Pressure in the heating system: what should it be and how to increase it if it drops
Following a failure of pressure in the heating system, a problem comes - the quality of heating the premises in the house decreases.You can, of course, adjust the heating operation once and for a long time, but this period will not be indefinitely long. One day, the normal pressure in the heating system will change, and significantly.
We will tell you how to keep the physical parameters of the coolant under control. Here you will learn how to ensure a stable speed of movement of heated water through the pipeline to the devices. You will understand how to obtain and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
The article proposed for consideration describes in detail the reasons for the pressure drop in closed and open systems. Effective balancing methods are given. The information presented for review is supplemented with diagrams, step-by-step instructions, photos and video tutorials.
The content of the article:
Types of pressure in heating systems
Depending on the current principle of coolant movement in the heat pipeline of the circuit, in heating systems the main role is played by static or dynamic pressure.
Static pressure, also called gravitational pressure, develops due to the gravitational force of our planet. The higher the water rises along the contour, the more its weight presses on the walls of the pipes.
When the coolant rises to a height of 10 meters, the static pressure will be 1 bar (0.981 atmosphere).An open heating system is designed for static pressure; its maximum value is about 1.52 bar (1.5 atmospheres).
Dynamic pressure in the heating circuit develops artificially - using an electric pump. As a rule, closed heating systems are designed for dynamic pressure, the contour of which is formed by pipes of significantly smaller diameter than in open heating systems.
The normal value of dynamic pressure in a closed heating system is 2.4 bar or 2.36 atmospheres.
Consequences of instability in circuits
Insufficient or higher pressure in the heating circuit is equally bad. In the first case, some of the radiators will not effectively heat the rooms; in the second, the integrity of the heating system will be compromised and its individual elements will fail.

An increase in dynamic pressure in the heating pipeline occurs if:
- the coolant is too overheated;
- the pipe cross-section is insufficient;
- the boiler and pipeline are overgrown with scale;
- air pockets in the system;
- a booster pump that is too powerful is installed;
- water replenishment occurs.
Also, increased blood pressure closed circuit caused by incorrect balancing of the taps (the system is over-regulated) or malfunction of individual regulator valves.
To monitor operating parameters in closed heating circuits and for their automatic adjustment, a safety group is installed:
The pressure in the heating pipeline drops for the following reasons:
- coolant leak;
- pump malfunction;
- rupture of the expansion chamber membrane, cracks in the walls of a conventional expansion tank;
- security unit malfunction;
- water leakage from the heating system into the feed circuit.
The dynamic pressure will be increased if the cavities of the pipes and radiators are clogged, if the catch filters are dirty. In such situations, the pump works under increased load, and the efficiency of the heating circuit decreases. The standard result of exceeding pressure values is leaks in connections and even pipe ruptures.
The pressure parameters will be lower than required for normal functionality if a pump of insufficient power is installed in the main line. It will not be able to move the coolant at the required speed, which means that a somewhat cooled working medium will be supplied to the device.
The second striking example of a drop in pressure is when the flow is blocked by a tap. A sign of these problems is the loss of pressure in a separate segment of the pipeline located after the obstacle to the coolant.
Since all heating circuits contain devices that protect against excessive pressure (at least safety valve), the problem of low pressure occurs much more often. Let's consider the reasons for the drop and ways to increase pressure, and therefore improve water circulation, in open and closed heating systems.
Pressure in an open heating system
Unlike a closed thermal circuit, a properly constructed open heating system does not require balancing over years of operation - it is self-regulating.Boiler operation and static pressure ensure constant circulation of water in the system.
The density of the heated water following the supply riser is lower than the density of the cooled coolant. Hot water tends to occupy the highest possible point of the circuit, and cooled water tends to be at its very bottom.
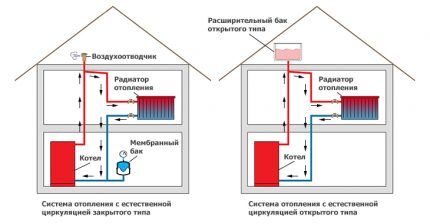
The pressure developed by the water column in the supply riser promotes the circulation of the coolant and compensates for the resistance present in the circuit pipeline. It is caused by friction of water on the inner surface of the pipes, as well as local resistance (turns and branches of the pipeline, boiler, fittings).
