Heating cable for water supply: how to choose and install it yourself correctly
In winter, during severe frosts, owners of country houses risk being left without water supply.Ice jams in the external water supply will not only leave residents without a shower, an efficient system for supplying water to sinks and other amenities of civilization, but will also cause damage to the pipes.
Agree, the prospect is unattractive. It will be possible to prevent such a development of events if you install a heating cable for the water supply along with the pipes and connect it to the electrical network. It is quite possible to carry out all the work yourself.
We will tell you how the heating element works and describe the main parameters for choosing it. We will also consider in detail the methods of installing the heating cable and illustrate the stages of work with visual photographs.
The content of the article:
Why do you need a heating cable?
It is reasonable to argue that one can easily do without heating water supply. It is enough to find out the level of soil freezing in the area, and then, based on the indicators, dig a trench of the required depth. Usually this is 1.5-1.7 m for the middle strip, depending on the type of soil.
Pipes buried at such a depth and insulated do not freeze, since the surrounding soil has a positive temperature (let's say + 2-4 ° C).
However, not all so simple. In wetlands or areas close to water bodies, high groundwater levels are a common occurrence. This means that during floods or snow melting, communications will be flooded, which will negatively affect their functional properties.
If you bury the pipes only half a meter, but at the same time connect the electrical cable and provide proper thermal insulation, then you won’t have to dig deep ditches.

Let's not forget about the critical areas that are most susceptible to the effects of cold - the places where the pipeline enters the house. If the building is built on a pile-screw foundation, then underneath there is an open section of the pipeline, which is easiest to insulate with a heating cable.
Conclusion: if it is technically possible to install a heating system for a water supply system, you should definitely use it, at least for the sake of insurance against freezing.
When contacting a specialized company, you may encounter some variety of offers. Let's look at the assortment.
Design and scope of application
Depending on the type and technical characteristics, heating cables are used to heat drains, water supply And sewer pipes, tanks. The main purpose is to protect liquids from freezing by increasing the temperature.
Heating systems are relevant for external communications, that is, for use in the ground or in the open air.

Heating systems have one useful ability - zonal application. This means that you can take a set of elements and assemble a mini-system from it for heating a separate area, without connecting to the entire network.
This results in savings in materials and energy. In practice, you can find miniature “heaters” of 15-20 cm, and 200-meter windings.
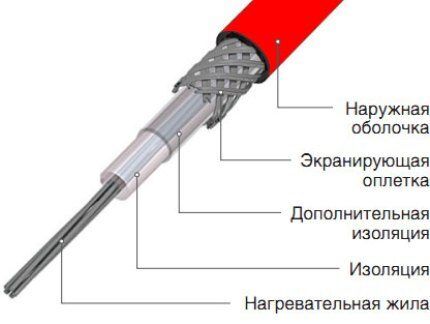
The main components of the heating cable are the following elements:
- Inner core - one or more. It is made using alloys with high electrical resistance. The higher it is, the greater the specific heat release value.
- Polymer protective shell. Together with plastic insulation, an aluminum screen or copper wire mesh is used.
- Durable outer shell PVC covering all internal elements.
Offers from different manufacturers may differ in nuances - the alloy of the core or the method of protection.
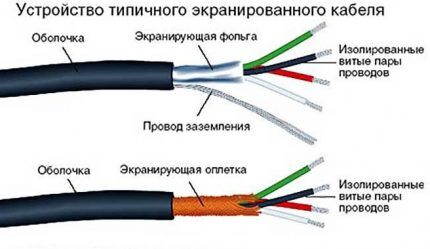
To improve the characteristics, the copper braid is nickel-plated, and the thickness of the outer layer is increased. In addition, the PVC material must be moisture resistant and not susceptible to ultraviolet radiation.
Types of heating cable
All heating systems are divided into 2 large categories: resistive and self-regulating. Each type has its own area of application.
Suppose resistive ones are good for heating short sections of pipes with a small cross-section - up to 40 mm, but for long sections of water supply it is better to use self-regulating cable (in another way – self-regulating, “samreg”).
Type #1 – resistive
The principle of operation of the cable is simple: a current passes through one or two cores located in the insulating winding, heating it. Maximum current and high resistance add up to a high heat dissipation coefficient.
Pieces of resistive cable of a certain length that have a constant resistance are available for sale. During operation, they give off the same amount of heat along their entire length.
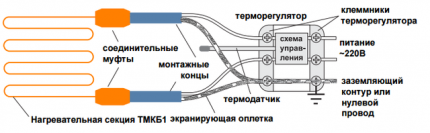
When installing the system, it must be remembered that the single-core cable is connected at both ends, as in the following diagram:
Closed heating circuits are often used for heating roof drainage system or for installing a “warm floor”, but an option applicable to plumbing also exists.
For internal installation, one core is not suitable, since laying the “loop” will take up a lot of internal space, and accidental crossing of wires can lead to overheating.
A two-core cable is distinguished by the separation of the functions of the cores: one is responsible for heating, the second is for supplying energy.
Two-core resistive cables are used for plumbing systems as actively as samregs. They can be mounted inside pipes using tees and seals.
The main advantage of a resistive cable is its low cost. Many note reliability, long service life (up to 10-15 years), and ease of installation.
But there are also disadvantages:
- high probability of overheating at places where two cables intersect or are close together;
- fixed length – you can neither increase nor shorten;
- impossibility of replacing a burnt-out section – will have to be changed completely;
- no power adjustment – it is always the same along the entire length.
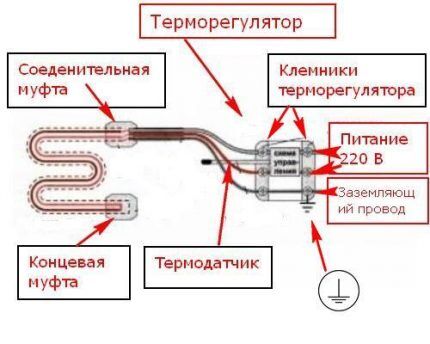
In order not to spend money on constantly connecting the cable (which is impractical), install a thermostat with sensors. As soon as the temperature drops to + 2-3°C, it automatically starts heating; when the temperature rises to + 6-7°C, the energy is turned off.
Type #2 – self-regulating
This type of cable is universal and can be used for various applications: heating roofing elements and water supply systems, sewer lines and liquid containers.
Its feature is independent regulation of power and intensity of heat supply. As soon as the temperature drops below the control point (assuming +3°C), the cable begins to heat up without outside intervention.

