How to make garden drainage with your own hands: analysis of arrangement technology
Not all owners of suburban plots are “lucky” with ideal hydrogeological conditions.It is often only during the process of cultivating the land or building that they realize that groundwater lies high and that during flood periods there are puddles for a long time. There is no need to worry, drainage will solve this problem. Agree, building it is much easier than looking for a perfect site.
The drainage system will remove excess moisture from the soil and plant layer, which will ensure the normal growth of cultivated green spaces. It will divert underground water from the foundation in case of contact, and protect the basement and inspection pit of the garage from flooding.
Those who want to arrange the drainage of a garden plot with their own hands or through the efforts of a team of landscape workers will find detailed answers to all sorts of questions from us. Our material describes in detail the options for groundwater drainage systems and methods for their construction.
The content of the article:
Prerequisites for the construction of drainage
A drainage system that collects and drains excess groundwater is necessary in the following cases:
- The plot is flat, i.e. there are no conditions for spontaneous movement of water downhill.
- Groundwater is noted at a level close to the earth's surface.
- The site is located in a lowland, river valley or drained swamp area.
- The soil-vegetative layer develops on clay soils with low filtration properties.
- The dacha was built on a slope, not far from its foot, which is why when precipitation falls on the site and around it, water accumulates and stagnates.
Installation of drainage is almost always necessary in areas with underlying clay soils: sandy loam, loam. During periods of heavy rainfall and snow melting, this type of rock allows water to pass through its thickness too slowly or does not allow it to pass at all.
Stagnation of water at the level of soil development is associated with waterlogging. In a humid environment, the fungus actively multiplies, infections and pests (slugs, snails, etc.) appear, which leads to diseases of vegetable crops, rotting of the roots of bushes, perennial flowers and trees.

If the problem of waterlogging of the soil is not addressed, erosion of the soil may occur over time. In frosty weather, soil layers containing water will swell, which can cause damage to the foundation, paved paths and other landscaping facilities.
To check whether drainage is necessary, you need to find out the throughput of the soil layers on the site. To do this, dig a small hole 60 cm deep and pour water into it to the maximum.
If the water is absorbed within a day, then the underlying soil has acceptable filtration properties. In this case, there is no need for drainage. If after two days the water does not go away, it means that clay rocks lie under the soil and plant layer, and there is a risk of waterlogging.

If not in a timely manner implement a drainage system, then country estates are threatened by the following problems:
- flooding of cellars, basement floors, additional buildings located below ground level - this subsequently leads to damage to wall materials, the formation of mold and fungi, rotting of furniture, stairs and other wooden structures;
- waterlogging of the soil due to its saturation with moisture, which leads to low yields, rotting of the roots of vegetable crops, plants, death of trees and other plantings;
- Dips, depressions, and pits may form on the site, resulting in the destruction of paved paths and tiles - all this negatively affects the landscape of the garden area.
In winter, when the PRS and the underlying heaving soils, lying above the seasonal freezing level, freeze, the water contained in the pores of the earth will expand. An increase in the volume of soil threatens the destruction of structures buried in it and resting on the ground.
Organizing a drainage system will allow you to solve the following problems in the simplest and most affordable way:
Let's look at the types of drainage systems and their features.
Main types of soil drainage systems
Before you start drawing up a work plan, purchasing equipment and materials, you need to determine which system is appropriate to implement so that it works as efficiently as possible.
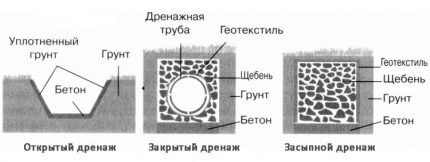
There are three types of drainage systems:
- superficial (open) - is a ditch on the surface of the earth, used to remove excess moisture formed due to partial rains or melting snow;
- deep (closed) – water is drained using a system of pipes and wells; the system is used in case of risk of flooding of the garden by precipitation and/or groundwater;
- backfill – the principle of its construction is the same as the deep one, only drainage material without pipes is used; Suitable for drying areas during precipitation.
Each of the above technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The surface drainage network is often combined with storm sewers that collect and drain atmospheric precipitation. Storm drains are equipped with two types of water collectors: point and linear.
Storm water as an effective addition
Storm sewer - a set of drainpipes with a well for accumulating moisture, through which it is transferred to the water intake. Before the water enters the well, there is a special siphon partition (grid) designed to clean the incoming liquid from debris, as a result of which the system does not become clogged and an unpleasant odor does not appear in it.
A storm sewer system with linear catch basins is a series of trays located at a slope towards the place where moisture is collected. The containers are placed in ditches with a layer of gravel at the bottom.The technology is used when the slope of the daytime surface of the site does not exceed 30 degrees relative to the horizon.