By the way, pipes of increased diameter are used for assembly open heating system precisely for the purpose of reducing friction.
To understand how to increase pressure in an open heating system, you must first understand the principle of achieving circulation pressure in the thermal circuit.
Its formula:
Rts = h • (pO-RG),
Where:
- Rts – circulation pressure;
- h – vertical distance between the centers of the boiler and the lower heating radiator;
- RG – density of the heated coolant;
- RO – density of the cooled coolant.
The static pressure will be higher if the distance between the central axes of the boiler and the battery closest to it is as significant as possible. Accordingly, the intensity of coolant circulation will be higher.
To achieve the maximum possible pressure in the heating circuit, it is necessary to lower the boiler as low as possible - into the basement.

The second reason for the drop in pressure in an open heating system is related to its self-regulation. When the heating temperature of the coolant changes, the intensity of its flow changes. By increasing the heating of water for the heating circuit on cold winter days, owners sharply reduce its density.
However, when passing through heating radiators, water gives off heat to the room atmosphere, and its density increases. And according to the formula presented above, a high difference in the densities of hot and chilled water helps to increase the circulation pressure.
The more the coolant is heated and the colder it is in the rooms of the house, the higher the pressure in the system will be. However, after the atmosphere of the premises warms up and the heat transfer from the radiators decreases, the pressure in the open system will drop - the difference between the supply and return water temperatures will decrease.
Balancing a double-circuit open heating system
Gravity heating systems are made with one or more circuits. In this case, the horizontal length of each looped pipeline should not exceed 30 m.
But to achieve optimal pressure and pressure in open natural movement system It is better to make pipelines even shorter for coolant – less than 25 m. Then it will be easier for water to deal with hydraulic resistance. In a circuit with several rings, in addition to limiting the length, the condition for heating radiators must be observed - the number of sections in all rings must be approximately equal.
Balancing of the horizontal rings included in the vertical circuit is required at the design stage of the heating system. If the hydraulic resistance of any ring turns out to be higher than that of the others, the static pressure in it will not be enough and the pressure will practically stop.
To maintain the required pressure in a double-circuit heating system, it is necessary to reduce the cross-section of the pipes approaching the radiators. You can also install valves in front of the radiators that perform thermoregulation (manual or automatic).
You can balance an open-type dual-circuit system:
- Manually. We start the heating system, then measure the temperature of the atmosphere of each heated room. Where it is higher, we screw the valve, where it is lower, we unscrew it. To adjust the thermal balance, you will have to perform temperature measurements and adjust the valves several times;
- Using thermostatic valves. Balancing occurs almost independently; you just need to set the desired temperature in each room on the valve handles. Each such device will control the supply of coolant to the radiator itself, increasing or decreasing the supply of coolant.
It is especially important that the value of the total hydraulic resistance of the heating system (all rings in the circuits) does not exceed the value of the circulation pressure. Otherwise, warming up the coolant and attempting to balance the system will not improve circulation.
Circulation pump for open heating system
It happens that measures to balance the heating circuit of a gravity system have no effect. Not all causes of low pressure can be solved by adjustment - choosing the wrong pipe diameter cannot be corrected without a complete reconstruction of the circuit.
Then, in order to increase pressure and improve water movement without significant modifications to the heating system, circulation pump is installed or booster pump device. The only thing that its installation will require is moving the expansion tank or replacing it with a membrane expansion tank (closed tank).

The energy consumption of circulation pumps does not exceed 100 W. Therefore, there is no need to fear that it will push the coolant out of the circuit.
The volume of water in the heating system is more or less constant, provided that the filling of the open circuit is controlled. Therefore, no matter how much water the circulation pump pushes along the circuit in front of it, the same amount will flow into it from the return pipe.
By bringing the pressure in the thermal system to the required level, the pump will make it possible to lengthen it, reduce the diameter of the pipeline and achieve circuit balance with high hydraulic resistance.
