pipes connecting the heating devices gives the wiring its name: there are horizontal and vertical varieties. According to the assembly method, collector, tee and mixed pipelines are distinguished.
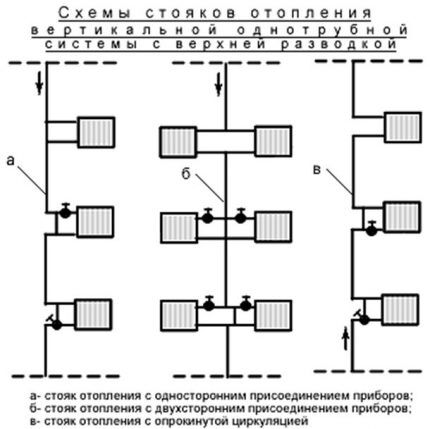
In those residential buildings where there are no basements, but there is an attic, heating systems with overhead wiring are used. In them, the supply line is located above the heating devices.
For buildings with a technical basement and a flat roof, heating with bottom wiring is used, in which the water supply and drainage lines are located below the heating devices.
There is also a wiring with “inverted” coolant circulation. In this case, the return heat supply line is located below the devices.
Requirements for the operation of the heating system
With all the variety of water heating systems, there are a number of general requirements for their operation.
They have to:
- uniformly warm up all the air in the rooms;
- be repairable;
- do not create difficulties during operation;
- be linked to ventilation systems;
- be regulated.
The operating principle of the heating system itself is also common: water is heated, after which it circulates through the pipeline and releases the resulting heat, warming the rooms.
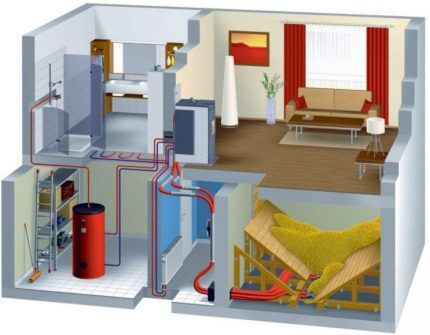
Equipment power calculations
The indoor temperature depends on the following factors:
- air temperature outside the building;
- house wall thickness and the quality of its individual elements;
- heat capacity of materials, from which the house is built.
When calculating your home's heating needs, you need to take into account all factors, including heat loss through windows and doors, walls and floors with ceilings. Special standards required in the calculation process must be applied taking into account the climatic conditions of the area in which the residential property is located and the degree of existing thermal insulation.

The greatest heat loss occurs through the outer walls of the house. As the temperature difference between inside and outside the building increases, heat loss also increases.
If we take into account the material from which the external walls were built and the thickness of these walls, then for an external air temperature of – 30°C, the heat loss will be different and amount to:
- brick with internal plaster - 89 W/m² (2.5 bricks), 104 W/m² (2 bricks);
- chopped with internal lining (250 mm) - 70 W/m²;
- from timber with internal lining - 89 W/m² (180 mm), 101 W/m² (100 mm);
- frame with expanded clay inside (200 mm) – 71 W/m²;
- foam concrete with internal plaster (200 mm) – 105 W/m².
However, heat loss occurs not only through external walls, but also through other enclosing structures.
At the same – 30°С they will be for:
- wooden attic floors - 35 W/m²;
- wooden basement floors – 26 W/m²;
- double wooden doors without insulation – 234 W/m²;
- windows with double frame made of wood – 135 W/m².
To calculate the total heat loss of a building, you need to calculate the area of all enclosing structures in square meters, multiply by the standard heat loss by type of structure, taking into account the materials from which they are made, and summarize the results.
The calculation should be made based on the minimum seasonal temperature of a particular area. Heat losses through the walls are calculated separately, because it is necessary to take into account the area of glazing and doorways.
Losses through floors without hatches into the attic or underground are calculated for the entire area as for single structural elements.
The heating boiler is chosen taking into account the fact that its power should be enough to compensate for heat loss with a 20-30 percent margin.
The procedure for calculating the thermal power of the equipment that will be used to install the heating system is given in the video clip at the end of the article.
