Designing heating systems for country cottages: how not to make mistakes
If you are building a country house or are seriously renovating an existing one, already at the planning stage you need to take care of how the premises will be heated during the cold season.
Correct design of heating systems in private residential construction is a guarantee of winter comfort, rational use of resources and efficient operation of equipment.
In this material we will look at heating systems for a private home, tell you how to choose the best option and show with an example how to properly design a heating system.
The content of the article:
Step 1 - heating diagram
The primary task when designing heating is to decide on a heating scheme. There are one-pipe and two-pipe schemes. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Think about what is more important to you: cost savings, uniform heating or aesthetics.
What is a one-pipe scheme?
A single-pipe house heating circuit is a chain of radiators connected in series. The coolant at the required temperature flows from the riser into the heating main.
It moves from one radiator to another, gradually releasing some of the heat. Therefore, heating may be uneven.
When implementing a single-pipe scheme with top distribution, the main pipe is laid along the perimeter of the entire heating circuit above the appliances and window openings. In this case, the radiators are connected at the top, which in itself is not very aesthetically pleasing.
Both at the inlet and outlet the radiator is equipped with shut-off valves. A thermostatic head can be installed at the inlet.
In schemes with bottom wiring, the pipeline runs below the heating devices. This option looks much better, but requires the mandatory installation of Mayevsky taps on each battery.
They are necessary to remove excess air from the top of the batteries, formed as a result of the coolant being supplied from below without first passing through an open expansion tank for degassing.
Advantages of single-pipe heating of a country house:
- savings on materials;
- ease of design and installation.
A relatively small number of pipes has a noticeable impact on the appearance of the heating system, which in most cases is laid in an open way.
Flaws:
- Difficulty controlling temperature;
- the operation of each radiator depends on the condition of the entire system;
- limited length, the ability to process a contour no more than 30 m long.
To ensure the possibility of temporary or permanent shutdown of one or more radiators without stopping the system, a bypass is laid under each of them - a bypass pipe with a valve system.
Improvement Leningradka schemes connecting the battery by installing two or three shut-off valves allows you to turn off a separate device for repairs without stopping the system and draining the coolant from it. Read more about installing a single-pipe heating system in a private house Further.
Two-pipe heating model
A much more advanced scheme is a two-pipe one. The principle of its operation is that there are two pipes - supply and return, to which radiators are connected in parallel.

The coolant flows through the supply pipe to each device at the same temperature. After passing through the radiator, the water enters the return pipe. This scheme can ensure uniform heating of the entire cottage.
Advantages of a two-pipe heating scheme for a country house:
- independence of devices from each other;
- uniform heating;
- the ability to control the heat transfer of each radiator using thermostats installed on the devices.
In addition to the relatively high consumption of materials and design costs, two-pipe system heating has virtually no disadvantages.
Step 2 - calculations and architectural part
The architectural part of heating design involves the arrangement or construction of a room for equipment - a boiler room in a country house, as well as the selection and calculation of a chimney.In order to correctly design the equipment power, pipe diameter, coolant volume and other parameters, calculations should be made.
The calculation part does not require deep knowledge from the field of higher mathematics; it is enough to substitute the necessary coefficients into the formulas and use a calculator.
Boiler room design according to all the rules
Before you start designing the wiring and purchasing materials, you need to choose a suitable location for the heat generator. This could be a separate room in the house - a boiler room. If there is no extra room, you can build an extension.
For a gas boiler that will operate from a central gas pipeline, you need to organize the boiler room in accordance with all the rules, because gas services strictly monitor compliance with the operating standards of gas equipment. If the boiler is placed in the wrong place or with violations, the project will not be signed and the use of the boiler will be prohibited until the comments are eliminated.

