Plastic ventilation pipes for exhaust hoods: nuances of selection and installation
Laying communications in a house or apartment is not as simple as it seems at first glance.In order for the equipment to work normally, and also to avoid claims from inspection authorities, it is necessary to carry out installation taking into account all norms and rules, not forgetting the aesthetic component.
We will tell you how to correctly select the best exhaust pipes, focusing on their technical and practical qualities. Here you will learn how to choose the optimal section and calculate its size. Together we will look at the set of components from which ventilation ducts are assembled.
We offer independent craftsmen two options for installing plastic air ducts. The information presented for consideration is supplemented with diagrams, photo collections, and video tutorials.
The content of the article:
Use of ventilation pipes in everyday life
Ventilation pipes with a set of connecting and fastening elements are usually called air ducts. They are designed to ensure air circulation and are installed in those rooms where there is no access to natural air movement or there is an additional need for ventilation: in kitchens, bathrooms, toilets.
Before the appearance of plastic parts on the market, air ducts were made of galvanized metal; they are still often found in production shops or in catering establishments (their use is associated with high temperatures).
But for everyday use, that is, for installing ventilation in apartments and cottages, they are more suitable polymer products.
They have the following advantages:
- have less weight than metal ones, so they are easier to install with your own hands;
- smooth walls have minimal resistance to air movement;
- airtight, as they have no seams;
- resistant to high humidity, do not rust;
- On sale you can always find a set of fittings that fit the cross-section.
Products that meet GOST standards and have certificates of conformity are allowed for sale, so we can talk about the safety of plastic elements.

Main characteristics of plastic parts
You need to know the properties of pipes in order to correctly design and install a ventilation system in an apartment or house. The characteristics of the elements may vary depending on the installation location (above a plasterboard ceiling, in a closet, in the attic) and on the geometry of the room.
Let's consider what features become decisive when choosing.
Air duct material
On sale you can find products for creating ventilation structures made from four types of materials, which in everyday life are commonly called plastic:
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polypropylene;
- polyurethane;
- polyethylene.
Polyvinyl chloride. Lightweight, inexpensive, easy to install, PVC air ducts are the most common material for the construction of household ventilation structures. They are durable, airtight, but have some limitations.
They cannot be heated to 160°C, since chlorine, which is harmful to all living things, begins to be released, and according to standards, the upper heating limit without a risk to human health is +120°C.
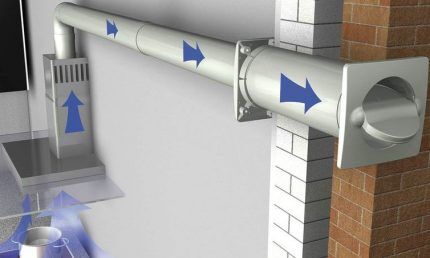
When the temperature drops below +5°C, PVC becomes brittle, so for installing a ventilation system in premises with temporary residence it is better to choose another type of pipe, for example, made of polyethylene or vinylurethane.
Polypropylene – an excellent dielectric, non-hygroscopic, and has high resistance to aggressive chemical environments. The tensile strength is approximately 4 times higher than that of products made from high-density polyethylene.
The main disadvantage is flammability, the maximum possible temperature is +85ºС. However, there is a fire-resistant variety with fire retardant additives - PPS.
Polyurethane its characteristics resemble PVC, but can withstand higher temperatures - up to +280ºС.

HDPE - low-pressure polyethylene. It does not crack over time and, unlike PVC, withstands negative temperatures more easily (relevant for houses with temporary residence). Possible heat resistance – up to +80ºС, cooling – up to -50ºС. Easy to process, like all types of plastic products.
Polypropylene and polyethylene pipes for household ventilation are rarely used; PVC products are in the lead.
Types of pipes by degree of flexibility
There are two categories of plastic ventilation pipes for hoods - rigid and flexible. Sometimes a combined option is necessary, but much less often. If the hood is installed next to the ventilation hole, there is no need for a complex design.
When purchasing rigid pipes of round or rectangular cross-section, you must also purchase a set of additional parts to design turns or transitions.

Along with rigid straight pipes, corrugated pipes are used - flexible polyurethane products or aluminum, allowing you to do without corner parts.

