Do-it-yourself site drainage: features of the construction of various types of drainage
In areas where groundwater layers lie very close to the surface and an impressive amount of precipitation falls throughout the year, natural waterlogging occurs, the foundations of permanent buildings are undermined and basements are flooded.
To protect your home from these unpleasant phenomena and remove excess moisture from the ground, you can hire a construction crew with special equipment. She will quickly and professionally carry out all the work, but this “pleasure” will not be cheap, which is not always acceptable, do you agree?
In order to save the family budget, you can do the drainage of the site yourself, spending much more time on it and saving a very substantial amount. We will look at how to do this correctly and where to start in our article - we will analyze the features of surface and deep drainage, and provide recommendations for the design of each of these types of drainage.
The content of the article:
What problems does a drainage system solve?
Correct drainage of excess water from the sole foundation residential buildings and outbuildings protects buildings from settlement, the appearance of unsightly damp spots, darkening of corners and the formation of mold, and basements from annual seasonal flooding.
The soil does not “float”, and at low temperatures the consequences of frost heaving do not occur, “squeezing” buildings out of the ground. Layers, paths and sidewalks placed on the territory do not crack and are kept in perfect condition.
In well-drained areas, treatment communications and structures operate for a long time and reliably. Even with an increase in the seasonal level, groundwater receives a path to outflow and does not provoke the release of septic tanks and sewage from cesspools to the outside.
Moisture from precipitation, which leaves in a timely manner through drainage channels, does not react with salts contained in the soil and does not form aggressive compounds that decompose building materials.
High-quality drainage does not allow puddles that form after rain to stagnate and waterlog the soil in garden, thereby causing water erosion.
In areas with a pronounced slope, the drainage system redirects water flows into drainage channels during heavy rainfall, thereby preventing soil erosion and maintaining the attractive appearance of the overall soil surface.
In combination with roof storm drainage communications, the drainage system quickly removes excess water from the perimeter of the land, prevents it from seeping into the basement and basement rooms and prevents flooding of both buildings and the entire site.

Where is water drainage necessary?
A flat area definitely needs drainage. If the moisture formed as a result of heavy rains and melting snow does not find an outflow route, it simply remains in place, intensively saturates the soil and leads to swampiness, the appearance of mud and global waterlogging of the earth.
A site located in a lowland disappears without a good drainage system. All the water from higher places flows onto it, and the area, at best, becomes oversaturated with moisture, and at worst, it becomes flooded.
Land located at a sharp slope loses a number of its valuable qualities without drainage.Too quickly receding water erodes the top fertile layer of soil and significantly reduces the level of productivity.
For areas with clay and loamy soils, drainage is an objective need. Rocks of this type are characterized by high density and poor conductivity. The moisture that falls in the form of atmospheric precipitation stagnates in it for a long time and leads to general waterlogging of the area, soil shifts and disruption of the fixed stability of the foundations of residential and commercial buildings.
You cannot do without a full-fledged drainage system even where the level of natural groundwater is less than 1 meter.If you ignore the drainage, there is a risk of flooding of the basement and basement rooms, the integrity of the foundation is compromised, and cracks appear on the main, load-bearing walls. All this in the future may lead to partial or complete collapse of residential and commercial buildings.
In the event of a seasonal increase in the natural groundwater level, residential buildings and outbuildings with buried foundations fall into the risk zone. In this case, its sole is at risk, and moisture and dampness may appear in basements and basements, even those equipped with good waterproofing.
To avoid these unpleasant moments, it is necessary design a drainage system and implement it at the planning stage of building a house or immediately after purchasing real estate.

For areas partially or completely concreted, paved with paving stones, paving slabs or colored mosaics, the presence of drainage channels and gutters just a must. Otherwise, after rains or melting snow, puddles will stagnate on the surface, causing cracking of the top decorative layer and compromising the integrity of the entire coating.
It is also necessary to equip drainage where lawns are located, equipped with progressive automatic irrigation systems. This will allow you to control the level of soil moisture and prevent the death of rare plants as a result of silting of the soil.
Drainage channels make it possible to quickly remove water from a site and prevent it from flooding buildings, spoiling landscape design and harming the area’s infrastructure.
Types and types of drainage systems
Drainage systems differ in technical characteristics, efficiency and method of arrangement. For creating with your own hands on private land, deep and surface type drainage is most suitable. The choice depends on the purpose for which the installed system is planned to be used in the future.
Features of surface drainage
Organizing surface drainage with your own hands on private land is justified and relevant.
Despite its simplicity, the system effectively removes excess moisture formed during precipitation and snow melting. In addition, it helps drain water that accumulates during the process of washing a car, watering lawns or rinsing concrete or paving stone paths located on the property.

