Types of ventilation systems: a comparative review of options for organizing ventilation systems
The presence of a ventilation system is necessary to ensure air exchange inside the building by removing excess moisture, heat, and harmful substances.Its presence is one of the main conditions for ensuring life.
If there are no types of ventilation systems in the room, this harms the human body and leads to the formation of fungi, because... in conditions of lack of air exchange, condensation forms.
We suggest you understand the existing types of ventilation systems and the principles of their operation.
The content of the article:
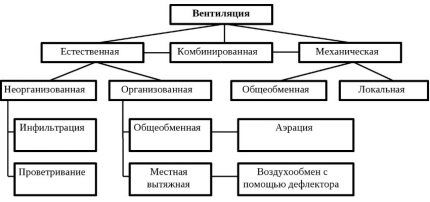
Classification of ventilation systems
Systems are classified according to different criteria:
- method of submission;
- purpose;
- air exchange method;
- design.
The type of ventilation is determined at the design stage of the building. In this case, both the economic and technical aspects, as well as sanitary and hygienic conditions, are taken into account.
Types of ventilation system according to supply method
Based on the methods of supplying and removing air from the room, 3 categories of ventilation can be distinguished:
- natural;
- mechanical;
- mixed.
Execute ventilation design, if such a solution is capable of providing air exchange that meets established standards.
When natural ventilation does not meet the requirements of sanitary and hygienic standards, the second option is chosen - a mechanical method of activating the air mass.
If it is possible, in addition to the second ventilation option, to partially use the first one, mixed ventilation is included in the project. In residential buildings, air flow occurs through windows, and exhaust equipment is located in the kitchen and sanitary room. Therefore, it is important to establish good air exchange between rooms.
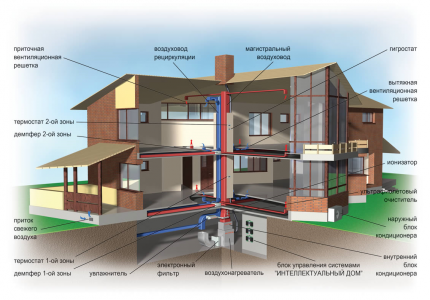
Types of ventilation by purpose
Based on the purpose of ventilation, there are working ventilation systems and emergency ones.While the former must constantly provide comfortable conditions, the latter come into operation only when the former are switched off and an emergency occurs when standard living conditions are disrupted.
These are sudden failures when air pollution occurs with toxic fumes, gases, explosives, toxic substances.
Emergency ventilation is not designed to supply fresh air. It only provides a gas outlet and does not allow the air mass with hazardous substances to spread throughout the room.
Ventilation systems by air exchange method
Based on this criterion, general and local ventilation systems are distinguished. The first must provide the entire volume of the room with sufficient air exchange while maintaining all the necessary air parameters. Additionally, it must remove excess moisture, heat, and contaminants. Air exchange can be carried out either through a ducted or ductless system.
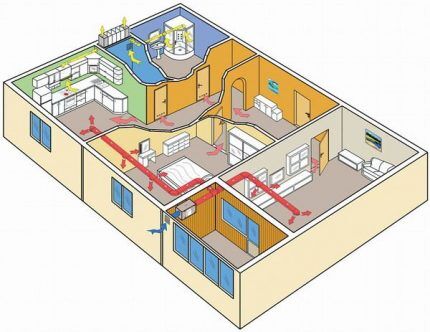
The purpose of local ventilation is to supply clean air to specific places and remove polluted air from the points where it is formed. As a rule, it is arranged in large premises with a limited number of workers. Air exchange occurs only in workplaces.
Separation of systems by design
Based on this feature, ventilation systems are divided into ducted and ductless.Duct-type systems consist of a branched route consisting of air ducts through which air is transported. Installation of such a system is advisable in large rooms.
When there are no channels, the system is called channelless. An example of such a system is an ordinary fan. There are 2 types of ductless systems - ceiling-mounted and under-floor. Ductless systems are easier to implement and consume less energy.
