How to choose the right RCD by power: existing types of RCD + subtleties of choice
The increase in the number of household appliances increases the risk of electrical injury during their operation.Therefore, it is recommended to install protective systems in premises that prevent current leakage.
To ensure stable operation and safe use of devices, it is necessary to correctly select and install the RCD. Before purchasing, you should evaluate the operational features of the room, the type of electrical wiring and decide on the connection diagram of the protective device.
Do you doubt that you can cope with the task? We will tell you how to choose an RCD, what parameters are important to take into account to ensure the normal functioning of the equipment, and which manufacturers you can trust.
The content of the article:
Operating principle of RCD
To prevent accidental electric shock from contact with household and industrial electrical appliances, it was invented residual current device.
It is based on a transformer with a toroidal core, which monitors the current strength at “phase” and “zero”. If its levels diverge, then the relay is activated and the power contacts are disconnected.
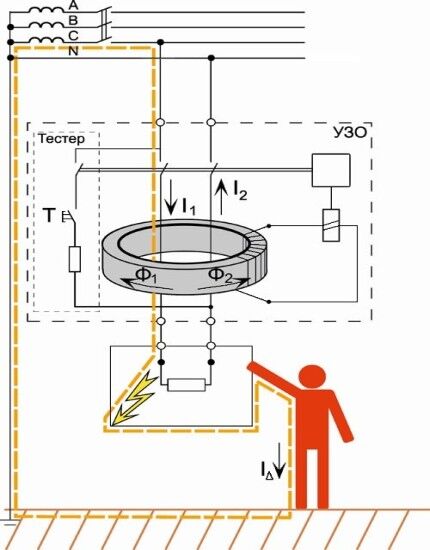
Normally, any electrical device has a current leakage. But its level is so low that it is safe for the human body.
Therefore, RCDs are programmed to operate at a current value that can cause electrical injury to people or lead to equipment breakdown.
For example, when a child inserts a bare metal pin into an outlet, electricity will leak through the body, and the RCD will turn off the light in the apartment.
The speed of operation of the device is such that the body will not experience any negative sensations at all.

Depending on the power of the connected equipment, the presence of intermediate protective devices and the length of the electrical wiring, RCDs with different limiting values of differential currents are used.
The most common protective devices in everyday life are those with threshold levels of 10 mA, 30 mA and 100 mA. These devices are sufficient to protect most residential and office premises.
It should be remembered that the classic RCD does not protect electrical wiring from short circuits and does not disconnect power contacts when the network is overloaded. Therefore, it is advisable to use these devices in combination with other electrical protection mechanisms, for example, automatic switches.
Classification of protective devices
Despite the simplicity of the internal structure, the choice of RCD models on the market is quite large. Each device has a certain set of technical parameters that cannot be adjusted during operation.

