Single-pipe heating system for a private house: diagrams + overview of advantages and disadvantages
Have you thought about installing water heating in your home? It is not surprising, because a single-pipe heating system for a private house can be traditional and completely energy-independent or, on the contrary, very modern and fully automatic.
But you still have doubts about the reliability of this option - you don’t know which scheme to choose and what pitfalls await you? We will help clarify these issues - the article discusses schemes for arranging a single-pipe system, the pros and cons that await the owner of a house with such a heating system.
The article is provided with detailed diagrams and visual photographs depicting individual elements used in heating assembly. In addition, a video has been selected with an analysis of the nuances of installing a single-pipe system with heated floors.
The content of the article:
Operating principle of water heating
In low-rise construction, the most widespread is a simple, reliable and economical design with one highway. The single-pipe system remains the most popular way of organizing individual heat supply. It operates due to the continuous circulation of the coolant liquid.
Moving through pipes from the source of thermal energy (boiler) to the heating elements and back, it releases its thermal energy and heats the building.
The coolant can be air, steam, water or antifreeze, which is used in periodic residences. Most common water heating circuits.
Traditional heating is based on the phenomena and laws of physics - thermal expansion of water, convection and gravity. When heated by the boiler, the coolant expands and creates pressure in the pipeline.
In addition, it becomes less dense and, accordingly, lighter. Pushed from below by heavier and denser cold water, it rushes upward, so the pipeline leaving the boiler is always directed as high as possible.
Under the influence of the created pressure, convection forces and gravity, water flows to the radiators, heats them, and cools itself.
Thus, the coolant releases thermal energy, heating the room. The water returns to the boiler already cold, and the cycle begins again.

system heating with natural circulation also called gravity and gravity. To ensure the movement of liquid, it is necessary to observe the slope angle of the horizontal branches of the pipeline, which should be equal to 2 - 3 mm per linear meter.
When heated, the volume of coolant increases, creating hydraulic pressure in the line.However, since water is not compressed, even a slight excess will lead to the destruction of heating structures.
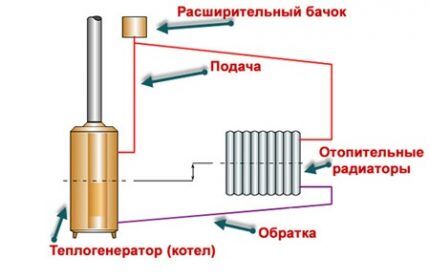
Therefore, in any heating system a compensating device is installed - an expansion tank.
The difference between one-pipe and two-pipe systems
Water heating systems are divided into two main types - single-pipe and double-pipe. The difference between these schemes lies in the method of connecting the heat-transfer batteries to the main line.
A single-pipe heating main is a closed annular circuit. The pipeline is laid from the heating unit, the radiators are connected to it in series, and lead back to the boiler.
Heating with one line is simply installed and does not have a large number of components, so it allows you to significantly save on installation.
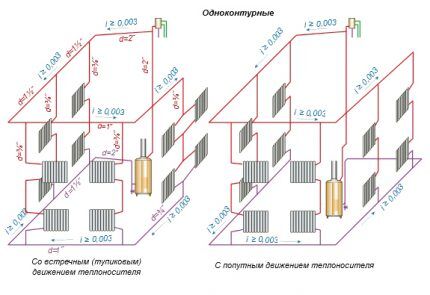
Coolant movement two-pipe heating carried out along two highways. The first is used to deliver hot coolant from the heating device to the heat-transfer circuits, the second is to drain cooled water to the boiler.
The heating batteries are connected in parallel - the heated liquid enters each of them directly from the supply circuit, and therefore has almost the same temperature.
In the radiator, the coolant releases energy and, when cooled, goes into the outlet circuit - the “return”.This scheme requires double the number of fittings, pipes and fittings, but allows you to arrange complex branched structures and reduce heating costs due to individual adjustment of radiators.
The two-pipe system effectively heats large areas and multi-story buildings. In low-rise (1-2 floors) buildings with an area of less than 150 m², it is more advisable to install single-pipe heating from both an aesthetic and economic point of view.
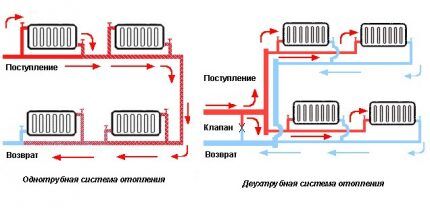
Options for single-pipe heating devices
Elements of any heating system:
- heat source – boiler (solid fuel, electric, gas boiler;)
- heat-dissipating devices – radiators, contours of heated floors;
- device that circulates coolant – special acceleration section of the highway, water pump;
- a device that compensates for excess coolant pressure in the line – open type expansion tank or closed type;
- pipes, fittings and related plumbing fittings.