Natural ventilation of premises
The movement of air masses during natural ventilation occurs naturally without additional stimulation due to:
- temperature difference inside and outside the building;
- pressure difference between the room and the hood located on the roof of the building;
- under the influence of the wind.
This is the simplest system. There is no need to install complex expensive equipment that consumes a lot of electricity. Such a system cannot be called reliable due to the fact that its effectiveness depends on factors uncontrollable by humans.
The system can be organized or unorganized. A regulated or organized system functions through aeration or the presence of deflectors. Aeration is a general exchange process during which air enters and leaves through open windows, lanterns, transoms.
Infiltration or unregulated ventilation - natural ventilation is the entry of air into a room through leaks in structures.
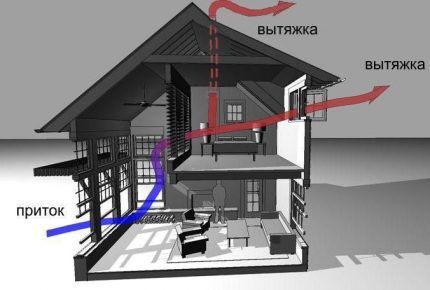
In industry, aeration is used in processes where, according to technology, work is accompanied by the release of heat in large quantities. Its use is permissible provided that the supply air contains less than 30% of harmful emissions from the permissible concentration directly in the zone of their formation.
Aeration should not be used if the air entering the room requires pre-treatment or condensation or fog may appear as a result of the influx of air from outside. Through aeration, multiple air exchanges occur with minimal energy consumption. This is its main advantage.
The principle of operation of a ventilation system with natural air flow is based on the difference in their temperature and pressure:
In some cases, deflectors - special nozzles - are mounted at the mouths of exhaust ducts. They operate by using wind energy. Deflectors do a good job of removing dirty and excessively heated air masses from small rooms. They are also used for local exhaust.
Normal operation of ventilation driven by pressure differences is ensured by a minimum difference of 3 m between the intake point and the exhaust outlet.

Characteristics of mechanical ventilation
The ventilation system, with the help of which air is supplied and removed using additional incentives over impressive distances, is called mechanical. There are other names for this type of ventilation - forced and artificial.
It is used both to ensure technological processes in various industries and to create comfortable conditions for people.
An easy-to-install and operate device that provides exhaust air exhaust from bathrooms, kitchens and toilets in private homes is a ventilation system with an automatic microprocessor:
Mechanical ventilation, unlike natural ventilation, does not depend on external conditions. She is completely controlled and manageable. The air supplied to the room is processed and, with a well-functioning system, all its parameters meet the standards. Emissions also enter the atmosphere already purified from harmful inclusions to the required extent.
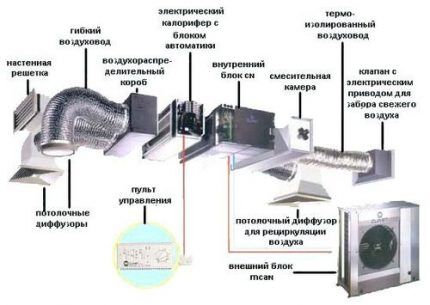
The presence of a mechanical ventilation system allows for optimal air distribution and delivery to a specific location. With its help, harmful emissions are captured at the source of their formation, preventing the air from polluting the entire room.
The disadvantage of mechanical ventilation is the large financial investments required during its installation and operation. To enjoy all its benefits, you will have to deal with channel contamination and regularly replace filters.
If a ventilation filter with a heat recovery function is installed, you need to switch to a summer liner before the onset of the summer period. If left in winter, it will reduce the efficiency of ventilation.
Mechanical ventilation can be both local and general. The latter is implemented in 2 versions - ductless and ducted. Replacing air in channel system occurs with the help of fans - centrifugal or axial, ejector units.

