Heating system of a two-story house: typical diagrams and specifics of the wiring project
Comfortable living in a private two-story house depends entirely on the complex of communications, among which one of the main places is occupied by the heating network.Is not it? It is she who is responsible for maintaining optimal temperature conditions and the safety of the building itself. Agree, room temperature is one of the main components of ensuring comfortable living.
The choice of heat source and its correct connection directly determines whether you can maintain the temperature necessary for living. Here we will help you understand how the heating system of a two-story house functions, and which wiring diagrams are considered the most effective.
Here you will find information about the types of coolants, methods and features of their connection. For clarity, the material is accompanied by connection diagrams, as well as videos that will help expand knowledge about heating systems in private houses.
The content of the article:
What does the heating system consist of?
It is quite difficult to independently select the equipment necessary to assemble a heating system. To do this you need to have special engineering knowledge, be able to calculate heat loss, navigate through detailed calculations and installation nuances.
We recommend that you contact professional heating engineers who, as a result of preliminary calculations, will select the optimal heating scheme.
If you have the appropriate education or you already have experience installing heating in a two-story house, then you can choose the heating circuit option yourself, using useful information and proven skills.
Selecting a thermal energy source
The heart of the heating network is a heat generator, which heats the coolant to the optimal temperature and, if its technical capabilities allow, maintains the set parameters around the clock.
Among modern heat sources in private two-story houses, almost all are used, sometimes 2-3 types are combined.
Possible types of heat generators:
- heating boilers;
- infrared emitters;
- stoves (Russian, Dutch, Canadian);
- fireplaces;
- solar collectors, heat pump units and other types of alternative equipment.
Heating boilers are actively used, which can be classified by type of fuel:
- liquid or solid fuel;
- gas;
- electric.
The second and third options are more economical, and if gas or electricity is supplied to the house, then you should prefer them.

If the cottage is built on a non-gasified plot, electric boiler becomes the main one, and a fireplace or infrared heating is used as a backup source.
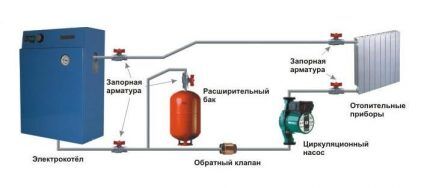
The use of alternative heat generators largely depends on the climatic conditions of the region; moreover, a minimum set of relatively expensive equipment (for example, solar collectors) will pay for itself in at least 3 years.
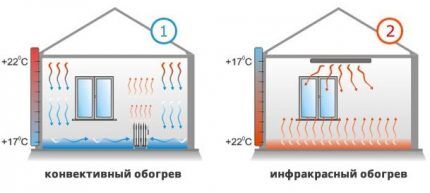
Which coolant is better?
The heat generated by a gas boiler or other heat generator cannot by itself spread throughout all rooms. For this purpose it is necessary coolant - a substance that moves freely through pipes and has the necessary technical characteristics.
There are technologies for using heated air, which are especially relevant in homes with stove heating, fireplace or electric heating. But, unfortunately, to ensure effective functioning it has insufficient parameters of heat capacity, density and heat transfer.

Unlike gaseous substances, liquid substances have an excellent ability to absorb heat, release it and maintain a given temperature for some time. In this sense, the ideal “conductor” is ordinary water. When heated, it fills pipes and radiators, gradually releasing heat to living spaces, and circulation ensures the consistency of the process.
For houses with permanent residence, systems with water as a coolant are optimal. To ensure that heating equipment lasts longer without repairs and that the pipeline does not become coated with plaque, water is passed through filters and enriched with special additives and inhibitors.

If the house is a temporary shelter or serves as a vacation spot on weekends, it is better to use antifreeze instead of water. This is a liquid solution with a chemical composition, one of the components of which is propylene glycol or ethylene glycol.
The chemicals prevent the coolant from freezing even when the building freezes and constantly maintain the network functionality in operating mode.
Convector and radiator heating of premises
When drawing up a heating project for a two-story or three-story house, both radiators and convectors can be used as heating devices.
Radiators, or heating batteries, most often equip centralized systems.They have a combined operating principle: they transmit thermal radiation and heat the air, which circulates around and passes through the “ribs” of the products.
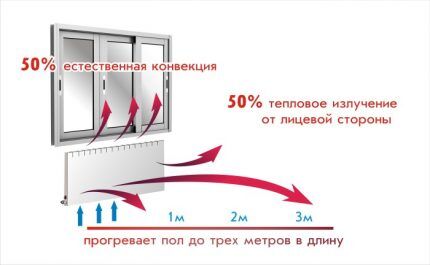
Heating devices with a combined operating principle are considered the best option for arranging a two-story private house.
Convectors have a more open design and consist of copper tubes and heat exchangers. The air enters the heat exchangers, heats up, rises, making room for a new portion of not yet heated air. The device is protected from cooling by a voluminous casing.
In heating schemes for two-story houses, both radiators and convector heaters are used; the choice of devices is large due to the variety of designs, sizes and shapes.

