What is an RCD: device, principle of operation, existing types and marking of RCD
Any electrical network must have a protection device, but not everyone knows what an RCD is and what the principle of its operation is.The decoding of the abbreviation looks like this - residual current device.
This low-voltage electrical device is designed to turn off the protected section of the circuit when a differential current exceeds the rated value for this device.
In our article we will try to analyze in detail the design and principle of operation of RCDs, consider the existing varieties and understand what information the marking of residual current devices contains.
The content of the article:
Purpose of the protection device
The RCD ground loop device is a PE conductor of neutral conductive housings or parts of electrical mechanisms with a resistance not exceeding 4 Ohms.
If a leakage current occurs, these equipment elements may be energized, which poses a danger to human and animal life in contact with them, as well as to property in general.
To save from electrical injuries is the calling of survey devices. When a leakage current is detected, they turn off the voltage.
The greatest danger lies in the fact that such disturbances in the circuit are invisible and, in rare cases, noticeable, when you can feel a slight electric shock when touching the device.
The main reason for this phenomenon is a violation of the insulating layer of the wiring. Uncontrolled processes can cause great harm, which is why protective equipment is becoming increasingly popular in domestic environments.

The use of RCDs is most widespread in single-phase networks with alternating current and neutral line grounding, as well as voltage ratings up to 1 kW in the household power supply format.
RCD design
Optional features of the protective mechanism will help you understand the principle of operation of the RCD, namely the reproducible response of the device to current leakage.
Key operating units include:
- transformer differential sensor;
- trigger - a mechanism that breaks an incorrectly functioning electrical circuit;
- electromagnetic relay;
- control block.
Opposite windings are connected to the sensor - phase and zero. During normal operation of the network, these semiconductor elements form magnetic fluxes in the core that have the opposite direction in relation to each other. Due to this, the magnetic flux is zero.
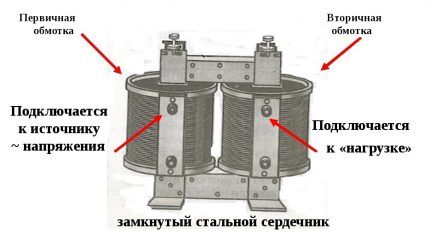
An electromagnetic type relay is connected to the secondary winding wound on the magnetic core of the transformer. If the network meets standard operating conditions, it is not used.
When a current leak occurs, the entire operation changes dramatically. The phase and neutral conductors begin to pass different amounts of current. Now the power value and direction of the magnetic fluxes on the transformer core will also have different parameters.
A current appears in the secondary turns and when the specified values are reached, the electromagnetic relay is activated. It is paired with a release mechanism. This connection reacts at the right moment and disconnects the electrical network.