General ventilation with mechanical drive
Mechanically driven structures can be either supply or exhaust. Supply ventilation is sometimes performed in conjunction with central heating.
The air intake in such a system can take the form of holes in the building envelope, a free-standing or attached shaft.When installed outside the building, the air intake shaft is located above ground level or on the roof.
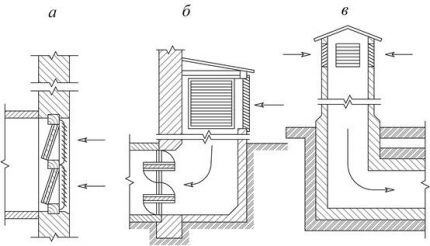
The choice of design and location of air intakes is influenced by the requirements for the degree of cleanliness of outdoor air, as well as the architectural features of the building. The bottom of the opening through which clean air enters must be located at a distance of at least 2 m from the ground, and if the building is located in a green zone - 1 m. External air intakes cannot be placed where there are harmful emissions.
Air masses enter the mine through fan. Passing through the heater, they are heated, moistened or, on the contrary, dried and enter through air ducts with holes.
Air can also be supplied through branches equipped with nozzles that guide the supply air masses. The volume of supplied air is controlled by dampers or valves located in the branches.
Mechanical local ventilation of supply type
Local mechanical ventilation operating in a limited space is called air showering. This ventilation option is used in those work areas where the radiant heat intensity is more than 300 kcal/h. or production involves the release of toxins that cannot be removed using local exhaust.
Showering units can be mobile or stationary. The former, when providing the workplace with clean air, take it from the room. Sometimes water is supplied into the sprayed air mass. When its drops come into contact with the human body, they become an additional coolant.The latter supply clean outside air or pre-treated air through shower pipes.
General exhaust ventilation
Removing exhaust air from a room is the task of exhaust ventilation. Removal of used air from a room occurs by lowering the pressure in it. Thus, conditions are created for air to enter it from outside or from an adjacent room.
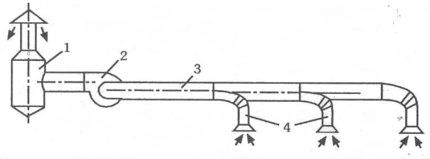
When designing general-exchange hoods for production workshops, the point is taken into account that the elimination of dirty air should be carried out directly from the original source of formation of harmful emissions in the direction of their natural trajectory and not pollute clean areas. Such places are biological laboratories, workshops with harmful conditions.
Mechanical supply and exhaust ventilation
The supply and exhaust ventilation is based on 2 flows moving towards each other. It consists of two independent systems - supply and exhaust, or one unit. It has built-in all the equipment necessary to operate both supply and exhaust.
If there are 2 separate systems, ventilation operates without recirculation and is called open. The second type of ventilation system is called closed, and it works with recirculation.
The recirculation system saves energy spent on cooling or heating the air, becausethe air mass is not completely heated, but only the volume that comes from outside. The removed air in a recirculation system is returned to the room again with an admixture of fresh air, amounting to 10-15% of the total volume of the air mass.
The installation of such ventilation is possible in places where there are no dangerous pollutants. In regions with cold climates, a closed system is ineffective because recirculation and external air masses do not mix well enough.
Mechanical ventilation in case of emergency
In case of unusual situations, in addition to the working option, emergency ventilation is arranged. Invariably it is always exhaust. Mechanical emergency ventilation is installed in rooms where there is a threat of breakthrough of explosive vapors or gases. In this case, explosion- and spark-proof fans are installed.

There are dangerous components that cannot be removed using fans. Then the ejector is included in the system. Emergency ventilation should be switched on automatically as soon as the main ventilation stops working. Opening of openings through which dirty air will escape must be done remotely.
Pipes and grilles designed to allow air to escape during emergency ventilation are placed in places where hazardous substances are most likely to be concentrated in large volumes. Openings through which air is removed in an emergency should not be located in areas where people are constantly present.Umbrellas must not be mounted on emergency system pipes and shafts.