Brief description of household radiators
All types of home heating radiators can be classified according to the material from which they are made. Modern models of heating devices are made from the following metals:
There are also designer models created in vintage style, but they are quite expensive and are most often made to order. Ceramic and forged products are much less common than factory stamping.

Previously, sectional radiators made of cast iron were common, and they can still be found on sale. Cast iron is valued for its wear resistance and undemanding characteristics of the coolant, but its high weight is considered a disadvantage. Weight should be taken into account if the project involves mounting the radiator on a light wall.
Sectional, that is, prefabricated, models are also made of aluminum.They are lightweight and aesthetically pleasing, but do not come into contact with copper parts and react negatively to some types of coolants.

Steel radiators can be panel, made from pieces of sheet steel, or sectional, consisting of several modules. The first option is considered more reliable due to the simple double-sided threaded connection. Steel perfectly tolerates any heat carriers; it is lighter in weight than cast iron, but heavier than aluminum.
Any type of radiator is suitable for a two-story house; when choosing, you need to focus on the type of coolant, features of the system installation and interior design.
Efficiency of forced circulation schemes
The prevailing part of modern heating systems can function fully only when created artificial circulation, that is, one in which the coolant moves within the network due to the operation of the circulation pump.
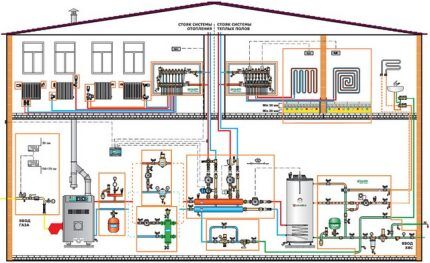
There are prerequisites for installing forced circulation in a building with several floors:
- installation of a pipeline with a smaller diameter, which facilitates the assembly of the wiring as a whole;
- providing zonal regulation (along with or instead of general regulation);
- the presence of 2nd and higher floors does not affect the heating efficiency;
- reducing the coolant temperature without changing heat transfer parameters;
- possibility of using inexpensive plastic pipes.
The disadvantages include the availability of power supply - interruptions are possible, but they can be easily avoided by using backup UPSs. The problem of louder noise can also be solved by installing a layer of sound insulation in the boiler room.
The most suitable place for inserting the circulation pump is where the temperature drops to a minimum, that is, directly in front of the boiler, on the return line.
Natural circulation as an alternative
Nowadays, autonomous heating networks with gravitational circulation, that is, operating according to natural physical laws, can be found extremely rarely.
The principle of operation is explained by the difference in density of cold and heated water and the presence of an additional control device - an expansion tank, which is installed in the upper part of the hot water riser.
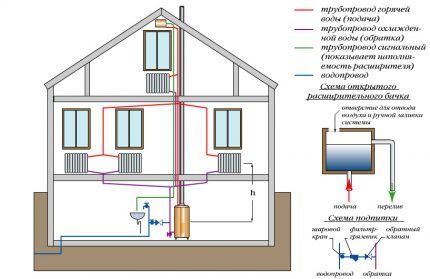
Feature natural networks is the inclined arrangement of horizontal pipes (return and distribution) and the location of the boiler - it is installed at the lowest possible level. The coolant is supplied through the expansion riser, and the cooled water (or antifreeze) is discharged through the return riser.
The advantages of the gravity circuit are independence from electrical power, ease of installation, and the absence of noise produced by the circulation pump.
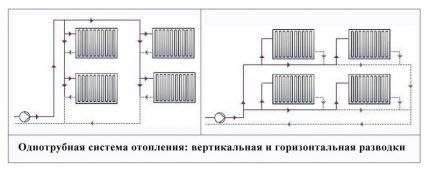
Features of a single-pipe heating system
The choice of one- or two-pipe heating does not depend on the number of floors of the house - both types are suitable, but for buildings with 2 or more floors, the installation of a circulation pump is required.