The testing unit is represented by a resistance mechanism - a certain load connected to bypass the differential sensor. This element simulates current leakage and thus checks the functionality of the device. We talked in more detail about verification methods In this article.
The operating principle of the RCD is as follows: supplying current from the phase line to the control resistance and then to the neutral wire, bypassing the sensor.
This creates conditions for different current indicators at the input and output of the device. This imbalance should lead to the startup of the shutdown unit.
Depending on the developers, the circuit design may vary, but the principle used in the operation of the RCD will be identical for all models.
The principle of operation of the protective mechanism
Let's consider why you need to use an RCD. The functioning of the protective device is based on a measuring method.
The incoming and outgoing parameters of the currents flowing through the transformer are recorded. If the first value is greater than the second, this means that there is a current leak in the electrical circuit and the device reproduces a shutdown. If the parameters are identical, the device does not work.
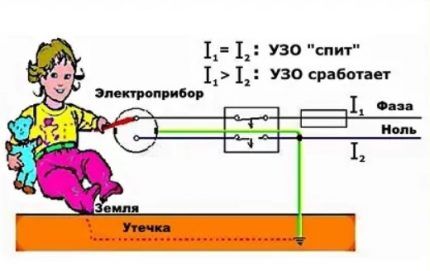
For a better understanding, let's consider how an RCD will work in a household distribution panel with a two-pole system.
The input two-wire wire (phase and neutral) is connected to the upper terminal blocks. Phase and neutral are connected to the lower terminal blocks, laid to the load area, for example, to the power outlet of a boiler or electric kettle. Protective grounding of the device will be carried out by cable, bypassing the RCD.
In standard operating mode, the movement of electrons is carried out along the line-phase from the incoming cable to the electric heater of the boiler/kettle, flowing through the differential protection device. They move back to the ground again through the RCD, but along the neutral line.
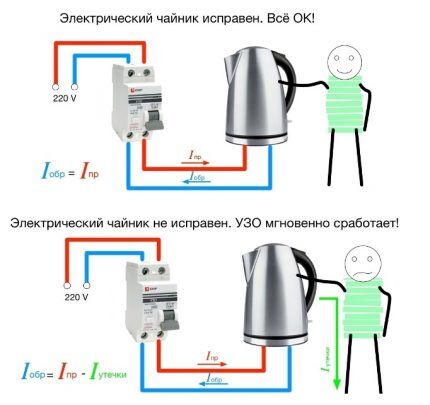
For example, the insulation in the heating element of the device was damaged.Thus, through the water inside, the current will be partially conducted by the housing, and then will go into the ground through the wiring of the protective device.
The remaining current will return along the neutral line through the RCD. However, its strength will become less by the amount of leakage compared to the incoming one.
The difference in indicators is calculated by a differential transformer. If the number is greater than the permitted value, the device instantly reacts and breaks the circuit.
In our other article we provided recommendations for selection and correct connection RCD for boiler.
The feasibility of using RCDs
Let's consider why you need to use an RCD and from what negative impact factors the device provides protection.
First of all, a phase short circuit to the electrical equipment housing. Mainly, problem areas include heating elements of heaters and washing machines. It is worth noting that breakdown occurs only when the heat-generating part is heated under the influence of current.
Also if the wires are connected incorrectly. For example, if twists without a terminal box are used, which are subsequently recessed into the wall and covered with a layer of plaster. Since the surface has high humidity, this twist will be a breakdown that will leak into the wall.
The differential protection mechanism in this case will constantly de-energize the line until the area is completely dry or until the connecting node is redone.
The scope of application of survey devices is quite diverse - from public buildings to large-scale enterprises. They complete electrical structures and circuits intended for reception and distribution: switchboards in residential buildings, current supply systems for individual consumption, etc. The main thing in this case is to do it right select RCD by power.
Types of devices and their classification
Development companies endow their products with diverse capabilities, which must be taken into account when determining the required type of RCD, based on the specific operating conditions of the electrical network.
In order for the average consumer to be able to select the necessary residual current device from the variety of models offered, a classification system was created based on the following characteristics:
- operating principle;
- type of differential current;
- time delay of disconnecting differential current;
- number of poles;
- installation method.
Next, we will consider each of these classifications in more detail.
Classification #1 - by inclusion method
There are only two switching methods - electromechanical and electronic. In the first case, the machine will turn off the power to the damaged line, regardless of the network voltage. The main working body is a toroidal core with windings.
When a leak forms, a voltage is generated in the secondary circuit to activate the polarization relay, which leads to activation of the shutdown mechanism.

The functioning of a device with electronic filling completely depends on additional voltage, i.e. external power required. Here the working body is an electronic board with an amplifier.
Inside such a mechanism there are no additional sources that accumulate energy, so the circuit uses electricity from the external network to operate and, if there is no voltage, the device will not break the circuit.
An example of the operation of an electronic RCD installed on a line with a socket from which a microwave oven is powered: a break in the zero phase has occurred, in addition to this, during the same period a malfunction occurs in the microwave wiring and a phase short circuit occurs to the housing, i.e. it has dangerous potential.
If you touch the stove, the electronic type of protection will not be activated, because no power supply. It is precisely because of unreliability in comparison with its electromechanical analogue that this device has become less widespread.
Classification #2 - by type of leakage current
All models of manufactured safety circuit breakers are additionally divided by the load current passing through the device. They process voltage of a given oscillation format.
The rated operating voltage is indicated on the housing of all devices and in the passport. This parameter must correspond to the rated current range of the electrical equipment.
The AC type will be activated when an alternating leakage voltage instantly appears in the controlled circuit or when it increases in waves. These devices are marked with the inscription “AC” or the symbol “~”.