Basic requirements for boiler rooms in cottages:
- ceiling height from 2.5 m;
- room volume from 15 m3;
- the boiler room enclosing structures must have a fire resistance limit of 0.75 hours;
- natural lighting should be provided;
- Ventilation is required.
The location of the boiler also depends on its power. So, if the power of the unit is 151-350 kW, it can only be located in a separate room in the basement or first floor, as well as in an extension. Boilers with a capacity of 61-150 kW can be located on the second or subsequent floors.
Appliances up to 60 kW can even be located in the kitchen of a country house, provided there is a window with a window. We also recommend reading the material on how to competently arrange a boiler room in a country house.
Choosing a chimney and deciding on the size
Another important detail when designing is chimney. It will remove combustion products outside. Basic requirements for chimneys:
- The fire resistance limit of the material should not be less than 1 hour;
- all connections and joints must be treated with fire-resistant materials;
- the chimney must be absolutely gas-tight;
The cross-section of the chimney is determined in accordance with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.05-91. The size of the chimney duct depends on the power of the heat generator.
Based on the materials used, chimneys can be:
- brick;
- metal;
- ceramic.
The brick version is usually designed during the construction of a country house. pipes are wall, mounted and root. The installation of a wall option is possible only during the construction of the walls of the building. The root and mounted type can be built both after the construction of the walls and after the construction of the roof.

Metal chimneys are now used everywhere. Stainless steel is a reliable, durable material that is not afraid of hot combustion products. Modern chimneys are designed in the form of so-called sandwich systems. A stainless steel pipe is placed in the same, but larger diameter. The free space between them is filled with insulation, usually basalt wool.
Ceramic chimney pipe is not used very often.Its main advantage is high heat resistance, and its main disadvantage is fragility. In addition, a ceramic chimney is quite heavy.
Designing a chimney is a crucial step. The hole size is one of the most important parameters. It depends on the performance and power of the boiler.
Average diameters of round chimneys:
- for boilers with a power of up to 3.5 kW - 16 cm;
- up to 5.2 kW – 19 cm;
- up to 7.2 – 22 cm.
When calculating the height of the chimney, the height of the roof and the distance from the chimney to the ridge are taken into account. If the pipe is located close to the top point of the roof (up to 1.5 m), the height of the chimney will be 0.5 m higher than the roof. If the distance between them is greater (from 1.5 to 3 m), the chimney must be at least on one level with the skate.
Calculation of the required system power
In order to calculate the heating system of a country house, you need to take into account several factors at once, these are:
- climatic zone in which the cottage is located;
- power of the thermal energy source;
- sources and volume of heat loss;
- area and volume of heated premises;
- number of radiators and their size;
- presence of insulation of enclosing structures.
To select the power of the boiler and heating radiators, use the following formulas:
MTo=Spom. x MINDTo/10 + 30%, Where:
MTo – boiler power;
Spom. – area of the room;
MINDTo – specific boiler power per 10 kW. m of heated area.
MINDTo depends on the region. For Moscow and the Moscow region, the value is 1.2-1.5 kW. A margin of 30% will be sufficient for a single-circuit boiler. If a dual-circuit circuit is assumed, it is necessary to add another 20% for water heating.
Thus, a 9×9 house in the Moscow region can be heated by a single-circuit boiler with a capacity of: MTo=81 x 1.5/10 + 30% = 16 kW.
Knowing the power of the equipment, you can calculate the minimum volume of water in the cottage heating system using the formula:
V= MTo x 15.
For the same house in the Moscow region, the system will need to be filled with V = 16 kW x 15 = 240 liters of coolant.
Circulation - natural or forced?
When designing heating for a country house, you need to decide how the coolant will circulate in the system: under the influence of gravity or using a pump.

