Site drainage project: choice of location, slope, depth, elements of the drainage system
Low filtration of the underlying soil is the cause of excess water in the area.It slowly goes into the lower layers or does not seep out at all. Cultivated plants grow poorly here or do not take root at all, the area becomes swampy, and there is a sense of slush. In such cases, a drainage system is needed, which should be properly organized.
We will explain in detail how to make a site drainage project. A system designed according to our advice will cope with its responsibilities perfectly. Familiarization with the proposed information will be useful for both independent owners and customers of landscape arrangement in a specialized company.
We have presented practical schemes for constructing drainage systems for suburban areas. The article describes in detail the factors that require consideration when designing and constructing drainage. The information offered for consideration is illustrated with photographs, diagrams, and videos.
The content of the article:
Purpose of garden drainage
Reclamation activities, in accordance with the standards (SNiP 2.06.15), are carried out in forest and agricultural lands so that the soil becomes as suitable as possible for growing fruit trees, grains and vegetable crops.
To do this, a branched system of open ditches or closed pipelines is formed, the main purpose of which is to drain overly wet areas.
The ultimate goal of collecting water through branches and branches of various types is artificial or natural reservoirs (if conditions permit), special drainage ditches, absorption wells or storage tanks from which water is pumped for watering and maintaining the area.

Using the same principle, a network of pipelines is designed for a summer cottage, regardless of its area - 6 or 26 acres. If an area suffers from frequent flooding after rain or spring floods, the construction of drainage structures is mandatory.
Clay soils: sandy loams and loams contribute to the accumulation of excess moisture, because they do not allow water to pass through, or very weakly, to the underlying layers.
Another factor that encourages you to think about a drainage project is the increased level of groundwater, the presence of which can be found out without special geological surveys.
If a pit was dug for a cesspool or septic tank on the territory of the dacha, and it filled with water, then the aquifers are located in close proximity to the surface of the earth. When a drilling organization constructs a well, you will receive data on the location of water horizons from specialists.
Even if the foundation holds up, there is no guarantee that a comfortable environment will be maintained inside the basements and basements: dampness, premature corrosion, mildew and mold may appear.
Over time, damp concrete and brick foundations become covered with cracks that are difficult to repair. On the contrary, they continue to grow, provoking movements of buildings. To prevent destruction, even at the stage of building construction it is necessary to think about the design effective drainage.

Drainage design elements
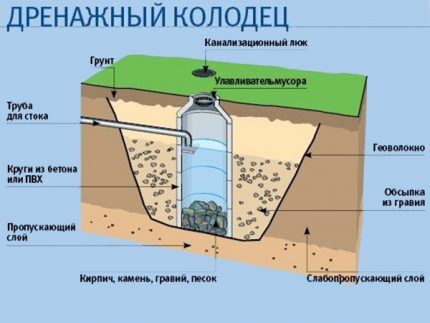
What is the drainage system? This is a network consisting of various components, the main purpose of which is to drain and collect capillary water contained in the pores of non-cohesive soils and cracks of cohesive rocks.
The main underground elements are drainage pipes. They should not be confused with water and sewer lines, since only water located in the upper ground layers moves through them. Storm sewers collect and drain rain and melt water.
More elastic corrugated models are popular. The diameter of the pipes depends on the volume of liquid discharged; standard section sizes are: 50 mm, 63 mm, 90 mm, 110 mm, 125 mm, 160 mm, 200 mm. For central highways, products of larger diameter are selected, for branches - smaller ones. Reinforced pipes consist of 2 layers.

At the junctions of several hoses or in areas where pipes turn at a large angle, technical (inspection) wells made of similar material are installed. These are wide sections of corrugated pipes or specially manufactured factory models.
The drainage system may also include storage wells, which for efficiency are installed at the lowest points of the site. Storage tanks are used if there is no way to discharge the drained water into a nearby body of water. All drainage lines lead to the wells. They transport water, which is often used for irrigation or household needs.

