Selecting a circuit breaker: types and characteristics of electrical circuit breakers
Surely many of us have wondered why circuit breakers so quickly replaced outdated fuses from electrical circuits? The activity of their implementation is justified by a number of very convincing arguments, including the opportunity to buy this type of protection, which ideally matches the time-current data of specific types of electrical equipment.
Do you doubt which machine you need and don’t know how to choose it correctly? We will help you find the right solution - the article discusses the classification of these devices. As well as important characteristics that you should pay close attention to when choosing a circuit breaker.
To make it easier for you to understand the machines, the article’s material is supplemented with visual photos and useful video recommendations from experts.
The content of the article:
Classification of circuit breakers
The machine almost instantly disconnects the line entrusted to it, which eliminates damage to the wiring and equipment powered from the network. After the shutdown has been completed, the branch can be restarted immediately without replacing the safety device.
Usually circuit breakers selected according to four key parameters - rated breaking capacity, number of poles, time-current characteristic, rated operating current.
According to rated breaking capacity
This characteristic indicates the permissible short circuit current (SC), at which the switch will trip and, opening the circuit, will de-energize the wiring and devices connected to it.
According to this parameter, there are three types of machines - 4.5 kA, 6 kA, 10 kA.
- Automatic machines for 4.5 kA (4500 A) usually used to prevent damage to power lines of private residential properties. The wiring resistance from the substation to the short circuit is approximately 0.05 Ohm, which gives a maximum current of about 500 A.
- 6 kA (6000 A) devices are used for short-circuit protection in the residential sector and public places, where line resistance can reach 0.04 Ohm, which increases the likelihood of a short circuit up to 5.5 kA.
- Switches 10 kA (10000 A) used to protect industrial electrical installations. Currents of up to 10,000 A can occur in a short electrical circuit located close to a substation.
Before choosing the optimal modification of the circuit breaker, it is important to understand whether short-circuit currents exceeding 4.5 kA or 6 kA are possible?

The machine is switched off when the specified values are short-circuited. Most often, switches of the 6000 A modification are used for domestic needs.
4500 A models are practically not used to protect modern electrical networks, and in some countries their use is prohibited.
If you are interested in how to correctly convert Amps to Watts, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material presented in the next article.
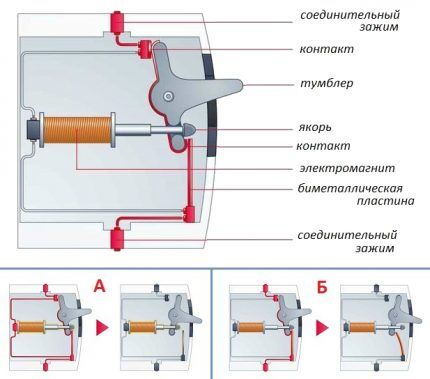
The job of a circuit breaker is to protect wiring (not equipment and users) from short circuits and from insulation melting when currents pass above rated values.
By number of poles
This characteristic indicates the maximum possible number of wires that can be connected to the AV to protect the network.
They are switched off when an emergency occurs (when the permissible current is exceeded or the level of the time-current curve is exceeded).
This characteristic indicates the maximum possible number of wires that can be connected to the AV to protect the network. They are switched off when an emergency occurs (when the permissible current is exceeded or the level of the time-current curve is exceeded).
Single pole circuit breakers
A single-pole type switch is the simplest modification of the machine. It is designed to protect individual circuits, as well as single-phase, two-phase, three-phase electrical wiring. It is possible to connect 2 wires to the switch design - the power wire and the outgoing wire.
The functions of a device of this class include only protecting the wire from fire. The neutral of the wiring itself is placed on the zero bus, thereby bypassing the machine, and the grounding wire is connected separately in the ground bus.

A single-pole circuit breaker does not perform the function of an input circuit breaker, since when it is forced to turn off, the phase line is broken, and the neutral is connected to the voltage source, which does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection.
Double pole circuit breakers
When it is necessary to completely disconnect the electrical wiring network from voltage, a two-pole circuit breaker is used.
It is used as an introductory one, when during a short circuit or network failure, all electrical wiring is de-energized simultaneously. This makes it possible to carry out timely repairs and modernization of circuits absolutely safely.
Two-pole circuit breakers are used in cases where a separate switch is needed for a single-phase electrical appliance, for example, a water heater, boiler, machine tool.