Heating with a liquid coolant (water or antifreeze) is considered the most effective, while for small one-story houses, for example, summer cottages, other options can be considered.
Operating principle and distinctive features
Heating radiators, according to a single-pipe scheme, are connected in series, that is, the coolant first enters one device closest to the boiler, from it through a pipeline to another, etc. The looped circuit, which is a network, is also suitable for a 2-story house, since it is conveniently located along the perimeter walls.
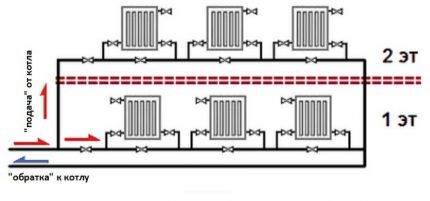
The presence of shut-off valves can improve the use of the system. For example, Mayevsky crane designed to remove air “locks” that often occur during downtime, that is, in the summer. In addition to it, various models of balancing valves, ball valves, and special regulators are used.
The forced circulation method in a single-pipe structure in the event of a temporary absence of electricity can be replaced by a natural one, but this requires the installation of a membrane tank and the placement of horizontal pipes at an angle of up to 5º.
Assessing disadvantages and advantages
The main advantage of single-pipe networks is considered to be easier drafting of the project and the installation itself.A minimum of pipes allows you not to rely on a complex room layout, but simply lay the pipeline strictly along the perimeters of both floors. Savings on purchasing fewer elements for a single main line - pipes, taps - are also appreciated.
One pipe takes up much less space than two, so it can be disguised under the floor covering, laid unnoticed in doorways, that is, installed without disturbing the interior.
The disadvantages include the need to purchase a more powerful circulation pump, as a result of which electricity bills increase. It is more difficult to regulate the temperature level in a design with a serial connection: when the heating intensity in the nearest radiator decreases, the temperature in the entire line will automatically decrease.
Common connection options
If you decide to install a single-pipe system, you will have to choose between two types:
- simple circuit without regulation;
- "Leningradka" with the ability to turn off individual radiators.
In terms of control method, the first option is clearly inferior to the second; its only advantage is its budget cost.
Installing the Leningradka will cost a little more, since in addition to the pipes you need to purchase a set of shut-off valves. Using bypasses and valves, you can reduce/increase the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator.
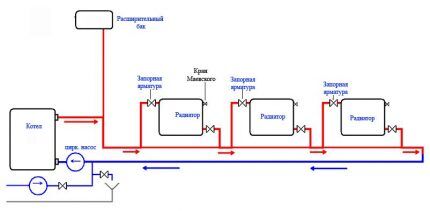
"Leningradka" is recognized by professional heating engineers as the best option for a single-pipe system for a 2-story residential building.
Complete set and installation of equipment
Standard equipment for system assembly:
- circulation pump;
- gas or electric boiler (power depends on the size of the house, characteristics of the coolant, etc.);
- expansion tank;
- pipes 20 mm and 25 mm;
- adapters, gaskets, plugs;
- set of radiators;
- Mayevsky cranes.
Along with steel pipes, polymer or metal-plastic pipes can be used, with the latter being preferred.
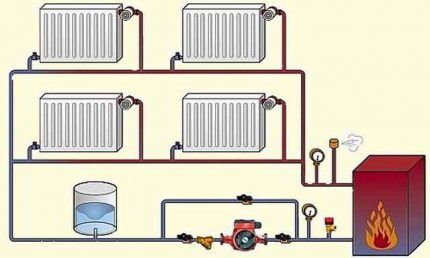
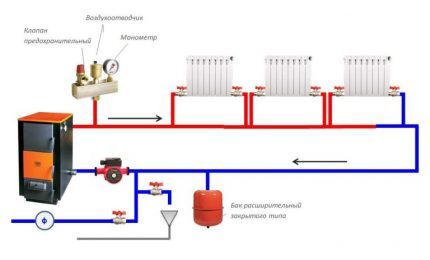
First, they find a suitable place for the boiler and install it, then assemble the pipeline leading to the radiators. In places where radiator branches and bypasses fix the tees. The pump is installed on the return line, next to the inlet to the boiler, and connected to the power supply.
The installation location of an open expansion tank is the highest point of the system; a closed one can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, in a boiler room. Radiators are suspended from the walls using special fasteners and equipped with plugs and taps.
Two-pipe heating system for a 2-story house
