How to make a house foundation drainage with your own hands: step-by-step instructions for arrangement
Groundwater has a negative impact on underground structures.Most of all, it “gets” from foundations and basements. The former are gradually eroded and lose the necessary strength, the latter remain flooded and unsuitable for use.
In order for the country estate not to suffer, it is enough to build drainage. But first you should familiarize yourself with the principles of its design. Right?
Do-it-yourselfers and zealous owners who want to make effective drainage of the foundation of their house with their own hands will find a lot of really useful information on our website. With our help, installing an underground water drainage system will become a simple, easy-to-implement task.
The article describes in detail the types of drainage systems designed to protect the foundation. The rules for their design are given and the requirements of the regulations are taken into account. Photographs and videos are used as visual aids.
The content of the article:
The need for a drainage system
Unpleasant odor and dampness in the basement, mold and mildew on the walls - such problems may be encountered by owners of houses located in areas with high groundwater flow. But these are not the most serious troubles that threaten an unprotected structure.
Water that periodically penetrates into the lower floors of the building gradually washes away the supporting structure, in addition, it exerts hydrostatic pressure on the floor and walls of the house.
It is especially important to protect buildings built on clay soils, since they retain moisture, and in winter they experience heaving, which can lead to complete destruction of the foundation, and ultimately the entire structure.
Properly performed site drainage helps solve several important problems at once:
- protect basements houses from flooding, mold formation and damage to building materials;
- protect the foundation from moisture and extend its service life;
- drain the soil around the house and eliminate stagnation of water;
- prevent soil oversaturation with moisture after heavy rains and stagnation of water on the surface.
However, it is not always necessary to install a water drainage system in all areas. Before planning and doing foundation drainage, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors: location of the site, composition and quality of the soil, groundwater level, terrain, climatic features of the region.
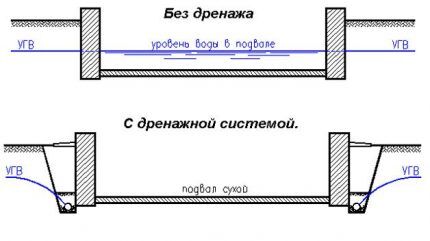
The installation of a drainage network is mandatory in the following cases:
- The basement of the house is located below the groundwater level during the flood period or rises above it by less than 0.5 meters.
- The building is built on clay soil: sandy loam, loam, even when groundwater flows significantly below the house.
- The site is located in a lowland or on a slope.
In areas located on sandy, gravel and crushed stone types of soil, on a hill or with low groundwater flow, it is not necessary to install a full-fledged drainage system. You can limit yourself to organizing a storm drain to drain rainwater from the building.
But this is only possible in those areas where the type of soil and the level of groundwater are precisely known. If it is planned to build a house in a new area, geotechnical surveys are now mandatory.

They are necessary for competently choosing the type of foundation for a house. At the same time, soil studies under future construction make it possible to resolve the issue of the need for drainage work.

Types of site drainage
There are several types of drainage that can be done on the site. Depending on the depth of the groundwater table, drainage is divided into surface and deep.
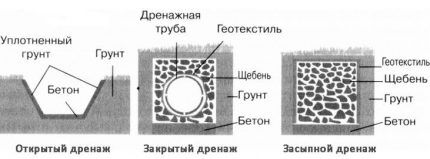
A feature of the surface system is that its elements are located at a shallow depth, which ultimately limits its functionality.

The standard depth of open drainage is about half a meter. It is used in areas with characteristic stagnation of flood water.If it is necessary to install the system at a greater depth, concrete trays are laid at the bottom of open ditches and the width of the trenches increases significantly, which is extremely undesirable for small suburban plots.

Features of an open drainage network
This is the simplest and least expensive drainage system, which is carried out in the form of a network of open trenches designed to collect and drain excess water from the garden area.
It is often used in arranging garden drainage. The open type of drainage also removes rain and melt water from the building, as well as excess liquid formed during washing or watering.
However, this type of drainage cannot be called a complete system; it will not be able to protect the structure from the penetration of groundwater into the part of the structure buried in the ground. If groundwater runs high enough in an area, such drainage can only be used as an additional liquid drainage system.
Stormwater as an effective supplement
To collect and remove water from the site that stagnates as a result of precipitation, a storm system is installed. It is constructed if there is a need to relieve drainage, which cannot fully cope with drainage of the territory. The storm line is equipped with point or linear water intakes.
A point or otherwise local water collector is designed to drain liquid from certain areas. It is installed in places where water periodically flows: under drains, in front of entrance doors, under taps, etc.
A pit is dug under it, where a rainwater inlet is installed, which in turn is connected to the pipes of the site’s sewer system. The top of the structure is covered with a decorative grille.

