Insulation of water pipes in the ground: rules for thermal insulation of external branches
The outer part of a stationary water supply system to a private house is usually placed in the soil. This way it does not take up space on the site and is protected from mechanical influences.However, it must also be protected from low temperatures during frosty periods. What can be done to prevent the formation of blockages in the pipeline in winter?
For uninterrupted water supply in winter, it is necessary to insulate the water supply system in the ground. We will tell you how to protect pipes laid in the ground from freezing. The article presented for review describes in detail the practical solutions to this problem that have been tested.
The content of the article:
Rules for the construction of underground water supply
Freezing of the underground water supply occurs due to the soil temperature reaching negative values. One way to prevent the problem from occurring is to install pipes at depths where sub-zero temperatures are unattainable.
If this requirement has not been met, other measures must be taken to solve the problem of uninterrupted water supply.
Basic provisions of regulatory documents
According to clause 11.40 of the set of rules SP 31.13330.2012, the depth of laid pipes, counting to the bottom, should be 0.5 meters greater than the calculated depth of penetration into the ground at zero temperature.This is necessary to prevent the formation of ice plugs in the pipeline and rupture of pipes in places where water crystallizes, increasing in volume as it freezes.
The calculated depth, according to clause 11.41 of the same rules, should be established by field observations of the soil freezing isoline, and also be guided by the experience of operating pipelines in the given area.
Such information may be owned by a hydrometeorological center or organizations involved in water supply. In the absence of field data, it is necessary to determine the depth using thermotechnical calculations.

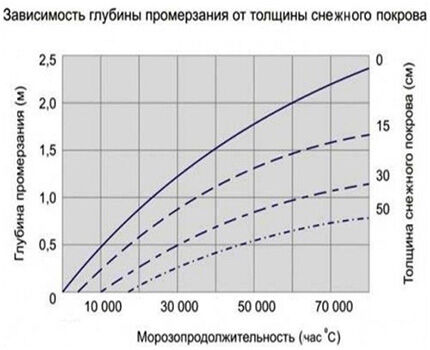
According to clause 5.5.3 of the set of rules SP 22.13330.2011, the standard depth of seasonal soil freezing in the absence of long-term observation data must be determined on the basis of thermal engineering calculations presented in the figure below.
The values of the average monthly air temperature for populated areas of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation should be taken from Table 5.1 of the set of rules SP 131.13330.2012.

If the obtained value exceeds 2.5 meters, as well as for mountainous areas with a sharp change in terrain, climatic or engineering-geological conditions, it is necessary to determine the standard depth of soil freezing in accordance with the formulas of Appendix “D” of the set of rules SP 25.13330.2012.
The calculated freezing depth in accordance with clause 5.5.4 of the set of rules SP 22.13330.2011 for areas with non-negative average annual temperature values is determined by multiplying the standard value by a factor of 1.1.For territories with negative values, this value is calculated according to SP 25.13330.2012.
Low temperature protection
It is not always possible to completely or partially lay the water supply system below the zero isotherm. Sometimes this cannot be done for technical reasons, for example, when the outlet of the water pipe from the well is above the boundary of the ground freezing zone.
The depth mark of the freezing level is determined in accordance with the climatic specifics of the region in which the water supply system is being built.
For the middle zone, this value is 1.0 - 1.3 m, depending on the type of soil; in areas with harsh winters, the depth of pipe placement, according to the rules, will be more than 2.0 - 2.5 meters, which is very expensive when laying, and in case of need for repairs.