The principle of operation of the samreg is based on the property of the conductor to reduce/increase the current depending on the resistance. As the resistance increases, the current decreases, which leads to a decrease in power.
What happens to the cable during cooling? The resistance drops - the current increases - the heating process begins.
The advantage of self-regulating models is the “zoning” of work. The cable itself distributes its “labor power”: it carefully warms up the cooling areas and maintains an optimal temperature where strong heating is not needed.

To fully automate the process of turning on/off the cable, you can equip the system with a thermostat that is “linked” to the outside temperature.
Installation methods for water supply
There are two ways to install a heating cable - external and internal. In the first case, it is attached along the pipe (or wound around it), in the second, it is wound inside. Both options have active practical applications, so let’s take a closer look at them.
Option #1 – external
Linear installation of cable along a water pipe is easy. The wire is fixed on one side using heat-resistant plastic clamps or fiberglass self-adhesive.
The holders are fastened at intervals of 0.3 m. Metal fasteners cannot be used.It is not difficult to calculate the length of the cable - it is equal to the length of the pipe that needs to be heated.
Line installation instructions:
For pipes buried in the ground, the cable is not placed strictly at the bottom or at the top, but slightly offset, which can be called the “8 (4) o’clock position.”
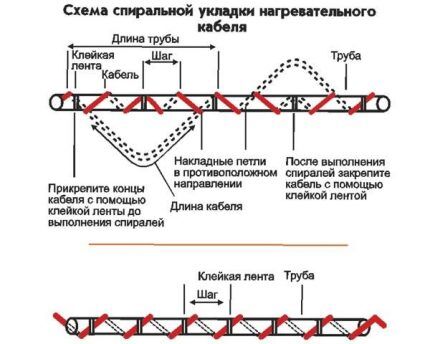
In addition to linear installation, spiral installation is used - the cable is wound along the entire length of the pipe with a uniform pitch. Plus – maximum contact with the pipe surface, minus – increased material consumption.