The main difference between a point system and a linear system is that a point system uses a pipe system located underground. Water is collected through so-called “points” - special storm drains equipped with a permeable grid.
This solution makes the structure almost invisible on the site.
Sometimes one type of system is not enough for an area, so they can be combined to maintain optimal moisture levels.
The type of system must be selected individually, taking into account landscape and geological features. For example, if the house is located far from a reservoir, then you can limit yourself to open drainage. If the mansion is located on a landslide-prone slope in a river valley, then it is better to use several systems simultaneously. You can read more about the arrangement of storm drainage Here.
Closed drainage device
A closed system is a network of trenches in which pipes and drainage material are laid. Drainage can be laid both over the entire area and in a specific area that requires drainage.
The deep drainage system consists of the following elements:
- drainage pipes;
- well (drainage);
- pump for pumping water.
To implement the system, it is necessary to dig trenches, install pipes, and construct drainage systems.

To install a water supply system in a trench you will need:
- geotextiles;
- crushed stone;
- gravel;
- sand.
The system is effectively used in case of flooding of the site with groundwater.
Standard structural components of a drainage system are:
Drawing up a diagram of the arrangement of elements
Before carrying out work, it is necessary to draw up a site plan, noting residential, domestic and commercial objects, as well as shrubs, trees, and flower beds.
Next, you need to determine the location for the well, taking into account the location of the drainage system. The drainage system can be a sewer, a well or any other natural source of water.
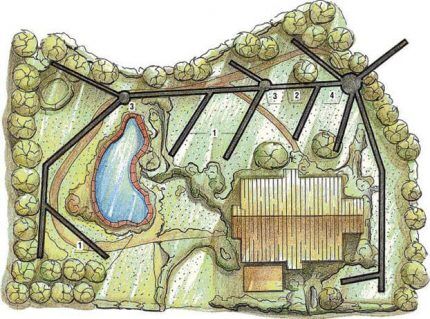
Then you need to draw up a diagram of the location of the trenches.
There are 4 main types of schemes:
- snake arrangement;
- parallel device;
- laying drains in a herringbone pattern;
- trapezoidal position.
You can choose the pattern yourself, but most often the herringbone marking is used.
Ditches can be located around the perimeter of the territory and along the contour of the house. In the area where vegetables and flowers will grow, a network is built taking into account the requirements, which will be discussed below.
Technical requirements for installation
When building a trench, the following requirements must be taken into account:
- the depth should be 1-1.2 m, and the width should be 35-40 cm;
- Near trees, a trench is dug to a depth of 1.2-1.5 m, near forest plantations - 70-90 cm, near flower beds - 60-80 cm;
- if peat soil predominates at the PRS level of the site, then, given that it shrinks quickly, the depth of the trench should not be less than a meter;
- if the area is relief, then the depth can reach a meter; if it is flat or with a slight slope, then digging a trench less than 1.5 m deep is ineffective;
- on clayey soils: sandy loam, loam, trenches are dug at a distance of 7-10 m from each other, on well-drained soils: sand, gravel and crushed stone deposits - at 15-20 m;
- The drainage system should be located further than 1 meter from the foundation of the house, and the minimum permissible distance to the fence is 50 cm.
To construct an open drainage system, you should select special pipes with a mesh.Their diameter can vary from 0.15 to 0.5 cm. It is better to avoid using asbestos-cement or ceramic drains, since they are impractical, require preliminary preparation, frequent washing, and quickly become clogged.

For the installation of closed drainage branches, it is recommended to give preference to perforated pipes made of polymer or composite materials. Some modifications are equipped with a special filter shell (geotextile), which prevents clogging of the system.
The diameter of the collector must be greater than the diameter of the pipe. If the area of the site being developed is more than 0.5 hectares, then the diameters can be equal.
The slope of the system towards the collector should be 2-3 cm for each meter of pipe with a diameter of 5-10 cm. If it is planned to use a pipe of a larger diameter, then the slope should be less. We have outlined in more detail how to correctly calculate the slope of a drainage pipe in this material.
Owners of land in a lowland or on a steep slope are faced with a problem when water stagnates in the lowest place, when the water intake may be located higher. In this case, in the lower part of the territory it is necessary to build a storage well into which a drainage pump must be installed. With its help, water is pumped upward and discharged into a ditch, ravine or other water receiver.
If it is planned to build a absorption well on the site to utilize the collected water, then the work on its construction is carried out in the following sequence:
Work progress during the construction of the system
The first thing to do before digging a trench is build a drainage well. Its depth should be 2-3 m, and its diameter should be up to 1 meter.
The most reliable well is a concrete one.However, it is not always possible to install concrete rings manually, so you will have to resort to the help of lifting equipment. In addition, high cost and fragility are disadvantages of concrete structures.
A plastic well is a special design made of polyethylene, polypropylene or polyvinyl chloride, which is practical and of high quality and effectively withstands soil pressure. The advantage of a reservoir well is that it has pipe bends, and the kit comes with rubber cuffs that ensure tight connections.