Depending on the type of devices used, the heat supply scheme will also depend.
Systems with natural and forced circulation
The circulation of the coolant in the heating system can be carried out naturally - under the influence of physical phenomena, or forced - through a circulation pump.
In the first case, the heating movement through the system is spontaneous and is called natural, in the second - forced or artificial.
To ensure the movement of fluid in the gravitational system, an accelerating section is required. This is a vertical pipe extending from the boiler through which the heated coolant rises.
At the top point, the pipeline is smoothly turned down, so the water rushes along the pipeline with acceleration.
For a heating scheme with overhead wiring, as well as for two-story houses, the supply pipe serves as such a section, since it rises to a sufficient level.
To heat a one-story building with lower horizontal wiring, an accelerating manifold is installed, the height of which should not be less than 1.5 m from the level of the first radiator.
The acceleration section is a device that ensures the circulation of coolant in a gravity heating system. The bore diameter of the pipes of this section of the main must be larger than its main part.
For example, if the main pipe diameter is 25-32 mm, a pipe with a diameter of 40 mm is chosen for the accelerating manifold.
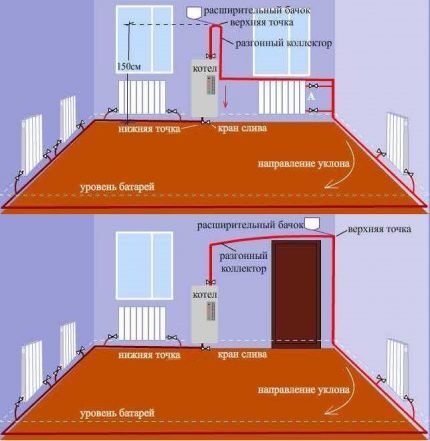
The main advantages of the gravity system are complete energy independence (in combination with a solid fuel boiler), simplicity and the absence of complex instruments.
There are quite a lot of disadvantages:
- To minimize hydraulic resistance, pipe diameters must be large enough.
- Each built-in device and device creates obstacles to the movement of liquid, therefore the system has a minimum number of shut-off valves. This creates difficulties during repairs, as it requires a complete shutdown of the system and draining of the coolant from the main line.
- For reliable operation, the gravity system must be carefully calculated and balanced, selecting the optimal pipe diameters and the number of radiator sections. The outermost radiators in the system should be larger than those into which the coolant flows after leaving the boiler.
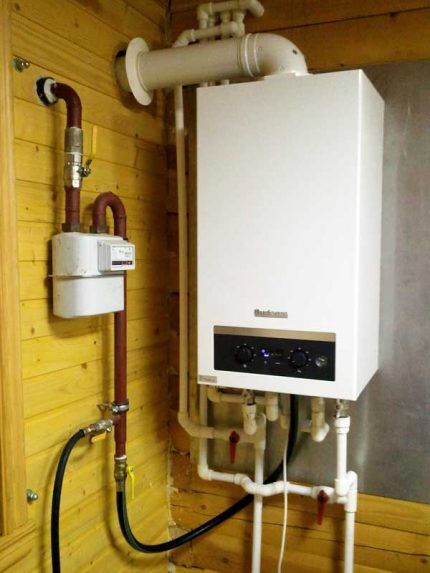
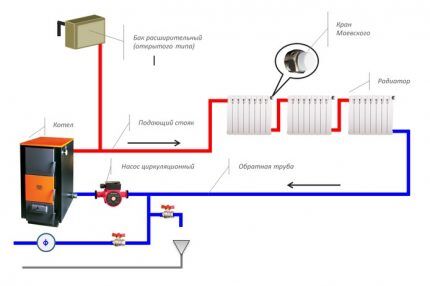
Installing a circulation pump in the system neutralizes almost all of its shortcomings. The device gives the coolant an additional impulse, allowing it to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipeline elements.
Forced single-pipe heating schemes are most often implemented in private homes.
The pump can be installed anywhere in the pipeline.But it is worth considering that hot water reduces its service life by affecting rubber parts (gaskets and seals).
Therefore, it is more advisable to install the unit on the return pipeline, where the cooled coolant circulates. Before it, it is mandatory to include a coarse filter to protect against possible contaminants.
