Liquid fuel heating boilers: design, types, review of popular models
Productive and economical liquid fuel heating boilers allow you to achieve complete autonomy from the centralized gas pipeline.When thinking about installing a unit, you need to understand its structure, operating principle and operating features.
The choice of boiler should be based on a comparative assessment of the characteristics and functionality of different models. An important factor is the reputation of the manufacturer.
In this material we will talk about the types of liquid fuel models of heating boilers, their advantages and disadvantages, and also consider several popular devices from well-known brands.
The content of the article:
Advantages and disadvantages of liquid fuel boilers
Liquid fuel boilers, despite their ability to effectively heat a building and technical excellence, are not as common as gas or solid fuel heat generators.
Equipment running on diesel fuel or waste fuel is very popular in Western European countries.
The significant advantages of an oil-fuel heating boiler include:
- High work efficiency. The efficiency of most models reaches 95%. Fuel is consumed with virtually no losses.
- Great power. The performance of the units allows heating both compact residential premises and spacious production workshops.
- High level of work automation. The boiler operates for a long time without human intervention.
- Autonomy from energy sources. Except for electricity. If necessary, you can get by with a generator.
- Possibility of switching to gas fuel.
There are additional advantages of such equipment. Installation of the boiler does not require approval or permission. In addition, the absence of a gas pipeline greatly facilitates installation work.
Difficulties in installing and operating an oil-fuel boiler:
- High costs for purchasing fuel. With intensive use of equipment, annual fuel consumption can reach several tons.
- A separate building is being built for fuel storage. As an option, a warehouse with containers made of opaque plastic or steel is installed in the ground. An important condition is protection from sunlight.
- The unit must be placed in a separate room with good ventilation and powerful exhaust hood.
- If the diesel boiler room is located close to the house, then additional sound insulation will be required - the burner makes noise during operation.
When equipping underground fuel storage facilities, it is necessary to take into account the hydrogeological characteristics of the area.

Design and principle of operation of the boiler
Liquid fuel units operate on the same principle as gas units. The main difference is the use of a fan burner (nozzle). The type of device largely determines the efficiency and economy of the boiler.

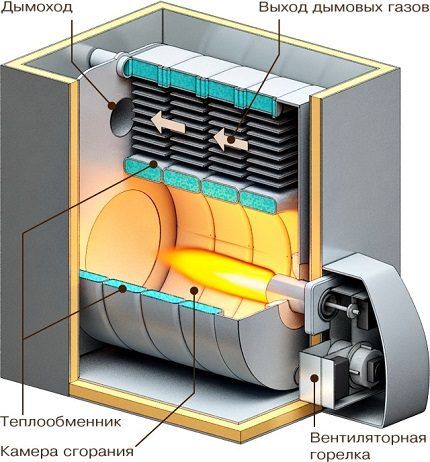
Main operating units of the heat generator
Structural elements of a liquid fuel boiler:
- burner;
- the combustion chamber;
- heat exchanger;
- chimney;
- Control block;
- frame.
The liquid fuel heating installation is equipped with a line with a pump that supplies fuel and a tank for storing fuel.
Heating unit burner
The main module of the installation, which is responsible for preparing the fuel-air mixture and transmitting it in the amount necessary to maintain the operation of the heat generator.
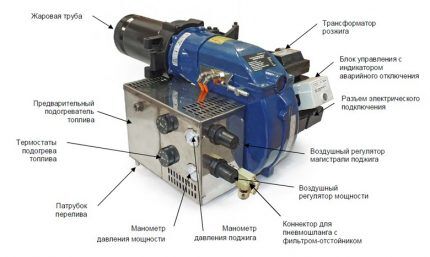
Standard burner equipment for an oil-fuel boiler:
- Ignition transformer. Generates a spark that ignites the fuel.
- Control block. Determines the start-up phases, performs control and stops the burner. The connection of a photocell, an ignition transformer and an emergency shutdown sensor is provided.
- Solenoid valve. Corrects the supply of fuel to the combustion chamber.
- Air regulator with filter. The device normalizes the air supply, preventing the ingress of solid particles.
- Preheater. Changes the state of the fuel, reducing its viscosity.The more liquid the fuel enters the nozzle hole, the more economically it is consumed.
- Fuel overflow pipe. It is connected to the tank where the fuel is heated.
- Flame pipe. Through the main line, thermal energy is supplied to the place where the coolant is heated, which then circulates in the heating system.
The burner can be initially built into the boiler without the possibility of increasing the power of the unit. Attachable modules allow you to modify the equipment.