Corrugated products are more economical, but lose in design.To preserve the beautiful appearance of the interior, it is better to disguise them under hanging structures or place them in a “blind” zone - on cabinets against the wall.
Varieties of elements according to sectional shape
Depending on the pipe configuration, the following types of air ducts are distinguished:
- round;
- rectangular;
- flat.
The cross-sectional shape largely affects the technical characteristics and method of installation. For example, straight round pipes have better throughput and excellent noise insulation, since air, moving along smooth walls, encounters virtually no obstacles (with the exception of corner sectors).
However, due to the cylindrical shape, installation problems may arise.
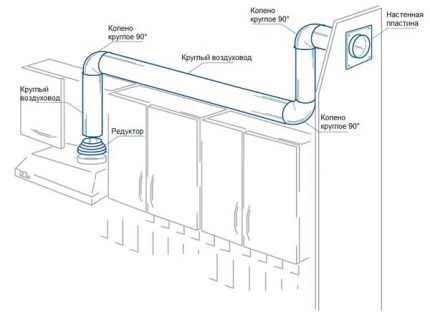
Rectangular ducts They fit tightly to any flat surfaces (walls, ceilings, kitchen cabinet walls), so installing them is much easier. But there is one drawback - the uneven distribution of air, which causes loud noise.
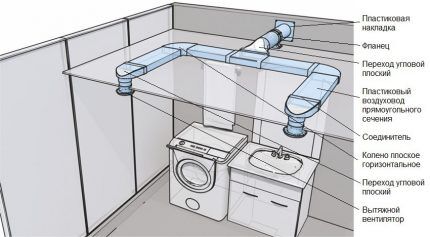
Flat ducts - these are the same rectangular ones, but with a big difference in the dimensions of the width and height of the section (for example, flat channels 110 mm x 55 mm). Due to their compactness, they are often used for installation when there is a shortage of free space (for example, above suspended structures or above high-hanging cabinets).
How to choose the section size?
The size of the section is more important than its shape, since the efficiency of air exchange in the room depends on this parameter. There are standards that take into account the specifics of various rooms, and when choosing ventilation elements it is better to focus on them.
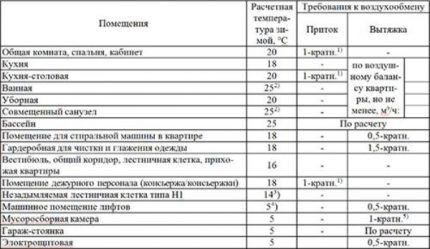
According to SNiP, the volume of air flow in houses and apartments must be at least 3 m3/hour per 1 m2 living space, while the number of people living is not taken into account.
The volume of circulating air for people constantly in the room is 60 m3/ h, temporarily located – 20 m3/h (meaning places of work, for example, offices).
It is not possible to make an accurate calculation of the cross section on your own, but there is simplified calculation methods. However, perfectionists are better off using the services of an engineer or a special program that will require the following data:
- shape of air ducts;
- pipe material;
- internal resistance;
- indoor temperature.
There is a way to determine the size of the ventilation hole based on the area of the room. For every square meter of room there is 5.4 cm² of air duct cross-section, and the pollution coefficient is important.
To accurately select the pipe cross-section, we recommend contacting professionals who perform calculations using complex formulas based on specific data.
What does exhaust ventilation consist of?
To install air ducts, pipes alone are not enough; shaped elements are needed - fittings for various purposes.They serve to hermetically connect parts into a single system, provide smooth transitions of pipes of different diameters, connect the air duct with the hood and ventilation hole, and allow you to create 90º angles.

One of the important elements is the transition (adapter). It is necessary in two cases: when you need to connect pipes of different cross sections or air ducts that differ in size.
They are used for assembling structures in rooms with complex geometries, and sometimes for parts built into cabinets.
To prevent the reverse draft effect from occurring and the used air not returning to the room, the air ducts are equipped with a check valve.
This is a built-in frame with a dynamic blade that opens only in one direction - along the direction of air movement into the ventilation shaft. The valve does not act as a connecting element, but as a part that increases the efficiency of ventilation.

To ensure 100% sealing, it is necessary to select fittings strictly according to the size of the pipes: for example, for ducts 150*100 mm, elbows of the specified size are also required.
Installation options for plastic pipes
Let's consider two options for installing plastic pipes for exhaust ventilation. They differ both in the installation location and in the choice of elements.
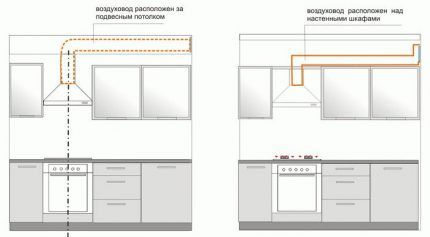
Option 1. Indoor air duct installation
More often plastic pipes for arranging ventilation, they are used in the kitchen to connect the hood and the ventilation hole located on the wall under the ceiling. To make work easier, the hob should be positioned as close as possible to the outlet.
If it is installed on the opposite side, it is better to move it closer than to pull the duct through the entire kitchen.
The shorter the overall length of the pipes, the better. It is estimated that each 90º turn of the pipe reduces efficiency by 10%, and systems longer than 3 meters lose the same amount for every extra meter.
To avoid any questions along the way, we make preliminary calculations and draw up a drawing indicating the dimensions and additional details of the air duct.