If it is impossible or expensive to install a water supply system at great depths, other measures are used to ensure its uninterrupted functioning. They can be divided into two categories:
- Insulation. Designed to reduce heat loss by an object per unit of time. It is carried out using materials with low thermal conductivity.
- Heating. Designed to increase the temperature of an object. To carry out this procedure, an external source of thermal energy is required.
Choice insulation option or heating of an external water supply branch depends on the operating conditions, temperature conditions, system geometry, simplicity of the work performed, as well as the efficiency, cost and reliability of the method for solving the problem.
Methods for insulating external water supply
There are many ways to insulate a street water supply system located in the ground. If only cold water is supplied, then due to the small temperature difference, the thermal conductivity of the materials used is not as important as their durability, strength or price.
Application of simple techniques
If the pipes are located almost on the border of the freezing zone, then to eliminate the possibility of stopping the water supply, you can perform simple actions that do not require large investments and qualified work.
For the southern regions, where the water supply is shallow, it is enough to dig up the pipes in the fall, cover them with environmentally friendly insulating material and bury the trench again.
For insulation, you can use leaves, straw, shavings or sawdust. They have low thermal conductivity, but by next winter they will have time to rot in the ground, so this procedure must be repeated annually.
If, according to calculations, the pipes are located slightly above the level that ensures that the system does not freeze, then instead of deepening the water supply, you can solve the problem by raising the zero isotherm.
This can be done in two ways:
- increase the thickness of the soil layer by pouring it on top;
- use fallen snow for insulation.
In both cases, the center of the strip of earth or snow is located along the water pipeline, and its width should be at least twice the depth of the pipes.
The filling of earth will change the landscape of the local area, and insulation with the help of plant and wood waste or snow must be carried out constantly. Therefore, for a long-term and reliable solution to the problem of water pipe insulation, specially developed materials are used.
A water pipeline laid below the level of seasonal soil freezing in the region is insulated only in the area passing through the thickness of rocks that freeze in winter. Thermal insulation is installed from the specified level before the pipe enters the house.
If water supply is brought into the house through an unheated basement located below the freezing depth, then insulation is carried out within the basement. Then a wooden box is placed around the water supply section, and the space between it and the pipe is filled with sawdust or basalt wool.
Types and forms of materials
To insulate water pipes, materials are used that are presented in the form of shells - shapes that follow the contours of pipes and system components. They are made from basalt wool, glass wool, polystyrene foam, extruded polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, foam glass.
In the case of using mineral wool and glass wool, a prerequisite for underground installation is the presence of a foil sheath. It prevents the insulation from getting wet, which practically destroys the insulating properties of the material. The shell can be replaced by winding a pipe with basalt insulation with roofing felt.
Due to the ability to easily absorb moisture, cotton wool insulation in the form of mats cut into slabs or rolled into bales without waterproofing external protection is not used in the construction of underground networks.
An exception may be when laying the pipeline in concrete trays and filling the free space between the tray and the pipe with expanded clay or similar material.

Thermal insulating shells are ready-made cylindrical blanks, whose internal diameter coincides with the external diameter of the pipes. Products ranging from 60 cm to 2 meters in length consist of a single tube with a construction seam, if the insulating material is elastic, or of several (usually two) sections. The main advantage of sectional insulation material is the ease of installation of the product.
The connection of the halves of a relatively thin shell occurs with the edge of the element overlapping the next element to avoid the formation of unprotected sections of the pipeline. The displacement of meter segments is usually 15-20 cm.
If you need to use thicker insulation, it is better to choose a shell with a mounting chamfer along the end edge. The second option for ensuring tight connections is to slightly shift the parts of the shell relative to each other.

When attaching parts of the shell, use plumbing tape. The junction of pipe bends, bends and other system components is protected using special shaped forms.
Thermal insulation paint and polyurethane foam spraying
One of the additional solutions to prevent freezing of the external water supply line located in the ground is liquid or sprayed thermal insulation.This method allows you to reliably, without seams or cold bridges, protect areas with complex geometry, for which it is difficult to use standard materials for insulation.
Polyurethane foam has a liquid consistency and is applied to insulated objects by spraying. Possessing one of the best thermal conductivity indicators, as well as a number of other positive properties, this material has a significant disadvantage: special equipment is required for its application.