The machine is connected to the protected device using 4 wires, two of which are power wires (one of them is directly connected to the network, and the second supplies power with a jumper) and two are outgoing wires that require protection, and they can be 1-, 2- , 3-wire.
Three-pole circuit breakers
To protect a three-phase 3- or 4-wire network, three-pole circuit breakers are used. They are suitable for star connection (the middle wire is left unprotected, and the phase wires are connected to the poles) or triangle type (with the center wire missing).
If there is an accident on one of the lines, the other two are switched off independently.

The three-pole switch serves as an input and common switch for all types of three-phase loads. The modification is often used in industry to provide current to electric motors.
Up to 6 wires are connected to the model, 3 of them are phase wires of a three-phase electrical network. The remaining 3 are protected. They represent three single-phase or one three-phase wiring.
Four-pole circuit breakers
To protect a three- or four-phase electrical network, for example, a powerful motor connected according to the “star” principle with a zero point removed, a four-pole circuit breaker is used. It is used as an input switch for a three-phase four-wire network.

It is possible to connect eight wires to the machine body, three of them are phase wires of the electrical network (+ one neutral) and four are outgoing wires (3 phase + 1 neutral).
Single-phase consumers are powered by a voltage of 220 V, which can be obtained by taking one of the phases and the neutral conductor (neutral) of the electrical network. That is, in this case, in addition to the three phases of the electrical network, there is one more conductor - neutral, therefore, to protect and switch such an electrical network, four-pole circuit breakers are installed, which break all four conductors.
According to the time-current characteristic
AB can have the same indicator rated load power, but the characteristics of electricity consumption of devices may be different.
Power consumption may be uneven and vary depending on the type and load, as well as when a device is turned on, turned off, or continuously operated.
Fluctuations in power consumption can be quite significant, and the range of their changes can be wide. This leads to the machine turning off due to exceeding the rated current, which is considered a false network shutdown.
To eliminate the possibility of inappropriate operation of a fuse during non-emergency standard changes (increasing current, changing power), circuit breakers with certain time-current characteristics (TCC) are used.
This allows you to operate circuit breakers with the same current parameters with arbitrary permissible loads without false tripping.
VTX show after what time the switch will operate and what indicators of the ratio of current strength and direct current of the machine will be in this case.
Features of machines with characteristic B
A machine with the specified characteristic turns off within 5-20 seconds. The current indicator is 3-5 rated currents of the machine. These modifications are used to protect circuits that power standard household appliances.
Most often, the model is used to protect the wiring of apartments and private houses.
Feature C - operating principles
The machine with the nomenclature designation C switches off in 1-10 seconds at 5-10 rated currents.
Switches of this group are used in all areas - in everyday life, construction, industry, but they are most in demand in the area of electrical protection of apartments, houses, and residential premises.
Operation of switches with characteristic D
D-class machines are used in industry and are represented by three-pole and four-pole modifications. They are used to protect powerful electric motors and various 3-phase devices.
The response time of the AV is 1-10 seconds at a current multiple of 10-14, which allows it to be effectively used to protect various wiring.
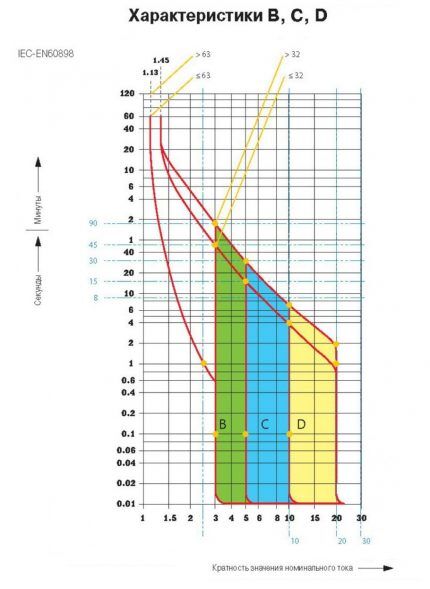
Powerful industrial motors operate exclusively with motors with characteristic D.
You might also be interested in reading marking of circuit breakers in our other article.
According to rated operating current
There are a total of 12 modifications of machines, differing in rated operating current – 1A, 2A, 3A, 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A.The parameter is responsible for the speed of operation of the machine when the effective current exceeds the nominal value.
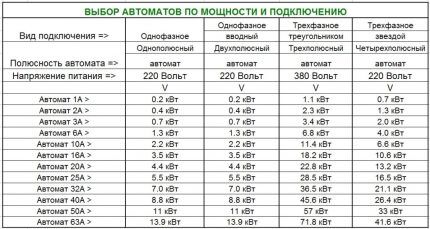
The selection of a switch according to the specified characteristic is made taking into account the power of the electrical wiring, the permissible current that the wiring can withstand in normal mode. If the current value is unknown, it is determined using formulas using data on the cross-section of the wire, its material and installation method.
