How to make stove heating in a private house with air or water circuits
There are many ways to heat a private home using gas and electricity.But despite the abundance of modern methods, stove heating is still relevant when arranging country houses and cottages.
Agree, nothing emphasizes the flavor of a Russian hut more than a wood-burning stove. In addition, solid fuel heating is considered one of the economical options.
The organization of a heating system begins with the selection of furnace equipment and determination of the type of heating circuit. We suggest you understand the structure and operating principles of water and air heating based on a furnace. For a better understanding of the issue, we have supplemented the material with diagrams and visual photographs.
The content of the article:
Heating with air system
The reason for the stable preference that owners of private houses give to the stove heating option is economical operation — availability of firewood, fuel briquettes or coal.
The disadvantage is the limited space to be processed, which can be eliminated by installing a water and air system based on a brick unit.
The specifics of heating low-rise buildings with a stove are presented in the photo selection:
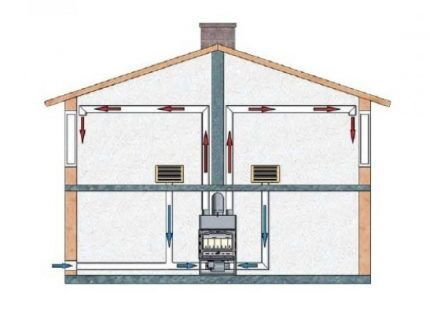
Operating principle air heating based on a stove or fireplace consists of transferring a warm flow heated to operating temperature in a heat exchanger or in a boiler. The air enters either directly into the room or through air ducts.
Thanks to the relatively short path, it does not have time to lose temperature. The result is an even distribution of heat throughout the house.
A chamber for heating air is placed above the firebox so that the hot upper surface of the firebox and the chimney transfer the maximum amount of heat to it. Air circulation occurs naturally or with the help of fans.

Natural circulation occurs as a result of the difference in density of cold and hot air. Cold air entering the heating chamber displaces hot air into the air ducts.
This method does not require electricity, but if the air does not move quickly enough through the heating chamber, it becomes very hot, which can cause problems.
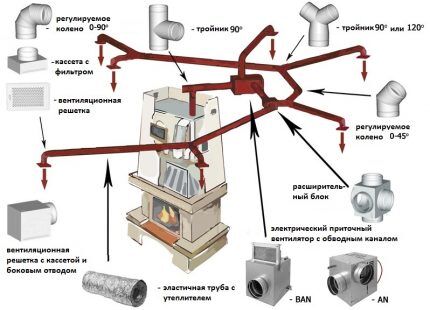
Forced circulation occurs using fans or pumps. However, the heating of the premises occurs more quickly and evenly. With forced ventilation, by adjusting its mode, you can easily control the volume of air supplied to various rooms, thereby determining the microclimate of individual rooms of the house.
Based on the type of cold air supply, systems are divided into two types:
- With full recycling. Heated air masses alternate with cooled ones within the same room. The disadvantage of the scheme is that the air quality decreases with each heating/cooling cycle.
- With partial reclamation. Part of the fresh air is taken from the street, which is mixed with part of the air from the room. After heating, the mixture of two air portions is delivered to the consumer. The advantage is stable air quality, the disadvantage is energy dependence.
It is clear that the first group includes duct systems with natural movement of air coolant. The second includes options with forced air movement, for the movement of which it is not necessary to install a network of air ducts.
The main advantages of air heating compared to water heating:
- high efficiency;
- accident-free;
- lack of radiators in the rooms.
The design of the circuit with forced movement allows you to do without the construction of an air duct system. In addition, this type can be combined with air conditioning, humidification and air ionization.
If installing a device that stimulates the movement of heated air is not planned, then the following methods are used to increase the performance of the stove:
Increasing the efficiency will spontaneously increase the speed of the air flow: the faster the air heats up, the more intense the change of cooled and heated air mass occurs.
The main disadvantages of air heating compared to water heating:
- when using a furnace, the temperature of the supplied air has a significant range, unlike the use of other heating means;
- air ducts have a large diameter, so installation must be carried out at the construction stage;
- It is advisable to locate the stove in the basement, otherwise it is necessary to use fans that make noise.
Air movement in the room has a negative side - it raises dust, but the use of filters at the outlet of the air duct allows you to effectively catch this dust, thus reducing the total amount of dust in the house.
Another feature of air heating that has both positive and negative sides is the rate of heat transfer. On the one hand, the rooms heat up faster than when heating using a water circuit, on the other hand, there is no thermal inertia - as soon as the stove or fireplace goes out, the room immediately begins to cool down.