Pressure in a closed heating system
Installing a modern boiler, especially a double-circuit boiler, is called by sellers the ideal solution for home heating. With high-quality installation of a new boiler closed coercive system It serves well for several years, but one day the pressure in it drops sharply or gradually. How to find the cause of low dynamic pressure?
A closed heating system requires close attention. A drop or rise in pressure is equally dangerous for her. Being left without heating in winter is a homeowner's worst nightmare.
First of all, both the increasing and circulation pump, available in the thermal circuit. This device wears out faster than a boiler, expansion tank or pipeline, so its condition is determined first. It is important to make sure that the “silent” pump is receiving power and only then take measures to replace the device.
In general, it is more rational to integrate two pumps into the heating circuit in advance - one in the main pipe, the second in the bypass. A closed heating system cannot operate at low dynamic pressure. Therefore, a spare pump, turned on in time, will protect the house and pipeline from freezing.
If the pump is working properly, the source of the pressure loss is in the boiler or piping system. We check the boiler last, first the heating circuit.
Steps to find a coolant leak
It is possible to independently detect leaks in the heating system if the pipes are installed openly and there is access to the taps and all connecting elements. It is also necessary to remove the decorative trim of the heating radiators.
You need to walk along the entire thermal circuit with a flashlight, carefully studying every connection, every element of the system (boiler piping too). We are looking for puddles of water, wet spots on the floor, traces of dried water, rusty streaks on pipes, batteries and shut-off valves.
We take a small mirror, illuminate it with a flashlight and inspect the back side of each section heating radiator. If the batteries are prefabricated, made of cast iron or aluminum, you should inspect the connections between the sections. Corrosion and streaks of rust are a sign of a leak, even if the floor is dry under the radiator.
There are situations when the pressure in the circuit drops slowly, day by day. Moreover, there are absolutely no visible traces of leakage on the elements of the heating system or on the floor. Or rather, there are leaks and there are a lot of them, but they cannot be detected.
Flowing water evaporates on a pipe, radiator or on the floor surface, i.e. no noticeable puddles are formed. It is necessary to identify places where coolant may leak, place sheets of soft paper under them - napkins or toilet paper will do. After a few hours, check the paper for moisture. If it's wet, that means there's a leak here.

In a house equipped with a partially hidden heating piping system, it is impossible to find leaks on your own. All that remains is to call heating engineers who will search for leaks in the heating circuit using special equipment.
Thermal technical search for leaks in the heating system is performed in a certain sequence. First, the coolant is drained from the circuit.
Then a compressor is connected to the entire heating pipeline or to its individual segments equipped with shut-off valves via a threaded connection. As a last resort, you can connect a car pump to the pipeline.
A few minutes after the start of pumping air into the heating circuit, a distinct sound of escaping air will be heard in places of leakage.Each section of the heating system embedded in a wall or floor with a leak detected by sound must be opened from the cement screed.
Next, the leak is eliminated by replacing the pipe segment, tightening the connection with winding tow or fum tape, removing and installing new shut-off valves.
Pressure drops in the heating boiler
Let us note right away that only a heating engineer from the service department can determine the exact breakdown of boiler equipment. Those. The homeowner will not be able to independently find out and, moreover, eliminate a serious breakdown that caused a drop in pressure in the heating boiler.
Let's consider the possible reasons for the “creeping” change in pressure on the boiler pressure gauge, which occurs when the boiler is in external condition.
Crack in the heat exchanger. Over the years of operation, the walls of the heat exchanger in the boiler may develop microcracks. The reasons for their formation are wear of the unit, weakening of strength during washing, pressure testing (water hammer) or manufacturing defects. The coolant flows through them and the boiler requires water replenishment every 3-5 days.
The leak cannot be detected visually - the water flows weakly, and when the burner is turned on, the moisture accumulated in the boiler evaporates. The heat exchanger needs to be replaced, less often it can be soldered.

