Current ratings of circuit breakers: how to choose the right machine
Devices for shutting off electricity during overloads and short circuits are installed at the entrance to any home network.It is necessary to correctly calculate the current ratings of circuit breakers, otherwise their operation will be ineffective. Do you agree?
We will tell you how to calculate the parameters of the machine, according to which this protective device is selected. From our article you will learn how to choose the device required to protect the electrical network. Taking into account our advice, you will purchase an option that will clearly operate at a dangerous moment for wiring.
The content of the article:
Circuit breaker parameters
To ensure the correct selection of trip device ratings, an understanding of their operating principles, conditions and response times is necessary.
The operating parameters of circuit breakers are standardized by Russian and international regulatory documents.
Basic elements and markings
The design of the switch includes two elements that react when the current exceeds the established range of values:
- The bimetallic plate, under the influence of the passing current, heats up and, bending, presses on the pusher, which disconnects the contacts. This is "thermal protection" against overload.
- The solenoid, under the influence of a strong current in the winding, generates a magnetic field that presses on the core, which then acts on the pusher. This is a "current protection" against short circuit, which reacts to such an event much faster than the plate.
Types of electrical protection devices have markings that can be used to determine their main parameters.
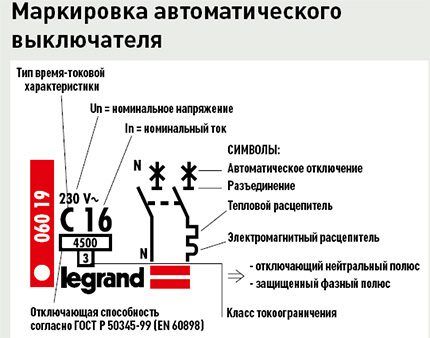
The type of time-current characteristic depends on the setting range (the magnitude of the current at which operation occurs) of the solenoid. To protect wiring and devices in apartments, houses and offices, type “C” or, much less common, “B” switches are used. There is no particular difference between them for everyday use.
Type “D” is used in utility rooms or carpentry in the presence of equipment with electric motors that have high starting power.
There are two standards for disconnect devices: residential (EN 60898-1 or GOST R 50345) and a more stringent industrial (EN 60947-2 or GOST R 50030.2). They differ slightly and machines of both standards can be used for residential premises.
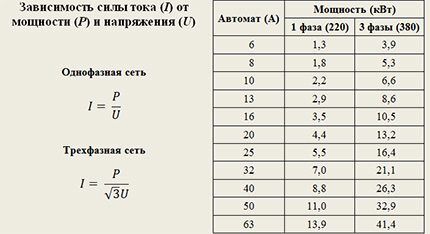
In terms of rated current, the standard range of automatic machines for domestic use contains devices with the following values: 6, 8, 10, 13 (rare), 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50 and 63 A.
Time-current response characteristics
In order to determine the speed of operation of the machine during an overload, there are special tables depending on the shutdown time on the coefficient of excess of the nominal value, which is equal to the ratio of the existing current strength to the rated one:
K = I / In.
A sharp drop down in the graph when the range coefficient value reaches from 5 to 10 units is due to the operation of the electromagnetic release. For type “B” switches this occurs at a value from 3 to 5 units, and for type “D” – from 10 to 20.
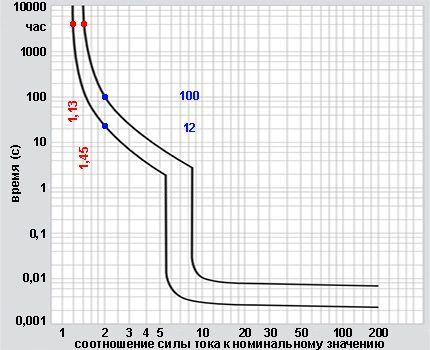
With K = 1.13, the machine is guaranteed not to disconnect the line within 1 hour, and with K = 1.45, it is guaranteed to disconnect within the same time. These values are approved in clause 8.6.2. GOST R 50345-2010.
To understand how long it takes for the protection to operate, for example, at K = 2, you need to draw a vertical line from this value. As a result, we get that, according to the above graph, the shutdown will occur in the range from 12 to 100 seconds.
Such a large spread of time is due to the fact that heating of the plate depends not only on the power of the current passing through it, but also on the parameters of the external environment. The higher the temperature, the faster the machine operates.
Rules for choosing denomination
The geometry of intra-apartment and house electrical networks is individual, so there are no standard solutions for installing switches of a certain rating. The general rules for calculating the permissible parameters of machines are quite complex and depend on many factors. It is necessary to take them all into account, otherwise an emergency situation may be created.
The principle of indoor wiring
Internal electrical networks have a branched structure in the form of a “tree” - a graph without cycles. Compliance with this construction principle is called selectivity of machines, according to which all types of electrical circuits are equipped with protective devices.