Unlike water heating, installing an air heating system is not difficult.All elements (pipes, bends, ventilation grilles) can be connected quite simply without welding. There are flexible air ducts that can take any shape, depending on the geometry of the premises.
Despite this, air heating systems based on stoves or fireplaces have not yet become widespread. Much more often in individual low-rise construction, a water circuit is used to heat rooms.
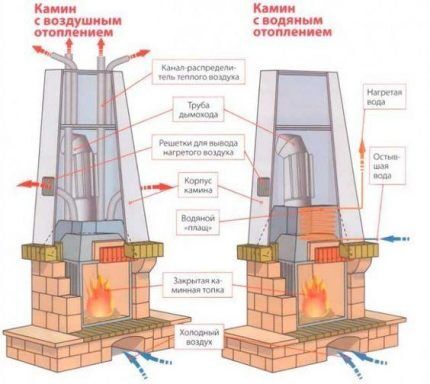
Stove-based water heating device
Operating principles of any water heating are based on the distribution of heat from a local source throughout the room, using the movement of water along the heating circuit.
Basic elements of water heating
For a stove heating scheme with a water circuit, the main elements are:
- stove or fireplace with heat exchanger, in which water is heated;
- heating circuitwhere heat transfer to the room occurs;
- expansion tank to prevent damage to the system as a result of increased pressure;
- circulation pump to ensure water movement along the circuit.
There are general rules for the operation of water heating, such as wiring diagrams, which are well known and must be followed. However, when using a stove as a heat source, there are specific requirements related to the temperature conditions.
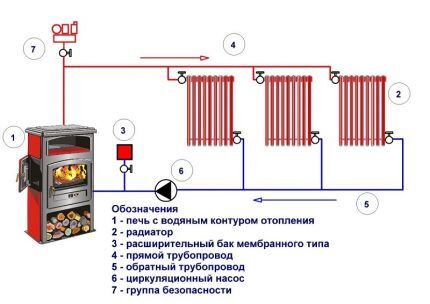
Furnaces do not heat up quickly and cool down slowly, uneven heat release occurs, and only the correct installation of all system components will avoid problems with high-quality heating of the premises of the house.
Types of heat exchanger and placement methods
For the manufacture of heat exchangers for furnaces, sheet “black” steel or heat-resistant stainless steel is used. The use of cast iron as a production material is difficult, but ready-made cast iron products, such as cast iron radiators, can be used.
It is possible to use copper, which has better thermal conductivity compared to steel, but the price of such a device will be high. It is recommended to make the heat exchanger from steel with a thickness of 3 mm. At high furnace temperatures that arise when using coal or, especially, coke, it is necessary to use steel 5 mm thick.
Heat exchangers can be divided into three types:
- registers, coils and radiators, consisting of a set of pipes;
- shirts (boilers), welded from sheet steel;
- combined option in the form of vertical walls connected by pipes (so-called “books”).
Sheet steel jackets are easier to manufacture and easier to clean from fuel combustion products, but tubular structures have a larger heating area. When making a jacket, it is necessary to take into account the excess water pressure that occurs when using a membrane expansion tank or raising water to a great height.
A heat exchanger for water heating based on a stove can be constructed from scrap materials:
In this case, it is necessary to use steel with a thickness of at least 5 mm and additionally reinforce the walls with stiffeners to avoid their deformation.
The shapes of tubular structures can be different, but it is necessary to comply with the condition that the internal size of the pipes is at least 3 cm in diameter. Otherwise, if the circulation speed is slow or the temperature is too high, the water may boil.
Registers are made, as a rule, from profile rather than round pipes to facilitate welding work.
You can make a heat exchanger of the required size yourself. In this case, increased attention should be paid to the quality of welding. If the heat exchanger leaks, all the water will pour into the furnace.
In addition, to fix the problem, you will have to do a lot of work: disassemble the stove, remove, weld and put back the heat exchanger, and then reassemble the stove.
There are two options for the location of the heat exchanger. In the first case, it is placed directly in the firebox, significantly narrowing its space.In the second, the registers are installed in the hood of non-revolving furnaces, but the furnace itself in this case has a more complex design.
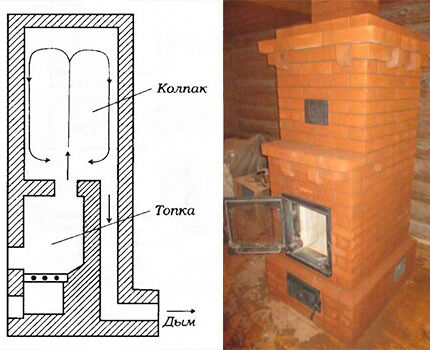
When installing a tubular type heat exchanger, it is necessary to leave a gap between it and the wall of the stove. This is necessary for better heating of the coolant, as well as the possibility of cleaning the register. It is necessary to clean both shirts and registers periodically, since in case of severe clogging with ash, the efficiency of heat transfer decreases.
If there is a hob, cleaning occurs after removing it. If the stove has only a heating function, then cleaning occurs through the combustion door.
Water circulation in the heating circuit
The basic principles of organizing the natural circulation of water in the system are to model the “acceleration collector” at the outlet of the heat exchanger and to create a constant slope of the heating circuit pipes of 3-5°.
The general meaning of the “acceleration manifold” is that heated water from the stove rises vertically upward, and then is distributed along the heating circuit.
Circulation occurs due to the difference in specific gravity of cold and hot water. Cold water is heavier than hot water, and flowing to the heat exchanger, displaces hot water up the pipe. The “return” entry point must be lower than the water outlets from the heating radiators, otherwise the water circulation will be very slow or not at all.