The linear water intake is designed to drain liquid from the house and from the ground surface throughout the entire site. It is connected to a network of channels located in accordance with the developed installation diagram.
Typically, the network is installed around the perimeter of the building; at the lowest point, a sand receptacle is installed for collecting waste. The system is connected to an underground storm sewer system, through which water is discharged into drainage wells.

To arrange linear drainage, a trench is dug around the foundation, then a concrete base is laid at its bottom, where special plastic or concrete trays are installed to receive water.
The network can be left open, but a closed outlet system, on top of which a decorative protective grille is mounted, is more popular.
Rules for the design of a closed system
If the foundation of the house is installed on clay soil, the problem of liquid drainage can only be solved by installing a full-fledged deep drainage system.
The low filtration properties of sandy loams with loams prevent the free seepage of water into the underlying layers, which is why watering is felt even at the level of soil development - 0.2-0.4 m from the day surface.
The situation is similar in areas with high groundwater levels. There it is precisely what prevents flood and atmospheric precipitation from penetrating into the underlying layers. In areas with high groundwater levels, usually located in lowlands, even a foundation buried in sandy soil requires the installation of a protective drainage system.
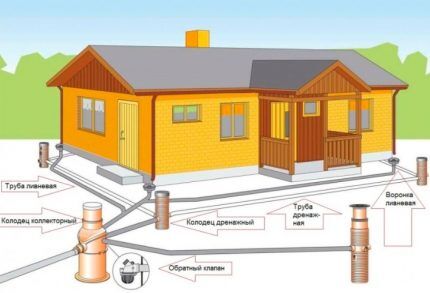
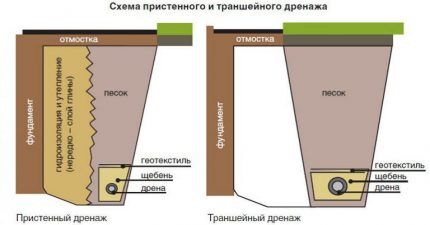
Closed, i.e. underground drainage to protect the base of a building can be made in two versions: wall or ring. In both cases, the drainage sewer is a closed network of perforated pipes laid underground, through which the liquid is discharged into a collector or filtration well.
The difference lies in the location of the pipeline in relation to the house:
- wall drainage performed in close proximity to the building;
- ring method - the trench is dug at a distance of at least 1.5 m and no more than 3 m from the foundation of the house.
In areas with a high level of groundwater and on clay rocks, they develop wall foundation drainage. It is also recommended to do it when the building has a basement floor.
The ring is most often installed on soils that have good permeability (sand, pebbles, crushed stones, gravelly) and in cases where the house does not have a lower floor.

It is recommended to carry out the work at the initial stage of construction; this option is more preferable and convenient. However, if drainage pipes were not laid during the construction of the building, ring drainage of the house can be done even when the house is already built.
As for the wall-mounted option, it is not advisable to carry it out next to a finished structure, since interference with the foundation structure can negatively affect its strength and durability.
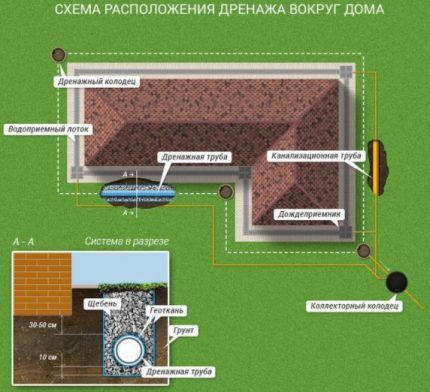
The effectiveness of the drainage network depends on two key parameters: installation depth and pipeline slope angle. The depth of drainage depends on the depth of the foundation of the house.
The main rule here is that the pipeline must run half a meter deeper than the base of the foundation. For good water outflow, it is necessary to ensure a certain pipeline slope in the direction from the house.
In areas with a natural slope, the pipeline is laid in accordance with the channel that the water has made. For flat areas, you will have to do the slope yourself, giving the bottom of the trench a certain relief. Water will drain well if the pipeline slopes 1-3 cm per linear meter.
If it is not possible to create the required slope, install water pump.
Underground drainage equipment
To lay the drainage system, special pipes are used - drains made of PVC or polyethylene. They differ from other types of pipes by the presence of small holes located on the surface at the same distance from each other. The holes are used to allow groundwater to penetrate into the pipeline.