On our website there is a block of articles devoted to the calculation of water heating, we recommend that you read:
- Hydraulic calculation of a heating system using a specific example
- Calculation of water heating: formulas, rules, examples of implementation
- Thermal calculation of a heating system: how to correctly calculate the load on the system
Water heating systems
Despite all the external differences and different connection schemes, the basic operating principle of water heating systems is the same. The coolant heated in the boiler is transported through a pipeline to the heating devices.
As the water cools, it transfers heat to the environment and then returns to the place where it will be heated. This cycle repeats itself over and over again.
Natural and forced circulation
The following types of heating systems are used in private homes:
- with natural circulation;
- with forced circulation.
Natural circulation. Its performance is based on the difference in density between hot and cold. The upper positions of such a system are occupied by warm water, and the lower positions by cold water. When warm water cools down, it moves down, and when it warms up, it moves up.
The second factor that ensures the natural circulation of water masses is the slope at which the pipes are installed.
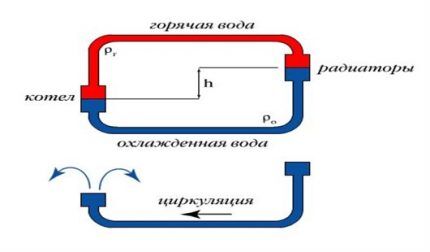
Advantage natural circulation schemes is its complete independence from power supply.
It has many more disadvantages:
- small rangei, not exceeding 30 m in horizontal dimension;
- warm-up duration — a long period of reaching operating temperatures at all points of the system upon startup after a long break;
- risk of work stoppage due to ice formation in the open expansion tank.
The diameter of the pipeline must be large enough due to the low circulation pressure in the circuit. This factor also influences the choice of batteries, because modern radiators have a too narrow cross-section, which creates additional resistance that counteracts circulation by gravity.
In order to further stimulate the movement of the coolant, the pipeline is constructed with a slope so that there is an average of 3 mm per 1 linear meter. Correct installation of pipes at the right angle is not an easy task, but without solving it, the system will function much slower and more efficiently.
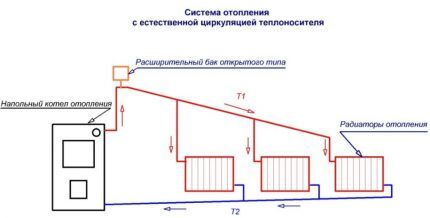
The coolant flows to the distant radiators of gravity systems when it has already cooled down significantly. To maintain the heating temperature, cast iron radiators should be used. To balance the temperature difference, the furthest batteries must have more sections than those closest to the boiler.
Forced circulation provides the pump. The circuit may contain one or several pumps. Using several pumps is preferable: an emergency shutdown of one of them will not damage the entire heating system.
The coolant moves cyclically along a closed circuit, which includes an expansion tank, which eliminates the evaporation of water.

Advantages forced circulation systems:
- for heating installation you will need more pipes, but of a smaller diameter;
- you can use different types of radiators and heat pipes with small diameters;
- the temperature of heating devices is easier to regulate;
- the range of action has been significantly expanded due to artificial stimulation of coolant movement;
- the possibility of using heating units with increased coolant characteristics.
The disadvantage of forced systems is their dependence on energy supply. In order to avoid incidents with complete heating inactivity, it is recommended to stock up on a diesel or gasoline generator.
In addition, the disadvantages include:
- the need for accurate calculation diameter of the pipeline, because too narrow channels will sharply increase the hydraulic resistance, and when circulating through excessively wide pipes, the coolant will “noise”;
- considerable cost of construction due to the almost double length of the pipeline, the inclusion of one or two circulation pumps, if necessary, a booster pump;
- mandatory use of expensive regulators coolant flow, its temperature and pressure in the system.
The correct choice of the type of circulation depends on the individual characteristics and location of the building in which the water heating will be installed. However, recently they have begun to resort to schemes with natural movement less and less, using them mainly in buildings for temporary residence.
Most often, private houses are equipped with systems with artificially forced coolant movement due to significantly greater capabilities.
Combined circulation systems
The combined system can operate in both natural and forced modes. This means that when installing it, it is necessary, as in the case of using natural circulation, to provide for a pipe slope of 3-5 mm per linear meter, as well as installing a pump, as for forced circulation.
Typically, such a heating scheme includes a solid fuel boiler.
