Copper pipes for heating: types, specific markings + application features
Copper pipes are not used very often in the assembly of heating circuits.Their cost is not very attractive to owners of private houses and apartment owners. However, if the installation is done correctly, the high cost of the copper pipeline will be recouped over many years of operation without repair costs.
We will tell you how to choose the right copper pipes for heating. The article we presented shows the features of marking and describes how to connect components. Independent owners will find instructions for assembling heating systems here.
The content of the article:
Types of Copper Pipe
There are two large groups of copper pipes: thick-walled and thin-walled. Pipes included in the first group have increased strength characteristics. They are produced using seamless and welded methods.
Pipes of the second group have found application in shipbuilding, automotive industry, aviation, i.e. where communication systems must be lightweight and highly durable. The cross-section of copper pipes can be either round, rectangular or square. As a rule, profile pipes are not used in heating systems.
Thick-walled pipes have a round cross-section, the wall thickness varies in the range of 0.8 - 10 mm. Different grades of copper are used in their production: M1, MP3, MP1 and others. The digital index here indicates the degree of purity of the alloy. This does not affect the characteristics of the pipe itself in any way. Thin-walled pipes have a wall thickness of 0.15 to 0.7 mm.
The state standard allows the measurement of copper pipes in both the metric system and inches.The designation of the former indicates the outer diameter, and the latter - the inner diameter. Marking of pipes used in the installation of heating systems is carried out in inches.
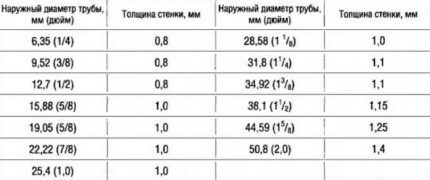
To make internal heat exchangers, copper pipes with a diameter of up to 10 mm are used. This diameter, combined with highly efficient energy transfer, guarantees maximum performance from this device.
Pipes of 3/8 inch or larger are used in the heating systems themselves. They provide efficient heating with low energy consumption.
Specifics of decoding markings
The regulatory document defining the standards for copper pipes used for heating is GOST 617-2006. It specifies the requirements for the grade of copper, range of sections, and wall thickness.
Copper products have their own markings, deciphering which you can find out the characteristics of the pipe:
- Preparation method. It is designated by the letters D and G. The first indicates that the pipe is cold-deformed drawn. They are made in lengths from 1.5 to 6 m. Second, the product is made by pressing. According to regulatory requirements, they are manufactured in lengths from 1 to 6 m.
- Geometry of the pipe section. KR - section in the form of a circle.
- Precision manufacturing. Letters N and P. N - normal, P - increased.
- State. M, P, T, L, R, Ch. These indices indicate soft, semi-hard, hard, soft with increased ductility, semi-hard with increased strength, hard with increased strength, respectively.
- Length. ND - the index indicates that the pipe is unmeasured, MD - means a measured pipe, KD - multiple measured, BT - in coils.
- Special conditions. Y - the length of the pipe in coils is increased, B - the pipe has increased accuracy in terms of length, K - the pipe has increased accuracy in curvature.
For clarity, an example: let’s say there is a marking on the pipe in the form of DKRNM 32 x 3 x 3000 M2 B.
It can be deciphered as follows: a cold-deformed pipe with a round cross-section of normal accuracy, made of soft copper, having an external cross-section of 32 mm and a wall thickness of 3 mm. It is a measured piece 3000 mm long, made from M2 grade copper.

During the production process, copper pipes can be subjected to heat treatment and are then called annealed. When this step is excluded from the process, the output is unannealed pipes.
All three types of copper pipes are suitable for furnishing private homes, since the pressure in the heating circuits in them never exceeds the values specified even for soft varieties.
The marking looks like this:
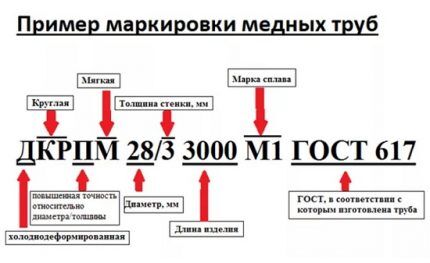
In the first case, the products acquire plasticity, but lose resistance to deformation. Pipes made without annealing have increased strength characteristics, but it is almost impossible to bend them.
Advantages of copper pipelines
All the advantages of copper pipes stem from the unique properties of this material, products from which:
- They are harmless and have bactericidal properties.