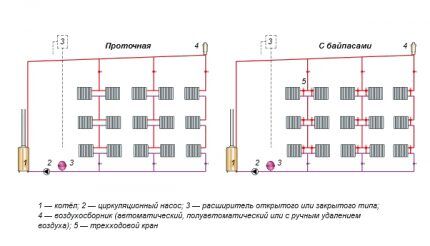
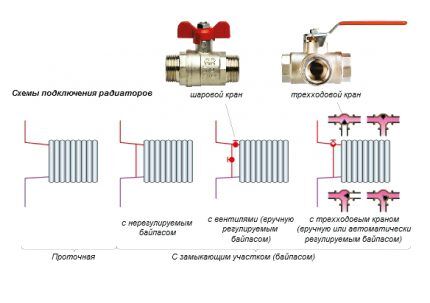
It is advisable to connect all devices and devices of heating systems through shut-off valves and bypasses.
Such installation will allow repair and maintenance of individual elements without the need to stop the entire system and completely drain the water.
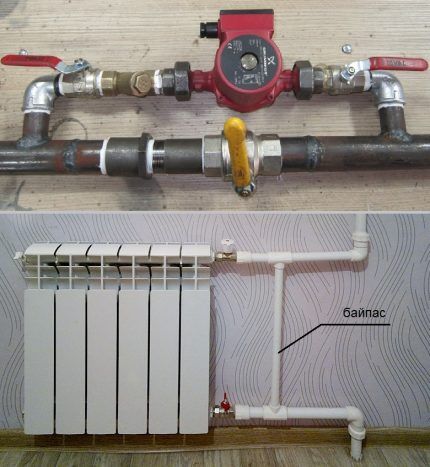

Advantages of a heating system with forced circulation:
- You can implement more complex and branched circuits, increase the length of the circuits;
- There is no need for increased pipe diameters - the pump creates pressure in the line sufficient for movement and uniform distribution of liquid;
- Circulation is carried out at a given speed and does not depend on the degree of heating of the coolant and the presence of an accelerating section;
- There is no need to observe inclination angles when laying the pipeline, because... the movement of the coolant is stimulated by the pump.
In addition, you can install control devices on each radiator and maintain optimal heating mode, reducing energy consumption and heating costs.
There are only three disadvantages of single-pipe forced heating:
- dependence on electricity supply;
- noise — some hum produced by a running pump;
- price - higher cost of the device compared to the gravitational scheme.
Neutralizing them is quite simple. Energy dependence is solved by installing an autonomous electric generator or by switching the system to a natural circulation mode.
To make the operation of the pump almost inaudible, it is enough to install it in a non-residential area - a bathroom, toilet, boiler room.
Open or closed heating system?
To prevent excessive increases in hydraulic pressure in the system and its surges, an expansion tank is installed. It accepts excess water during expansion, and then returns it to the main line when it cools, restoring the balance of the system.
There are two fundamentally different designs, which determine the appearance of the entire system.
An open type expansion tank is a partially or completely open container that is connected to the main line at its highest point, directly after the boiler.
To prevent liquid from overflowing over the edges at a certain level, a drain is provided through which excess water will be drained into the sewer or onto the street.
In one-story houses, the compensating tank is often placed in the attic - in this case it must be insulated.
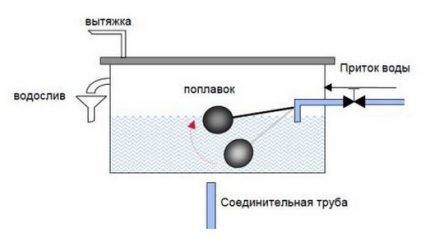
A heating system with such a compensating device is called open. It is used when installing energy-independent or combined heat supply.
It involves direct contact of the hot coolant with air, resulting in its natural evaporation and saturation with oxygen.
Based on this, the open heat supply scheme is characterized by the following disadvantages:
- When installing the pipeline of gravity systems, it is necessary to observe slopes - in this case, the air released in the system will be vented into the tank and the atmosphere.
- It is necessary to regularly monitor and replenish the volume of water in the container in a timely manner, preventing its excessive evaporation.
- Antifreeze cannot be used as a coolant, as toxic substances are released when it evaporates.
The oxygen contained in the circulating fluid causes corrosion damage in the steel parts of heating devices, reducing their service life.
However, it also has its advantages:
- There is no need to constantly monitor pressure in the line;
- Even with small leaks, the system will properly heat the house as long as there is a sufficient amount of liquid in the line;
- You can even replenish the coolant in the system with a bucket - just pour the expansion tank into the water to the required level.
The closed-type expansion tank is a durable, sealed housing, the internal volume of which is divided into two parts by a membrane. One cavity is filled with air, the second is connected to the main line.