To work you will need:
- flat duct for exhaust ventilation 204*60 (1.5-2 m);
- horizontal elbow 204*60
- connecting elbow;
- wall plate;
- round gearbox with adapter;
- plastic hacksaw;
- sandpaper;
- sealant;
- marking tool.
We prepare the pipes - we cut blanks from plastic boxes to the required length and clean the edges. If the air duct is mounted in free space, you can pre-assemble it on the floor, securing the connecting elements with sealant.
If part of the structure will be located in a cabinet, first secure it (gearbox + vertical pipe), then connect it to the horizontal pipe with an angular bend.
At the end, we connect the pipe to the hole formed by the plate with a special fitting. For strength, we coat the joints with sealant; heating should not be used.
If fastenings to the wall or ceiling are required, self-tapping screws should not be used. For this purpose, clamps are specially provided that tightly enclose the pipe. They are equipped with a rubber seal and are secured using brackets or studs. Some clamps are fixed with a simple snap, which simplifies the installation process.
Having chosen a suspended ceiling as a camouflage structure, try to carry out the work efficiently. Before starting construction, carefully check the tightness of the air duct - to repair or replace it, you will have to disassemble the ceiling structure made of plastic panels or plasterboard.
Not only plastic products are used in the construction of ventilation ducts. You will learn about the choice of material for installing air ducts from popular article our site.
Option #2. Thermal insulation of pipes in the attic
In a city apartment, installing exhaust ventilation comes down to: installation of plastic air ducts, leading to the hole in the common house shaft. In a private house, it does not end there, since there is another segment - from the heated room through the attic to the street.
To prevent condensation from forming on plastic pipes from the cold (the attic is often not heated), produce insulation.
The best materials for thermal insulation are:
- basalt wool (glass wool, mineral wool);
- shell made of polymer materials - polystyrene or foam;
- foamed polyethylene.
An example of basalt wool is rolled Rockwool mineral wool, non-flammable and tensile strength, with a minimum air permeability of 0.3 mg/m×h×Pa, a wide range of heat resistance (from – 180 ºС to + 500 ºС), hygroscopicity of about 1.5% by volume . Service life – up to 35 years.

Soft rolls are wrapped around the pipes with an overlap, covered on top with foil or roofing felt (if mats without waterproofing are used), secured by winding with metallized tape or steel wire.
Polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene have the form of rigid tubes consisting of several segments. Some of them are covered with a layer of foil. Polystyrene foam has a looser structure, so it is suitable for insulating curved fragments. Due to its low price, it is preferred by budget-conscious owners.
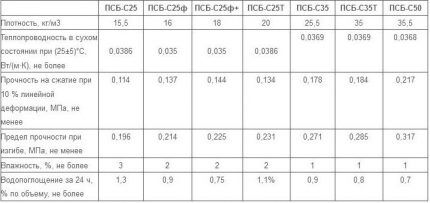
The leading position is occupied by foamed polyethylene Penofol, which is more elastic than the listed materials. The insulation has a minimal thickness, but at the same time it does not allow moisture to pass through (it is covered with waterproofing foil on one or both sides), provides a low noise level and retains heat perfectly.

The thickness of the insulation varies - from 3 mm to 10 mm, the thermal conductivity coefficient is within 0.038-0.051 W/(m*K), water absorption - up to 0.35%. For installation, it is enough to cut the material into pieces of the required size, remove the protective film and stick it on the pipe fragment.
For straight pipes that are large in length, you can use a roll of the entire width, without cutting.
Particular attention should be paid to the joints, the area where the air duct exits to the roof, and places of contact with external walls.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Informative videos will help you understand the types of plastic pipes and learn more about how to install them.
Video #1. Installation of a plastic box:
Video #2. Installation procedure in a plasterboard box:
Video #3. Thermal insulation of ventilation pipes in the garage:
As you can see, installation of plastic air ducts is not difficult and is suitable for independent work. However, when drawing up a project, we recommend turning to professionals who know the nuances of installing supply and exhaust ventilation and can accurately calculate the dimensions of the elements used.
If you have any questions while reading the information we provide, please write comments in the block below. Here you can talk about your own experience in installing air ducts and share useful information.




I have a corrugated vinyl urethane pipe. An extremely convenient thing, it can be both stretched and compressed, as well as bent at the desired angle. Suitable for any occasion: if the hood is low above the equipment, or high, almost under the ceiling. This pipe is already ten years old, everything is in perfect order with it. And there were no problems with the installation either, I installed it myself. I recommend to all.
I have an acquaintance who vehemently opposes corrugated pipes. He had installation experience (unsuccessful), with incorrect calculations, so he complains not about his amateurism in installation, but about the material.Personally, I don’t see much of a difference between PVC pipes and corrugated pipes, the whole problem is in the correct installation, and so that it fits into the interior. Corrugation, by the way, is cheaper, and it’s also easier to install.
Smooth-walled air ducts, Kirill, have the least aerodynamic resistance and the least noise generation. Of course, the length of apartment and part of cottage air ducts is not sufficient for a noticeable manifestation of this characteristic. Several studies have been devoted to the aerodynamics of air ducts. Attached is a screenshot with the interim conclusions of one of the studies.
I want to make my own ventilation at home, the developer offers a “beautiful turnkey solution” with corrugations, but 3 things scare me: 1) Cleaning the corrugations after a year? Fine dust will inevitably collect there, so how do you clean them? 2) Condensation when using cooled air (especially if the house is frame) 3) The cross-section of the pipes is small, I don’t understand how they can pass the required amount of air.