- They do not age for a long time and do not lose their performance characteristics.
- Resistant to corrosion and ultraviolet radiation. They operate in a wide temperature range - from -200 to +350⁰С.
- Immune to the effects of chlorine in tap water.
- They have high thermal conductivity, which increases the efficiency of the heating system.
- Plaque does not form on the surface of copper pipes with a low roughness coefficient.
- Freeze resistant. The pipeline does not collapse and does not lose its original characteristics, subjected to freezing up to four times.
- Capable of maintaining strength properties under pressure reaching 200 – 400 atmospheres.
- Vibration resistant.
- They have a wide range of products.
- 100% recyclable.
Many people are often stopped from choosing copper pipes for heating by both the high price of the pipeline itself and the consumables.

Copper pipes are lightweight and can be cut, bent and soldered. The most popular connection method copper pipeline - soldering at high temperatures using silver-bronze solder. Faster installation is carried out using fittings.
Features of choice for heating
Copper has its own individual characteristics, which impose both operational and technical restrictions on their use. These points must be taken into account when heating system installation.
Although copper pipes are known for their strength, they can easily withstand pressure surges, temperature changes, and repeated freezing; they do not withstand mechanical stress well. Therefore, when laying a pipeline, protection against impacts should be provided.
A coolant such as water contains sand and other suspended particles. The result of their impact on soft copper is erosion. To avoid this phenomenon, it is necessary to include water purification filters in the system.
The service life of pipes is also affected by water hardness. The value of this indicator in milligrams below 1.42 and above 3.1 significantly reduces their longevity. This is explained by the fact that chlorine dissolved in water reacts with the oxide film present on the walls of the pipe. The result is durable protective armor.
If the water hardness does not meet the standards, this protective layer begins to deteriorate, then due to the presence of chlorine it is regenerated. If this process is repeated many times, copper resources become depleted.
Connecting pipeline soldering method, overheating, which negatively affects strength, should be avoided. The flux that remains after soldering must be removed, as it can cause corrosion.
If you need to bend a copper pipe, you need to use a special tool for this. An unsuccessfully bent pipe can be corrected once, and then all that remains is to remove the crumpled section.
The ideal option is to install a heating system from the same pipes. If for some reason this does not work out, you need to use transition fittings - brass or bronze. Adapters made from other materials may not provide electrochemical compatibility.

To prevent pipes made from other materials from corroding under the influence of copper, a certain sequence of connecting such a combined pipeline relative to the vector of movement of the water flow is needed. Copper pipes must be installed after elements made of other metals.
If planned heating system device When laying pipes inside the wall, you need to use copper pipes in a plastic sheath. It will not only serve as thermal insulation, but will also protect the metal from destruction. Copper pipes and stray currents have a detrimental effect.
Joining copper pipes
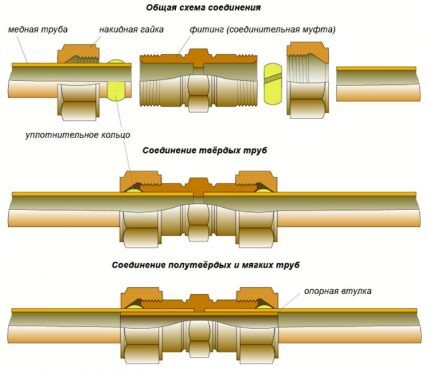
Copper pipes are connected using different methods. The most popular 2 approaches to this issue are soldering and assembly using compression or press fittings. Mainly permanent and conditionally detachable connections are made.
In such a pipeline there are practically no additional parts, except for the elements with which devices are connected to the pipeline. To install the system using this method, special tools are required. Without the appropriate qualifications, it is difficult to make a connection by welding or soldering.
The use of fittings facilitates installation, requires less effort and reduces pipeline assembly time. This type of connection can be detachable or permanent.
The detachable connection is made using self-locking, threaded and compression fittings. This method complicates the design; connections must be checked periodically, but even a person without experience can perform the installation.
Permanent crimp connections
In order to join copper pipes Manufacturers produce special fittings that differ in purpose, installation methods, and the material from which they are made.
Based on their purpose, the following fittings exist:
- Bends that are needed for joining pipes of different sections for corner connections.
- Crosses, which are also called tees and are used when installing branches from the main pipeline.
- Couplings used on straight routes to connect copper pipes of different diameters.