Boiler combustion chamber
Essentially, it is a heat-resistant container with an inlet and an outlet. As a rule, it has a round or rectangular cross-section.
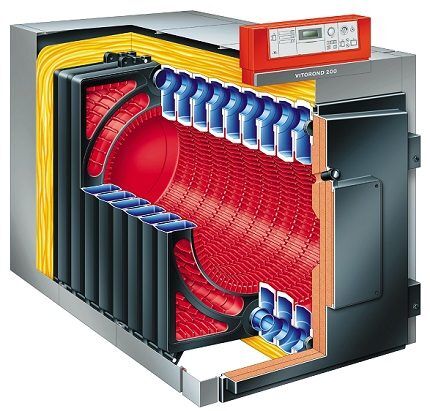
Heat exchanger device
Through the walls of the heat exchanger, thermal energy is transferred to the coolant. In modern models, the coating of this element is made according to the principle of a radiator device - this allows maximum use of the thermal energy obtained during the combustion process.

Chimney for liquid fuel unit
Air intake is carried out from the street or from the boiler room, for proper arrangement of which read this material.
When supplied from outside, air is supplied through coaxial chimney or via a separate channel. To increase efficiency, smoke channels are equipped with steel plates - the exhaust gases form turbulent flows, reducing their speed. The traction is maintained.
Device control unit
Automation is designed to maintain the set temperature.Auxiliary functions reduce the cost of boiler operation. From a technical point of view, the most advanced are weather-dependent units that change the heating temperature of the coolant based on the readings of external sensors.

Heating boiler body
All elements of the system are enclosed in a durable heat-insulating housing. This “shell” reduces heat loss and increases the efficiency of the boiler.
The outside of the body is covered with a layer of heat-insulating film, which, when heated, remains cold and protects the operator from burns.
How is the room heated?
The entire process of generating heat in an oil-fuel boiler and transferring thermal energy to heating radiators can be divided into several stages.
Stage 1. Diesel oil or other fuel is poured into the storage facility. The fuel pump supplies liquid to the burner device - pressure is created in the pipeline. At the same time, the fuel pump uses sensors to determine the quality of the fuel and the percentage of its thickening.
Stage 2. Diesel fuel enters the preparation chamber. Here the fuel is mixed with air, heated and liquefied.
Stage 3. The fuel-air mixture is supplied to the injector. Under the action of a fan, the mixture is atomized and the fuel mist ignites in the combustion chamber.
Stage 4. The walls of the chamber heat up. Due to this, the heat exchanger heats up and coolant. The latter enters and circulates in the heating system.
Stage 5. When a flammable substance burns, gases are formed that are discharged through the chimney. Rushing out, the smoke passes through a series of heat exchange plates and also gives off its heat.

Types of liquid fuel models
All liquid fuel boilers can be classified according to the following criteria: scope of application, functionality, type of adjustment, material of manufacture, type of fuel used and installation method.
By area of application
The main indicator that determines whether a boiler installation belongs to one of the types is power. Household models are available with power from 6 to 230 kW. This is enough to heat small houses with an area of 50 square meters. m and large country cottages of 2200 sq. m.
The performance indicator determines the fuel consumption in an liquid fuel heating boiler - about 1 kg of diesel fuel per hour is required to produce 10 kW of heat. Household units are designed for a maximum permissible operating pressure of 4-6 bar.
The power of industrial liquid fuel boilers ranges from 500 to 12,000 kW. Heavy-duty models work to heat buildings with an area of more than 15 thousand square meters. m. The control of industrial heating units is fully automated.
Industrial boiler equipment is divided into hot water and steam boilers. The former heat water under pressure, and the latter generate superheated or saturated steam.