To increase the speed of water movement along the heating circuit install a circulation pump. Thus, there is a faster and more uniform distribution of heat throughout the house. Several pumps can be used simultaneously for different heating circuits.
In the presence of voltage surges, it is necessary to use Voltage regulator, since pump failure can have serious consequences for the entire system.
Pumps can be divided into two groups relative to the position of the engine: with a “dry” rotor and a “wet” rotor. By voltage type: models operating from a 220 V network and pumps operating from 12 V power sources.
The motor in pumps with a dry rotor is isolated from the impeller submerged in water by sealing rings. Compared to pumps with a submerged motor, dry pumps have higher efficiency.
However, the disadvantages include high noise levels, the need for regular maintenance and shorter engine life. Therefore, in a private home, as a rule, circulation pumps with a “wet” rotor are used.
The choice of pump power type depends on the possibility of natural circulation of water in the system. If it is impossible without the participation of a pump, then the choice should be made in favor of an option that supports 12 V voltage and an uninterruptible power supply.
Otherwise, in the event of a power outage, the water may boil and the system may fail. If natural circulation is possible, then it is better to purchase a more common and cheaper option powered by a 220 V network.

When installing a pump with a 220 V power supply, it is necessary to ensure that the heating system can operate during a power outage. To do this, install a shut-off valve on the pipe, and bypass it by installing a bypass pipe with a pump (the so-called “bypass”).
A filter tap is installed on the bypass pipe in front of the pump, and then a shut-off valve. By adjusting the position of the shut-off valves on the main and bypass pipes, you can turn on the forced and natural circulation mode.
As a rule, the pump is installed on the “return” near the furnace so that the temperature of the liquid that will pass through the device is the lowest. This will significantly extend the life of the pump.
In addition, it is necessary to place the maximum possible number of heating system controls in one place, so that in the event of emergency situations, measures can be quickly taken to eliminate them.

Rules for using the expansion tank
When heated, a liquid expands, and if this happens in a closed system, the pressure inside it will greatly increase, and an increase in pressure is fraught with water breakthrough. Using a safety valve is not advisable, since after the water cools and its volume decreases, air will be introduced into the system.
Therefore, in heating circuits with forced water movement, special expansion tanks, which are of open or closed type. Their volume is calculated based not only on the maximum thermal expansion of the liquid (5-7%), but also taking into account the possibility of boiling of the system.
An open-type tank equips the water circuit of a gravity-type stove heating system, that is, with natural transportation of the coolant. It is a metal container of arbitrary shape located at the very top of the heating circuit. It communicates directly with the atmosphere, due to which the coolant partially evaporates.
The pipeline is connected to the bottom or lower quarter of the tank, and a pipe is welded to the top of it to drain water in case of overflow and allow air to escape from the system. Practice shows that the volume of an open tank should be at least 15% of the volume of water in the heating system.