The pressure rises due to the open make-up tap. Against the background of low dynamic pressure in the boiler and higher pressure in the water supply system, “excess” water enters the heating system through the make-up tap.The pressure in the heating circuit increases to the point where it needs to be released through the safety valve of the boiler unit.
If the pressure in the water supply drops, the coolant of the heating circuit will transfer its flow into the boiler, then the pressure in the heating system will decrease. A similar problem occurs with a faulty make-up valve. You need to either close the tap or replace it.
Increase in pressure due to three-way valve. If a valve installed on a double-circuit boiler malfunctions, water from the “household” heating sector will flow into the heating system. The three-way valve needs cleaning or replacement.
The boiler pressure gauge readings do not change. If, when the operating modes of the boiler change, or when the temperature in the circuit increases or decreases, the pressure gauge shows the same pressure, it is “stuck”. Those. dirt from the heating system got into it through the pipe. The pressure gauge needs to be replaced.
Low pressure due to expansion tank
WITH double-circuit boilers In closed heating systems, the following situation often occurs: when starting in heating mode, the pressure on the boiler pressure gauge increases sharply. If the circuit is completely filled with water, the pressure increases to 3 bar and the relief valve is activated, releasing part of the water.
The homeowner turns off the burner and waits for the water to cool. At the same time, the pressure drops to a minimum. Next, the owner then tries to turn on the boiler. But the unit does not work, it gives an “emergency” signal. Although sometimes it is possible to activate the operation of a double-circuit boiler if the pressure does not drop too much.
All that remains is to try to increase the pressure by adding water to the system in “cold” mode (with the burner off) and achieving a pressure gauge reading of 1.2-1.5 bar. But restarting the boiler occurs with the same result: the pressure increases; the relief valve is activated; the water is drained; pressure at minimum; the boiler does not want to work.
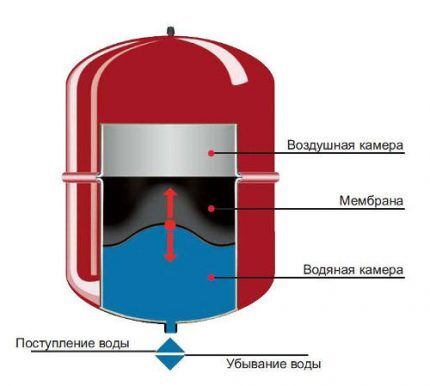
There may be several reasons for this malfunction. However, a common source of the problem is expansion tank. And it doesn’t matter where it is located - inside the boiler or outside it.
The expanzomat is divided into two parts by a flexible membrane. One contains coolant, the other gas (usually nitrogen) under a pressure of 1.5 bar. The water contained in the thermal circuit, expanding when heated, presses through the membrane onto the gas compartment of the membrane tank. To compensate for the increased pressure in the system, the gas in the expansion chamber is compressed.
After years of using a closed heating circuit, the nipple through which gas was pumped into the expansion tank begins to leak. It happens that the gas is dumped by homeowners themselves who do not understand the purpose of the nipple.
In any scenario, the gas in the expansion chamber becomes less and less. Soon the expansion tank is no longer able to compensate for the pressure of the expanding coolant in the system; its values reach a maximum.
Let's figure out how to solve the problem of lack of gas in the expansion tank. First we turn off the boiler; if it is electric, from the mains too.
If the expansion tank is built into the boiler, you need to block the access of water to both circuits (or one). Drain the water from the boiler completely. If the expanzomat is located separately from the boiler, you need “its” piece of pipeline from the general network and drain the water from there.
Then take a car pump equipped with a pressure gauge (a pressure gauge is required), attach it to the nipple on the expansion machine and pump it up. Water will flow from the blocked sector of the pipeline (or boiler, if the tank is in it) - pump further.
We monitor the pump pressure gauge. The water has stopped flowing out, and the pressure has reached 1.2-1.5 bar - we stop pumping air.
All that remains is to open the shut-off valves, fill the circuit with water to 1.2-1.5 bar, and then turn on the boiler. The heating system will work. If you discover that the problem with pressure has reappeared after a while, replace the expansion valve nipple, it is leaking heavily.