In addition to the main elements of the system, you will need fittings for connecting pipes, geotextiles and building material for constructing trenches and wells (sand, gravel or crushed stone, concrete rings, brick).
Types of water drainage systems from the site
There are many drainage schemes, but all varieties can be combined into three large groups: open, closed and combined. In accordance with this, there are three main types of drainage structures: surface, deep and also combined. Let's look at the features of each.
Features of open drainage
Water collection by open drainage is carried out thanks to a system of ditches and trenches, that is, objects not covered with a layer of earth from above.It is arranged to collect and drain water from the soil-vegetative layer, i.e. For site drainage. The operating principle of an open system is based on the ability of underground water to rush into the space freed from soil in the same way as it flows into a well.
The branched network is positioned at a slight angle so that the water flowing into the grooves moves by gravity beyond the boundaries of the site (quarry or fire reservoir) or is accumulated for irrigation in a storage well.
If necessary, the walls of the grooves of the open system are strengthened with compacted crumpled clay, laid out with cobblestones or tiles. It is permissible to carry out strengthening with flexible branches of bushes or suitable trees woven together.

The final point of water collection of the rafting drainage system is natural (rivers, lakes, ponds) and artificial reservoirs, as well as ditches, ravines, quarries located behind the fences of the summer cottage. A storage-type drainage network involves collecting transported underground water into a storage well.
System Features:
- coverage of all water storage points;
- calculation of the slope of drainage trenches;
- ensuring system protection from clogging;
- measures to prevent the emergence of new wetlands;
- location of the reservoir at the lowest point of the relief.
The norms for the slope angle of canals depend on the type of soil: for clay from 0.002, for sand – from 0.003.
There is an opinion that open drainage is not aesthetically pleasing. This is not true, because many ways have been developed to beautifully design external drainage systems.

A significant disadvantage of open drainage lies in a noticeable reduction in the usable area of the site. There are restrictions on the depth of ditches and grooves, because It is not customary to arrange them below 0.5 - 0.7 m from the day surface.
If it is necessary to build a drainage system at greater depths, it is necessary to increase the width of the trenches, install transition bridges, and carefully consider the drainage scheme so as not to impede the movement of people and personal equipment around the site.
Types of closed drainage
To arrange a closed drainage, an engineering project will be required, since all the elements are underground, and the functionality of the system depends on their correct location. There are local and general types of deep drainage.
If you need to protect the foundation of only one building or drain water from the road, this is the local variety; if you decide to drain the entire area, this is the general version.
Local types of systems, in turn, are divided into:
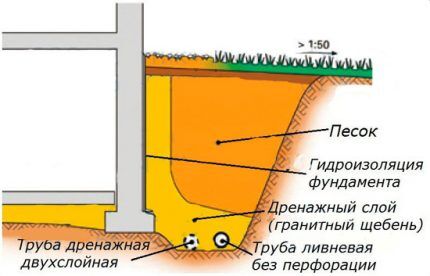
- wall (in clay soils, on the surface, along the perimeter of buildings - houses, bathhouses, garages);
- reservoir (in the ground under the building);
- ring (in sandy soils, around buildings, below the foundation).
All of the listed types of closed drainage are used forpreventing foundation flooding, as well as for protection against groundwater seepage into basements and basements.
Depending on location drainage pipes systems are divided into different types: horizontal (most popular in dachas), vertical and combined.
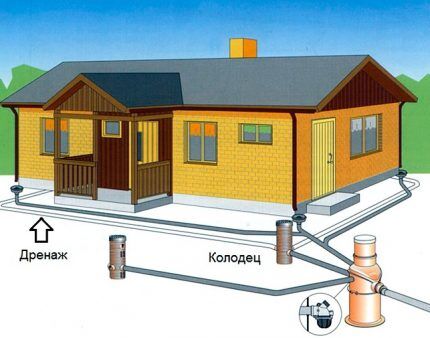
Pumping equipment is used to construct a vertical system. This is a complex design, therefore it is used extremely rarely for improvement of the private sector. Accordingly, the combined type of deep drainage is not common.
Drainage system design
To achieve maximum results and create a functioning water drainage system, it is necessary to draw up a drainage project. At drawing up a diagram and plan We recommend relying on the standards presented in SNiP 2.06.15-85. Here you can also find information about the size, quality and material of elements for drainage systems.
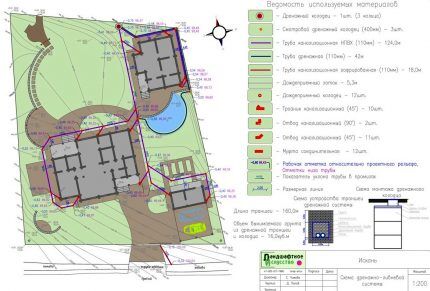
A mandatory attachment is an estimate indicating construction activities and amounts for materials and work.
Before drawing up a project, you must prepare the following materials yourself or with the help of specialists:
- data on soil and upper soil layers (composition, technical characteristics);
- location plan of all significant objects - buildings, swimming pool, gazebos, roads;
- diagrams of the foundations of buildings from different angles and in section, indicating the dimensions and depth of the foundation;
- topographic map of the dacha plot indicating the relief features;
- diagram of existing surface and underground communications;
- data on the hydrogeological features of the area.
It is also advisable to indicate decorative objects and places for planting green spaces on diagrams and drawings. This is necessary so that the elements of the drainage system do not damage fruit trees, flower beds, alpine slides, etc.
Designs for sandy and clay soils differ. For example, for sandy soils it is easier to develop a system aimed at lowering the groundwater level, while for loamy soils the most effective is local open drainage.
We remind you that the drainage system functions effectively only with a professional approach; amateur schemes often do not work.
Rules and nuances of design
The choice of drainage type for a country house or the location of channels is influenced by many factors. For example, the terrain is of great importance.If the house is located on a hill, and the rest of the territory is located at a slight slope, then wall drainage is most likely not required, and groundwater can be drained from the site by creating a canal system.
The location of groundwater is important.