Drainage communications are located around residential buildings and outbuildings, in paved areas and at the exit from the garage and from the site itself.
Variation #1 - linear system
The linear system is a structure of trays placed in specially prepared trenches level with the water level. During the installation process, channels are dug in compliance with the condition of a constant slope to the side catchment well.
In this option, water flows through the system by gravity and no additional means are used to move it.
To ensure full operation, the complex is equipped with sand traps that prevent siltation of communications, and the top is covered with durable gratings that allow both pedestrians and vehicles (not only small cars, but also trucks) to move safely across the surface of the site.
Linear channels have high permeability and have the ability to pass large amounts of water through them. They are considered the most successful drainage option for large areas and large land holdings.

Variety #2 - point drainage
Point drainage collects water in individual areas and redirects its excess to the general storm sewer system. Typically used where laying linear drainage is not possible or is not considered appropriate.
When installing communications, rainwater inlets are located in places where water accumulates the most, for example, directly under storm drains, irrigation taps, water pumps, at the entrance to a garage, under the entrance gate, or even simply in areas of the territory where water most often stagnates after irrigation or heavy rainfall.

The point drainage option effectively functions independently where local water collection is required or serves as a practical addition to any other system. Needs maintenance and regular cleaning.
The volumetric option is much less popular than the other two options described above. It is more labor intensive and entails large-scale excavation work. The system itself is formed from a mixture of sand, crushed stone, geotextile layer, gratings and soil. All these elements are located in areas where there is open soil.
In the presence of volumetric drainage, only the water necessary for natural hydration remains in the soil. All surpluses go through the system into the deeper layers and do not cause any inconvenience or difficulties to the owners of the property. Most often, such communications are installed in park areas, playgrounds and lawns in order to maintain optimal humidity in the useful area.
The choice of drainage system is carried out individually for each land plot, taking into account its location, size, topography, physical and mechanical properties of the soil, groundwater level and the tendency of the area to become waterlogged.
Based on the depth of installation, drainage systems are divided into deep and surface:
Distinctive features of deep drainage
Not in all cases it is possible to make do with only surface drainage. To solve more global problems, for example, lowering the general groundwater level or protecting a certain area from flooding, it is necessary to lay a deep drainage system on the territory.
Deep drainage can be:
- pipe;
- reservoir;
- ring
Next, we will analyze the features of each of these types of drainage.
Type #1 - pipe installation method
The pipe installation method is relevant where groundwater lies at great depths. The arrangement involves the use of drains - special pipes with perforation. They are placed underground, having previously provided an appropriate level of slope towards the collector.
Moisture penetrates into the drains through holes and, having passed through the channels, flows into the well of the storm sewer system, into a collector or natural or artificial reservoir located outside the land plot being developed.
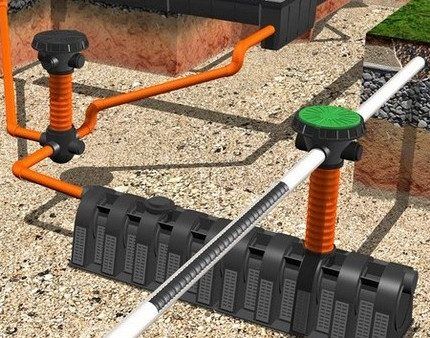
Type #2 - reservoir drainage
Reservoir drainage is very common and is carried out in areas with complex hydrogeological conditions.
In addition he:
- Ensures the outflow of moisture from residential buildings even in the presence of a nearby massive water layer or pressurized groundwater.
- Helps reduce groundwater levels where other types of drainage systems cannot cope with this task.
- It demonstrates high efficiency in areas with a layered aquifer structure and copes with the removal of moisture from buildings that require absolute dryness and categorically do not accept water penetration due to certain operational characteristics.
In case of urgent need, reservoir drainage can be installed on loamy and clayey soils, acting as a preventive barrier to dampness and moisture.
When laying at the foot of the building in the immediate vicinity of the foundation, it is necessary to install a crushed stone cushion, which acts as a natural filter for water flow.

Type #3 - ring drainage
Ring drainage is used to protect basements and basements of buildings built on sandy soil from flooding. If desired or if necessary, a drainage system around the house It is possible to equip not only one house, but also a group of buildings located on the site.
If groundwater comes very close to buildings on only one side, it is permissible to lay an open drainage ring and create a barrier to moisture and dampness specifically in the most vulnerable place.
For private plots of land, it is possible to organize drainage of one of the most suitable types or to arrange several systems to ensure the most effective drainage of excess moisture.
The drainage system for collecting water penetrating into the first layer of soil from the surface or soil in the green area of the site is arranged in the traditional sequence:
How to organize surface water drainage?
Before you begin to carry out drainage measures on your personal plot of land with your own hands, they determine what kind of system is needed, and then draw up a rough work plan.
If difficulties with water drainage concern only certain parts of the territory and arise only during periods of heavy rain or active snowmelt, owners, as a rule, limit themselves to local drainage.

