Heating cable for sewer pipes: types, how to choose and install correctly
Drilling the external sewer system deeper than the freezing level of the soil is a troublesome job, especially if the work is carried out in winter. An alternative option for frost protection is a heating cable for sewer pipes. It’s worth familiarizing yourself with the features of its installation, don’t you agree?
From the article we have proposed, you will learn everything about the installation of cable heating of a sewer pipeline. We will tell you how a heating cable works and how to choose the best option wisely. For independent owners, a step-by-step guide on installation and fastening is provided.
The content of the article:
Why do the sewers freeze?
The problem of sewer pipe freezing is not immediately detected. Unlike water supply communications, here the flow of liquid is not constant and does not completely fill the cross-section of the pipe.
In addition, sewage entering the sewer system usually has a higher temperature than, for example, water from a well. Therefore, freezing of wastewater occurs gradually.
At first, only a small part of the contents of the sewer may freeze, then another layer of frozen sewage appears, etc. Gradually, the entire lumen of the pipe is filled with a dense frozen mass, after which the problem becomes obvious. Faulty plumbing, such as a leaky faucet or tank, can make the problem worse.
Small portions of water enter the sewer, quickly cool down and freeze.Even the correct installation of sewer pipes and the presence of a layer of insulation do not always prevent freezing of drains. Defrosting a frozen sewer is troublesome; in addition, this phenomenon can lead to damage to the pipes, some of which will have to be replaced.

Therefore, it is recommended to lay sewerage below the ground freezing level with mandatory insulation of communications. If in the southern regions and the middle zone digging a sufficiently deep trench is usually not a problem, then in the north everything is a little more complicated. In this situation, the use of a special heating or hot cable is more than appropriate.
When using a system of this type, the volume of excavation work is noticeably reduced, since the depth of the trench can be reduced to an acceptable level without worrying about soil freezing.
How does a heating cable work?
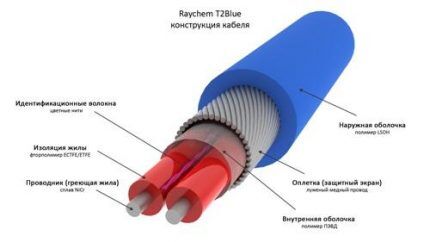
A heating or hot cable is a heating system for pipes laid deep into the soil. An electrical cable in an insulating sheath is fixed to the pipe and connected to the power supply. The pipe heats up, as a result the wastewater acquires a consistently high temperature, which reliably protects it from freezing.
There are cables for external or internal pipe heating. The first is laid on the outside of the structure, and the second on the inside. It is believed that external installation is easier to carry out than internal installation, which is why it is more in demand. In addition to the outer cable, a heating film is also used.

The structure is completely wrapped with this material and then secured. The film provides more uniform heating of the pipe than cable; it has less power, which allows for a slight reduction in operating costs.
Three types of cable can be used to heat pipes:
- self-regulating;
- resistive;
- zonal.
A self-regulating cable is considered an extremely convenient option, since it can automatically change the heating temperature depending on climatic conditions. Cable resistance decreases as the ground heats up and increases as the temperature decreases.