It is not difficult to find companies that deal with insulation using polyurethane foam, since it is actively used at various facilities. However, all service providers have restrictions on the minimum spray area, so it is unlikely that it will be possible to find an affordable option solely for the sake of 10 or 20 meters of pipeline.
Special heat-insulating paint for pipe insulation, similar to polyurethane foam, can be applied by spraying. It is sold in cans, so this procedure is easy to do yourself. There is also an option in liquid form, which allows you to paint the plumbing elements using an ordinary paint brush.
Thermal insulating paint contains additives in the form of ceramic microspheres, foam glass or perlite. The thermal conductivity of this material is quite low, however, due to the thin layer of application, it alone may not be enough to solve the problem of insulating a section of a water pipeline crossing the thickness of freezing soils.
Due to the high cost, applying a thick layer of insulating paint is expensive. Therefore, its use for insulation is justified only in areas with complex geometry or in places where cold bridges may occur.

However, in the case of using steel pipes, using paint along the entire length together with other insulation may be advisable for another reason. The presence of porous material in the composition leads to a high adhesion rate, eliminating the possibility of external corrosion, which is important for metal structures located in the ground.
Ready-made integrated solutions
The problem of freezing of a street water supply branch is very relevant. Demand creates supply and, therefore, there are a large number of ready-made integrated solutions on the market in the form of thermally insulated pipes and connecting elements.They are pipelines surrounded by insulation, which is enclosed in a hard or flexible shell.
There are both single-pipe and double-pipe options for a ready-made solution for insulating external pipe installations. For regular cold water supply, the best option is structures containing plastic pipes. They are cheaper than their metal counterpart and are characterized by high installation speed.
Insulated HDPE pipes are supplied in coils up to 200 meters long. The installation of water supply systems based on them can be done with a minimum number of joints.
If corrugated material is used as the outer shell, it is possible to lay the pipeline without the use of corner joints. This is possible due to the ease of making small radius bends of all parts of the kit.

Protection of insulation from negative factors
Protection against freezing of a water supply system located in the ground has its own specifics. The material should not completely or partially lose its thermal insulation properties under the influence of external factors.
Re-insulating or repairing the outer layers requires expensive and time-consuming excavation work, so immediate care must be taken to maintain the integrity of the protective structure.
Destructive effects of earth and water
The underground water supply system experiences soil pressure, so the material used for insulation may be crushed. This can significantly increase its thermal conductivity. To prevent such developments, it is necessary to create a hard outer shell using larger diameter pipes or special trays.

In the case of using hygroscopic materials as thermal insulation of pipelines, it is necessary to prevent the possibility of influence of groundwater on them, which is always located in the ground, regardless of the degree of water saturation of the soil.
To protect mineral and glass wool, additional means of protection are used - plastic pipes larger than water pipes, which at the same time solves the problem of insulation collapse.
You can also use the following materials to create a waterproofing shell:
- rolled aluminum foil;
- reinforced (plumbing) tape;
- roofing felt;
- high density polyethylene film.
Styrofoam, extruded polystyrene foam They poorly absorb moisture, but over time they also become unusable with constant defrosting.Foam glass, polyurethane foam, and heat-insulating paint are completely unaffected by wrinkles and moisture.

Solving the problem of insects and rodents
Another cause of damage to the insulation of the water supply system can be rodents and insects. Ants gnaw numerous passages in the thermal insulation that is attractive to them, and mice use it to build a nest. These actions expose parts of the pipes, which negatively affects the quality of insulation.
Neither insects nor mice can spoil polyurethane foam or foam glass, but they do an excellent job with basalt wool. It and similar materials for external insulation of water supply pipes must be protected from rodents if they are located at a depth of less than 2 meters. Earth ants do not penetrate below 1 meter, while forest ants build a large anthill, the above-ground part of which is impossible not to notice.
To protect against rodents, you can wrap the insulation with a fine-mesh metal mesh. To prevent access not only to mice, but also to ants, it is necessary to wrap the material with aluminum foil, reinforced tape, or use plastic pipes or trays of any shape as the outer shell.