To facilitate the selection of RCDs, options for classifying these devices should be considered.
- By response speed RCD mechanisms are divided into conventional and selective models. The former disconnect power contacts almost instantly, while the latter disconnect with a delay.Selective RCDs are used in multi-level systems where the sequence of operation is important.
- By type of relay RCDs are divided into electromechanical, which breaks the contact mechanically, and electronic, which prevents the flow of current using a semiconductor circuit.
- By type of current. RCD type AC is disconnected from alternating current leakage, type A – from alternating and direct current.
- By additional functions: without and with network overload protection. RCDs with a short circuit or high current trigger mechanism are usually called difavtomats.
- By design. There are RCDs that are attached to a DIN rail, to the wall, as well as devices in the form of a socket, a portable device, or an adapter.
- According to operating voltage: for 220V, 380V, combined.
- By energy dependence. There are RCD models that are capable and unable to disconnect the power load in the absence of operating voltage.
- By number of connected poles: two-pole and four-pole.
To choose the right RCD, it is not enough to know its technical characteristics. In order for the device to effectively perform its protective function, when purchasing it, you need to take into account the length of the home electrical wiring, the power of the connected devices and some other parameters.
Rules for choosing protective devices
Before purchasing an RCD, you can visit electrician forums to seek advice on the reliability of a particular manufacturer.
However, it is necessary to select the maximum and threshold current, number of poles, mounting scheme and other technical parameters strictly individually, based on the characteristics of the room and electrical wiring.
Selecting a device by power
The residual current device does not control the power consumption of connected devices, but has limitations on the maximum current flow.
Therefore it is important to know how select RCD by powerso that when installing the wiring diagram, the energy consumption of each group of rooms is correctly taken into account. After all, if the rated current exceeds the threshold value for the device, it may burn out.
In apartments and private houses, a one-level or two-level RCD system is usually used. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Single-level circuit with a single RCD — the rated current is calculated based on the total power of devices simultaneously connected to the network.
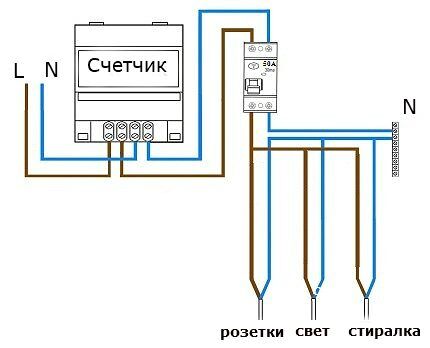
For example, if the energy consumption of a washing machine is 2.4 kW, lighting is 1.1 kW and other devices are 2.8 kW, the RCD should pass (2400+1100+2800)/220=28 A.
In this case, with a rated current of the residual current device of 30 A, it will not burn out even with simultaneous operation of all household appliances and lighting.
When installing a single RCD, there may be a problem with finding the location of the breakdown. No matter in which room the current leak occurs, the entire apartment will lose electricity. Therefore, it is better not to save money and install an extensive protection system.
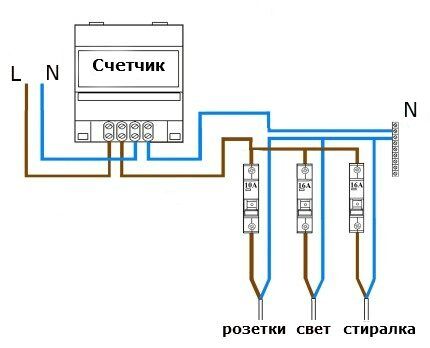
Branched single-level RCD installation diagram. In such a situation, the wires from the meter are branched into several groups using a special bus, each of which is controlled by a separate protective device.
The calculation of the rated current for each RCD in a branched single-level system is carried out separately. This takes into account the maximum power of devices potentially connected to the device.
For example, when connecting only a washing machine with an energy consumption of 2.4 kW to the RCD, its rated current will have to be at least 2400/220 = 10.9 A.
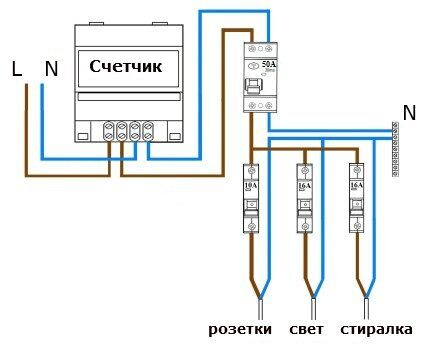
Two-level RCD system is considered optimal from the point of view of safety and maintainability.
Its first level is installed at the entrance to the apartment and ensures fire safety. The rated current of this protective device must be not lower than the maximum capabilities of the electricity meter.
The second level of energy protection is assigned to certain consumer groups. These could be rooms, floors, extensions, street lighting, single sockets.
Level 2 devices usually cost less and have a lower current rating. The sum of its values for all installed devices must be less than that of the basic RCD at the entrance to the room.
For example, with second-level protective devices with a rated current of 10 A, 16 A and 16 A, you will need to install a device with a minimum capacity of 10+16+16=42 A at the common input.
The advantage of a two-level system is the ability to turn off individual groups of electrical appliances in the presence of current leakage.This allows you to repair equipment or find problems with insulation in the wall without cutting off power to the entire apartment.
Calculation of the required differential current
Each RCD model is triggered at a certain level of differential current that occurs between the two conductors of the electrical cable. Therefore, it is important to know how to choose an RCD with safe characteristics for your home.