Type A is triggered by the instantaneous formation of an alternating or pulsating breakdown current in the controlled circuit, or by their slow increase.
This mechanism can be used in any of the situations presented. The abbreviation “A” or symbol is marked on the body of the machine, as in the graphic image in the rectangle
Most often, the A-type is connected to a circuit where load regulation is reproduced by cutting off the top of the sinusoid, for example, adjusting the speed of motor rotational movements with a thyristor converter.
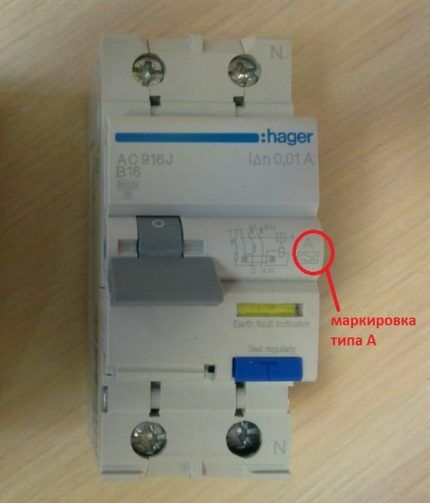

Subtype B RCDs are effective for reproducing the reaction in a subordinate electrical circuit of direct, alternating or converted (rectified) leakage current.
This is expensive equipment intended for industrial facilities. They are not used in domestic conditions.
The presented tripping protection devices of type A, B and AC are designed for an activation time of 0.02-0.03 s.
Classification #3 - by type of time delay
This classification involves a distinction between two types: S and G.Type S automatic protection can be characterized by a selective format response. The response time delay corresponds to the range of 0.15-0.5 s. It is advisable to choose it in the case of group connection of an RCD.
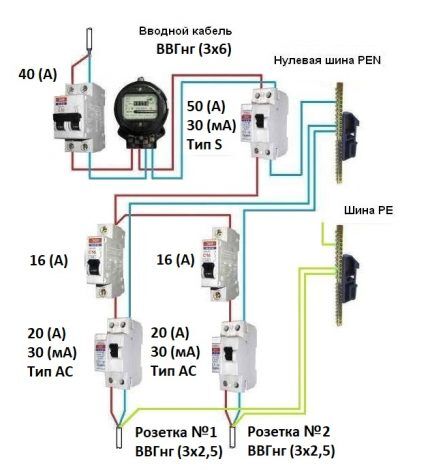
According to the diagram, the panel contains two load groups in the form of sockets No. 1 and No. 2, to which a type A RCD is connected, and a second circuit breaker - S - is connected to the entrance of the room.
If a breakdown occurs in one beam, the input device is activated only when the collective device does not fulfill its function and does not turn off the defective section.
Selectivity of circuit break activation can be achieved using another method - through leakage current settings. This method is most widespread.
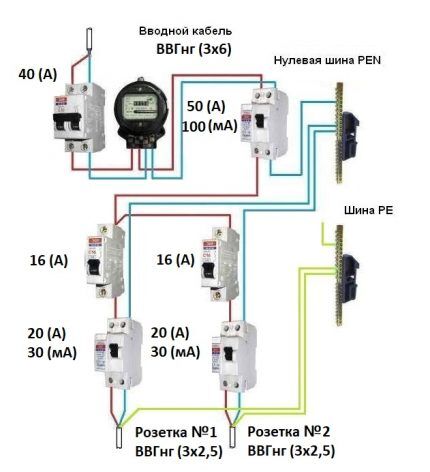
Let's take a circuit similar to the previous one and modify it in this way: we select a group automaton of the AC type only with a diftoka setting of 0.03 A, and at the input there will be a similar device with only 0.1 A.
There are situations when the differential current in the fault circuit exceeds the rated settings of the two protection devices. For the first circuit, selectivity will not be impaired, but in the second, any of the connected devices can supply the cutoff current.
The G form factor device is also represented by a selective triggering principle and has a shutter speed of 0.06-0.08 s. All described selected types are designed for exposure to extreme currents - up to 15 kA.
The limiting current is an important selection parameter because This is precisely what ensures safety.
For example, in rooms with high humidity, electrical appliances are powered by connecting disconnect devices to the circuit with a setting of 0.01 A. For standard living conditions - 0.03 A.
To organize fire safety of buildings - 0.1-0.3 A. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the tips on choosing a fire protection RCD and the subtleties of its installation.
Classification #4 - by number of poles
Due to the fact that the automatic device operates on the principle of comparing the magnitudes of current passing through it, the number of poles of the machine will be identical to the number of current-carrying lines.
A two-pole RCD is designated as 2P. It is included in a single-phase circuit to ensure human protection and prevent possible causes of fire.
Marking of four-pole RCDs is 4P. They are designed to work in a three-phase network. An installation combination is also possible, for example, a device with four poles is connected to a two-wire network.
However, this will not realize the full potential of the device, which is economically unprofitable.