The nature of the surrounding area should also be taken into account. If the area around the site is swampy or a river flows nearby, and the plot seems dry, then for preventive purposes it is also necessary to design a drainage system.
Let us consider in more detail the nuances that should also be taken into account when laying pipelines and trenches.
#1: Line depth and dimensions
The location of the pipes of a closed drainage system is chosen based on the design development, taking into account the slope towards the drainage basin. The depth of installation of system elements depends on the groundwater level. For a wall-mounted device, trenches are dug at the level of the foundation base, since its goal is to enhance the waterproofing qualities of the underground structure and protect the basement.
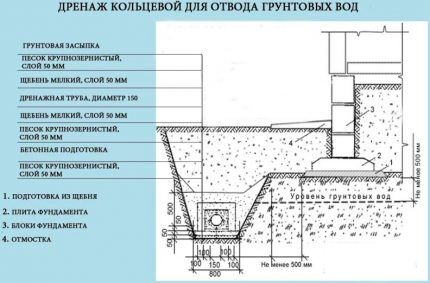
Ring drainage is chosen if the construction of the house has already been completed, and accordingly, all waterproofing and protective measures have been completed.
If the soil of the garden plot constantly suffers from flooding by precipitation or seepage of groundwater, systemic drainage is required throughout the entire territory. There are many options - from arranging a system around the perimeter to an extensive network that includes all dacha objects (buildings, road surfaces, garden plots).
The direction of canals and pipelines is strict - towards drainage structures or ditches located outside the territory of the personal plot. This way drainage pipes are laid with a slopenecessary for the free movement of groundwater collected by drains to unloading facilities.
#2: Slope standards for drainage pipes
Water in horizontally located pipes will stagnate if installation is carried out without a slope, the parameters of which are specified in regulatory documents.
For clay and sandy soil, which has different degrees of water permeability, the standards are different:
- loams and clay – from 0.003 or more;
- sand and sandy loam - from 0.002 or more.
If you convert the values into millimeters, you get 3 mm/linear. meter and 2 mm/linear. meter respectively.