The natural method is good because the system does not require electricity to function. Circulation is carried out due to the physical properties of the liquid when the temperature changes.
Disadvantages of a system designed according to this principle:
- need more coolant;
- pipes must be larger in diameter;
- a slope of 2% must be maintained.
In addition, to balance the temperature in the network with natural circulation it is necessary to increase the number of sections for batteries located furthest from the boiler.
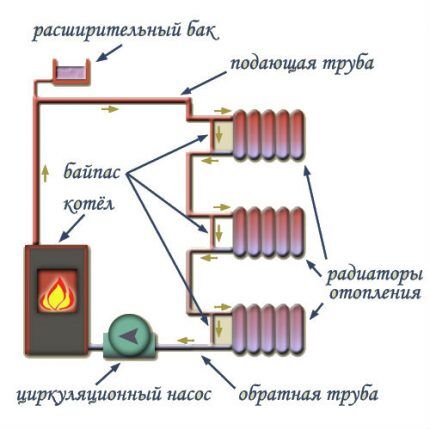
Forced circulation operates with a much smaller amount of liquid and pipeline diameter, no slope is required, and the choice of radiators is significantly expanded.
However, for full operation, it will be necessary to equip the system not only with a pump, but also with measuring instruments and an expansion tank. All this must be taken into account when designing the system with forced circulation.
Step 3 - choosing an energy carrier
The basis of the entire heating system is the boiler. Depending on the type of fuel used for heating, there are 4 categories of boilers:
- solid fuel;
- diesel;
- gas;
- electric.
Having learned the main characteristics of all types of thermal energy generators for a cottage, you will not be mistaken in choosing the appropriate option.
Solid fuel - a proven method for centuries
For country cottages it is often chosen solid fuel models boilers This is due, first of all, to the availability of raw materials.
A solid fuel boiler can operate not only on coal or wood, but also on wood processing waste, pellets, briquettes, peat, and even organic fuel made from manure. The main thing is to have somewhere to store the entire fuel supply. As for the efficiency of solid fuel systems, it is quite low - about 75% on average.

Another advantage of such a boiler is ease of operation. In addition, when using solid fuel, the system heats up very quickly, which is important for country cottages. But at such a heating rate, you have to constantly add fuel to the firebox, otherwise the system will soon cool down.
When buying a solid fuel model, be prepared to load it every 4-5 hours. At the same frequency, you will have to clean the ash pan from soot and ash.
How does a diesel boiler heat?
Diesel boilers run on light heating oil – a type of diesel fuel. It differs from automobile diesel fuel in that the requirements for its quality are not so high, but such fuel is cheaper due to the absence of a road tax.
To use a diesel boiler, you need to install a diesel fuel tank with a volume of at least 750 liters. You can imagine how much space it will take up in the boiler room.

The advantages of this type of heating include the low cost of equipment, automatic switching on and off. But it is undesirable to leave such a system unattended for a long time.Another disadvantage of this device is noise during operation.
Eco-friendly electric heater
Using electricity to heat a country house would seem to be a simple and profitable solution. But here everything is not so simple. The fact is that the total power of electrical equipment that you can install in your cottage is limited by the energy supplier.
Look at the electrical panel. Let's say the current indicated is 16 A. Knowing the voltage in the network (220 V), you can calculate the permissible power.
16A x 220V = 3520W.
3520 W – maximum permissible power. This means that a boiler with a power exceeding 3.5 kW is not suitable for your country house. All that remains is to write an application for permission to install machines of higher power. The electric boiler can be connected to a regular outlet, or it can operate on three-phase current (380 V).

Advantages of an electric heating source:
- autonomy (does not require constant supervision);
- automatic temperature support;
- no chimney needed;
- environmental friendliness - no combustion products;
- ease of use.
The disadvantages include high energy consumption. We also recommend reading our other article, which describes the system in detail. electric heating.
We use blue fuel - gas model
A gas boiler is one of the most common and widely represented on the market. It runs on natural gas and can be connected to a gas pipeline or cylinder if the gas is imported.
For liquefied gas in cylinders, this type of boiler is not the most convenient.One 50-liter cylinder is enough for 1-2 days of heating a country cottage.