The wound method is relevant for pipes of medium and large diameter - sewer, drainage, but is also used for heating water pipes.
Option #2 – internal
The internal installation method is not suitable for all pipes, but only for water pipes with a cross-section of more than 40 mm.In pipelines with a smaller diameter, the cable will partially block the flow of water. It is difficult to equip a long pipe with internal heating, but for sections several meters long this is one of the best ways.
It is easiest to pull the cable in vertical sections - from top to bottom. The procedure takes place using a tee and a sealing coupling, which prevents the cord from slipping.
In some cases internal cable installation more rational than external - for example, for repair or replacement of elements. It is not difficult to insert and connect a finished system; it is much more difficult to assemble it.
You can learn how to properly prepare the wires for insertion into the pipe from the following instructions.
Thermal insulation of heating cables
Regardless of the cable type, you must insulate. Thermal insulation is mounted on top of the heating system and water pipe. If the water supply along with the heating cable is not placed in a sealed “cocoon”, the heating will go in all directions, that is, mostly into the air.
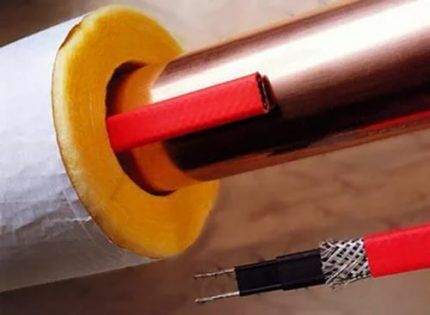
Expanded polystyrene or foamed polyethylene act as reliable and effective insulation materials. They are moisture resistant and provide some protective cushioning for the pipe, but also need protection.
For this reason, the “pipe-in-pipe” design is often used, when water pipes located in the ground or in the air, together with insulation, are placed inside another pipe of a larger diameter.
What characteristics are important for selection?
Before going to the store, be sure to check the diameter of the water pipe, the length of the area that needs heating, the lowest possible air (soil) temperature - this will make it easier to make a choice, because there are really a lot of offers.
So, let's pay attention to the following points:
- the presence of a protective film - provides grounding and makes the cable more reliable;
- type of external insulation;
- temperature class and power;
- manufacturing company.
A cable with polyolefin insulation may be suitable for a sewer system, but for internal installation in a water pipe we recommend protection made of fluoroplastic.For outdoor installation, a fluoropolymer is suitable, which will protect both from moisture and ultraviolet radiation.

Medium temperature systems are suitable for larger diameter pipes. Maximum heating temperature is +120°C, power reaches 33 W/m.
High-temperature systems with a maximum temperature of up to +190°C and a specific power of up to 95 W/m are considered the most powerful. However, they are usually not used in everyday life - these are products for industrial use.
The appropriate power can be selected based on the diameter of the pipe. For example, for water pipes with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm, cables with a power of 10 W/m are suitable, from 2.5 cm to 4 cm - 16 W/m, from 4 to 6 cm - 24 W/m, etc.
There are several brands of heating cable that have long proven themselves only from the best side.
Famous products of foreign companies:
- Nelson;
- Lavita;
- Devi;
- Ensto;
- Raychem.
Among Russian manufacturers, the company stands out SST (Teplolux), producing high-quality household products.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The videos provide an opportunity to see the practical application of the instructions.
Tips for installing a heating cable on a pipe:
Screed mounting option:
Instructions for connecting the cable inside the pipe:
Even a beginner can select and install a heating system for a water supply system. With the help of theoretical knowledge, you will quickly understand the types of cables, and for installation you do not need to master any special skills.
The result of the work may be worthy: you will forever forget about the problem of water freezing in the water supply during the cold season.
Do you have experience installing a heating cable for an autonomous water supply? Or maybe you want to share your impressions about using the heating element? Please share your opinion and leave comments.




A good thing is the heating cable, it helped us out during one cold winter (it was -30 degrees at night). The water supply was seized in the basement of our house; the foam around the pipe did not help. At that time, resistive cable appeared on sale, they did not yet know how to work with it, and the price was very high per linear meter. There is nothing to do, we bought it, figured out the installation, and it still works in any frost.
I buried the cable along with the pipe 2 years ago, I want to check its functionality now, what should be the resistance at the terminals at -10 degrees. Celsius. Is the cable Korean gray?
I have EASTEC STB 16-2 (16 W/M). Economical, consumes little electricity. Happy as an elephant.
I want to try it as heating
Will it work?
The devi cable will be stretched inside the pipe L= 26 meters? polypropylene pipe 25 in diameter, worked conscientiously for 4 years and “Kerdyk. They promised a service life of 25 years. For those reasons, it is impossible to extend a new one. The pipeline was not buried, but “built up” was carried out at the initial stage of construction with good access to installation. Sadness.
And I burned PND 32 in the ground. I don’t know what kind of one I had, 2 years ago 4 tr cost 4 meters. Maybe I installed it wrong somehow, it was fine for 2 seasons, but literally a week ago there was no water in the kirdyk, I went to dig and there was a hole in the HDPE.