This improves the stability of the system in the event of an emergency and simplifies the work to eliminate it. It is also much easier to distribute the load, connect energy-intensive devices and change the wiring configuration.
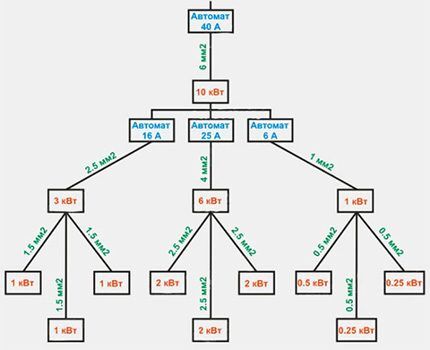
The functions of the input circuit breaker include monitoring the general overload - preventing the current from exceeding the permitted value for the object. If this happens, there is a risk of damage to the external wiring. In addition, it is likely that protective devices outside the apartment, which are already part of the common property or belong to the local power grid, will be triggered.
The functions of group machines include current control on individual lines. They protect the cable in a dedicated area and the group of electricity consumers connected to it from overload. If such a device does not operate during a short circuit, then it is insured by an input circuit breaker.
Even for apartments with a small number of electrical consumers, it is advisable to install a separate line for lighting. When you turn off the circuit breaker of another circuit, the light will not go out, which will allow you to eliminate the problem in more comfortable conditions. In almost every panel, the nominal value of the input machine is less than the amount on the group ones.
Total power of electrical appliances
The maximum load on the circuit occurs when all electrical appliances are turned on at the same time. Therefore, usually, the total power is calculated by simple addition. However, in some cases this figure will be less.
For some lines, the simultaneous operation of all electrical appliances connected to it is unlikely, and sometimes impossible. Homes sometimes specifically place restrictions on the operation of powerful devices. To do this, you need to remember not to turn them on at the same time or use a limited number of sockets.

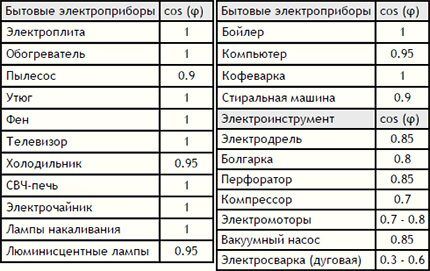
When electrifying office buildings, the empirical simultaneity coefficient is often used for calculations, the value of which is taken in the range from 0.6 to 0.8. The maximum load is calculated by multiplying the sum of the powers of all electrical appliances by a factor.
There is one subtlety in the calculations - it is necessary to take into account the difference between the rated (total) power and consumed (active), which are related by the coefficient (cos (f)).
This means that for the device to operate, a power current equal to the consumed divided by this coefficient is required:
Ip =I/cos(f)
Where:
- Ip – rated current strength, which is used in load calculations;
- I is the current consumed by the device;
- cos(f) <= 1.
Usually the rated current is indicated immediately or through the indication of the cos (f) value in the technical data sheet of the electrical device.
For example, the coefficient value for fluorescent light sources is 0.9; for LED lamps – about 0.6; for ordinary incandescent lamps - 1. If the documentation is lost, but the power consumption of household devices is known, then for guarantee take cos (f) = 0.75.
How to select a circuit breaker based on load power is written in next article, the contents of which we advise you to familiarize yourself with.
Selection of core cross-section
Before laying a power cable from the distribution panel to a group of consumers, it is necessary to calculate the power of electrical appliances when they operate simultaneously. The cross-section of any branch is selected according to calculation tables depending on the type of wiring metal: copper or aluminum.
Wire manufacturers provide similar reference materials to their products. If they are missing, then they are guided by the data from the reference book “Rules for the Construction of Electrical Equipment” or produce cable cross-section calculation.
However, consumers often play it safe and choose not the minimum acceptable cross-section, but one step larger. So, for example, when purchasing a copper cable for a 5 kW line, choose a core cross-section of 6 mm2when according to the table a value of 4 mm is sufficient2.
This is justified for the following reasons:
- Longer service life of a thick cable, which is rarely subjected to the maximum permissible load for its cross-section. Re-wiring is not an easy and expensive job, especially if the room has been renovated.
- The bandwidth reserve allows you to seamlessly connect new electrical appliances to the network branch. So, you can add an additional freezer to the kitchen or move the washing machine there from the bathroom.
- The start of operation of devices containing electric motors produces strong starting currents. In this case, a voltage drop is observed, which is expressed not only in the blinking of the lighting lamps, but can also lead to breakdown of the electronic part of the computer, air conditioner or washing machine. The thicker the cable, the smaller the voltage surge will be.
Unfortunately, there are many cables on the market that are not made according to GOST, but according to the requirements of various specifications.