To do this, water intakes are placed in places of maximum water accumulation: sealed containers or drainage wells connected by channels to a common storm sewer. In case of a more global problem, communications are laid across the site for linear drainage.
For the equipment of the system, they first draw up a project for the location of all communications and determine the location of the main reservoir for collecting excess water. The entire territory of the site is covered with a network of trenches about half a meter deep. The frequency of location is determined based on the level of swampiness of the entire territory. If the ground is very wet, prepare the maximum number of channels for drainage.
For full and high-quality operation of the system, drainage trenches are laid with a slope towards the location of the future water intake. If the land on the territory has an uneven surface, channels are dug strictly downward in relation to the relief.
When the site is a flat area, slopes are created artificially.This is necessary to ensure that water does not stagnate in drainage communications, but rather quickly flows into natural or artificial water intakes.
The most common drainage mesh is installed in areas with clay and loamy soil. On lighter soils, channels are laid less frequently. Narrow trenches are dug along the edges of the perimeter of the entire area, gradually increasing their width as they approach the main drainage well. The widest possible trench is left for the channel through which the entire volume of water passes into the drainage compartment.

Once the system is fully installed, it is tested for functionality. To do this, powerful streams of water are released from several points using hoses. If water flows out evenly in all areas, then the complex is functioning normally.
When in some places moisture flows more slowly or stagnates, the slope of the trench is increased. Then the tray channels are covered with grates to prevent leaves, small debris and other foreign elements that can clog the drainage system from getting there.

Upon completion of work related to the arrangement of linear drainage, the surrounding area is decorated in accordance with one’s own tastes and the general idea of landscape design adopted on the site.
How to properly make deep drainage?
To correctly install deep drainage on a personal plot of land, first of all, a clear project of all work is formed, establishing the types of soil available on the territory, the features of the relief and the level of groundwater.
This type of research is entrusted to engineering and geological organizations. They will conduct a full study of the area, and then provide the customer with a topographic survey that describes in detail the relief, hydrogeological features and geological structure of the site. With this information at hand, installing an effective drainage system is easy.
The construction of the system is carried out in the following order:
The main elements of a deep drainage system are drains (pipes of a specific design). They are located below the foundation pad of the building that they plan to protect, or along the entire perimeter of the land at a depth of 80 centimeters to one and a half meters.
Necessary pipe slope done towards a collector, drain well or any other natural or artificial reservoir located outside the site.
In this way, moisture collected as a result of precipitation is collected and the general level of nearby groundwater is reduced to a non-critical state. In the center of the site and along the edges, drains are located at a distance of 10-20 meters from each other.The structures are given a herringbone shape, where the outermost channels redirect all the water into the main trench leading to the main water intake.

On absolutely flat areas, the required slope is achieved by lowering it when digging the bottom of the trench. For loamy and clayey soils, the optimal slope level is 2 centimeters per meter of pipe, for sandy soils – 3 centimeters. If the site has a large area, in order to avoid too extensive excavation work, several inspection wells.
Communication pipes are equipped with rotary and water intake wells. If necessary and if it is impossible to remove excess water outside the site, add to the remaining elements absorption (filter) well, designed to drain the main volume of water.
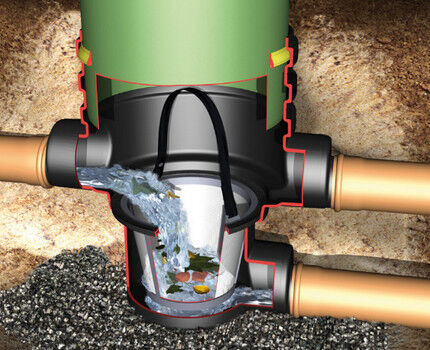
Immediately before laying the pipes, a 10-centimeter layer of coarse sand and the same layer of crushed stone are poured into the trenches.
The resulting shock-absorbing cushion prevents communications from breaking under the weight of the soil. To avoid silting of pipes, the channels are lined with geotextiles.

On top of the laid out pipes, another layer of sand and crushed stone is made, and the remaining voids are filled with earth, making mounds on the surface. When the system finally “sits” in the trenches, the poured earth itself will drop to its natural level.
A correctly and clearly installed system ensures timely and rapid removal of moisture from the site and reliably protects buildings from flooding and subsequent destruction.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video tips for those who decide to independently install a drainage system on their own dacha or garden plot.
The video clearly shows how to arrange a surface drainage system on a site:
Useful video information on organizing drainage around a residential building:
Knowing the rules for installing drainage systems and following the above tips, making drainage on your personal plot of land will not be difficult. If difficulties arise, you can contact specialists, and they will professionally help in solving problems.
Have you thought about installing drainage around your home? Do you still have questions after reading our material? Ask them under the article - we will try to clarify the controversial issues as much as possible.
Or have you built an effective drainage system with your own hands and want to tell other users about your experience? Write your recommendations, add photos - newcomers to this business will be very grateful to you.




The site is located below the neighboring ones and is constantly flooded in the spring, then the water remains until May. The soil is sandy loam. Will drainage help or will I have to bring in soil and raise it?