Two-pipe heating system for a private house: device diagrams + overview of advantages
Providing heat in the house is the most important task for its owner. It can be solved in various ways, but according to statistics, most buildings in our country are heated using a water heating system.
It is the water option that is most effective and practical in our rather harsh climatic conditions. A two-pipe heating system for a private house is considered one of its most popular varieties.
We suggest familiarizing yourself with the options and technologies for assembling heating with a coolant supply and removal line. The information is based on building codes and requirements. To complete the perception of a difficult topic, the information presented is supplemented with photo selections, visual diagrams, and videos.
The content of the article:
Features of two-pipe heating
Any heating system with liquid coolant includes a closed circuit connecting radiators that heat the room and a boiler that heats the coolant.
Everything happens as follows: the liquid, moving through the heat exchanger of the heating device, is heated to a high temperature, after which it enters the radiators, the number of which is determined by the needs of the building.
Here the liquid gives off heat to the air and gradually cools. Then it returns to the heat exchanger of the heating device and the cycle repeats.
Circulation occurs as simply as possible in a one-pipe system, where only one pipe fits to each battery. However, in this case, each subsequent battery will receive the coolant released from the previous one, and, therefore, colder.

To eliminate this significant drawback, a more complex two-pipe system was developed.
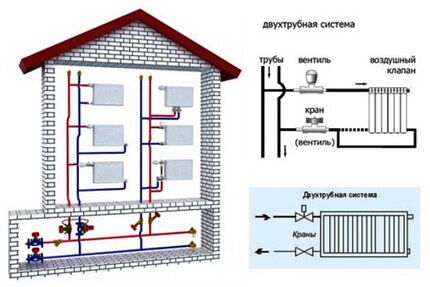
In this version, to each radiator two pipes are connected:
- The first is the supply, through which the coolant enters the battery.
- The second is the outlet or, as the experts say, “return”, through which the cooled liquid leaves the device.
Thus, each radiator is equipped with an individually adjustable coolant supply, which makes it possible to organize heating as efficiently as possible.

Why choose such a system?
Two-pipe water heating is gradually replacing traditional single-pipe designs, since its advantages are obvious and very significant:
- Each of the radiators included in the system receives a coolant with a certain temperature, and it is the same for all.
- Ability to make adjustments for each battery. If desired, the owner can install a thermostat on each of the heating devices, which will allow him to obtain the desired temperature in the room. At the same time, the heat transfer of the remaining radiators in the building will remain the same.
- Relatively small pressure losses in the system. This makes it possible to use an economical circulation pump of relatively low power to operate the system.
- If one or even several radiators fail, the system can continue to operate. The presence of shut-off valves on the supply pipes allows for repair and installation work to be carried out without stopping it.
- Possibility of installation in a building of any number of floors and area. You just need to choose the optimal type of two-pipe system.
The disadvantages of such systems usually include the complexity of installation and higher cost, compared to single-pipe structures. This is due to the double number of pipes that have to be installed.
However, it must be taken into account that to install a two-pipe system, pipes and components of small diameter are used, which provides certain cost savings. As a result, the cost of the system is not much higher than that of a single-pipe analogue, but it provides much more advantages.

Types of systems with supply and return
The two-pipe design is characterized by many varieties, which can be classified according to different criteria. Let's look at the main ones.
Open heating circuit
Any hydraulic heating system is a closed circuit, which includes an expansion tank. This element is necessary because the heating liquid increases in volume.
For open wiring a tank is selected that allows the liquid to communicate with the atmosphere. In this case, part of it inevitably evaporates, which leads to the need to constantly monitor its level.
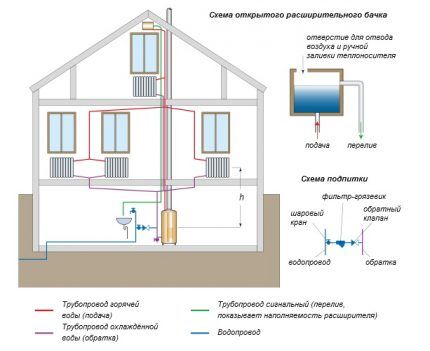
This is a very important nuance that must be treated very responsibly. An insufficient liquid level in the system leads to boiler boiling and failure. In addition, an open system involves using only water as a coolant.