When calculating the threshold differential current of an RCD, several parameters are taken into account:
- length of the wire to the device consuming electricity;
- natural leakage of current in equipment;
- power of devices.
The general formula for determining diphtoc is as follows:
IΔ=(0.4Icalc(A)+0.01Lwire(m))/1000
For example, let’s take the above-described diagram of electrical appliances and their power. Let the cable length to each group of household devices be 12 m.
The calculation of the RCD parameters for the above circuit will be as follows:
- IΔmash=(0.4*2800/220)+0.01*12=5.21 mA;
- IΔosv=(0.4*1100/220)+0.01*12=2.12 mA;
- IΔrose=(0.4*2400/220)+0.01*12=4.48 mA.
According to the recommendations, the threshold current of the device should be three times greater than the calculated differential one. Which is associated with increased electrical load in the first second of turning on household appliances.
If this rule is not followed, then frequent false alarms of the RCD are possible, which will create problems for consumers.

Therefore, for each group of electrical appliances under consideration, the minimum value of the threshold differential current will be as follows:
- 5.21 mA*3=15.63;
- 2.12 mA*3=6.36;
- 4.48 mA*3=13.45.
That is, for a washing machine and a group of sockets you will need an RCD with a 30 mA current, and for a lighting group a 10 mA device will be sufficient.
Such characteristics of the devices will ensure the normal functioning of the equipment and protect people from electric shock. It is not recommended for these purposes to install an RCD with a parameter higher than 30 mA.
With a two-level scheme, the leakage current of the main protective device located at the entrance to the room is selected within the range of 100-300 mA.
These RCDs are triggered when old or damaged insulation inside the walls breaks down. Thus, the premises are protected from fire in case of hidden electrical wiring defects.
RCD response time
In a two-level system, the occurrence of significant current leakage can lead to the operation of the protective device at both levels.
To exclude such a situation, you can set the base selective protective device. Its response time is 150-500 ms, which is several times longer than that of a standard RCD (20-40 ms).
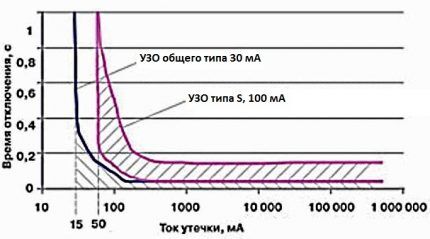
With this selection of devices, only the power supply on the second level will be turned off, which will not lead to a loss of electricity in the entire apartment.
As for conventional RCDs, the shorter their reaction time, the safer they are. This fact must be taken into account when purchasing them.
Choosing a reliable manufacturer
The direct protective function of an RCD depends little on its manufacturer.A device from any company, with the exception of clearly defective models, will turn off the power supply when the differential current exceeds the threshold value.
The disadvantages of protective devices may be the following:
- false positives;
- increased buzzing;
- heating during operation;
- fragility of the case, which can lead to damage during installation;
- short warranty period.
The more reliable and reputable the RCD manufacturer is, the fewer of the listed disadvantages its equipment will have.