Truly comfortable living conditions can only be achieved by installing two-pipe heating system. Its design allows you to regulate the temperature in individual rooms and save energy resources.
How does a two-way circuit work?
Unlike a single-pipe circuit, a two-pipe circuit consists of a pair of lines with different purposes: one of them supplies coolant, the second returns it back. The radiators are connected not in series order, but in parallel. One circuit, with heated coolant, extends from the riser to the radiators of both floors, the second is mounted to the boiler outlet and is also distributed to both floors.
Radiators are equipped with thermostatic valves that allow you to set a comfortable temperature. If desired, you can reduce the heating intensity partially or completely block the flow of water into the device.
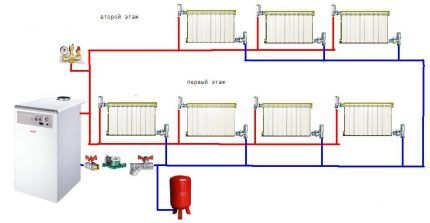
In modern 2-story houses, two-pipe structures are used, since they are much more efficient than single-pipe ones:
- reduce pressure loss;
- do not require a powerful pump;
- keep the coolant temperature the same for each radiator;
- allow you to use many different thermal devices within one system (for example, radiators, convectors and “warm floors”);
- make it possible to repair and replace parts without compromising overall functionality.
The main disadvantage is the difficulty of self-installation - during assembly, consultation and supervision of professionals is required.
Successful solutions for installing a two-pipe system
There are many incarnations of various schemes, but when drawing up a project you should start from individual requirements.
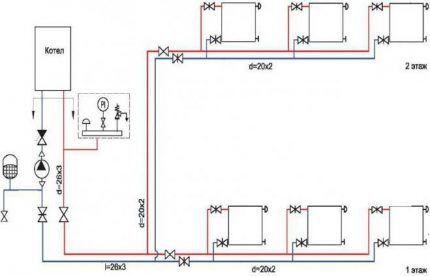
A number of universal schemes are suitable for providing heat to houses of various sizes and number of floors.
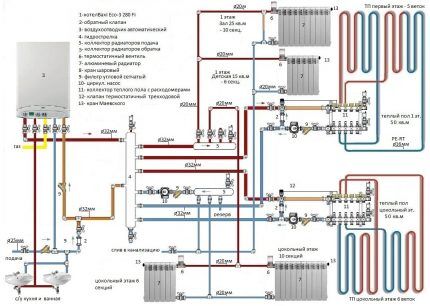
If you install additional equipment, such as a membrane tank, the capabilities of the heating system will expand.
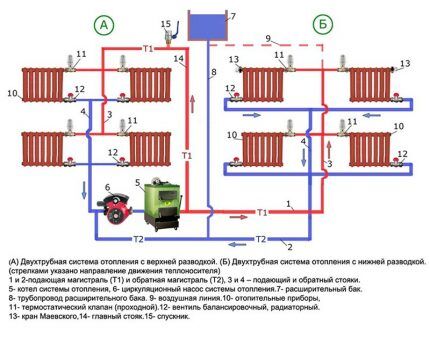
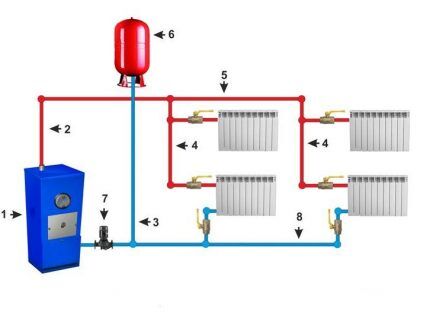
The following diagram combines the three most popular wiring diagrams.
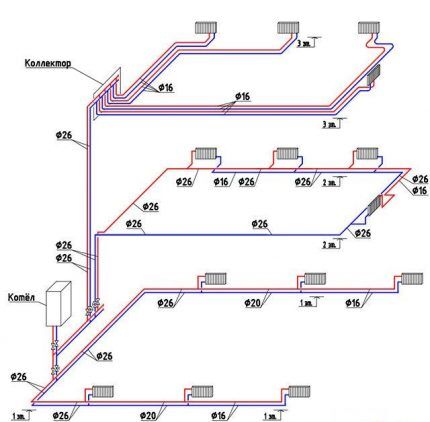
All of the above schemes are suitable for heating a 2-story building.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Informational videos will expand your knowledge about heating systems in 2- and 3-story buildings.
Video #1. Connection diagram for a double-circuit radiator heating system with “warm floors”:
Video #2. Option for wiring a heating system in a 3-story building (using Leningradka):
Video #3. Practical application of a system with natural coolant circulation (on a solid fuel boiler):
Thus, two-pipe heating systems with a liquid coolant, equipped with a gas or electric boiler and a circulation pump, can be considered the most effective.Combined systems are more efficient; the selection of heat sources depends on the number of floors and the design of the house.
In any case, to draw up an individual scheme, we recommend consulting with heating engineers and designers.
Do you have any questions, is there an opportunity to give valuable advice, or have you found any shortcomings in the text? Your opinion is important to us. Please leave posts in the block below, share your opinion and post photos on the topic of the article.




The article is good, but not everyone can figure it out so easily and install heating on their own, we invited specialists for this task - they did it efficiently, for 2 years now we have had heated floors and our own autonomous heating.
We study, we reflect, we ponder.
I always read your professional and useful reviews with interest. A year ago I didn’t think that we would decide to independently install the heating of our two-story house, since at the moment there is a not very efficient system with large heat losses. Here we read the information before going to a consultation with builders, so that we know what to talk to them about.