Inspection wells for drainage: types, design and installation features
A high groundwater level is a hydrogeological situation that negatively affects the technical condition of underground structures.When water comes into contact with concrete or brick structures, it gradually but extremely persistently destroys them.
A drainage system is designed to lower the groundwater level and drain water. One of its functional parts is inspection wells for drainage, necessary for inspection and cleaning of underground communications.
Before starting installation work, you should decide on the optimal type of well, prepare the necessary materials and read the installation instructions. We have studied all these questions in detail, and the answers to them are presented in this article.
The content of the article:
- Types of drainage inspection wells
- Types of drainage inspection wells
- Which material to choose?
- How to install an inspection drainage well
- Development of the pit and its dimensions
- Construction of the base of a drainage well
- Installation or production of the bottom
- Making a receiving tray for pipes
- Installation of the first ring of the working chamber
- Installation of overlap and neck
- Waterproofing the working chamber
- Finishing work: filling and installing the hatch
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Types of drainage inspection wells
A drainage inspection well is an underground hydraulic structure designed to monitor the condition and periodically clean the system.
The shape of the well in plan can be rectangular or round. They are used for pressure and non-pressure drainage systems, but with some differences.
Usually, arrangement of drainage circuits done according to a non-pressure scheme. This is a network of interconnected drainage collectors through which flood and infiltrated groundwater collected by drains moves by gravity.The force of gravity stimulates the movement of flows to collection and disposal sites.
The pressure system is characterized by the forced movement of wastewater, the transportation of which is carried out thanks to the operation of pumping equipment.
A pressure system is installed where their spontaneous movement to storage tanks for removal and disposal or to treatment facilities for processing is impossible. For example, if it is not possible to install the storage tank below the level of the drains.
Both types of sewer systems are constructed in accordance with SNiP 2.0403-85 “Sewerage. External networks and structures."
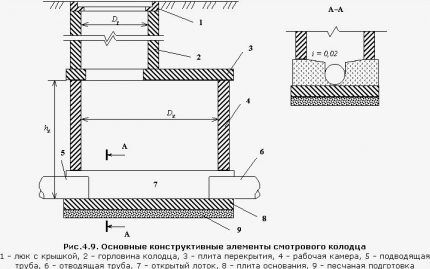
Structures for gravity networks
When installing a non-pressure system, calculate drainage pipe slope. I lay the main in a straight line and connect the branches with wells.
It is necessary to provide inspection drainage wells in the areas:
- direct drainage piping for inspection and maintenance;
- connection and branching of the drainage pipeline;
- changes in the diameter of the drainage pipeline;
- changes in the slope of the drainage pipeline;
- changes in flow direction (rotary well).
For straight sections of the drainage pipeline, a maximum length has been established at which the installation of an inspection well is mandatory.
This value depends on the diameter of the pipeline:
- 35 m — Ø 150 mm or less;
- 50 m — from Ø 200 to 450 mm;
- 75 m — Ø 500 to 600 mm;
- 100 m — Ø 700 to 900 mm;
- 150 m — from Ø 1000 to 1400 mm;
- 200 m — from Ø 1500 to 2000 mm;
- 250-300 m - over Ø2000 mm.
This dependence of the pipeline length on the diameter is given in the regulatory documentation regulating the rules for the construction of all types of sewer systems. It is based on many years of construction, control and maintenance practice.
The size of the inspection wells (working chamber in plan) also depends on the largest diameter D of the drainage pipe.
Values for rectangular wells:
- up to Ø 600 mm — 1000 mm for length and width;
- Ø 700 mm or more, - D+400 mm for length and D+500 mm for width.
Most inspection wells have a round-shaped working chamber.
Dependence of well diameter Ø on pipe diameter D:
- Ø 1000 mm — up to D 600 mm;
- Ø 1250 mm — D 700 mm;
- Ø 1500 mm — from D 800 mm to 1000 mm;
- Ø 2000 mm — D 1200 mm.
The dimensions of the rotary well can be increased to ensure a minimum turning radius of the trays.
There are several reservations regarding the size of the inspection well related to the depth of the bottom of the structure:
- if the depth of the inspection well is 1.2 m or less, for pipelines no more than 150 mm, a well with a diameter of 700 mm is allowed;
- for wells with a depth of 3 m or more, the minimum size of the working chamber is at least 1500 mm.
Shallow inspection wells, maintenance and inspection of which can be carried out from the surface are called inspection. Well structures that require the performer to be immersed to a depth of more than 1 m are classified as serviceable.

The height of the working chamber of the manhole is measured from the bottom (base plate) to the top edge of the neck.It depends on the depth of the drainage system and its purpose: drainage of groundwater from the foundation or drainage of a private site.
The well neck provides access for people and equipment inside the working chamber; the most suitable diameter for this is 700 mm. To descend into the working chamber, the inspection well is equipped with brackets or a ladder.
When installing trays for drainage pipes, the height of the tray shelf is determined by the largest diameter of the pipe. The top lines of the tray shelves should be flush with the top of the pipe.