Heating of external water supply systems
If we consider any system, then insulation is just a way to increase the time for its temperature to decrease to a value corresponding to the environment.Therefore, sometimes you have to resort to another option to prevent water pipes from freezing - heating.
Happening heating of water supply due to external energy sources and there are several ways to organize this process.
Organization of water circulation
The simplest source of additional thermal energy is water, the temperature of which is higher than in the insulated section of the water supply system. If warmer water constantly replaces cooler water, the system does not freeze. For this reason, the “half-open tap” method works, when a slow but constant movement of liquid through the pipes is organized.
For cold water supply to individual housing, it is possible to periodically replace the water in the outer branch with a warmer one. In the case of supply from the main water supply, it is necessary to drain frequently in small portions to ensure replacement of the liquid.
For this purpose, it is rational to use a special container located in the house, which also performs the functions of a sump, from which to subsequently draw water for your needs.

If the supply is organized from wells in which the water temperature is usually from 7 to 10 degrees Celsius, then it is necessary to turn on the pump more often. You can also use a regular storage tank or hydraulic tank to store water.
You can use a second pipe and a three-way valve to organize the circulation of the liquid and drain it back into the well. At one time, it is enough to pump 1.5 - 2 volumes of a section of water supply located in the ground between the head of the well and the entrance to the house.
When drawing water from a well There is also an option to drain it back by gravity after stopping the pump. This method is not advisable to use in the case of metal elements of the water supply system. Constant change of liquid and air leads to intense corrosion of the inner surface of pipes and deterioration of water quality.
In autonomous water supply systems based on wells, it is required insulation of the water source as well as the thermal insulation of the pipeline itself. We recommend that you read the article on methods of thermal insulation of water wells.
If there is a possibility of long-term idle water and, as a result, its freezing, then despite insulation, it is necessary to use other heating methods.
Using the Electrical Cable
Most often, as an additional heat source for an individual water supply located in the ground, it is used electrical cables. They can be placed both inside the pipe supplying water and on its external surface. The principle of heating is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy.

Cables located inside the system have a higher efficiency than external ones due to direct heating of the liquid.
The disadvantages of this cable arrangement include:
- higher price per linear meter due to compliance with environmental requirements;
- the difficulty, and sometimes the impossibility, of passing through curved sections of the water supply system;
- specialists strongly recommend that the connection be made through an RCD, despite certificates of compliance with increased electrical protection requirements.
Installation of both options is approximately equal in complexity. The cable running inside the pipe is sold complete with a special termination coupling. Its connection is made through a standard tee. The outer cable is secured with aluminum tape, and an insulating shell must be placed on top so that the energy does not go into the ground.
Complete with a resistive cable that produces a constant amount of heat, to save energy it is better to use a thermostat to automatically turn the heating on and off. When using a self-regulating cable option, it is necessary to select its parameters correctly, then there is no need to use a temperature regulating device.
There are ready-made complex solutions that, in addition to a water pipe, insulation and a rigid waterproof shell, have an embedded heating cable.Such kits significantly reduce the installation time of the system, but purchasing all the elements separately will be much cheaper.

The heating cable can be used to heat both part of the system and the entire outer section of the pipeline, making it unnecessary to lay the pipeline below the seasonal freezing mark of the soil.
Application of warm air
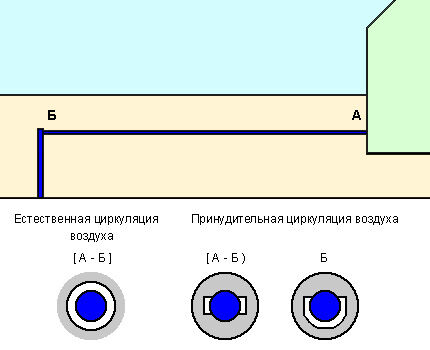
Another effective way to protect a water pipe laid in the ground from freezing is to heat it with warm air from the house. There are two options - with natural and forced air circulation, and both require the installation of an additional closed tray or pipe of a larger diameter.
In the case of natural air circulation, a pipe is placed on the water supply and insulated from the outside. It has access to a warm room and, therefore, there is a slow circulation of air enveloping the water supply system with the transfer of heat from the basement or first floor of the house.
In the second case, two channels (U-shaped profiles) are attached along the entire length of the water pipeline, through which air passes. They are wrapped with insulation and covered with an outer pipe to prevent the insulation and profiles from being compressed by the earth.
At the end of the heated section, these profiles are connected, thus obtaining a closed system with input and output indoors. The air supply is forced using a hair dryer.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. Laying a pipeline in the ground from the well to the house with its insulation and the nuance of freezing near the foundation:
Video #2. Insulation of a water supply system implemented on the basis of a plastic pipe and a method of insulating an elbow using a cylinder of a larger diameter:
Video #3. Detailed instructions for attaching an external heating cable, taking into account the correct bypass of fasteners and taps:
High-quality insulation or heating of the water supply system located underground will ensure its uninterrupted supply in winter. If the rules of installation and protection from cold are neglected, a complex defrosting procedure and expensive water supply repairs may follow.
Would you like to talk about your own experience in installing thermal insulation for water pipes in a suburban area? Would you like to share useful information with us and site visitors? Please write comments in the block below, ask questions, post photos on the topic.