Often the cross-section of their cores does not meet the requirements or they are made of conductive material with greater resistance than required. Therefore, the actual maximum power at which permissible heating of the cable occurs is less than in the standard tables.
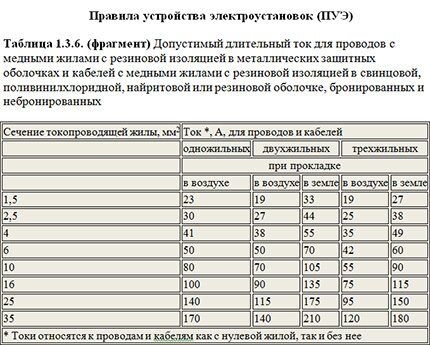
Calculation of the circuit breaker rating for cable protection
The machine installed in the panel must ensure that the line is disconnected when the current power goes beyond the range permitted for the electric cable. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the maximum permissible rating for the switch.
According to the PUE, the permissible long-term load of copper cables laid in boxes or in the air (for example, over a suspended ceiling) is taken from the table above. These values are intended for emergency situations when there is a power overload.
Some problems begin when relating the rated power of the switch to the long-term permissible current, if this is done in accordance with the current GOST R 50571.4.43-2012.

Firstly, the decoding of the variable I is misleadingn, as the rated power, if you do not pay attention to Appendix “1” to this paragraph of GOST. Secondly, there is a typo in formula “2”: the coefficient of 1.45 was added incorrectly, and this fact is stated by many experts.
According to clause 8.6.2.1.GOST R 50345-2010 for household switches rated up to 63 A, the conditional time is 1 hour. The set tripping current is equal to the nominal value multiplied by a factor of 1.45.
Thus, according to both the first and modified second formulas, the rated current of the circuit breaker must be calculated using the following formula:
In <=IZ / 1,45
Where:
- In – rated current of the machine;
- IZ – long-term permissible cable current.
Let's calculate the ratings of switches for standard cable sections for a single-phase connection with two copper conductors (220 V). To do this, we divide the long-term permissible current (when laying through the air) by a tripping coefficient of 1.45.
Let's choose a machine so that its face value is less than this value:
- Section 1.5 mm2: 19 / 1.45 = 13.1. Rating: 13 A;
- Section 2.5 mm2: 27 / 1.45 = 18.6. Rating: 16 A;
- Section 4.0 mm2: 38 / 1.45 = 26.2. Rating: 25 A;
- Section 6.0 mm2: 50 / 1.45 = 34.5. Rating: 32 A;
- Section 10.0 mm2: 70 / 1.45 = 48.3. Rating: 40 A;
- Section 16.0 mm2: 90 / 1.45 = 62.1. Rating: 50 A;
- Section 25.0 mm2: 115 / 1.45 = 79.3. Denomination: 63 A.
13A circuit breakers are rarely on sale, so devices with a rated power of 10A are often used instead.
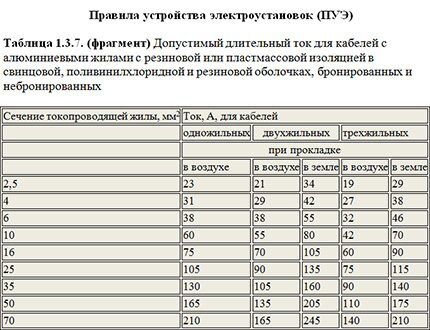
In a similar way, for aluminum cables we calculate the ratings of the machines:
- Section 2.5 mm2: 21 / 1.45 = 14.5. Rating: 10 or 13 A;
- Section 4.0 mm2: 29 / 1.45 = 20.0. Rating: 16 or 20 A;
- Section 6.0 mm2: 38 / 1.45 = 26.2. Rating: 25 A;
- Section 10.0 mm2: 55 / 1.45 = 37.9. Rating: 32 A;
- Section 16.0 mm2: 70 / 1.45 = 48.3. Rating: 40 A;
- Section 25.0 mm2: 90 / 1.45 = 62.1. Rating: 50 A.
- Section 35.0 mm2: 105 / 1.45 = 72.4. Denomination: 63 A.
If the power cable manufacturer declares a different dependence of the permissible power on the cross-sectional area, then it is necessary to recalculate the value for the switches.
How to determine the technical parameters of a circuit breaker by marking, in detail stated here. We recommend that you read the educational material.
Prevention of overload from consumer work
Sometimes a machine is installed on the line with a rated power significantly lower than what is necessary to ensure that the electrical cable remains operational.
It is advisable to reduce the rating of the switch if the total power of all devices in the circuit is significantly less than the cable can withstand. This happens if, for safety reasons, when after installation of the wiring some of the devices were removed from the line.
Then reducing the rated power of the machine is justified from the position of its faster response to emerging overloads.