There are single-circuit and double-circuit gas boilers. A single-circuit boiler is intended purely for heating a room. The double-circuit one also has a function for preparing hot water - it acts as a gas water heater. If you plan to periodically live in your country house in winter, then it makes sense to install a double-circuit boiler.
But if during the cold season you will be away for a long time and turn off the boiler, it is better to purchase a single-circuit one. The experience of many users shows that draining water from the system for temporary preservation in double-circuit models is difficult; some of the water may remain in the system, which is very dangerous and threatens freezing and cracking of pipes.
Step 4 - other components of the system
In addition to the heart of the cottage heating system - the boiler, it also includes other equipment. Correctly designing the circulation pump, expansion tank, radiators or underfloor heating coils and piping material is no less important than choosing the boiler itself.
Therefore, do not neglect a detailed study of the characteristics of additional equipment and the subtleties of its selection.
Pump - where to install it?
Designing heating with forced circulation assumes the presence of a pump. For country houses, as a rule, wet-type circulation pumps are used.
When choosing a pump, consider the following parameters:
- pressure;
- performance;
- operating conditions (room area, selected coolant, type of connection, pipe diameter);
- additional aspects (noise level during operation, unit dimensions).
When designing heating in your own country house, it is important to find the most suitable place in the circuit for inserting the pump. By and large, a properly selected pump will do its job equally well in any part of the system.
The reason why it is recommended to install it in front of the heat generator - on the return line - is that there is less wear on the equipment when pumping water at a relatively low temperature.

For reliable operation of the pump, it is important to take care of the filter when designing. The coarse filter is installed directly in front of the pump. It catches particles that have entered the water in the heating circuit. If you ignore installing the filter, the pump can quickly fail.
Safety group and expansion tank
Since the heating circuit is a closed system, and water tends to increase in volume when heated, an expansion tank must be designed into the heating system of a country house. As the pressure in the pipes increases, excess coolant enters the tank, thereby reducing the dangerous pressure.
The safety unit is a set of three devices that ensure reliable and safe operation of the entire heating system of the cottage.
These include:
- pressure gauge - for measuring pressure;
- safety valve;
- air vent.
There are no questions with the pressure gauge - it should be designed to measure pressure of 2-3 atmospheres. That is, a 4 atm pressure gauge. it will be just right. The safety valve performs the same function as the expansion tank, but in emergency cases when the tank does not work for some reason.
When the pressure increases critically, the excess is removed from the system through the valve drain hole.

The air vent must protect the boiler from air accidentally entering the heating circuit. Since air bubbles in the water rise upward, devices for removing excess air are installed at the top of the riser or each battery.
Pipeline and radiators - calculation and selection
The next step is to decide on the pipe material for the heating circuit. The options could be:
- steel;
- polypropylene;
- metal-plastic;
- polyethylene.
Steel pipes Previously used for heating country houses. They are durable and not afraid of high pressure. Their main disadvantage is their susceptibility to corrosion. Rust can eat through the steel, fistulas appear in the pipes and the entire system becomes unusable.
Due to corrosive deposits on the inner surface of steel pipes, the clearance decreases over time. And to install them you will need at least a qualified welder.
The weak point of any pipeline is the connections. When designing a heating circuit made of polypropylene, you don’t have to worry about this. The pipes are connected by welding - with a special soldering iron. The joints are monolithic.
Polypropylene pipes are not subject to corrosion, they are practically not contaminated from the inside, durable, lightweight and inexpensive.