When heated, the coolant, increasing in volume, pushes the membrane towards the air chamber, which plays the role of a damper. As the water cools, the hydraulic pressure decreases and the compressed air balances the system, squeezing excess water back into the pipeline.
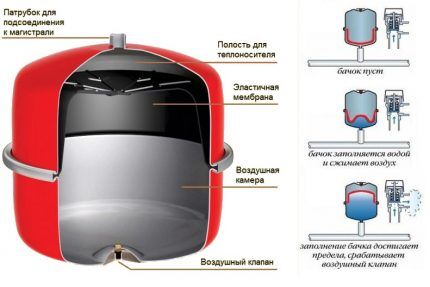
A system with a membrane-type expansion tank is called closed. This is a closed hydraulic line completely devoid of air access.
A compensating tank can be built in anywhere in the system, but most often it is installed on the return pipeline near the boiler to increase ease of maintenance.
A closed heating system is characterized by the presence of slight excess pressure. Therefore, a mandatory element of the highway becomes security group.
The unit consists of an air vent, a pressure gauge and a safety valve for discharging the coolant in emergency mode. Mounted with shut-off valves on the supply pipeline to allow shutdown in case of repair.
If there is a rise in the pipeline, then it is located at its highest point.
Efficient single-pipe system design
When designing heating, many factors are taken into account - the availability of a stable power supply and a separate room for equipment (boiler room, boiler room), the number of floors and layout, the aesthetics of the future structure, etc.
In each individual case, the location of the equipment and methods of connecting it will be different.
For a very small room - a country house - the most effective will be a simple gravity flow scheme for sequentially connecting batteries directly into the main pipeline.
When installing two or three radiators, it is not necessary to install a large number of shut-off valves - in this case it is easier to drain water from the system if necessary.
In buildings with a larger area, the heat supply system is a complex, sometimes branched, structure. In this case, the best option is forced heating according to the Leningradka scheme with diagonal connection of heat-dissipating batteries and adjustable bypasses.
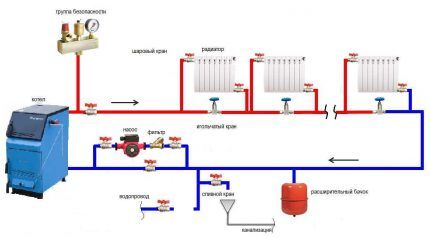
Methods for connecting a radiator to the main line
The heat transfer of radiators depends on the method of their connection to the main line.
There are three main types of connection:
- Diagonal;
- Lateral;
- Lower.
Let's look at the features of each of these methods in more detail.
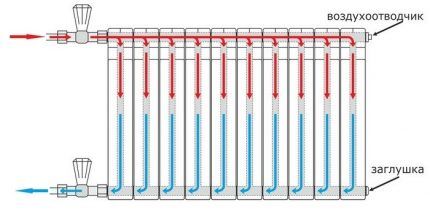
Diagonal or cross connection
Diagonal, or cross, connection is the most effective. Maximum heating of the battery area is achieved, and there is practically no heat loss.
According to this scheme, the supply pipeline is connected to the upper radiator pipe, and the outlet pipe is connected to the lower pipe located on the opposite side of the device. For devices with a large number of sections, only the diagonal connection type is used.
Lateral or one-sided connection
Lateral, or one-sided, connection allows for uniform heating of all sections of the device.
For connection, the supply and discharge pipelines are connected on one side. Most often, this connection is used for heating installations with overhead wiring.
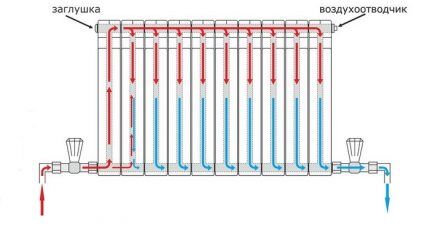
Bottom connection of radiator with pipeline
Bottom connection is not the most efficient heating scheme. However, it happens quite often, especially when the main pipeline is hidden under the floor.
The inlet and outlet pipes are connected to the lower pipes located on different sides of the radiator.
Advantages and disadvantages of a single-pipe system
Single-pipe heating has gained wide popularity in the field of private construction.
The main reasons are the relatively low cost of the structure and the ability to install it on your own, without the involvement of specialists.
But a single-pipe heating system has other advantages:
- Hydraulic stability - the heat transfer of other elements of the system does not change when individual circuits are disconnected, radiators are replaced or sections are expanded;
- The construction of the main line requires a minimum number of pipes;
- It is characterized by low inertia and warm-up time due to the smaller amount of coolant in the line than in a two-pipe system;
- It looks aesthetically pleasing and does not spoil the interior of the room, especially if the main pipe is hidden;
- Installation of the latest generation shut-off valves - for example, automatic and manual thermostats - allows you to precisely adjust the operating mode of the entire structure, as well as its individual elements;
- Simple and reliable design;
- Easy installation, maintenance and operation.