Note that there may be another problem with the tank, a more complex one - rupture of the membrane. Then pumping with air will not help, you will have to change the expansion chamber.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. How to balance heating radiators in a home heating system. Let us remind you that without valves on each heating radiator it will not be possible to balance the system.
Video #2. Recommendations from a heating engineer for restoring operating pressure in closed-type heating circuits. The video also explains the procedure for pumping an expansion tank that has lost its “factory” gas:
A properly balanced heating system will perform its functions for several years. But one day the characteristics of the coolant will change or critical elements of the thermal circuit will fail.Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor coolant indicators using pressure gauges in order to promptly respond to pressure changes.
Please write comments if you have any questions about the topic of the article. We are waiting for your stories about your own experience in normalizing pressure in the heating circuit. We and site visitors are ready to discuss controversial issues in the block located under the text of the article.




When we were building a new house, we thought for a long time about what kind of heating to install. In general, we decided to make a closed heating system, which is described a little higher. It’s a pity that I didn’t come across this information earlier, it would have been much simpler and, perhaps, even better. No matter how difficult it is to build such a system, it performs its functions with a bang!
I was faced with a heating problem when buying a house; the old owner was absolutely ignorant about heating the premises in winter. The boiler itself was installed in the basement and pipes were used throughout the house instead of radiators. The consumption of gas and water was simply crazy. I replaced the boiler with a German Junkers one and installed modern radiators everywhere for the second winter. The efficiency of the boiler has increased sharply and gas consumption has decreased significantly. There was no longer any need to heat huge amounts of water in pipes. And the automation installed in different corners easily copes with the control and management of room heating.
To the main question “how to increase blood pressure?” there was no answer. We limited ourselves to the answer: “If the pressure in the system drops, then it turns out that you need to open the feed tap or look at the expansion tank.”
The article is about nothing. And for whom was it written? An example of how to stretch something that could be written in 3 words into a whole article - look at the expansion tank.
I don’t know, I found at least a dozen reasons for low blood pressure in the article:
— coolant leak;
— pump malfunction;
— malfunction of the safety unit;
— water leakage from the heating system into the feed circuit;
— cavities of pipes and radiators are clogged;
— catch filters are dirty
— leaks in connections and pipe ruptures;
— using a pump of insufficient power;
— the difference in temperature between the coolant and the room (the principle of achieving circulation pressure in the thermal circuit of an open system);
— the looped horizontal circuit is too long (double-circuit imbalance);
— and finally, the problems you voiced with the expansion tank. Breakthrough of the expansion tank membrane and cracks in its walls.
Take this list and go ahead and check everything point by point. Good luck.
This is not an answer to the question of how to increase the pressure in the system, but a listing of a number of problems as a result of which the pressure decreases. But the article does not contain the answer to how to increase the pressure in the system! Here's how to increase the pressure in the heating system if the pressure in the water supply system is very low?
I liked your article, thank you. There is only one ambiguity left and therefore I really ask for your help. Last year I installed an autonomous system in the apartment, a new Vitopend 100 W double-circuit boiler. It worked all summer without problems, for three months the heating was fine, but little by little the pressure dropped. I didn’t do any replenishment because I didn’t pay attention.In January, the boiler stopped, the pressure was 06, the technician from the center said that all the air had come out of the tank, adjusted the operation of the boiler, set the pressure to 1.5, there seemed to be no leaks, he checked. The boiler is working, but the pressure is still dropping very slowly. Now, after 1.5 months of operation, it’s already 1.3 when it cools down. Question is this normal? Or is there still some kind of manufacturing defect? How often is it normal to top up the boiler with water to increase pressure? Please help me figure it out.
Tell me, will installing a circulation pump on a heating system with a closed-type gas boiler help increase the pressure?
Hello. please tell me - I have a battery section on the veranda on the second floor of my house. It is powered by a battery located in the room, behind the wall, at an angle of 180 degrees and heats weakly. The question is whether it is possible for me to install an additional circulation pump to increase the pressure. if so, where to put it on the return or supply and whether this installation will damage it. boiler Wissmann Vitopend-100 31 kW. Thank you.