When calculating the maximum possible speed, the properties of the surrounding soil, as well as the quality of the sprinkling, are taken into account. The slope cannot be made at intervals - it must be maintained throughout the entire length of the pipeline/channel. For hilly areas, options for installing drainage with differences are possible, with the installation of adapters in inspection wells.
Popular drainage system schemes
Let's look at several schemes that are often included in a project drainage of a dacha house plot. Among them are systems for draining water from the house, as well as expanded drainage structures.
One of the most common schemes is wall drainage to improve the waterproofing protection of the foundation and plinth.
The design of a storage well for the collection and further use of drainage water will be useful to those who are accustomed to using natural resources economically.
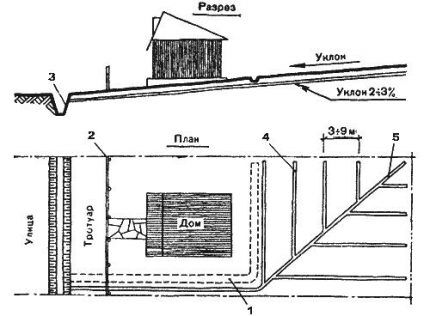
Variant of open drainage scheme. The best option for summer residents who own personal plots with a slope or uneven terrain.
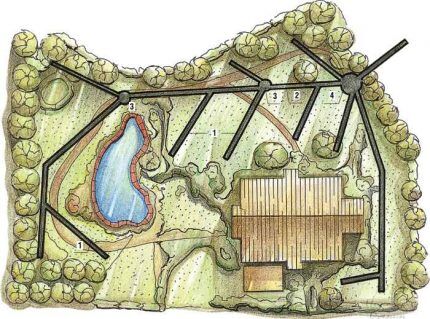
Sketch drainage for landscaping a garden plot and the area adjacent to the house. Judging by the picture, the house does not need a separate drainage structure.
Of course, the choice of scheme depends entirely on the conditions of a particular summer cottage; therefore, design should begin with a study of your own territory.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
A few useful tips will help expand your knowledge about drainage systems, and may be useful when building structures or trenches with your own hands.
Video #1. Recommendations for the construction of budget drainage to protect the foundation:
Video #2. Useful information about different drainage methods:
Video #3. Tips for choosing drainage pipes:
Designing a drainage system is a responsible task that only a specialist can handle. Improper pipe installation or errors in the design of engineering structures can cause significant harm.
To protect a house or site from groundwater or rainwater, we recommend contacting a design organization. This does not exclude the possibility that you can carry out some landscaping activities yourself.
Would you like to share your own experience in installing or operating a drainage system? Do you have questions or useful information about the topic of this article? Please write comments in the block below.




The drainage system is the first thing you should take care of. Yes, it's troublesome, but the result is worth it. Our entire village drowns in mud when the snow melts or a good rain falls. Previously there were norms, but now everything is on the conscience of the people themselves. I took care, I made drains and ditches on the site and around it. Everything is neat and clean for me. And the lawn does not wash away, and there is no dirt. I want to organize a pond now.
Installing drainage on a site is a very useful thing, especially when the snow and ice begin to disappear in the spring. Here in the Leningrad region, if there are errors in the design and installation of such systems, it is quite possible to end up with a swamp instead of your favorite garden plot. There is a question that has arisen in the practice of drainage design. The article states that surface runoff can be diverted to a special system or to a water body.
We do not have a special drainage system for the village, and many people solve the problem by directing the “sleeve” into the river. I talked with a fellow lawyer and he explained that such a sleeve violates the law, they say, the Water Code requires in this situation to obtain a decision on the provision of a water body for use. In general, it’s strange (what am I pouring into the river there - there’s a lot more flowing from the banks), but I don’t want to get into a bad situation. Maybe there is some technical solution to this problem? (some kind of homemade filter or something else). Thank you!
My site is in a lowland. The neighbors located above my site decided to raise it even higher. We leveled our site by bringing in soil. The height difference at the border ranged from 0.7-1m. Further, the height difference is even higher (up to 3m). I demanded, through the SNT Board, that drainage be installed along the closed border (using a 110mm drainage pipe). Where can I find standards for the dimensions of the drainage system? Do they have the right to raise the level of the site, artificially creating such a height difference? This will lead to flooding of my site in the spring. Are there any standards for creating such an artificial height difference?
In fact, there are no standards for ground levels, especially in private areas, everyone sculpts what they want, we have the same story. I ordered drainage from the Zemlyochist company, an engineer came and measured it, dissuaded me from some of my wishes, in the end everything was done as it should be, I hope, but at least everything works. Along the border with the same neighbor they made intercepting drainage, trench - geotextile - sand, drainage pipe 110 - crushed stone to the very top.