Wells are important elements of the drainage network. Typically, several types of wells are installed in the system. At all turning sections of the highway, as well as at junctions inspection tanks are installed.
Rotary wells are needed for periodic inspection of the system and, if necessary, carrying out cleaning work. Wells are plastic containers with a diameter of 315 or 400 mm. You can make them yourself using plastic pipes of the required diameter.

In areas where, due to the terrain or for technical reasons, it is impossible to drain water into natural reservoirs, water intake wells are installed.
They are designed to collect liquid, which can later be used for watering the site or other household needs. To prevent incoming water from flowing back into the pipes, a check valve is installed.

In soils with high absorption capacity, filtration wells are installed. In these structures, instead of a bottom, a special drainage backfill is provided, through which the liquid, after undergoing preliminary cleaning, goes into the ground.
The diameter of such a well is from one and a half to two meters. The design can serve drainage systems in which the volume of incoming liquid does not exceed 1.5 m2 per day.
A short photo course on drainage construction
Let's consider the process of installing a drainage system designed to drain groundwater from the foundation of a newly built house. Up to the level of the foundation of the building, the geological section is represented by loam and a soil-vegetative layer on top, the thickness of which did not exceed 20 cm.
Loam has low filtration properties and passes water poorly and extremely slowly. During the flood period, the area is flooded, and during the freezing and thawing of the soil it subsides unevenly.
In order to get rid of groundwater, it was decided to build a drainage system with its discharge into a collector well with an absorbent bottom.
Now let's proceed to constructing a well with an absorbing bottom, thanks to which the water collected by drains will be utilized in the underlying layers with good filtration qualities:
Now we can safely admit that the system is actually installed, all that remains is to carry out the finishing work and arrangement of the site:
System installation work
When arranging a wall drainage network, before doing the foundation drainage itself, it is necessary to properly waterproof it. To do this, you need to first coat the walls of the house with two layers of bitumen mastic. In this case, the first layer is reinforced with a painting mesh.
This work allows you to strengthen the foundation and prevent its destruction.
A trench is dug around the perimeter of the entire house, half a meter deeper than the base of the foundation. In turning areas it is necessary to provide places for installing drainage wells. When installing a wall system, a trench is dug either near the house itself or at a distance of no more than half a meter from the house.
If the ring option is chosen, 1.5-3 m are retreated from the building. The bottom is carefully compacted, then sand is poured into the very bottom with a layer of 5 cm and also compacted well. Using sand at the bottom of the trench, create the necessary slope. First, geotextiles will fall onto the sand cushion - its edges should protrude approximately 50 cm on each side.
The geotextile will serve as a filter that protects the system from silting. Next, crushed stone 10 cm high is poured, and then drainage pipes are being laid, which are also covered with crushed stone on top.

The resulting structure is covered with both edges of the geotextile overlapping so that the pipe is completely wrapped in the fabric. Inspection wells are installed at pipeline turning points.
Bends for inserting pipes are made at a distance of at least 20 cm from the bottom. This indentation is necessary so that debris that gets into the drains along with water settles at the bottom of the well and does not enter the collector.When the system is inspected, debris can be removed with a stream of water.
After the pipes are connected to the rotary wells, the trench is finally backfilled with soil excavated from it. On top of the wall drainage, after compacting it, make a blind area of the building.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
This video describes in detail how to properly drain a site:
The video tells how to drain the foundation of a finished house:
To prevent dampness and mold from settling in the house and turning the life of its inhabitants into a complete nightmare, it is necessary to promptly drain the foundation. It is recommended to carry out this work during the construction stage of the structure. It is better to hire a specialist to carry out the calculations, and you can arrange the drainage yourself.
Do you have anything to add, or do you have questions about organizing the drainage of the foundation of your house? You can leave comments on the publication, participate in discussions and share your own experience in arranging drainage systems. The contact form is located in the lower block.




For our site, open drainage was not at all suitable, yes, it is easy to implement, but we had to constantly clean it, and the appearance of the site deteriorates, plus you constantly stumble and fall. It was quite difficult to maintain an inclination angle of 1/100, so in practice it is still better to use 2 cm per 1 linear meter, but I did not want to install a pump; additional noise was excluded.
Please tell me, is ring drainage also relevant for a non-buried monolithic slab foundation? If we assume that the foundation is not buried, the depth of the drains from the base of the foundation is 0.5 m, which is higher than the freezing depth.Is this acceptable? Or is the depth of freezing not taken into account for drainage?