Classification #5 - according to the method of installation of the device
Since differential protective devices come in a variety of housings, they can be used as stationary or portable.
In the second case, the device is equipped with an extension cord. DIN rail mounted devices mounted in electrical panel, which is located either in the corridor or in the apartment.
There are also options like RCD socket and RCD plug. In both the first and second cases, any electrical device connected through such a mechanism does not pose a danger to humans if it breaks down.
Full decoding of marking values
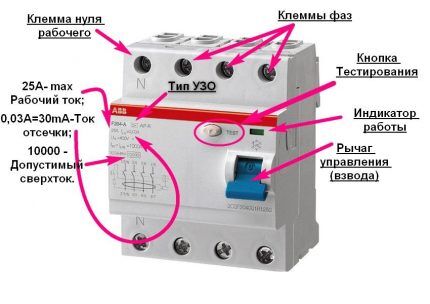
The name of the developer company must be on the device body. This is followed by standardized markings indicating the serial number.
To decipher the abbreviation we will use the following example: [F][X]00[X]-[XX]:
- [F] – residual current device;
- [X] – performance format;
- 00 – digital or alphanumeric designations of the series;
- [X] – number of poles: 2 or 4;
- [XX] – characteristics by type of leakage current: AC, A and B.
The nominal parameters of the device will also be indicated here, which you need to pay special attention to when choosing.
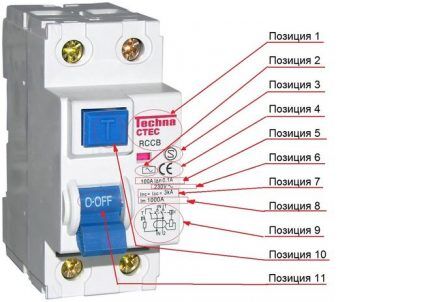
The maximum parameters for which the devices are designed include: voltage Un, current In, differential value of circuit opening current IΔn, ability to turn on and off I'm switching capacity during short circuits Icn.
The main markings must be located in such a way that they remain visible after installation of the device. Some parameters may be marked on the side or on the rear panel, visible only before installation of the product.
Outputs intended only for connecting the neutral wire are designated by the Latin symbol “N" The disabled RCD mode is indicated by the symbol “ABOUT" (circle), included - short vertical bar "I».
Not every product is marked with optimal environmental temperature indicators. In those models where there is a symbol
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video material with a detailed overview of all the constituent elements of the review protection mechanisms, their purpose and the principle of interaction with each other:
Description of all types of circuit breakers, as well as tips on how to make the right choice:
The answer to the age-old question: what to choose – a differential circuit breaker, or an RCD + installation secrets:
The use of an RCD is a profitable and correct solution not only from the point of view of economy, but, from the point of view of fire safety, and human protection.
It is recommended to make maximum use of its potential in domestic conditions, installing it on all groups of electrical equipment to ensure complete isolation from the effects of electricity.
Do you still have questions about the operating principle or classification of residual current devices? Or do you want to supplement the presented material with useful information? Please write your clarifications in the comments block, ask questions - experts and competent visitors to our site will try to answer you as fully as possible.




I had regular traffic jams in my apartment, and when power surges occurred, they did not work. At first I didn’t pay attention to this, but after learning that it was unsafe, I decided to install an RCD. I bought a certified RCD in order to completely protect my apartment. After this, during voltage surges, the RCD is triggered, which protects the apartment from a short circuit and subsequent fire.
Good afternoon, Mikhail. It turns out that the RCD was installed, but the traffic jams, which are an anachronism, were left? You did not specify which device was installed, so I would like to warn you that the PUE imposes a number of restrictions on the installation of an RCD as the only protection - paragraph 7.1.6 is devoted to this. In order not to quote, I have attached a screenshot of a fragment of the Rules.