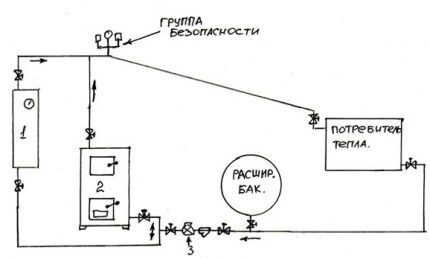
The point of using a combined system is that it will continue to operate even in the event of a power outage. But a sudden cessation of heating in winter threatens not only a decrease in the temperature in the room.
Elements of the heating system may simply fail because water, expanding when freezing, will break their tightness.
Methods for installing water heating systems
Let's consider two main installation schemes for heating systems.
Single pipe heating system
The design of the pipeline in the single-pipe version is characterized by a direct sequence of supplying coolant to the radiators. The coolant fills and warms up the first battery, then the next, and so on.
Two pipes are connected from one pipe to each radiator: the first is needed to supply coolant, and the second is to drain partially cooled water.
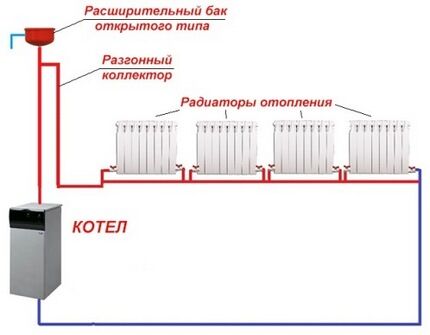
The peculiarity of this scheme is the relatively low heating of the last battery compared to the first, since the water “reaches” it, having already given up part of its heat.
Another disadvantage single-pipe heating option It is believed that it is impossible to stop the supply of coolant to one specific radiator in the event of a breakdown. You'll have to shut down the entire system.
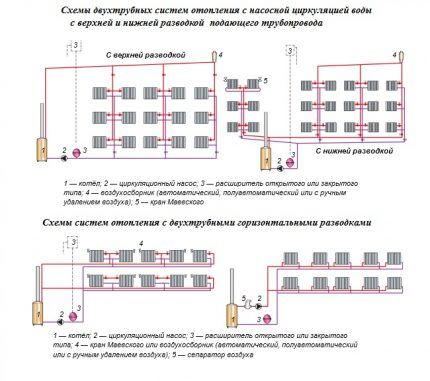
Two-pipe system and its varieties
In a two-pipe heating scheme, as is already clear from the name, not one, but two pipes are involved. In this case, each of the batteries is connected by one pipe to the main line through which the coolant is supplied, and by the second to the return pipe. It turns out that separate pipes are provided for hot and cooled coolant.
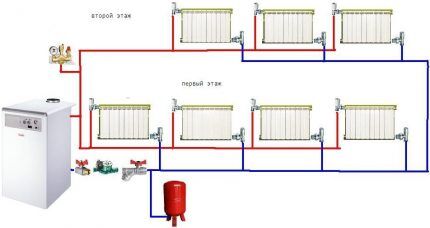
Thanks to this heating design, the water in all radiators has almost the same temperature. The operation of such a system is easier to control, adjust and automate.
The two-pipe system, in turn, is divided into two types:
- with the upper gasket of the supply pipe, i.e. with top wiring;
- with the bottom gasket of the supply pipeline, i.e. with bottom wiring.
Systems with overhead wiring are built mainly in multi-storey buildings with an attic space. Schemes with bottom routing are a priority in private low-rise construction, because they make it possible to hide the laying of the pipeline to the maximum and eliminate or reduce the number of risers.
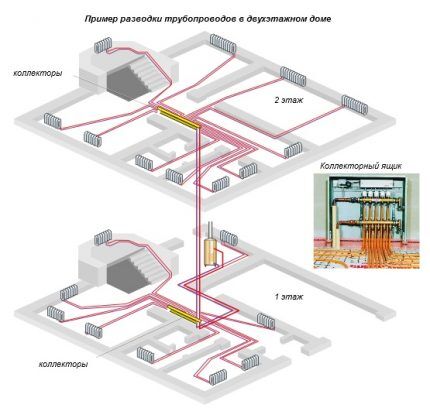
Comparative characteristics of single-pipe and two-pipe heating system is given in the video material, which is located at the bottom of our article.
Open and closed heating systems
In addition to the types of water heating systems we have already discussed, there is a division into open and closed structures.