Metal-plastic pipe sold in long coils - up to 500 m.Thus, you can completely avoid connecting the pipeline from separate parts by laying metal-plastic pipes along the entire heated perimeter of the cottage. They also do not rust, nothing is deposited in them, they are durable. But you need to protect metal-plastic pipes from UV rays and damage during installation.
Polyethylene pipes used for hot water supply, heating and installation of warm water floors. They have the same advantages as others, but their main disadvantage is the high cost of the pipes and fittings themselves.
What is better - a radiator or a warm floor?
In a country house, sectional, plate or panel radiators are used as a heat emitter.
Such batteries can be:
- cast iron;
- aluminum;
- steel;
- bimetallic.
Cast iron batteries very heavy and fragile, but give off heat well. Aluminum models are lightweight and inexpensive, but are chemically unstable, subject to corrosion and are susceptible to pressure surges. Steel batteries also suffer from corrosion, but are chemically resistant.
Bimetallic battery type combines the advantages of aluminum and steel radiators. The coolant moves in a steel pipe and does not come into contact with the aluminum body. This option is suitable when using antifreeze rather than water in the circuit.
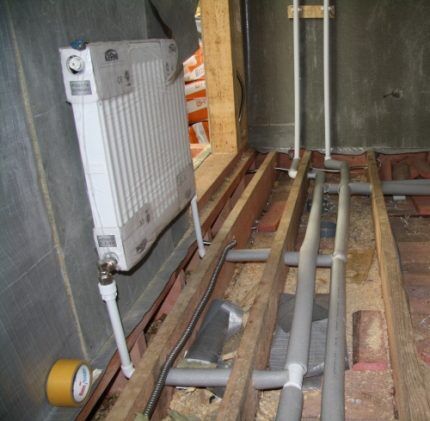

The batteries are located under window openings - in places where the wall cools the most. As a result, you can avoid fogging up the glass and causing condensation on the walls. The number of radiators depends on the number of openings, but not less than 1 per heated room. Read more about calculating heating radiators Here.
When building a cottage, it is important to design a heated floor to heat the room. Water heated floors are pipes laid under the floor covering, which are part of the heating circuit. This design is very effective.
You need to design a heated floor together with the entire system and take its presence into account when calculating the boiler power and the number of radiators.
Features of choosing a coolant
The coolant is clean water or antifreeze. Water, of course, is cheaper and more accessible. It has a high heat capacity and copes well with its function. However, which is especially important for country houses, when the boiler is stopped, there is a risk of water freezing inside the system and damage to the pipeline.
For such cases, you can design a system with antifreeze as a coolant. It does not freeze, has good fluidity and heat capacity.However, this is an environmentally unsafe substance. It is prohibited to pour it into the sewer. Most boilers are not designed to work with antifreeze. And besides all of the above, antifreeze is also much more expensive than water.

Step 5 – Wiring Design + Examples
Pipeline assembly can be done in several ways:
- tee assembly type;
- collector
The second name for a collector connection is radial. A manifold is connected to the boiler, and pipes run from it under the floor to each of the radiators.