Compounds of glycols or antifreeze, which are more practical in this regard, produce toxic vapors when evaporating, so they are used only in closed structures.
Closed circulation system
It differs from the open one in the presence of a closed expansion tank. Does not require constant monitoring by the owner. The design involves installation membrane type expansion tank, which is designed to compensate for a sudden decrease or increase in pressure in the system. Thus, it prevents equipment breakdowns as a result of sudden overloads.
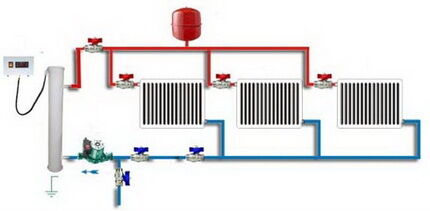
The membrane tank makes it possible to maintain the optimal pressure in the system for the pump and boiler.In addition, the closed design allows the use of any liquid suitable for its parameters as a coolant.
This makes it possible to obtain the most efficient and economical system with the required parameters. For example, it is not afraid of freezing if it uses antifreeze.
According to the method of circulation of the coolant liquid, two-pipe heating systems are divided into two large groups.
Natural circulation design
The basic principle of operation of the system is as follows: the boiler heats up the coolant, which expands as the temperature increases. The density of the liquid decreases.
Due to this, colder and therefore dense water gradually displaces the heated liquid upward.It rises to the highest point of the system, where it begins to cool little by little and moves by gravity to the radiators.
In the batteries, the water releases the accumulated heat and, cooling even more and increasing its density, moves to the boiler. Obviously, the coolant goes through the entire cycle by gravity, without the use of additional equipment.
Due to the fact that this happens quite slowly, the air displaced by water has time to move to the peak upper point of the system, which allows you to get rid of excessive airing.
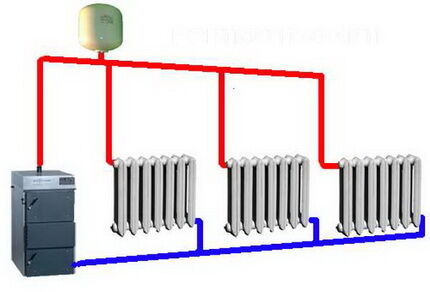
Indisputable dignity natural type structures its service life is considered to be long. The absence of moving elements and a circulation pump, as well as a closed circuit of the system with a finite amount of mineral salts and suspensions, significantly extends its operation time.
Experts say that the service life of structures with natural circulation, equipped with polymer pipes and bimetallic radiators, can be about fifty years.
The disadvantage of such schemes is the relatively low pressure drop. It is also necessary to take into account a certain resistance that radiators and pipes provide to the movement of the coolant. Therefore, the range of such a system will be limited. Building codes recommend using heating with natural circulation within a radius of no more than 30 m.
In addition, such a system has a fairly high inertia, so a fairly large amount of time passes from the heating of the boiler until the temperature in the heated building stabilizes.
A negative point can also be considered that all pipes must be laid at a certain slope so that the liquid can move in the desired direction. A heating system with natural circulation is capable of self-regulation.

The lower the ambient temperature, the higher the coolant circulation rate. In addition, several more factors influence the movement of liquid along the heating circuit: the cross-section and material of the distribution pipes, the radius and number of turns in the two-pipe heating scheme of a private house, as well as the presence and type of installed shut-off valves.
By influencing these factors, you can achieve the greatest efficiency of the heating system.
Wiring with forced circulation of coolant
The scheme described above includes circulation pump, moving the coolant along a closed heating circuit. This offers significant benefits. First of all, the speed of fluid movement increases, due to which the building warms up much faster.
In this case, all radiators connected to the system receive coolant at approximately the same temperature. This allows them to heat up as evenly as possible.
