Features of connecting automatic machines and RCDs in the panel: diagrams + installation rules
The comfortable living of all its inhabitants and the uninterrupted operation of household appliances depend on the correct connection of electrical wiring in the house.Do you agree? To protect the equipment in the house from the consequences of overvoltage or short circuit, and the inhabitants from the dangers associated with electric current, it is necessary to include protective devices in the circuit.
In this case, it is necessary to fulfill the main requirement - the connection of the RCD and circuit breakers in the panel must be done correctly. It is equally important not to make a mistake when choosing these devices. But don't worry, we'll tell you how to do it right.
This article will discuss the parameters by which RCDs are selected. In addition, here you will find features, rules for connecting machines and RCDs, as well as many useful connection diagrams. And the videos given in the material will help you put everything into practice, even without the involvement of specialists, if you have at least a little knowledge of electrical engineering.
The content of the article:
Basic principles of connection
To connect the RCD in the panel, two conductors are needed. Through the first of them, the current flows to the load, and through the second, it leaves the consumer along the external circuit.
As soon as current leakage occurs, a difference appears between its values at the input and output. When the result exceeds the specified value, RCD triggers in emergency mode, thereby protecting the entire apartment line.
Residual current devices are negatively affected by short circuits (short circuits) and voltage surges, so they themselves need to be covered. The problem is solved by including automata in the circuit.
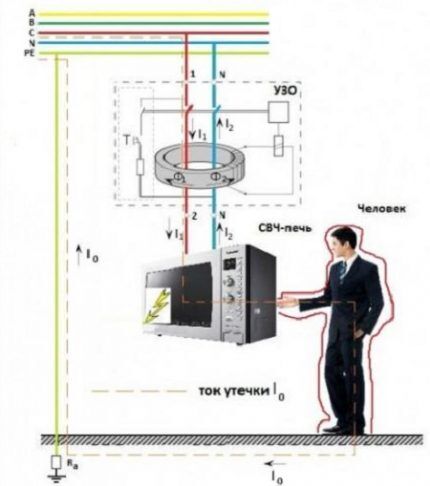
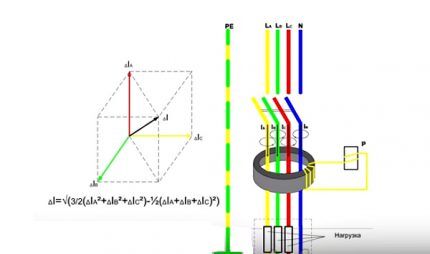
The current powering electrical appliances flows through one of the core windings in one direction. It has a different direction in the second winding after passing through them.
Independent installation of protection devices involves the use of diagrams. Both modular RCDs and machines for them are installed in the panel.
Before starting installation, you need to resolve the following issues:
- how many RCDs should be installed;
- where they should be in the diagram;
- how to connect so that the RCD works correctly.
The rule of electrical installation is that all connections in single-phase network must fit into the connected devices from top to bottom.
Professional electricians explain this by saying that if you start them from below, the efficiency of the vast majority of machines will decrease by a quarter. In addition, the foreman working in the switchboard will not have to further understand the circuit.
RCDs designed for installation on separate lines and with low ratings cannot be installed in a general network. Failure to comply with this rule will increase both the likelihood of leaks and short circuits.
Selection of RCD according to main parameters
All technical nuances associated with the choice of RCDs are known only to professional installers. For this reason, specialists must select devices when developing a project.
Criterion #1. The nuances of selecting a device
When choosing a device, the main criterion is the rated current passing through it in long-term operating modes.

The value of In is in the range of 6-125 A. Differential current IΔn is the second most important characteristic. This is a fixed value, upon reaching which the RCD is triggered. When choosing it from the range: 10, 30, 100, 300, 500 mA, 1 A, safety requirements take priority.
Affects the choice and purpose of installation. To ensure the safe operation of one device, they are guided by the rated current value with a small margin. If protection is needed for the house as a whole or for an apartment, all loads are summed up.