For example, when an electric motor bearing jams, the current in the winding increases sharply, but not to short circuit values. If the machine reacts quickly, the winding will not have time to melt, which will save the engine from an expensive rewinding procedure.
They also use a value less than the calculated value due to strict restrictions on each circuit. For example, for a single-phase network, a 32 A switch is installed at the entrance to an apartment with an electric stove, which gives 32 * 1.13 * 220 = 8.0 kW of permissible power.Suppose that when wiring the apartment, 3 lines were organized with the installation of group circuit breakers with a nominal value of 25 A.

Let's assume that there is a slow increase in load on one of the lines. When the power consumption reaches a value equal to the guaranteed tripping of the group switch, only (32 - 25) * 1.45 * 220 = 2.2 kW will remain for the remaining two sections.
This is very little relative to total consumption. With such a distribution panel design, the input circuit breaker will turn off more often than devices on the lines.
Therefore, in order to maintain the principle of selectivity, it is necessary to install switches with a rating of 20 or 16 amperes in the areas. Then, with the same imbalance in power consumption, the other two links will account for a total of 3.8 or 5.1 kW, which is acceptable.
Let's consider the possibility switch installation with a rating of 20A using the example of a separate line dedicated to the kitchen.
The following electrical appliances are connected to it and can be turned on simultaneously:
- Refrigerator with a rated power of 400 W and a starting current of 1.2 kW;
- Two freezers, power 200 W;
- Oven, power 3.5 kW;
- When operating an electric oven, it is allowed to additionally turn on only one additional device, the most powerful of which is an electric kettle, consuming 2.0 kW.
A twenty-amp machine allows you to pass current for more than an hour with a power of 20 * 220 * 1.13 = 5.0 kW. A guaranteed shutdown in less than one hour will occur with a current flow of 20 * 220 * 1.45 = 6.4 kW.

When the oven and electric kettle are turned on simultaneously, the total power will be 5.5 kW or 1.25 parts of the machine’s nominal value. Since the kettle does not work for long, it will not turn off. If at this moment the refrigerator and both freezers turn on, the power will be 6.3 kW or 1.43 parts of the nominal value.
This value is already close to the guaranteed tripping parameter. However, the likelihood of such a situation occurring is extremely low and the duration of the period will be insignificant, since the operating time of the motors and the kettle is short.
The starting current that occurs when starting the refrigerator, even in the sum of all operating devices, will not be enough to trigger the electromagnetic release. Thus, under the given conditions, a 20 A circuit breaker can be used.
The only caveat is the possibility of increasing the voltage to 230 V, which is permitted by regulatory documents. In particular, GOST 29322-2014 (IEC 60038:2009) defines the standard voltage as 230 V with the possibility of using 220 V.
Now most networks supply electricity with a voltage of 220 V. If the current parameter is adjusted to the international standard of 230 V, then the ratings can be recalculated in accordance with this value.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Switch device. Selecting an input machine depending on the connected power. Power distribution rules:
Selecting a switch based on cable capacity:
Calculating the rated current of a circuit breaker is a complex task, for which many conditions must be taken into account.The ease of maintenance and safety of the local electrical network depends on the installed machine.
If you have doubts about the ability to make the right choice, you should contact experienced electricians.
Please write comments in the block below. Tell us about your own experience in selecting circuit breakers. Share useful information and photos on the topic of the article, ask questions.




In the search, I asked the question: Standard range of circuit breakers from 2A to 63A. The link was to your site. But you don’t have this row!
In general, a good article, however, please delete or edit the second sentence in the following phrase: “To protect wiring and devices in apartments, houses and offices, switches of type “C” or, much less common, “B” are used. There is no particular difference between them in everyday use.” - I can’t see him!
The difference between them is very significant, especially for private residential buildings, where the phase-to-zero circuit resistance very often exceeds 2 ohms. In this case, the expected single-phase short-circuit current will be no more than 110 A, therefore, type “C” circuit breakers with a rating of 16 A and higher will not operate in the standardized time, which should be no more than 0.4 seconds! But type “B” machines with a nominal value of 16A and even 20A will work! Now do you understand what the difference is?
Of course, there is a difference between type B and type C machines and it cannot be called insignificant. They differ from each other in terms of instantaneous tripping current. For clarity, I will attach detailed diagrams with these indicators of protective circuit breakers.
It should also be noted that the machines have two types of release:
1. Electromagnetic;
2. Thermal (bimetallic plate).
The electromagnetic release in a class B machine is triggered when the rated current is doubled in 0.015 seconds. The thermal release responds in 4-5 seconds. with a similar jump. Whereas on a type C machine, the electromagnetic release is triggered at five times the rated current in 0.022 seconds. And the thermal release responds in 1.5 seconds. with a similar jump.
I would also like to draw your attention to the fact that the data may vary depending on the temperature and current strength.