When using a natural circulation circuit, this is not possible, since the temperature of the liquid entering the radiator depends on the distance at which it is removed from the boiler. The further away the battery is, the colder the coolant is.Forced circulation makes it possible to regulate the heating level of individual network elements. In addition, if necessary, you can block its individual sections.
The use of a circulation pump allows you to include a membrane expansion tank in the system, that is, to perform it in a closed version. Thus, the amount of evaporated liquid is significantly reduced.
In addition, the installation of the structure is significantly simplified, since there is no need to lay pipes strictly at a certain angle, or to accurately calculate their diameter and lifting height.
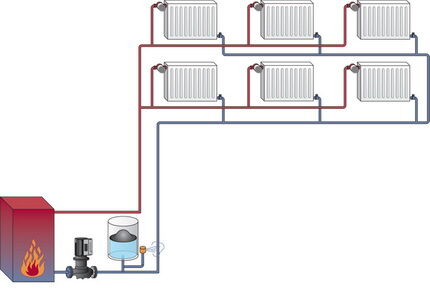
Another advantage forced circulation designs – the ability to make the necessary changes to its diagram and layout quite painlessly. To construct such a structure, pipes and components of a smaller diameter are used, which significantly reduces the cost.
In addition, such systems are more economical due to the fact that the difference in temperature of the coolant liquid at the inlet and outlet of the boiler is much less than that of an analogue with natural circulation.
The presence of a pump in the circuit prevents airiness in the heating line. In general, wiring using forced circulation is considered more effective, but they also have disadvantages.
The most significant of them is energy dependence. The pump cannot operate without being connected to a power source. During a power outage, this heating system stops. If there are frequent outages, it is advisable to have an uninterrupted power source.
Disadvantages usually include financial costs.Some of them are the price of the circulation pump, as well as the cost of the fittings that are necessary for its normal functioning. Which generally increases the cost of installing the system. In addition, you will need to pay monthly bills for electricity, which ensures the operation of the circulation pump.

The heating circuit can be configured in two different ways, which determine the location of risers and pipelines in space.
Horizontal and vertical layout type
It involves connecting heating devices to a horizontal line. Mostly mounted in one-story buildings large area. In this case, it is optimal to place the risers in corridors or utility rooms.
The advantage of this type of arrangement is the lower cost of the system itself and its installation. The main disadvantage is the tendency of the structure to air, so the installation of Mayevsky cranes is necessary.
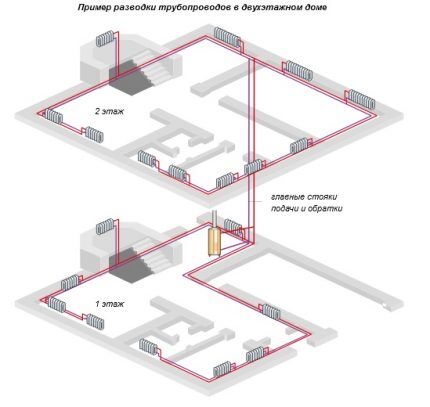
Radiators are connected to vertical risers. This option is especially good for buildings with several floors, since it makes it possible to connect each floor separately to the heating riser. The main advantage of the system is the absence of air locks.At the same time, the arrangement of a heating circuit with a vertical layout will cost more than for a horizontal analogue.
Two-pipe heating system with top wiring
The main distinctive feature of this design is that the supply pipeline is laid along the upper part of the room, the return pipe is discharged along its lower part.
An important advantage of such a system: high pressure in the main line, which is due to a significant difference in the levels of the return and supply pipes. Due to this circumstance, their diameter can be the same even when arranging a circuit with natural circulation.
But at the same time, the expansion tank, which is located at the highest point of the circuit, most often ends up in an unheated attic, which can cause problems. As an option, you can consider arranging the tank inside the ceiling, when its lower half remains in the heated room, and the upper part is taken out into the attic and insulated as much as possible.
If the owner is not particularly concerned about the presence of pipes under the ceiling of the room, it is advisable to locate the supply line above the level of the windows.