Automatic machines 1A, 2A, 3A are used to protect circuits with low currents. They are suitable for providing electricity to a small number of devices, for example, a lamp or chandelier, a low-power refrigerator and other devices whose total power does not exceed the capabilities of the machine.
The 3A switch is effectively used in industry if it is connected three-phase in a delta type.
Switches 6A, 10A, 16A can be used to provide electricity to individual electrical circuits, small rooms or apartments.
These models are used in industry; they are used to supply power to electric motors, solenoids, heaters, and automatic welding machines connected by a separate line.
Three- and four-pole 16A circuit breakers are used as input circuit breakers for a three-phase power supply circuit. In production, preference is given to devices with a D-curve.
Circuit breakers 20A, 25A, 32A are used to protect the wiring of modern apartments; they are capable of providing electricity to washing machines, heaters, electric dryers and other high-power equipment.Model 25A is used as an introductory machine.
Switches 40A, 50A, 63A belong to the class of high-power devices. They are used to provide electricity to high-power power equipment in everyday life, industry, and civil construction.
Selection and calculation of circuit breakers
Knowing the characteristics of the AB, you can determine which machine is suitable for a particular purpose. But before choosing the optimal model, it is necessary to make some calculations with which you can accurately determine the parameters of the desired device.
Step #1 - determining the power of the machine
When choosing a machine, it is important to take into account the total power of the connected devices.
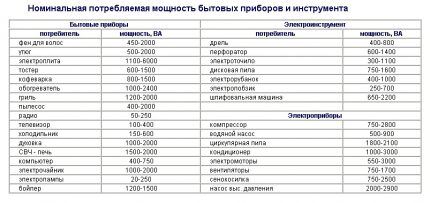
For example, you need an automatic machine to connect kitchen appliances to power. Let's say a coffee maker (1000 W), a refrigerator (500 W), an oven (2000 W), a microwave oven (2000 W), and an electric kettle (1000 W) will be connected to the outlet. The total power will be equal to 1000+500+2000+2000+1000=6500 (W) or 6.5 kV.
If you look at the table of circuit breakers by connection power, take into account that the standard wiring voltage in domestic conditions is 220 V, then a single-pole or double-pole 32A circuit breaker with a total power of 7 kW is suitable for operation.
It should be noted that more power consumption may be required, since during operation it may be necessary to connect other electrical appliances that were not initially taken into account.To provide for this situation, a multiplying factor is used in calculations of total consumption.
Let’s say that by adding additional electrical equipment, it was necessary to increase the power by 1.5 kW. Then you need to take the coefficient 1.5 and multiply it by the resulting calculated power.
In calculations it is sometimes advisable to use a reduction factor. It is used when the simultaneous use of several devices is impossible.
Let's say the total wiring power for the kitchen was 3.1 kW. Then the reduction factor is 1, since the minimum number of devices connected at the same time is taken into account.
If one of the devices cannot be connected with others, then the reduction factor is taken less than one.
Step #2 - calculation of the rated power of the machine
Rated power is the power at which the wiring does not turn off.
It is calculated using the formula:
M = N * CT * cos(φ),
Where
- M – power (Watt);
- N – mains voltage (Volts);
- ST – current strength capable of passing through the machine (Ampere);
- cos(φ) – the value of the cosine of the angle, which takes the value of the shift angle between phases and voltage.
The cosine value is usually equal to 1, since there is practically no shift between the phases of current and voltage.
From the formula we express ST:
CT=M/N,
We have already determined the power, and the network voltage is usually 220 Volts.
If the total power is 3.1 kW, then:
CT = 3100/220 = 14.
The resulting current will be 14 A.
For calculations with a three-phase load, the same formula is used, but angular shifts, which can reach large values, are taken into account. Usually they are indicated on the connected equipment.
Step #3 - Calculate Rated Current
You can calculate the rated current using the wiring documentation, but if it is not available, then it is determined based on the characteristics of the conductor.
The following data is required for calculations:
- square conductor cross-section;
- material used for the cores (copper or aluminum);
- laying method.
In domestic conditions, the wiring is usually located in the wall.