Inspection wells for pressure networks
Pressure pipelines do not require slopes. In addition to standard functions, inspection wells of pressure networks form rational places for installation, adjustment and maintenance of equipment.
They are installed in the installation locations:
- shut-off equipment;
- pumping stations;
- at junctions with highways.
The size of the working chamber depends on the equipment being mounted. The laying depth should be 0.5 m deeper than the penetration of zero temperature. If this is not possible, the well shaft should be insulated to the specified depth.
The distance from the walls of the working chamber to the pipeline must be at least:
- 0.3 m for pipes Ø 400 mm and less;
- 0.5 m for pipes from Ø 500 to 600 mm;
- 0.7 m for pipes Ø 700 mm and more.
The height of the working chamber must be at least 1.5 m. To lower the well, it is equipped with iron brackets or a ladder.

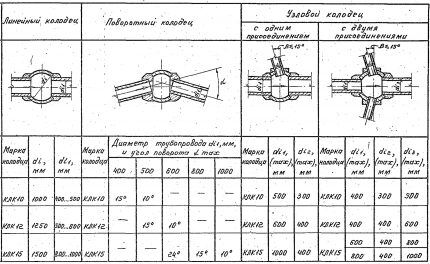
Types of drainage inspection wells
Inspection wells intended for non-pressure drainage systems are divided into the following types:
- linear;
- rotary;
- node with one or two connection nodes.
Standard designs of prefabricated reinforced concrete inspection wells are developed in accordance with the series 3.003.1-1/87 “Prefabricated reinforced concrete solid-molded wells for underground pipelines.”

Linear wells They are installed on straight sections of the pipeline and have two pipes: supply and discharge.
Rotary wells characterized by the permissible angle of rotation of the pipeline, which depends on the diameter of the pipe and the size of the working chamber.
Nodal wells They are built in such a way that the connected pipelines have an acute angle with the main pipeline in the direction of liquid movement.
Which material to choose?
Manholes can be industrial or self-made. As a rule, the well design is agreed upon with the operating organization.
The industry offers various options for ready-made inspection drainage wells made of: concrete, polymers or composites. Self-made wells can additionally be made of brick or rubble. Each material has its pros and cons.

The vast majority of drainage wells are made of reinforced concrete rings.
The use of concrete has its advantages:
- excellent resistance to water buoyancy;
- ability to hold heavy loads;
- possibility of manual production at the construction site;
- low price.
Reinforced concrete has a density approximately 2.5 times greater than water. It has a large mass and a high coefficient of friction with the surrounding soil, which well compensates for the buoyant force of water.
However, a large mass of concrete has its disadvantages:
- the need to use lifting equipment;
- the difficulty of making holes for the input and output of drainage pipes;
- the need to arrange access roads for the period of installation work;
- inability to achieve complete waterproofness.
Composite and polymer inspection wells factory-ready can be used on pipelines up to 400 mm.

Modern urban planning is increasingly using polymer drainage wells.
There are a number of reasons for this:
- ease of installation;
- wide selection of fittings;
- high construction speed;
- tightness;
- light weight.
Transportation of polymer or composite wells is carried out by conventional freight transport. Three people are enough to assemble and install the well.
However, such wells also have disadvantages:
- high price;
- lack of stability;
- Manufacturing according to individual design data is very expensive.
When purchasing a plastic well, you need to pay attention to the loads it can withstand, especially if the well is installed within the roadway.
Brick wells have pros and cons similar to concrete wells. An additional advantage of a brick well is the ease of achieving the specified dimensions. However, such a well requires more time to construct.

How to install an inspection drainage well
By the time work on constructing a drainage well begins, the pipeline must be laid, but not backfilled.
General progress of construction work:
- digging a pit;
- foundation device;
- installation or production of the bottom;
- manufacturing or installing a tray;
- mounting the working chamber of the well;
- mounting the top of the working chamber and neck;
- waterproofing of the working chamber;
- backfilling and hatch installation.
Let's consider the option of constructing a factory-ready inspection well. With independent construction, the construction stages are similar.
Development of the pit and its dimensions
Before starting to develop a pit, you must make sure that there is no groundwater at the bottom of the well. If there is water, then it is necessary to build a temporary drainage pit or carry out periodic pumping.
The pit is excavated according to the dimensions of the well planned for construction. The bottom of the pit should be larger than the base of the future structure. The less dense the soil and the fewer clay particles in its composition, the less its ability to “hold” the shape of the excavation.
Usually, when developing a pit in loose, easily crumbling sandy soils, the work required to remove the dump is much greater than when developing a pit in sandy loams and loams. If the shedding of waste rock interferes with the development of the pit, the walls of the excavation will need to be strengthened.
The depth of the pit is 35-40 cm greater than the bottom mark of the drainage pipe. Pipe marks are checked with a level.

Construction of the base of a drainage well
After the pit has been dug, coarse gravel or crushed stone of a fraction of 10-20 mm is poured onto the bottom. A preparatory layer thickness of 20 cm is sufficient.