Criterion #2. Existing types of RCDs
RCDs should also be distinguished by type. There are only two of them - electromechanical and electronic. The main working unit of the first is a magnetic circuit with a winding. Its action is to compare the values of the current going into the network and returning back.
There is such a function in the second type of device, but it is performed by an electronic board. It only works when there is voltage. Because of this, the electromechanical device protects better.

In a situation where a consumer accidentally touches a phase wire and the board turns out to be de-energized, if an electronic RCD is installed, the person will come under voltage. In this case, the protective device will not work, but the electromechanical device will remain operational under such conditions.
The subtleties of choosing an RCD are described in this material.
Installation of RCDs and automatic machines in the panel
The electrical panel, in which the metering and load distribution devices are located, is usually the place for installing the RCD. Regardless of the chosen scheme, there are rules that are mandatory when connecting.
Main rules of connection
Along with the automatic shutdown device, the panel is also equipped with machine guns. All you need for this is a minimum of tools and a competent diagram.
The standard set should consist of:
- from a package of screwdrivers;
- pliers;
- side cutters;
- tester;
- socket wrenches;
- Cambric.
Also for installation you will need a VVG cable of different colors, selected in cross-section in accordance with the currents. The PVC insulating tube is used to mark the conductors.
When there is space on the DIN block available on the panel, a residual current device is mounted on it. Otherwise, install an additional one.
The key principle of installation is the following: contact of the neutral conductor after the RCD with either the input zero or grounding is unacceptable, therefore it is insulated in the same way as other conductors.
The circuit breaker must be switched on in series with the RCD. This is also one of the most important rules.
When the entire home is protected using one RCD, a circuit that includes several circuit breakers is used.

The project includes, in addition to additional AVs, one more component - a zero bus insulator. Mount it on the panel body or on a DIN rail.
This addition is introduced due to the fact that with a large number of neutral conductors connected to the output terminal of the disconnecting device, they simply will not fit in one clamp. An isolated zero bus is the best way out of this situation.
Sometimes electricians, in order to place the entire bundle of neutral wires in the socket, decide to cut the cores of a single-core cable. In the case where the cable is multi-core, several cores are removed.
It is better not to use this option, since due to a decrease in the cross-section of the conductors, the resistance will increase, and therefore the heating will increase.
Both the number of mounting holes and their diameter may vary. The ground bus is attached directly to the body.
Neutral wires in one twist are an additional inconvenience when identifying damage on the line, as well as when you need to dismantle one of the cables. Here you cannot do without unscrewing the clamp and unwinding the harness, which will certainly provoke the appearance of cracks in the veins.
You cannot install two wires simultaneously into one socket. The inputs of the circuit breakers are connected by jumpers. As the latter, during professional installation, special connecting tires called “comb” are used.
Features of connection diagrams
The choice of scheme involves taking into account the characteristics of a particular electrical network. Among the numerous options, there are only two circuits used to connect machines and RCDs in shield, considered basic.
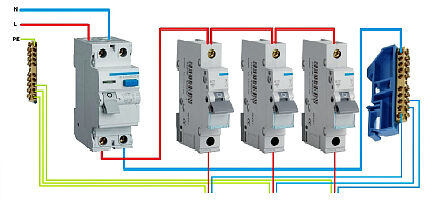
The first and simplest method, when one RCD protects the entire electrical network, has disadvantages.The main one is the difficulty in identifying the specific location of the damage.
The second is that when some kind of failure occurs in the functioning of the RCD, the entire system will be taken out of operation. The residual current device is allocated a place immediately after the meter.
The next method provides for the presence of such devices on each individual line. If one of them fails, all the others will be in working order. To implement this scheme, a larger shield and greater financial costs are required.
Details about a simple scheme
Let's consider connecting an RCD with automatic circuit breakers to a simple residential switchboard. At the entrance there is a two-pole automatic switch. A two-pole RCD is connected to it, to which there are two single-pole circuit breakers.
A load is connected to the output of each of them. In principle, RCDs are introduced into the circuit in the same way as circuit breaker.