However, as quality increases, so will the price.
The most reliable manufacturers of protective devices are:
- Legrand;
- ABB;
- AEG;
- KEAZ;
- Schneider Electric;
- Siemens;
- DEKraft;
- General Electric.
When purchasing an RCD, you should remember that this device is not installed to comply with building codes, but to preserve the health and lives of loved ones.
Therefore, you should not buy products from dubious manufacturers. They may not only fail to work, but also lead to a fire hazard.
There are other criteria for selecting residual current devices, but they are of much less importance for consumer safety.
General tips for selection and installation
In addition to the criteria for selecting an RCD, there are general useful recommendations when purchasing and installing this equipment.
They will help you avoid making mistakes and immediately purchase a model suitable for a specific apartment or house.

Tips for choosing the following:
- It is recommended to take RCDs, which, when triggered, turn off not only the phase, but also the “zero”;
- There should be no grounded electrical appliances within the circuit controlled by the device;
- the device must operate during short-term voltage drops of 50% of the nominal voltage, which can occur in the first moments of a short circuit;
- RCD terminals must be made of slightly oxidized material and equipped with a reliable wire fixation system;
- preference when purchasing should be given to devices with short circuit and overload protection functions;
- The second level RCD need not be installed on safe groups of equipment, for example, on ceiling lighting sources;
- It is recommended to install devices with a threshold current flow of 10 mA on shower stalls and Jacuzzis;
- You should pay attention to the possibility of connecting aluminum wires to the device - some devices do not work correctly with them.
You can install the correctly selected RCD yourself. This process is not much different from installing a socket or switch.
It is important to carefully consider the wiring diagram and do as indicated on it.
Detailed information about the rules and diagrams for connecting RCDs in an apartment and house is presented in this article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Selection of RCD with consideration of options, as well as explanations of the features of various connection schemes:
Rules for choosing an RCD, part 1:
Rules for choosing an RCD, part 2:
The choice of a suitable RCD, especially when installing two-level systems, is best left to professionals.
It’s easier to invite an experienced electrician into your home once and consult with him than to change an unsuitable product in a store.After all, the health and lives of loved ones who will use household electrical appliances are at stake.
Do you have anything to add or have questions about choosing a protective device? You can leave comments on the publication, participate in discussions and share your own experience in selecting an RCD for a house or apartment. The contact form is located in the lower block.




Many people doubt whether to install an RCD in their home. I will say this: if there is grounding, then it is necessary, if not, even more so. I determined for myself that the most preferable is the RCD from IEK. A big plus is its time-tested performance. The price is cheaper than most brands. If you find cheap RCDs from other companies, then most likely they will be “left-handed”. IEK RCD can be easily purchased in stores.
I believe that it is necessary to install an RCD. It is better to spend a little more money once during installation or repair than to then spend large sums on equipment repairs, etc. Over several years of operation, we have not had any electrical failures. But anything can happen. As far as I know, the installation of RCDs has become mandatory in new houses. In my opinion, this is absolutely true.
Good afternoon, Peter.
The obligation to protect networks and people with RCDs in houses under construction is an exaggeration. The PUE, which dedicated “Section 7” to protective shutdown, obliges to provide a device if the shutdown time of the group network by an automatic circuit breaker exceeds the standard. If the mentioned devices “cope with their responsibilities,” the RCD need not be installed. For plug sockets that power portable electrical receivers, installing an RCD is simply recommended.
The instructions regulating the power supply of private houses are no different in their categorical wording. But it requires designers involved in electrical safety issues to provide a solution to the RCD - this implies a detailed conclusion on why the device can be dispensed with or, on the contrary, to highlight the reasons prompting its installation.
I have attached a screenshot with the exact wording.
Why not install an input RCD in your favorite apartment, with 5 kW of total power, 63A? The sizes are the same. Reliability is higher. One-time costs. Here Amir Gumarov writes - you can get by if the machine copes with the responsibilities... But no machine will ever cope with the responsibility of turning off the network at the initial stage of a current leak in very expensive home equipment, for example. And if by hand in any accident, only an RCD can help. Without any options, you should always install an RCD, or a difavtomat, an RCD is better. The costs of RCDs are not considered at all as an important point; install only reliable ones with time-proven quality.