In this case, the expansion tank can be located under the ceiling, provided that the height of the riser is sufficient to ensure normal coolant velocity. The return line will need to be mounted as close to the floor level as possible or even lowered under it. True, in the latter case, when constructing the main line, it will not be possible to use connecting elements to prevent the occurrence of leaks.
The appearance of a room with pipes laid under the ceiling is not aesthetically pleasing. In addition, part of the heat goes up, which makes a heating system with overhead wiring insufficiently efficient.
Therefore, you can try to assemble a circuit with a supply line passing under the radiators, but this will only improve the appearance of the system and will not in any way affect its shortcomings.
Connecting a pump makes it easy to achieve optimal pressure in the system even when using pipes of minimal diameter. The maximum effect from a heating system with overhead wiring can be obtained in a two-story private house, since natural circulation is stimulated by a large difference in the installation height of the boiler located in the basement and the radiators on the second floor.
Once again heated coolant will be sent to an expansion tank, which is placed in the attic or on the second floor. From where the liquid will begin to flow through the inclined line into the radiators.
In this case, you can even combine the distribution tank responsible for the presence of hot water and the expansion tank. If a non-volatile boiler is installed in the house, you will get a completely autonomous heating system.
Another very successful option for a two-story house is a combined system that combines two and one-pipe sections. For example, a single-pipe structure is installed on the second floor in the form of a water-heated floor, and a two-pipe structure is installed on the first floor. The ability to regulate the temperature in all rooms is fully preserved.

The main advantage of a two-pipe heating system with overhead wiring is considered to be the high speed of coolant movement and the absence of airing in the line.
That is why it is used quite often, without paying attention to significant disadvantages:
- unaesthetic appearance of the rooms;
- high consumption of pipes and components;
- inability to heat large areas;
- problems with the placement of the expansion tank, which cannot always be combined with the distribution tank;
- additional costs for decoration so that the pipes can be disguised.
In general, a system with top wiring is quite viable, and with proper calculations, it is also very effective.
Two-pipe design with bottom routing
The scheme involves installing the supply and return from below the batteries. Unlike a system with top-type wiring, the direction of movement of the coolant here is changed. It starts moving from bottom to top, passes through the batteries and is sent along the return line to the heating boiler.
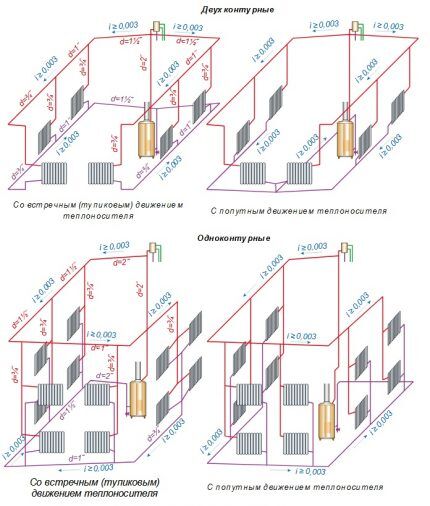
Bottom-wired systems may include one or more circuits. In addition, it is possible to arrange dead-end wiring and circuits with associated movement of the coolant liquid.
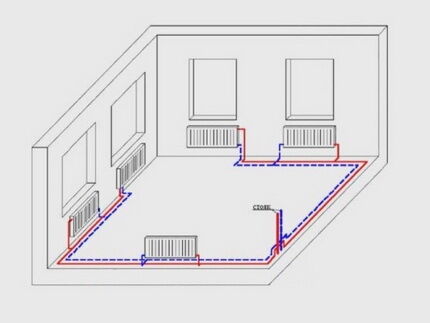
The main disadvantage of the design is airing. To get rid of it, Mayevsky cranes are used. Moreover, if the system is installed in a two or more storey building, it is assumed that such a tap will have to be on each battery.This is certainly not very convenient, so it is recommended to lay special overhead lines that are included in the system.