The phase supplied to the circuit breaker enters the input of the RCD with output to the circuit breakers. The zero output from the machine goes to the zero bus, and from it to the input to the device.
From its output, the neutral conductor is directed to the second neutral bus. The presence of this second bus contains a special nuance, without knowing about which it is impossible to achieve normal functioning of the circuit.
During operation, the RCD controls both incoming and output voltage - as much as is at the input, so much should be at the output.
If the balance is disturbed and the output is greater by the value of the setting to which the RCD is configured, it is triggered and the power is automatically turned off. The zero bus is responsible for this process.
In electrical circuits where the installation of a residual current device is not provided, there is only one common zero.
In circuits with RCDs the picture is different - there are already several such zeros present. When using one device, there are two of them - the common one and the one in relation to which the protective device operates.
If two RCDs are connected, there are three zero buses. They are designated by indices: N1, N2, N3, etc. In general, there are always one more zeros than residual current devices. One of them is the main one, and all the others are tied directly to the RCD.

If not all equipment is supposed to be connected through the RCD, then zero is supplied from the common bus. In this case, the residual current device is removed from the circuit.
When adding a single-pole circuit breaker operating from an RCD, the phase from the output of the latter is supplied to the input of the circuit breaker. From the output of the switch, the conductor is connected to one load contact. Zero on it is brought to the second conclusion. It comes from the zero bus created by the RCD.
There is one more element on the shield - a protective grounding bus. Correct operation of the RCD without it is impossible.
Three-wire network is only available in new houses. It must have a zero phase and grounding. In houses built a long time ago, there is only a phase and a zero. In such conditions, the RCD will also function, but slightly differently than in a three-phase network.
As a way out, the grounding is carried out by a third conductor to the sockets, and then to the ceiling to the place where the chandeliers are connected. Ground is not supplied to the switches.
Option for connecting machines without RCD
There are times when one of the machines needs to be connected without bypassing the residual current device. Power is connected not from the output of the RCD, but from the input to it, i.e. directly from the machine. The phase is supplied to the input, and from the output it is connected to the left terminal of the load.
Zero is taken from the common zero bus (N). If a fault occurs in the area controlled by the RCD, it will be removed from the circuit, and the second load will not be de-energized.
RCD in a three-phase network
A network of this type includes either a special three-phase RCD with eight contacts, or three single-phase ones.
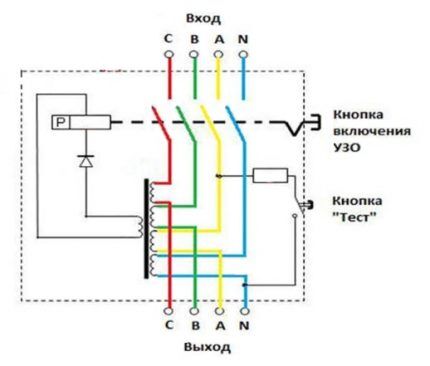
The connection principle is completely identical. Mount it according to the diagram. Phases A, B and C supply power to loads rated at 380 V. If we consider each phase separately, then in tandem with cable N (0), it provides a series of single-phase 220 V consumers.
Manufacturers produce three-phase trip protection devices adapted to high leakage currents. They only protect electrical wiring from fire.
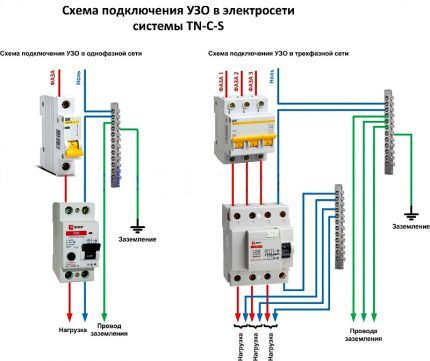
In order to protect people from the effects of electric current, single-phase two-pole RCDs are installed on the outgoing branches, configured for leakage current in the range of 10-30 mA. For cover, a machine gun is placed in front of everyone. In the circuit after the RCD, the working zero and ground cannot be connected.