Open heating system consists of a boiler (any type except an electric one is used), pipelines, heating radiators and an expansion tank into which excess water flows as it expands during the heating process.
The tank is not sealed, water from the system can evaporate, so its level must be monitored and topped up if necessary.
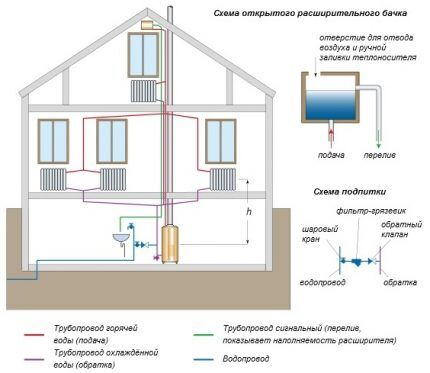
Pump in open heating system does not apply. The heating boiler is located at its lowest point, and the expansion tank is located at its highest point.
Closed design is airtight. It includes all the same elements as the open one. But since the movement of coolant in it is forced, the mandatory list of elements is supplemented by a circulation pump.
The expansion tank, which is part of a closed structure, consists of two rolled parts, separated by a diaphragm. When an excess of expanded liquid occurs in the system, it enters one of the chambers of the tank, pushing the diaphragm into the second chamber filled with nitrogen or air.
As the coolant expands, the pressure in the system increases, and the part of the tank filled with water tends to displace and compress the gas mixture. When the pressure limit in the tank is exceeded, a safety valve is activated, releasing excess coolant.

Each heating system has its own advantages and disadvantages. They differ in a number of characteristics and are suitable for various objects. If you need to heat a small private house or cottage, use a simple and reliable open design.
More difficult to install and operate closed heating system more often used in solid cottages and multi-storey buildings.
Heating system elements
Since we are going to install water heating in the house with our own hands, we need to have an idea of the components of the proposed design.
Determining the right boiler
The boiler is the heart of the heating system.It is very important to choose it correctly, since the reliability of heat supply largely depends on it.

Depending on the fuel used in the boiler, the following types of these devices are distinguished:
- Gas. This boiler is most popular among consumers. It is easy to install and works without unnecessary noise. Gas is relatively inexpensive and produces a lot of heat when burned. But to use it, you need to obtain permission, order the installation of a supply line and organize exhaust ventilation in the boiler room.
- Electrical. These boilers are the safest. Their installation location does not require any additional equipment. Their operation does not produce open flames or combustion products that could cause poisoning. But the efficiency of this device is relatively low, electricity is expensive, and the energy-intensive boiler requires a reliable power grid.
- Liquid fuel. Unlike gas boilers, these boilers are equipped with a special type of burner. This equipment requires a special boiler room. Liquid fuel quickly pollutes the boiler.
- Solid fuel. These devices burn coal briquettes and other types of solid fuel. If you are ready to prepare firewood or coal for the entire cold season, then you can use this option.
Combination boilers are considered the most reliable, in which different types of fuel can be used. There is only one drawback to such equipment - such boilers are expensive.
What are heating radiators?
In order not to be disappointed with the results of the work performed, you need to take a responsible approach to the choice of radiators. In this case, you should focus not so much on aesthetic qualities, but on the technical characteristics of the batteries. And the technical properties largely depend on the material used to make these products.

Radiators are:
- Steel. These inexpensive products are too susceptible to corrosion. If in the summer, when heating is not used, the water is drained from the system, the service life of steel radiators can be significantly reduced.
- Aluminum. These attractive looking radiators heat up fairly quickly. Only significant pressure drops have a negative effect on them. In private homes this danger does not threaten them.
- Bimetallic. Such batteries are resistant to corrosion from aluminum, and high heat dissipation from steel.
- Cast iron. These products are expensive, but they will last a very long time. They take a long time to heat up, but they also take a long time to cool down. The significant weight of cast iron products is not a hindrance during their operation, but can slow down the installation process.
There are new radiator models, on the inner surface of which a protective coating is applied. These batteries are a little more expensive, but the money spent on them is more than worth it.
How not to make a mistake with pipes
Installing a heating system will require a lot of pipes.
Which one should you prefer:
- Metal. The service life of such pipes is not very long. Over time, metal products can rust. They are mounted using threaded connections.