By functionality
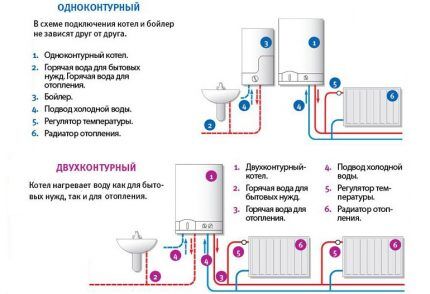
Single-circuit boilers are intended exclusively for heating the premises.They are connected to radiators, and the coolant circulates through a closed heating system. Such a unit does not heat water for domestic consumption - this must be taken care of separately by installing a boiler.
Double-circuit models are more functional. Boilers provide heating of the house and supply of warm water to different water intake points (shower, washbasin, etc.). The design of the equipment provides an additional heat exchanger to provide hot water supply.
By regulation method
The boiler operating mode is determined by the type of burner installed.
According to the type of adjustment, all devices are divided into several groups:
- single stage;
- two- and three-stage;
- modulated.
Single-stage modules operate on the principle of alternating on and off. After heating the coolant to a certain temperature, the flame goes out, and after cooling, the burner turns on again. Such burners are ineffective and lead to excessive fuel consumption.

Two- and three-stage devices operate in the following modes:
- Two-stage modules operate at 30 and 100% power. After heating the water to maximum, the burner switches to a reduced output mode. This allows you to reduce fuel consumption by 5-10%.
- Three-stage operate at 30-60-100% power. The efficiency and high thermal efficiency of the device are achieved.
Modulated - the fuel combustion process is regulated automatically.The intensity of the flame is influenced by: the temperature inside and outside the building, the quality of the fuel and the set mode. The range of power changes is 10-100% of performance.
Microprocessor automation determines the composition of the fuel-air mixture, the optimal rate of fuel supply to the injectors and pressure.

By material type
Manufacturers equip heating units with cast iron or steel heat exchangers. The material of manufacture affects the efficiency and durability of the boiler.
Cast iron models have a long service life - more than 30 years. However, they are quite “capricious” and can crack if there is a critical temperature difference between the “return” and “supply”. The temperature difference between the inlet and outlet water should not exceed 20 °C.
If the boiler will be used periodically, for example, during visits to the country, then it is better to choose a model with a steel heat exchanger. Heat-resistant steel is less durable, but withstands temperature changes.
By fuel type
Diesel (diesel) or waste oil is most often used as a fuel material in liquid fuel boilers. Externally, diesel plants do not differ from their counterparts working in “working off”. The main difference is in the technical component.
The boiler uses clean, certified diesel fuel to operate. When burning fuel, the formation of ash is minimal. This allows the design to use a firebox and smoke pipes of smaller diameter.
The combustion of used oil results in a large emission of ash. In “exhaust” boilers, there is no turbulator inside the smoke tubes, and all sediment is deposited in a special smoke collection chamber. We recommend reading our other article, which discusses in detail calorific value various types of fuel.

By installation method
Depending on the installation method, there are wall-mounted and floor-mounted units. Mounted boilers are compact, easy to install, but low in productivity. Their power is enough to heat a room whose area does not exceed 300 sq.m.
Floor-standing liquid fuel boilers are more bulky and efficient. These include all industrial units and high-power household models.
Review of models from leading companies
A worthy niche in the heating equipment market is occupied by liquid fuel boilers from foreign manufacturers: ACV, EnergyLogyc, Buderos Logano, Saturn, Ferolli and Viessmann. Among domestic companies, Lotos and TEP-Holding have proven themselves well.
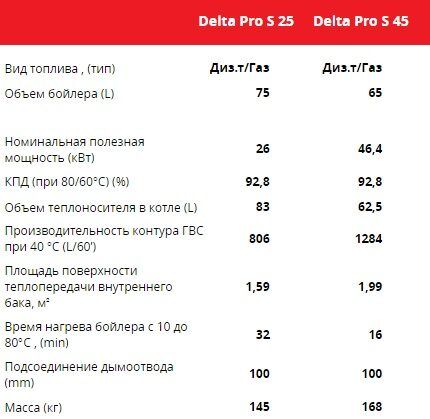
Universal boilers ACV Delta Pro
The Belgian company ACV sells models of the Delta Pro S line - double-circuit boilers with a built-in boiler. The power of heating units ranges from 25 to 56 kW.