You can also pave a brick well yourself, make a structure from rubber and other available materials.
The well is subsequently installed drainage pump, which pumps water into a drainage system - sewer, well or other natural water intake.
Next, you can begin digging trenches according to the scheme, taking into account the technical requirements.
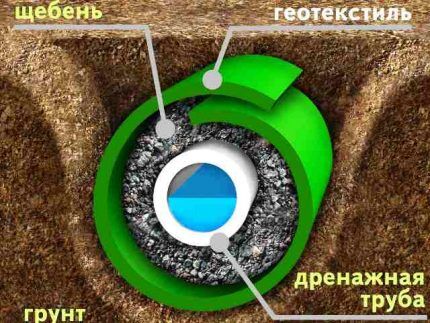
To protect conventional plastic pipes from clogging, so-called “external” filters made from straw, fibrous peat, and weaving waste are used.
After digging trenches, perform the following steps:
- Fill the trench with 10 cm of sand, after which a layer of geotextile is laid so that the edges of the fabric are higher than the recess.
- Cover the geotextile with crushed stone to a depth of 20 cm.
- Drainage pipes are laid.
- The pipes are covered with gravel or crushed stone of sedimentary rocks to a height of 30-40 cm, then with coarse or gravelly sand to a height of 30 cm.
- Roll up the geotextile - it will retain small particles and allow the system to clog.
- Geotextiles are sprinkled on top with a fertile layer of earth - soil.
- The pipes are connected to the well.
The technology for constructing a backfill drainage system differs from a deep drainage system in that it does not include pipes. The trenches are filled with large crushed stone or broken bricks and covered with small stones or gravel.
Implementation of the open option
To create surface systems, the same rules for constructing a trench are used as for implementing deep ones.
For an open system, it is enough to build ditches 0.7 m deep and 0.5 m thick. The walls are made with a slope, the bevel angle is 30 degrees. The ditch is drained into a drainage well, which is common to the plots, or into any other water intake.

The walls of open drainage ditches are compacted, sometimes reinforced with cobblestones or rubble stones, and lined with concrete tiles.
On our website there are other materials about arranging a drainage system on the site and around the house, we invite you to familiarize yourself with them:
- Installing drainage around the house: designing and installing a do-it-yourself drainage system
- Drainage diagram around the house: nuances of designing drainage systems
- How to make foundation drainage for a house with your own hands: secrets of proper organization
- Site drainage project: design rules + choice of location, slope, depth, system elements
Extending drain life
A backfill type drainage system can function effectively for 5-7 years, while deep and open drainage structures with high-quality pipes allow you to forget about the problem of waterlogging for 50 years. But this is possible subject to periodic network maintenance.
There are 4 rules for caring for the system.
- Large equipment should not pass through the area where the pipes are located; the road for it should be paved separately.
- Regular loosening of the soil will improve its water permeability, which will ensure good operation of the system.
- Once every 2-3 years, the pipes should be washed under high pressure of water, cleaning them from particles of clay and rust.
- Excavation work for installation should be carried out on damp ground.
By following simple tips, you can extend the life of your equipment and avoid repairs.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video describes all the nuances of constructing a private drainage system:
Installing drainage into the ground saves owners of acres of land from many problems. By installing a drainage system, you don’t have to worry about the condition of the crops or the general appearance of the area when humidity rises.
Do you have any questions about arranging the drainage system for your garden plot? Found any inaccuracies? Or maybe you have interesting information that you can share with our readers? Please leave your comments under our material.




Everything seems to be presented in an accessible way. And there is plenty of similar material on the Internet. But when I look at the site... in general, “my eyes are afraid.” I have thirty acres, almost half of which floods in the spring, especially after snowy winters. I keep thinking and wondering about the water drainage scheme.Here, after all, you need to select the pipe material so that it is not too expensive, but suitable, and make all the calculations. In general, I don’t know whether to save money or entrust everything to professionals?
Good afternoon, Oleg. I would recommend that you first contact a construction organization to draw up an individual drainage project for the site, taking into account all the features. Having already a complete layout diagram, the number of necessary inspection wells, pipes, draw conclusions about how feasible it is to carry out all the work yourself.
In any case, I advise you to order the project from specialists - this will save you from mistakes, and therefore from additional expenses in the future to eliminate them.
The fact that an open drainage system will cost much less than a closed version is understandable. We started building one in our village, but after a year we decided to make it a closed one, because we had to clean the canals from silt and leaves, and it takes up quite a lot of space. They installed a plastic well and buried the pipes, everything is fine now. The water that has settled in the collector well is discharged into our ravine.
What if there is nowhere to send water? Are the ditches below your neighbor's property silted or blocked? How then?
Good afternoon, Dmitry. The district administration or dacha association is responsible for the proper condition of the ditches. I advise you to contact them in writing to resolve the problem.
Fundamentally, the issue can be solved in two ways: by organizing one or two filtration wells on your site or by creating a perimeter boundary where water can be discharged.It is important to pay attention to the soil water absorption rate in a particular case. Simple methods of determination are outlined in this article. You can familiarize yourself with the principles of arranging filtration wells Here.
The boundary is a ditch 20 by 20 cm wide; permission from neighbors or government agencies is not required for its arrangement. It is also recommended to organize it in case of severe waterlogging of the area in the spring when the snow melts.