This change in operating mode reduces the overall power of the system, i.e. allows you to save energy. Moreover, the change in resistance may be different in individual sections of the pipeline. The result is a higher quality of heating, self-regulating cable will last longer, and there is no need to install thermostats.
A resistive cable does not have such abilities, but it has a more reasonable price compared to self-regulating systems. When installing this type of cable, you will need to install a set of temperature sensors and thermostats to ensure that the system's operating mode changes when the weather changes.
If this requirement is neglected, the risk of cable overheating and breakage increases. The zone cable also does not have the ability to regulate resistance, but this system does not generate heat along the entire length, but only in certain sections. Such a cable can be cut into separate fragments, which is convenient when installing pipelines of complex configurations.
It is also widely used when installing metal sewers or for heating containers. It is worth noting that heating structures buried in the ground is not the only area where heating cables can be used. It is also used to heat pipes laid on the surface or in rooms that are not heated.
Sometimes the cable is used only for certain sections of the pipeline, for example, parts that go to the surface. Systems that are mounted inside a pipe are used relatively rarely. Most often they are used if the pipeline is already laid in the ground, and installation of an external cable would require extensive excavation work.
This way, installing an internal cable will cost much less. But such cables are usually recommended for use only inside small-diameter pipes, since their power is low.
It varies between 9-13 W/m, which is usually not enough for large sewer pipes. The length of such a cable, for obvious reasons, should be equal to the length of the pipe. The internal heating cable is made only of the self-regulating type.
How to choose the right cable?
When choosing a suitable hot cable, you need to decide not only its type, but also the correct power.
In this case, it is necessary to take into account such parameters as:
- purpose of the structure (calculations are performed differently for sewerage and water supply systems);
- the material from which the sewerage system is made;
- pipeline diameter;
- features of the area that is supposed to be heated;
- characteristics of the thermal insulation material used.
Based on this information, the heat loss per meter of the structure is calculated, the type of cable and its power are selected, and then the appropriate length of the set is determined. Calculations can be performed using a special formula, using calculation tables or using an online calculator.
The calculation formula looks like this:
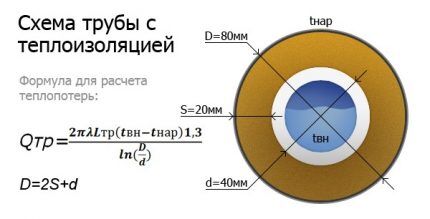
Once the heat loss has been calculated, the length of the system should be calculated. To do this, the obtained value must be divided by the specific power of the heating device cable. The result should be increased, taking into account the heating of additional elements. The power of the sewer cable starts at 17 W/m and can exceed 30 W/m.
When it comes to sewerage pipelines made of polyethylene and PVC, then 17 W/m is the maximum power. If you use a more efficient cable, there is a high probability of overheating and damage to the pipe.Information about the characteristics of the product can be found in its technical data sheet.
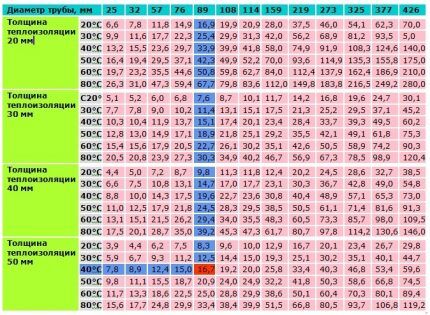
Using the table, choosing the appropriate option is a little easier. To do this, you first need to find out the diameter of the pipe and the thickness of the thermal insulation, as well as the expected difference between the temperature of the air and the contents of the pipeline. The latter indicator can be found using reference data depending on the region.
At the intersection of the corresponding row and column, you can find the value of heat loss per meter of pipe. Then you should calculate the total cable length. To do this, the size of the specific heat loss obtained from the table must be multiplied by the length of the pipeline and by a factor of 1.3.
The result obtained should be divided by the power density of the cable. Then you need to take into account the influence of additional elements, if any. You can find convenient online calculators on specialized websites. In the appropriate fields you need to enter the necessary data, for example, pipe diameter, insulation thickness, ambient and working fluid temperatures, region, etc.
Such programs usually offer the user additional options, for example, they help calculate the required diameter of the sewer, the size of the thermal insulation layer, the type of insulation, etc.
Optionally, you can select the type of installation, find out the appropriate step when installing the heating cable in a spiral, and get a list and number of components that will be needed to install the system.
When choosing a self-regulating cable, it is important to correctly take into account the diameter of the structure on which it will be installed.For example, for pipes with a diameter of 110 mm, it is recommended to use the brand Lavita GWS30-2 or a similar version from another manufacturer. For a 50 mm pipe, a Lavita GWS24-2 cable is suitable, for structures with a diameter of 32 mm - Lavita GWS16-2, etc.
Complex calculations will not be needed for sewerage that is not used often, for example, in a summer cottage or in a house that is used only occasionally. In such a situation, simply take a cable with a power of 17 W/m with a length corresponding to the size of the pipe. A cable of this power can be used both outside and inside the pipe, and it is not necessary to install a gland.

For laying the heating cable inside the pipe choose a cable with special protection against aggressive influences, for example, DVU-13. In some cases, the Lavita RGS 30-2CR brand is used for internal installation. This is not entirely correct, but an acceptable solution.
This cable is intended for heating the roof or storm drains, so it is not protected from corrosive substances. It can only be considered as a temporary option, since if used for a long time in unsuitable conditions, the Lavita RGS 30-2CR cable will inevitably break.
Rules for installing cables on pipes
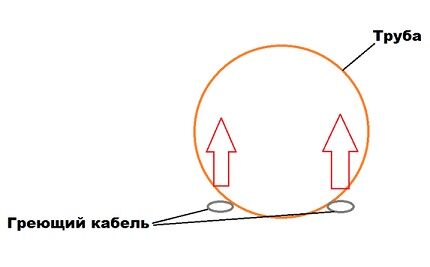
Laying a heating cable is a relatively simple process. It is simply fixed to the surface of the pipe, usually lengthwise, in one strip. Some projects include spiral installation. In this case, the calculated pitch between the turns of the spiral must be precisely maintained so that the pipe is heated evenly.