A closed or membrane type tank is a closed vessel with a membrane inside. When the water heats up, it increases the pressure, stretches the membrane and enters the tank. If the pressure exceeds, the automatic system is activated and the excess coolant is discharged into the sewer.
After the first discharge, there is usually no longer any reason to produce it again, since the volume of coolant becomes equal to the volume of the system.
A closed membrane tank is mounted in front of the pump. Such a container, unlike an open-type tank, cannot get rid of air on its own, so at the top of the heating circuit it is necessary to install a Mayevsky valve (mechanical air vent) or its automatic equivalent.
The only element of a membrane tank that can fail over time is the membrane, so it is better to buy a tank with the ability to replace it.
When purchasing a closed-type tank, which is sometimes called a hydraulic accumulator, the main thing is not to confuse it with a hydraulic accumulator for water supply.
For a membrane tank used in heating, the operating temperature is up to 120°C and the pressure is up to 3 Bar. For water supply, tanks with temperatures up to 70°C and pressure up to 10 Bar are used.
Choosing between pipes and radiators
As a water circuit for stove heating, you can use a system of plastic pipes with radiators (batteries) or a system of metal pipes. The main advantage of using radiators is that they look more beautiful compared to massive air ducts.
Plastic wiring can be easily hidden in the floor, as it does not give off heat. Although according to the rules, the water heating wiring must be open. However, polymer pipelines have limitations: they cannot be laid where there is a risk of melting and direct UV exposure.
The advantage of metal pipes is the lower price of the entire heating circuit, ease of installation and fewer problems encountered during operation of the system.

Significant advantage systems with radiators is the ease of temperature adjustment. Even the most accurate calculations of room temperature can be adjusted. For example, a temperature of 19-21°C is recommended for a small child under 6 months, while a comfortable temperature in the rest of the house is considered to be 25°C.
To ensure this temperature for a long period of time in the room, you must completely or partially close the heat supply valve to one of the radiators. In the case of a metal pipe, the issue can also be solved, but in a more complex way: reduce the heat transfer of a pipe segment using polyurethane foam or foil shell.
Another heating circuit option could be water heated floor. This is a very comfortable type of heat supply for a person, but installing a heated floor is much more labor-intensive than the previously discussed options.
In addition, when using a heated floor, it is not possible to provide a slope for the natural circulation of water, which, in combination with the small diameter of the underfloor heating pipes, leads to a mandatory condition for the use of a circulation pump.

Preventing heating system freezing
Using water as a coolant has one drawback - if the heating system freezes, the pipeline and appliances will be damaged. It is especially difficult to restore in this case the heat exchanger integrated into the furnace.
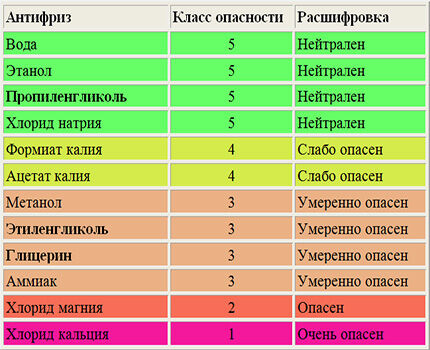
This problem is relevant for houses that may not be heated for a long time in winter. One way to prevent system damage is to use antifreeze designed for heating systems instead of water.
For residential premises, liquids based on propylene glycol are used as antifreeze, as a non-toxic substance, unlike ethylene glycol.
However, the idea of using antifreeze has its downsides:
- antifreeze based on propylene glycol is expensive (from 80 rubles / liter);
- the specific heat capacity of antifreeze is less than that of water (approximately 15%), therefore a larger furnace power and a large surface area of room heating devices are required;
- antifreeze has a higher dynamic viscosity than water, so a more powerful circulation pump is required, and natural circulation is impossible;
- when heated, antifreeze expands up to 40%, so it is necessary to use a large closed expansion tank;
- propylene glycol is very fluid, so it penetrates through connections in the heating system through which water cannot penetrate;
- propylene glycol is incompatible with galvanized pipes because antifreeze additives lose their properties upon contact;
- when antifreeze boils (which is likely when using furnaces), an irreversible chemical reaction occurs, as a result of which the entire system will have to be drained and antifreeze refilled.
For antifreeze, the heating system must be calculated in advance - its use in projects implemented for water is quite problematic.
Moreover, a project using antifreeze will be much more expensive than a water heating system. Therefore, its use has not yet become widespread in private homes with stove heating, and other methods are used to prevent freezing.
Draining water from the circuit and jacket or register of the furnace is the most common solution to the problem when the owners of the house are absent for a long time.In addition to the additional work, the disadvantages of this method include access of air to the metal elements of the system from the inside and, as a result, the spread of corrosion.
Also, as a solution to the problem for a short period of time, they use the integration of a low-power electric boiler into the heating circuit. Its operation at a minimum level of energy consumption is able to temporarily maintain a positive water temperature.