Sand is poured over the coarse rocks in a layer of 10-15 cm. Then it is abundantly moistened and thoroughly compacted.A good level of base density can be considered compaction in which a person’s foot does not sink into the sand (shoes do not leave imprints).
Installation or production of the bottom
The construction of the bottom is a critical stage in the entire construction of the manhole, since it is the bottom that takes the entire weight of the structure and determines its verticality.
There are two options: make it on site manually or install it ready-made.
Option one. It is necessary to ensure that there is no water for at least 2 days, otherwise most of the binder will be washed out of the concrete. The thickness of the bottom should be at least 10-15 cm.
To reinforce the bottom, rods with a diameter of 6 mm are used. A mesh with a cell size of about 10 cm is made from reinforcement.
First, half the volume of concrete is poured. After the bottom part has set, a mesh is laid and concrete is poured to the required thickness of the well base. The ends of the reinforcement along the perimeter of the bottom must be covered with concrete. This design is suitable for wells up to 10 m deep.
Option two. The finished bottom is a reinforced concrete slab, mounted on a prepared and compacted base. The quality of installation is checked using a building level.

After all operations have been completed, the bottom of the well should be 5-10 cm below the bottom point of the outlet pipe.
Making a receiving tray for pipes
A layer of cement mortar is laid on the mounted bottom and a bed is formed for the drainage pipes. Marks are checked using a level.
The bottom of the finished plastic well, as a rule, already has the necessary trays.

Installation of the first ring of the working chamber
Drainage pipes must first be laid on the receiving trays. Corresponding holes are cut out from the bottom of the first concrete ring opposite the receiving trays.
Installation of shaped parts of a concrete well, sealing of joints and holes is carried out with cement mortar grade 100.

The working chamber of the plastic well is mounted entirely. If there is a risk of flooding of the pit, the well is placed under pressure until it is filled with soil.
Installation of overlap and neck
The top of a reinforced concrete serviced well is a floor slab. The standard opening for access to the shaft of a storage or collector structure should be 700 mm in diameter.
The opening of inspection wells is accepted from 600 mm or more: it should provide free entry of devices for cleaning the network if necessary.
After installing the top of the working chamber, functional equipment for pressure drainage is installed.
Next, the well neck is being constructed. The number and size of rings are selected taking into account the required height.
The neck of some plastic wells is a short cone-shaped pipe that can be easily cut to the required size.
The neck is covered with a support ring under the hatch.

For a plastic well, the top and neck are shaped parts installed on the seal.
In the case of self-production, the top of the working chamber is made in such a way as to withstand the weight of the soil, pedestrians, and vehicles, if the structure is installed under the roadway. It is made of reinforced concrete using bottom manufacturing technology.
Waterproofing the working chamber
If ground or flood water can come into contact with the inspection well, waterproof the walls 500 mm above its level during the period of greatest precipitation.
For well waterproofing coating waterproofing based on bitumen mastic is used, applied:
- on the bottom and working chamber of the well;
- on cement seams, entry points of drainage pipes.
Additionally, on the outside of the well, the pipes are sealed with a clay lock.
Instead of bitumen mastic, you can use specialized waterproofing compounds. Waterproofing is applied to the inner surface of the well. Additives are added to the masonry mortar to increase the waterproofing properties of the mortar.
Finishing work: filling and installing the hatch
Mounted on the well neck sewer hatch.
The installation level of the hatch depends on the type of coating:
- on the roadway – flush with the roadway;
- in the green zone – 50-70 mm above ground level;
- in an undeveloped part – 200 mm above ground level.
The backfill around the well is made with a gravel-sand mixture.A layer of about 20 cm is poured at a time, after which the soil is compacted. To facilitate compaction, it can be spilled with water.
Partial penetration of the soil-vegetative layer into the backfill is extremely undesirable, since it includes organic matter. Over time, organic matter will decompose and decrease in volume, and the soil around the well will subside.

Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Installation of a plastic well:
Comparison of plastic wells:
Inspection wells installed on drains are part of the hydraulic system. When properly designed and executed, they require one-time maintenance every 5 years. Moreover, the service life is measured in decades.
Do you have experience in installing inspection drainage wells? Or still have questions on the topic? Please share your opinion and leave comments. The feedback form is located below.






In our production, during the reconstruction of the drainage system, all concrete inspection wells were replaced with polymer ones. I read that to use them you need to draw up an individual plan - a project, and redo the entire drainage system completely, and not partially, as we did. In general, my question is: what problems might arise with such a replacement? And is it possible to somehow eliminate them without reworking the system?
It is impossible to say with certainty, since in general terms the whole situation is not clear.A project to replace inspection wells, especially at an enterprise, had to be agreed upon with someone.
Well, it cannot be that they simply replaced concrete inspection wells with plastic ones, without taking into account the current operation of the drainage system as a whole.
If the replacement was carried out taking into account the design of the current system, then no difficulties should arise. If the replacement was made without taking into account design features and current characteristics, then the following problems are possible:
- blockages;
— deformation under heavy loads;
— violation of tightness.
I advise you not to fix anything if there are problems, since they should be solved by the specialists who were involved in the installation of inspection wells.
Please tell me why the bottom of inspection wells is made? Is this something that is regulated? Is it possible to make an inspection well for wall drainage without a bottom by simply pouring crushed stone?