Crossing individual sections of the heating cable is unacceptable. Depending on the type, the cable is secured using heat-resistant adhesive tape or mounting ties. The pitch between the fastening points must be at least 200 mm. To secure the cable in the mineral sheath, metal fasteners are used: tie strips or a special bandage.
But most often I still use heat-resistant tape. Fasteners must not only withstand high temperatures, but also be resistant to the influence of natural factors and chemicals. Sometimes aluminum tape is used as fastening. But at the attachment points, the thermal power of the cable will increase.
This is not always useful and can lead to overheating of communications. It is not recommended to use metal fasteners when installing a heating cable enclosed in a polymer insulating sheath. But in some cases, aluminum tape can even improve the situation.

When laying on a polymer pipe, metallized tape is placed both under the cable and above it. This slightly increases the thermal output and also helps to heat the pipeline evenly. Heating cables are rarely used inside sewers.
Typically, small areas of the system that are not located in the ground are heated this way, for example, sewage pumps, stimulating the movement of wastewater if natural movement is difficult or impossible.

To install the internal cable into a pipe whose installation has been completed, you will first need to cut a tee into the system. This will make a hole for inserting the cable into the pipeline.
In addition, a special nipple coupling may be required. Such a solution may slightly worsen the characteristics of the sewer system, for example, at the location where the tee is installed, the pipe clearance will slightly decrease.
This increases the likelihood of debris accumulating and causing clogs. Difficulties with the internal cable are inevitable if the pipeline has several turns, bends, etc. It is not easy to carry out internal work on hot cable installation, as well as sewer systems of considerable length.
Of course, you should not connect the system to the power supply until the installation work is complete. Before covering the cable with insulation, you should carefully check all connection points. If you use thermal sensors, it will be easier to determine the time of activation and shutdown of the system.
You can automate the process using a relay. If the power of the cable laid in one line is not enough, you can install it in a spiral or lay two parallel lines. The main thing is that individual sections do not overlap and there is no overheating. To make the heating of the structure more uniform, sometimes the pipe is first wrapped with foil, and then a cable is placed on top.

Temperature sensors are installed after the insulation is installed.It is recommended to apply markings on top that reflect the position of the heating elements. For connecting the heating cable You will need a piece of heat-shrinkable pipe to connect to the electrical network. Then about 50 mm of insulation and 10 mm of braid are removed from the edge of the cable.
The separated and stripped ends are protected with pieces of heat-shrinkable tubing of suitable diameter and heated with a hairdryer. Now you need to strip about 6 mm of wire, roll it into a spiral and clamp it in a metal tube. Similar manipulations will have to be done with the power cable.
About 80 mm needs to be cleared of insulation and sheathing and divided into separate wires. The resulting ends are cut to 35 mm, but one wire should be left uncut for grounding. 6 mm wires are also stripped here.
Now the ends of the heating element and power cables are connected in a heat-shrinkable tube equipped with a metal sleeve. It is heated and clamped, the contact point is wrapped with thermal tape, and then covered with another protection tube.
He will introduce you to the specifics of choosing pipes directly for installing an autonomous sewer system. next article, the contents of which we advise you to familiarize yourself with.
An example of a heated sewer system
Let's consider an example of constructing a sewerage system for a private household. According to the project, several branches are connected to the common sewer main. All of them are laid above the horizon of seasonal soil freezing, therefore they are supplied with a heating cable.
In order for the operation of the heating electrical system to be effective and aimed directly at maintaining the positive temperature of the sewer pipe, communications are laid in an insulated trench:
Having made sure that the assembled sewer pipeline is tight or has eliminated the leakage, if any, proceed to laying the heating cable.
Having decided on the optimal position of the heating cable, proceed to its fastening:
In order for the system for heating communications to function automatically, a temperature sensor is connected to it:
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Detailed recommendations for installing a hot cable on a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm can be found here:
This video presents an option for laying a sewer system using an internal cable:
Here is an overview of the functioning and installation features of a self-regulating cable:
Hot cable solves the problem of freezing sewer pipes in winter much more effectively than other means. Electricity consumption is minimal. If the installation is done correctly, the cable will work for many years without any breakdowns.
Would you like to share your experience gained while installing a heating cable on your own sewer pipes in a suburban area? Is there information that may be useful to site visitors interested in the issue? Please write comments in the block below, ask questions and leave photos on the topic.




Educational, interesting material with information worth reading. Our neighbors also often had their pipes freeze in winter, and they were left without water until the weather began to warm up.They didn’t know that it was possible to install a heating cable parallel to the pipeline. This is a wonderful invention. We'll definitely order and buy it. A necessary thing in the management of private houses.
In my opinion, it is best to choose a heating cable for external winding and with a self-regulating heating function. The outer winding is not only easier to install and maintain, but also minimizes the likelihood of a short circuit in the event of damage to the cable insulation and its contact with wastewater. I think there is no need to write down the advantages of self-regulation of heating - they are already clear.