Technical and operational features:
- heat exchanger material – steel;
- polyurethane foam insulation of the body;
- operation on diesel fuel or gas;
- control panel with thermometer, control thermostat.
The liquid fuel boiler “adjusts” to the season - a “winter/summer” switch is provided.
EnergyLogyc units – intelligent automation
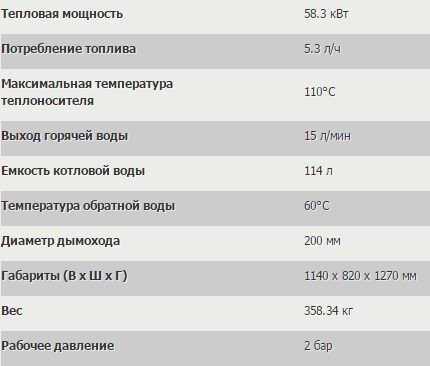
Waste oil boilers from the American company EnergyLogyc differ from their analogues in the automated processes of setting up the burner and burning fuel.
The fuel used is waste oil, diesel fuel, vegetable oil or kerosene.

EnergyLogyc liquid fuel units are available in three modifications:
- EL-208B – power 58.3 kW, fuel consumption – 5.3 l/h,
- EL-375B – performance 109 kW, fuel consumption – 10.2 l/h;
- EL-500B – thermal power – 146 kW, fuel consumption – 13.6 l/h.
The maximum coolant temperature in the presented models is 110°C, operating pressure is 2 bar.
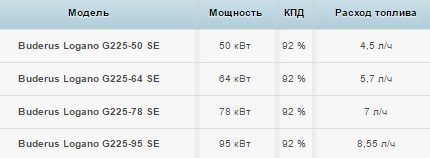
Buderos Logano – German quality
The Buderos company (Germany) produces diesel boilers, nozzles, burners and other equipment necessary for operating the heating system. The range of power characteristics of the units is 25-1200 kW.

Buderos Logano boiler systems are produced in two series:
- Buderos Logano category “G” - intended for private use, their power is 25-95 kW;
- Buderos Logano category “S” - equipment for industrial use.
The units are distinguished by a streamlined design, a convenient control system, and a built-in silencer.
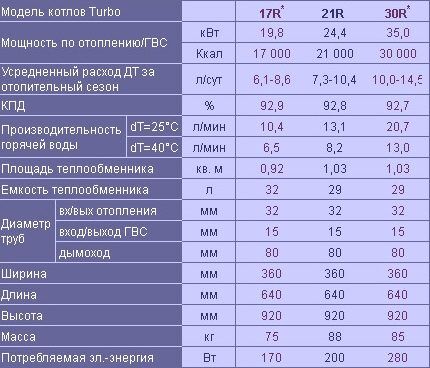
Boilers from the Korean company Kiturami
Kiturami Turbo series floor-standing double-circuit boilers are designed for domestic use. The power of the units is 9-35 kW.
Distinctive features of the model:
- provision of heating and hot water supply for premises up to 300 sq.m;
- the boiler heat exchanger is made of high-alloy steel;
- the additional DHW heat exchanger consists of 99% copper, which increases heating efficiency;
- Antifreeze and water are suitable as coolants.
A distinctive feature of Turbo models is the presence of a turbocyclone burner. It operates on the principle of a turbocharged car engine.
In a special metal board, secondary combustion occurs due to high temperature. This allows for economical fuel consumption and reduces the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Watching videos will help you understand the design and operating principle of liquid fuel heating units.
Comparison of a diesel boiler and a unit operating on “exhaust”:
The rules for choosing liquid fuel heating equipment will be discussed in the following video:
Liquid fuel boilers have a high level of automation. Heating based on diesel devices makes it possible to achieve autonomy, and the absence of strict documentation frameworks makes them an attractive offer. However, a number of significant shortcomings in boiler installation maintenance are holding back the demand for diesel units.
If you are concerned about choosing an oil boiler, please leave your questions in the block below. There you can write practical advice on the topic of the article or share your experience of using such heating equipment.