RCDs and circuit breakers on a three-phase switchboard
Let us examine in detail a not entirely standard circuit assembled on a three-phase distribution panel.
It contains:
- three-phase input circuit breakers - 3 pcs.;
- three-phase residual current device - 1 pc.;
- single-phase RCDs - 2 pcs.;
- single-pole single-phase circuit breakers - 4 pcs.
From the first input circuit breaker, voltage is supplied to the second three-phase circuit breaker through the upper terminals. From here, one phase goes to the first single-phase RCD, and the second to the next.

Single-phase RCDs installed on the panel are two-pole, and automatic machines are single-pole. For the protective device to function correctly, it is necessary that the working zeros after it are not connected anywhere else. Therefore, after each RCD, a zero bus is installed here.
When the machines are not one-pole, but two-pole, then there is no need to install a separate zero bus. If two zero buses are combined, false positives will occur.
Each of the single-pole RCDs is designed for two circuit breakers (1-3, 2-4). A load is connected to the lower terminals of the machines.
The common ground bus is installed separately. Three phases enter the input circuit breaker: L1, L2, L3 and the working neutral wire.
The zero is connected to the common zero, and from it goes to all the RCDs. Then it goes to the load: from the first device - to three-phase, and from the next single-phase - each to its own bus.
Although this distribution panel has a three-phase input, the wire is not divided into PEN and PE, because five-wire input. Three phases, zero and grounding come to the shield.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Nuances of installing all elements on the apartment panel:
RCD installation details:
RCDs and automatic machines are technically complex equipment. It is advisable to install it in places where electric current can pose a threat to both the safety of people and home appliances.
Its installation requires taking into account many parameters, so both calculation and installation are best performed by qualified specialists.
If you have experience in installing RCDs yourself, please share it with our readers. Tell us what points should be given special attention. Leave your comments and ask questions in the block below the article.




In all the photos and drawings here (and on other sites), the phase wire passes through the left arm of the RCD (etc.), and “N” through the right. Whereas on the RCD of the company “DIN Electro Craft”, Moscow, the symbols “N” are brightly affixed on the left shoulder. What is more correct, if I can ask the question this way?
And another question - on the RCD (etc.) it is often stamped “Remove the plug (or plugs) for installing additional devices.” It’s clear what the plugs are, but I haven’t come across what devices and what they look like. Which?
Good afternoon, Boris.
Correct connection is guaranteed by symbols printed near the terminals. If there are no symbols, then you need to read the passport. For example, on a Schneider Electric RCD modification EASY 9 2P with a leakage current of 30 mA, the zero is connected on the left, and on a TDM RCD - model VD63 (rated 16 A, leakage current 30 mA) - on the right. I have attached screenshots of these RCDs.
Regarding the second question, I can assume that additional devices are, for example, complete busbars that provide quick installation of machines connected to an RCD.In the article, please note that all photos contain wiring. A number of foreign manufacturers offer accelerated installation using tire kits. I have attached a screenshot of such a layout.
Where in nature is there even a five-wire automatic machine that you write about...
“The common grounding bus is installed separately. Three phases enter the input circuit breaker: L1, L2, L3, the working neutral wire N and PE - protective.” - There are none, there are only four wires: three phases and zero, ground, ne. PE, in English, earth potential, is never switched, otherwise it is not earth.
Good afternoon, Victor.
Of course, there are no five-wire circuit breakers. The sentence you highlighted should have ended with the words “working neutral wire.” By the way, the image preceding this text is correct.
During operation, the RCD monitors both the incoming and outgoing voltage... - current, and controls the leakage current.
Three-wire network is only available in new houses. It must have a zero phase and grounding. In houses built a long time ago, there is only a phase and a zero. In such conditions, the RCD will also function, but slightly differently than in a three-phase network. What do you mean by three-wire?
This is the essence of all printed incidents... Especially in technical literature! one wrong word completely changes the meaning, which is fraught in electrics...