When connecting control and monitoring devices to the heating system, it can be switched to a fully automatic operating mode.
Possible integration with "Smart Home" system - in this case, you can set programs for optimal heating modes depending on the time of day, season and other decisive factors.

The main disadvantage of single-pipe heat supply is the imbalance of heating of heat-transfer batteries along the length of the main line.
The coolant cools as it moves along the circuit. Because of this, radiators installed far from the boiler heat up less than those located close to them. Therefore, it is recommended to install slowly cooling cast iron appliances.
Installing a circulation pump allows the coolant to warm up the heating circuits more evenly, however, if the pipeline is of sufficient length, significant cooling is observed.
The negative effects of this phenomenon can be reduced in two ways:
- In radiators remote from the boiler, the number of sections is increased.This increases their heat-conducting area and the amount of heat given off, allowing rooms to be heated more evenly.
- They draw up a project with a rational arrangement of heat-emitting devices in the rooms - the most powerful ones are installed in children's rooms, bedrooms and “cold” (northern, corner) rooms. As the coolant cools down, the living room and kitchen proceed, ending with non-residential and utility rooms.
Such measures minimize the disadvantages of a single-pipe system, especially for one- and two-story buildings with an area of up to 150 m². For such houses, single-pipe heating is the most profitable.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Not only radiators, but also underfloor heating circuits are connected to the single-pipe heating main. The video shows how to carry out such installation.
Single-pipe heating is a simple and reliable system. However, for effective heating it is necessary to carefully select its individual elements. To do this, it is advisable to seek advice from a specialist, who will help you perform an assessment calculation.
Do you disagree with the diagrams presented in our article? Or do you have practical experience in installing single-pipe heating in a private home? Your experience will be useful to our readers. Feel free to share your knowledge in the comments below.




In my house, which my grandfather built, there is a single-pipe system. I can confirm that it is simple and high quality. She has been working “with a bang” for fifty years now, and nothing has been done to her, the house is warm in the most severe frost. An exceptionally successful system. If I were building a new house, I would also make a single-pipe one, only I would install modern radiators, and not cast iron, as in the old house.
I installed heating in a private house and gave preference to a single-pipe system, since it really allows for significant savings on materials. The most important thing is to maintain the slope so that there is a natural flow of water. It was easier for me to do this - the boiler itself was located in the basement. This arrangement was a big plus because there was no need to buy a powerful pump. During operation, I noticed a minus - the water in the distant devices of the system is already warm, because it releases most of the energy at the beginning.
Is it possible to carry out the return in the same way as the supply? Or does it have to be around the perimeter of the house?
I understand that you want to implement a two-pipe heating system? You do not have to lay the return line around the perimeter; there are different options for how to do this. If it is a one-pipe system, then in this case it will definitely not be necessary to lay it along the perimeter. I am attaching a sample diagram.
If you run pipes through the upper entrances to the batteries as a one-pipe system, will it work? Example in the photo.
It is possible, but only so that the return does not heat up against the supply if there is natural circulation, there is no need to worry about the forced option. But we need an alternative source of electricity. energy, if the boiler is TV. fuel, gas ones have protection.
I want to make three radiators for the fireplace stove, but I won’t be able to tilt it. I want to connect the batteries in series from one to the other. The return route will go the same way, not along the perimeter. There will be a pump. The return flow will flow from the last battery directly into the fireplace. Is it possible?
I don’t see any problems in implementing such a wiring for the heating system. But I would strongly recommend using an expansion tank in the system. I think there is no need to explain how much more practical such an implementation will be than without an expansion tank. I am attaching an approximate wiring diagram for your case.
The single-pipe system is an excellent solution for small spaces. Easy installation and operation. Thanks for the info.
I want to install a one-pipe system. The area of the house is approximately 80 square meters. 4 radiators - 3 meter and one 0.8. I have a question - is it necessary to install shut-off valves on both sides of each radiator or can it be connected directly? I understand that it will be inconvenient to repair the radiator without valves .but still
Hello, my house has 2 floors, the heated area is 250 sq. m. m is heated by a gas floor-mounted non-volatile boiler installed in the basement, the wiring is single-pipe, gravity, from the attic of the house five risers pass in series through the radiators of the second and first floors. The system works stably, the question is - will the circulation pump increase the efficiency of the system? Will gas consumption decrease?