This is currently a large selection of building materials. And before there was only glass wool. By the way, even in the Kolyma regions no one dug the pipeline to a depth of two meters. There they simply built either external or slightly recessed heating mains, which consisted of a concrete or wooden box with pipes wrapped in glass wool and roofing felt.
It’s strange, I didn’t even know that there were such cases of pipes freezing. I thought that if the pipes were underground, then they were completely safe from the cold.Although I have never had such a problem, if this happens, I will already know what and how to do. I’m not going to dig up pipes and insulate them now, we’ll see what happens in the winter, I hope it will blow through. And the information is quite interesting and useful, I’ll take it into account.
Our water supply lies at a depth of 2.7 meters. And now it comes into the house from underground (cold water only). And the supply hangs in the air underground, the first year it did not freeze, but in the remaining years you have to turn it on so that the water flows a little at a time, otherwise both the supply and the drain into the septic tank freeze. How to insulate this half meter from the ground into the house? and how to insulate a drain into a septic tank and it is at an angle of 15 degrees. And there are three meters in the drain pipe, and the slope is insignificant, because There was no other way.
I read about Energoflex insulation, everyone praises them. Advertising or something really worthwhile? Has anyone encountered them?
Hello. Does it make sense to look for real reviews if the official representative issued the following message on the Energoflex website:
«An important indicator for making the right decision is the depth of soil freezing in your area. It must be taken into account that this value is not a constant, that is, it can change from winter to winter in a fairly wide range. On average, the depth of soil freezing in the Moscow region ranges from 60 cm to 180 cm and depends on both the geographical location and the terrain. First, you need to understand that if you lay pipes at a depth above the freezing point of the soil, then there is a risk of utilities freezing and failing.To prevent this situation, we recommend using a self-regulating electric heating cable in combination with Energoflex thermal insulation«.
Tell me what insulation materials can be combined? for example, I would like to lay a 25mm heating cable along a HDPE pipe using the longitudinal method and insulate it with synthetically foamed rubber from the K-Flex company, and on top of it with another layer of cheaper stenoflex, but after reading your article, in particular the point about rodents and insects, I decided that it would be better for the outer layer use something made of polyurethane foam.
Tell me, is this design advisable, or can we not bother and just use one layer of polyurethane foam on top of the heating cable?
I'm going to dig no more than a meter deep, because... close Groundwater level. In winter, sprinkle the laying area generously with snow. I took a self-regulating heating cable, but I want to take a thermostat for it and connect a temperature sensor to the pipe in order to regulate the heating temperature of the heating cable depending on fluctuations in atmospheric temperature. In this way I want to achieve maximum energy savings.
I don’t see any problems with rodents if you use insulation with foil sheathing, for example. In this case, rodents will not be scary; you can use various materials:
— basalt fiber;
- Merilon;
— polyisol;
- Styrofoam;
- mineral wool;
— polyurethane foam;
- foam rubber.
It all depends on your budget. The cheapest option is polyisol. I would also recommend considering a material such as laminated “Teploizol”. Cheap, practical and rodents will not damage the insulation.