- Polymer. This is an inexpensive but fairly reliable material that is resistant to corrosion. Even a non-professional can install these pipes. A pipeline made of polymer pipes will last a very long time.
- Metal-plastic. These pipes contain aluminum and plastic. The pipeline from them is assembled using threaded or press connections. As a byproduct of the high coefficient of thermal expansion of these pipes, they can crack if the water temperature changes suddenly.
If the home owners have no budget restrictions, it makes sense to install heating systems using copper pipes.This is a very expensive material, but the costs are worth it. Such pipes are reliable and durable.
They tolerate increases in temperature and pressure well. For their installation, soldering is used - silver-containing high-temperature solder.
Everything we told you above concerned the radiator water supply. But water can also be used as a coolant in other heating systems.

Read more about the characteristics and selection of heating pipes in this article.
Water system "Warm floor"
“Warm floor” can either successfully complement radiator water heating or become the only source of heating for rooms if we are talking about a low-rise building. A huge advantage of the “Warm House” is that this system provides conditions that fully meet the sanitary and hygienic standards of the premises.
The air is heated unevenly along the height of the room: in the upper part of the rooms it is colder, and in the lower part it is warmer.
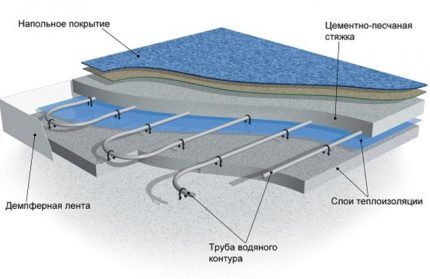
The system temperature is only 55°C, which meets design standards. Implementation installation of heated floors carried out across the entire area of each room. This is quite a complex job that can only be done efficiently at the stage of building a house. Operating the system also poses a number of difficulties.
Baseboard heating system
If installing a “Warm House” is difficult, and radiators spoil the interior of the room, you can use a baseboard heating system.
With this type of heating, the pipes are installed behind the baseboard, that is, slightly above the floor level. In this case, the room, as in the case of “Warm Floor,” warms up in the correct sequence.
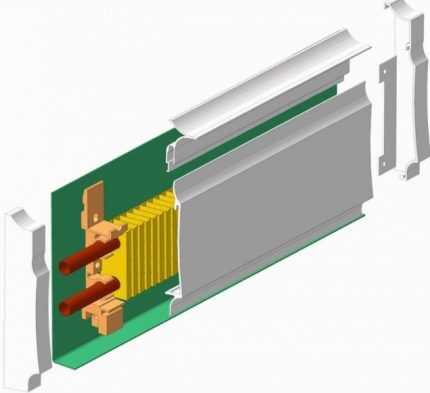
At the same time, the floor is heated, which creates favorable conditions at any time of the year. Heating under the baseboard is becoming more and more popular and is gradually becoming fashionable.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparison of two-pipe and one-pipe heating systems:
The house you plan to live in all year round needs heating during the cold season. To make your living conditions comfortable, you need to choose a water heating system that is most suitable for your individual conditions.
We hope that the information contained in this article will help you make the right choice. After all, high-quality heating is not only comfort and coziness. This is also a prerequisite for maintaining your health.
Do you have anything to add or have questions about water heating systems? You can leave comments on the publication and participate in discussions. The contact form is located in the lower block.




The “warm floor” system and baseboard heating system are truly wonderful, convenient, practical and aesthetic ways to heat your home. This is undeniable.But all this is great only under one condition - competent design and QUALITY installation. As well as high-quality materials of such systems. And that is, there are such clever people who make “warm water floors” not in country houses, but in ordinary high-rise apartments. Naturally, while looking for cheaper offers and trying to save as much as possible. And then the neighbors below begin to drip from the ceiling, and the ceiling is not designed to support the weight of such a system. This is the joy of people - examinations and courts.
Heating installation is actually simple for those who know how to solder plastic pipes. I did it extremely efficiently - a low-power boiler (Chinese Solly18h) was installed by plumbers, and I installed the wiring with radiators myself, and as operation showed, it was very successful. I used a training video as a basis - almost identical to this information. I did everything for three days (3-room apartment). Saved a lot of money and gained useful experience.