The collector circuit is implemented using flexible metal-plastic pipes. After laying the flooring materials, all heating pipes are completely hidden and do not spoil the appearance of the room. Inputs and outputs to each radiator are supplied from below directly from under the floor.
Tee connection is carried out through the connection of all heating devices with tees to the supply and return pipes. It is easier to implement such a scheme; you do not need to spend money on collectors and look for a place to install them, which is usually done in the center of the building to equalize the length of the rings connected to the comb.
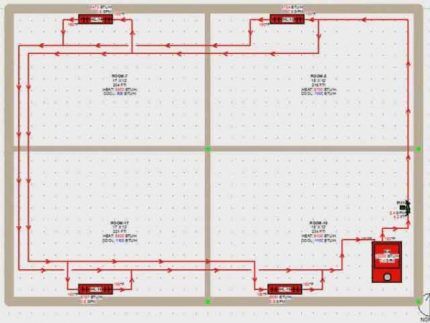
In order not to reinvent the wheel, you can use one of the standard heating layouts for a country house, which are successfully used in construction. The traditional single-pipe model is well illustrated in the following drawing.
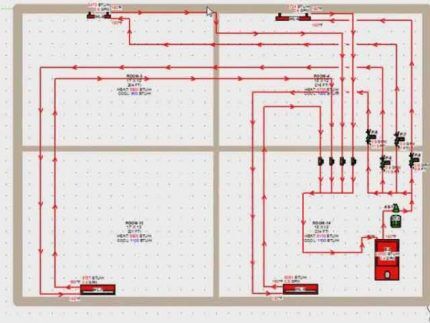
For a typical cottage, a combination of one- and two-pipe schemes is often used. In this case, the wiring diagram looks like this.
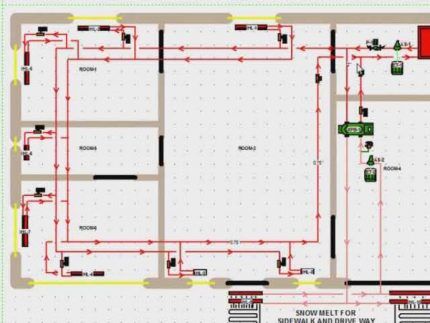
The same house can be heated using a collector circuit.
In this diagram, a separate branch leaves the boiler and goes to the porch of the house. This is heated steps to prevent ice formation.
The main part of the circuit is a two-pipe system, while the additional branch is a single-pipe system.
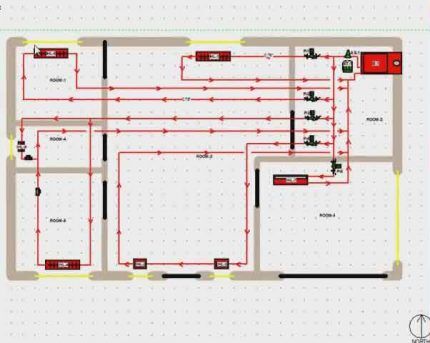
In the following diagram, the heat pipe has outlets to each of the rooms. That is, each room is heated by a separate circuit.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video shows the main methods for connecting radiators and describes the advantages of each of them:
This video describes in detail all the nuances that should be taken into account when choosing heating pipes:
Here is a good example of designing a combined system for heating a two-story cottage:
Since the heating system of a country house must, first of all, be reliable and efficient, maximum attention should be paid to the development of the project. Any unaccounted for detail can negatively affect the performance of the heating.It is better to entrust the design to a professional to avoid mistakes.
If you have already had to design and install a heating system for your home yourself, and you know the subtleties that you definitely need to pay attention to, please share your knowledge and experience with our readers. Leave comments in the block below.

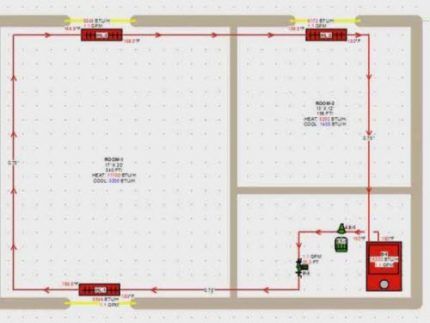




Aesthetics are good, but single-pipe systems are best used only in one-story small houses, so that the length of heating branches is no more than 30 m.
Make two-pipe ones, but it’s better to have a slope, so that if the pump or boiler fails, the coolant would still continue to move to the boiler. Place the pump at the outlet of the boiler, so that if the house defrosts and the pipes freeze, you can push through the ice with hot water without resorting to heating the pipes and radiators along the entire length. In single-pipe schemes, take into account that the further the room is from the boiler, the lower the temperature of the coolant reaching it will be, so add battery sections to the calculation.
I will add that it is better not to connect a warm floor with a heating system. It is difficult to calculate and adjust hydraulics if radiators and heated floors are powered by adjacent circuits from one boiler. And in general, in my opinion, it is better to make heated floors electric, except in cases where there is a clear excess of coolant (which, to put it mildly, is rare in practice).
Where can I order a heating and water supply project for a one-story house?