- Push-in fittings, which are used when installing automation in a heating system.
For copper pipes, compression fittings made of copper, brass, and bronze are most often chosen. Sometimes brass fittings are treated with nickel to give them extra strength.
Brass elements for connecting copper pipes are cheaper than copper ones, and are not inferior in strength to stainless steel. All fittings, regardless of manufacturer, have dimensions regulated by international standards and are interchangeable.
Permanent is a connection using the pressing method. Since copper is very ductile, installation is carried out using press fittings and crimp sleeves. In terms of tightness and strength, such a connection can be compared to soldering, and it is stronger than a compression one.
Visually, press fittings are similar to connectors for capillary soldering. The difference is the presence of an O-ring made of high-quality polymer.

When installing a heating system using copper pipes of small and medium diameters, low-temperature soldering is mainly used. Welding is used when large cross-section pipes are used. The pressing method is in demand when installing heated floors.
Compression connectors
To install compression fittings, there is no need for special equipment or the use of open flame. All you need are wrenches, a calibrator mandrel, and a cutter. To make such connections, push-in or compression fittings are required.
There are 2 types of compression fittings - some, with index A, connect hard and semi-hard pipes, others, designated with index B, connect soft and semi-hard pipes. The fitting includes a body, a crimp nut, and a copper crimp ring, which is flattened when pressure is applied to it.
This makes the connection sealed and resistant to vibration fatigue. The connection is made according to the same scheme as when installing press fittings.
The joining ends of the copper pipe segments are cleaned, the section geometry is checked using a gauge, a crimp ring is put on, and the ends of the pipe are inserted into the fitting until it stops. The nut is first tightened by hand, and when the pipe becomes motionless in relation to the connector, they take the tool and tighten it.
For strength copper pipe connections With the help of fittings, temperature instability and pressure surges have a weakening effect.After a certain time, the seals wear out. To monitor this weak link in the system, connectors must be located so that they are easily accessible.
Copper pipes cannot be threaded. To connect them with threaded parts, special adapters are produced. Their design provides for the presence of a socket that connects the fitting to the pipe by crimping or soldering and threading on the opposite side.
Emergency situations in a heating system assembled from copper pipes are extremely rare, but if this happens, pipes of equal diameter are temporarily connected with turnbuckles. You should know that all types of connections do not reduce the strength characteristics of the heating system.
Fittings increase the thickness of the pipe walls, and at the welding site, over time, the connection becomes stronger, exceeding the strength of the pipeline itself.
Copper Soldering Fittings
Such fittings are called capillary. The connection with their help requires the presence of solder.The key is to get it right choosing a fitting for a copper pipe. Its internal cross-section should be 0.1 - 0.15 mm larger than the outer diameter of the pipe.
The technology is simple:
- cut off the required pipe size;
- protect;
- remove the chamfer from the outside and inside using a chamfer remover;
- clean the pipe, as well as the inside of the fitting, again until a matte shine appears;
- coat the end of the pipe. Designed to be placed into the fitting and the fitting itself from the inside with a special paste;
- insert the pipe into the connecting element and turn it;
- wipe off the protruding paste, otherwise it will interact with the metal;
- heat the connection using a gas burner or a hair dryer;
- bring solder to the gap after the flux begins to melt and lighten;
- The process is completed when the solder flows over the entire surface and fills the gap evenly.
In order not to waste excess solder, you can wrap it around the pipe before soldering and cut off the excess. Upon completion soldering copper pipes the compound is allowed to cool at room temperature.
After installing the entire heating system, flush it using hot water. This procedure will help flush out any remaining paste from the pipes. The connecting points are inspected from the outside of the pipeline. If flux or solder remains somewhere, remove it with a damp cloth.
Will familiarize you with the guidelines for choosing copper pipes for the construction of a water supply system next article, dedicated to their technical characteristics and marking specifics.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. About the pros and cons of copper pipes:
Video #2. Training in working with copper pipes:
If we compare copper pipes with polymer and steel pipes, the former are distinguished by higher quality and reliability. Despite the high cost, they find their consumers and their popularity is growing.
The main thing is to choose the right consumables, and if you do the installation yourself, a heating system made of copper pipes will cost much less.
Would you like to tell us about how you bought copper pipes for the construction of a heating circuit? Do you know the technological nuances of assembling copper pipelines that are not covered in the article? Please write comments in the block below, post photos related to the topic of the article, and ask questions.