Conclusions and useful video on the topic
A working heating system based on a stove and a water circuit in a private house with an area of 80 square meters:
Heat is supplied to the heating system from stoves and fireplaces in portions, which complicates the task of calculating the parameters of the heating circuit elements. Carrying out work on altering the circuit is quite problematic, so if you lack experience in this area, it is better to turn to specialists who have the skills to solve such problems.
Do you have experience in organizing stove heating? Or do you heat your home this way and would like to share your impressions of using the stove? Please leave comments and ask questions. The feedback form is located below.




Now in my house there is an ordinary red brick stove. Steam heating system. I’m not happy with this look, but I bought a house with this system and haven’t changed anything in this regard yet. It takes a very long time to heat all the pipes so that all the pipes heat up, while they cool down in an hour if the briquette does not smolder in the stove, maintaining the temperature of the boiler.Sometimes the pipes begin to bubble, a very unpleasant sound. In addition, I often add water to the pipes. You have to resort to all sorts of tricks. I'm thinking about changing the system to an air system.
We used to have a large Russian stove. It took up half the kitchen. They took it apart and installed another one. The boiler remained the same. It’s a pity, of course, that the grate bars are ordinary. You could put the tubes in, connect everything into one and it turned out just great. Our house is small. We recently insulated the outside, and now the savings are clearly visible. There are plans to install a pump that would circulate the liquid through the system. Well, I think pouring antifreeze into pipes is complete nonsense. Only water and nothing more.
For as long as I can remember, there have always been pipes at home, not radiators. Neat and beautiful. I don’t want to change anything, it’s always warm at home.
The question is different. We've added a new half to the house - is it possible to feed it in different directions? I'm afraid that if I attach it to the old system, already to the return line, it will be cold in the new half. Both the old and new parts of the house are 60 sq.m.
Please, those who understand, tell me how to save the old system!?
Hello. Marina, you should at least sketch out a diagram of your heating system and describe what type of boiler you have. We would tell you the best way to provide heating in your extension with a minimum of losses. Theoretically, this is possible using valves to regulate the flow.
We decided to break down the old stove with a gas burner. And build a new one with a burner too. But I don’t know whether it is necessary to make a metal casing for the stove, because... old one in a casing. Previously, gas workers did not allow connection if the stove did not have metal piping.
Hello, we also have stove heating combined with an electronic boiler, we decided, in the event of a power outage, to connect a diesel generator to the house (we have it in the garage). When the electricity is turned off, we disconnect from the general network and switch the switch to the network connected to the generator. Very comfortably. I have a question: please tell me, is it possible to combine stove heating at home and heating water for washing, i.e. I would like that at the same time, while heating the house, I would also have hot water so that I can wash the dishes and wash myself?
Hello!
I would like to consult about heating in an apartment that is located in a two-story building. This is the only apartment and it is private in a municipal building. Apartment with an area of 100 square meters. Now it is undergoing a major renovation and the previous heating system has been completely removed from the apartment. She has fallen into disrepair. The heating was gas. The building itself has gas heating.
I would like to install stove heating in the apartment. How reasonable is this? The apartment is located in the south of Russia in the Rostov region. What type of stove heating would you recommend? Ideally, I would like to move away from the gas system and use a more environmentally friendly type of energy.
I considered heating options from solar collectors/panels, but the company I spoke with explained that the apartment should have another heating system: electric, gas, etc.
What would you recommend in this case? What companies could you recommend in my region? I did not find any companies on the Internet offering stove heating in Rostov-on-Don and the Rostov region.Do you work in other regions? What could be the price for such heating in an apartment with an area of one hundred square meters? Meters
Thanks a lot.