Emissions accidentally released into the atmosphere must be dispersed as much as possible and not allowed to enter confined areas of the territory adjacent to the building. MPCs are monitored using gas analyzers adjusted accordingly.
Ventilation against smoke
The main task of smoke ventilation is to remove smoke from a room or building as quickly as possible, block its spread and thereby protect people during their evacuation.
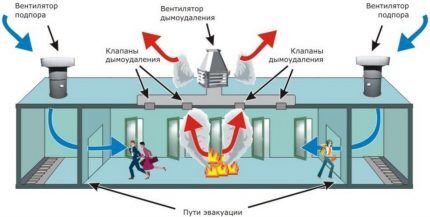
Such ventilation is installed where, with the constant presence of a large number of people, natural air flow is impossible. These are elevators, stairwells, back corridors and similar places. The operation of anti-smoke ventilation is based on a supply and exhaust circuit.
The channels and powerful fans that make up the ventilation have increased fire resistance and the ability to resist deformation under prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Sections of the system are equipped with two types of valves - smoke control and fire suppression. The components of the smoke control system include durable screens and doors that are impenetrable to gases and smoke.
To avoid troubles during the evacuation of people, 2 types of control are included in the design of smoke ventilation - automatic and remote manual.
The system must include elements that notify of a fire:
- detectors, when triggered, exhaust fans and smoke dampers are automatically opened;
- "Fire" signal on the central console;
- turning on smoke ventilation manually.
Smoke exhaust valves are distributed evenly under the ceiling. The coverage area should not exceed 900 m². The system is zoned into sections and, in addition to hatches and valves, is equipped with smoke exhausters.
It not only removes smoke, but also removes carbon monoxide and fine suspensions formed during combustion. You can read more about installing a smoke removal system in this material.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
This video is a kind of educational program about ventilation. Here the very concept of ventilation is discussed in detail and all issues related to its competent design are covered:
Master class on installing a ventilation system:
Both business managers and private developers must understand that the normal functioning of those for whom they are responsible depends on the effectiveness of ventilation. Sometimes people's lives are also in question. You cannot miss this moment and save on it.
Have questions about the topic of the article, found any shortcomings, or have valuable information that you could share with our readers? Please leave comments, share your experience, and participate in discussions.




I have the following question: we live on the fifth floor, renovations have been done, and in general there are no cracks in the floor or walls. But from time to time there is a smell in the bathroom. Most likely from the basement, although it’s amazing how the smell can rise to such a height.We noticed that this usually happens in windy weather... Tell me how to deal with this? And there are still suspicions about the washing machine, can the smell spread through it?
If you are guilty of using the washing machine, you can simply try moving it to another room for a while and check whether the smell goes away or not. It is unlikely that the smell from the basement will reach you, but just in case, it is worth talking to other residents of the house and asking if they have a similar problem.
And if on topic, I think that a mixed ventilation system is really the best option. This is exactly what we have in our country house.
I came across a similar case. There, the cause of the smell was not the ventilation, but the bathroom drain. The siphon had a small bend and because of this, the water seal constantly broke down (the water simply did not stay in). After replacing the siphon the problem was solved.
Hello. I also suspect that the reason is most likely in the sewer... but it is still problematic to diagnose accurately based on the information provided.
Hello. Here the answer cannot be given correctly, since you did not accurately determine the source of the smell and did not tell us what type of “smell” you have. You can cite recent renovations or smells from the plumbing, washing machine, problem with the vent, or a burst pipe in the basement. But you don't need all this. Invite a specialist from the management company, that’s what they exist for. Let them check the ventilation, basement, and sewer system. It is easier to diagnose the problem on site than from your description. Again, clean the washer and check the drain connection.
Alexandra, install a overhead bath fan in the “Turbo” bathroom for 200 m3. And all the unpleasant smell will disappear.