Such air vents collect air from the heating main and direct it to the central riser. Next, the air enters the expansion tank, from where it is removed. Heating circuits with bottom wiring and natural circulation are used quite rarely, as they have a number of limitations. First of all, most of the batteries included in the circuit are finite.
For this reason, they have to be equipped with descenders. If the system has an open expansion tank, then you will have to bleed the air almost daily. Installation of air lines that loop the supply pipes makes it possible to eliminate this drawback. However, they significantly complicate the scheme and make it more cumbersome. Moreover, the “air” is laid along the top of the room.
The significant advantage of the lower wiring, which consists in the absence of a highway laid in plain view, is lost in this case. The number of pipes used for installation in this case is quite comparable to the number of parts required for the upper wiring. Therefore, to arrange a two-pipe system with bottom wiring, the option with forced circulation is most often used.

The significant advantages of such a system include:
- Compact placement of the control area for the entire system. Most often it is installed in the basement.
- Reduction of heat loss, which is achieved by laying pipes along the bottom of the room.
- Possibility of connecting and operating the heating system until construction or repair work is completed. For example, the first floor can be heated, and the necessary work will be carried out on the second.
- Significant heat savings due to the ability to distribute it throughout heated rooms.
The disadvantages of the lower wiring include a large number of pipes and components required for installation and low fluid pressure in the supply line. In addition, the need for installation can be considered a negative point Mayevsky cranes on heating radiators, as well as the constant removal of air pockets from the system.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Review and assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of heating systems with natural and forced circulation:
Video #2. Detailed analysis of a two-pipe heating scheme for a three-story country house:
Video #3. How to independently arrange a two-pipe heating system in a country house:
A two-pipe type heating system is a widespread method of practical and efficient home heating. There are many modifications of this scheme. It is important to choose the right option for your home and make a competent calculation of all system parameters. Only then will the house be guaranteed to be warm and cozy.
Are you interested in the topic of the article, do you want to understand the unclear points? Do you have any questions or want to share valuable experience? Please write comments in the block located below the text.




Interesting water supply system, cleverly thought out. I just have a problem in my house - in one of the rooms the radiators are always cold.This is despite the fact that in the room closest to the boiler it is impossible to grasp the radiator with your hand: it is so hot. I looked at the wiring diagrams. I think that the lower one is more acceptable for our house. I'll install a pump for forced circulation and everything will be fine.
In order not to freeze when the electricity is turned off, and I have heating with a pump, I combined a forced system with a gravity system. Pipes with a slope, since initially the system had a natural type of coolant movement. Batteries are not installed (large diameter pipes). When there was frost outside the window, it was cool in the house, so I decided to install a circulation device. Now I combine the work depending on the external temperature, turning on the pump only when necessary. The energy savings are noticeable.
In the figure “diagram of a two-pipe heating system with forced circulation,” where does the pump pressure go when all the thermostatic heads are closed?
Evgeny, the circulation pump does not create pressure as such, it simply mixes the water, to put it simply. Otherwise, when it was operating in an open system, water would splash out of the expansion tank.
Mikhail, you floored me with your words about turning on the pump and splashing water out of the expander. Look for such nonsense...
Let's start with, why actually close the thermostatic heads? Maybe you are not entirely familiar with the operating principle of this heating system device? Let's figure it out then. And then people started giving advice and arguing that everything was wrong. It's time to set the record straight.
So, for example, let’s take the Icma 28x1.5 thermostatic head, but they all have the same operating principle.The operation of the device is based on the compression and expansion of a special internal cylindrical corrugated device, which is filled with process fluid.
To reduce the room temperature, the regulator is placed in the appropriate position, the heat-sensitive cylinder expands and presses on the thermostatic valve rod. Thus, the passage opening of the valve is blocked and the amount of incoming water is reduced. To increase the temperature, the regulator is placed in the desired position and everything happens exactly the opposite. It makes sense to close all thermostatic heads if you can simply turn off the boiler or set it to minimum power, for example.
And the pressure in the heating system is regulated by an expansion tank, this is immediately visible from the diagram.