Having made the necessary measurements, we calculate the cross-sectional area:
S = 0.785 * D * D,
Where
- D is the diameter of the conductor (mm);
- S — cross-sectional area of the conductor (mm2).
Next we use the table below.
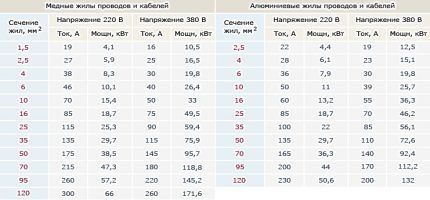
Taking into account the data obtained, we select the operating current of the machine, as well as its nominal value. It must be equal to or less than the operating current. In some cases, it is permissible to use machines with a rating exceeding the effective wiring current.
Step #4 - determining the time-current characteristic
To correctly determine the VTX, it is necessary to take into account the starting currents of the connected loads.
The necessary data can be found using the table below.
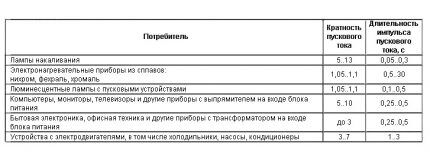
According to the table, you can determine the current strength (in Amperes) when the device is turned on, as well as the period after which the maximum current will occur again.
For example, if you take an electric meat grinder with a power of 1.5 kW, calculate the operating current for it from the tables (it will be 6.81 A) and, taking into account the multiple of the starting current (up to 7 times), we obtain the current value 6.81*7=48 (A).
A current of this strength flows at intervals of 1-3 seconds. Considering the VTK graphs for class B, you can see that if there is an overload, the circuit breaker will trip in the first seconds after starting the meat grinder.
Obviously, the multiplicity of this device corresponds to class C, so an automatic machine with characteristic C must be used to ensure the operation of an electric meat grinder.
For domestic needs, switches that meet characteristics B and C are usually used. In industry, for equipment with large multiple currents (motors, power supplies, etc.), a current of up to 10 times is created, so it is advisable to use D-modifications of the device.
However, the power of such devices, as well as the duration of the starting current, should be taken into account.
Autonomous automatic switches differ from conventional ones in that they are installed in separate distribution boards.
The functions of the device include protecting the circuit from unexpected power surges and power outages in the entire or a specific section of the network.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The choice of AV according to the current characteristic and an example of current calculation are discussed in the following video:
The calculation of the rated current of the AV is demonstrated in the following video:
The machines are installed at the entrance of a house or apartment. They are located in durable plastic boxes. The presence of AV in the home electrical circuit is a guarantee of safety. The devices allow timely shutdown of the power line if the network parameters exceed a specified threshold.
Taking into account the main characteristics of circuit breakers, as well as making the correct calculations, you can make the right choice of this device and its installation.
If you have knowledge or experience performing electrical work, please share it with our readers. Leave your comments about choosing a circuit breaker and the nuances of installing it in the comments below.




The following question arose: can a single-pole circuit breaker be used as an input circuit breaker? I heard that this option is not entirely applicable, since it cannot provide reliable protection due to the fact that during shutdown there is only a break in the phase line, and the “neutral” still remains energized. But I haven’t encountered any categorically opposing opinions. Thank you!
What, you can’t read it?
Good afternoon, Vadim.
To ensure safe replacement of the meter, PUE require breaking all wires suitable for the meter (attached a screenshot of the item). There are also typical diagrams of input panels with meters - in order not to describe them, I have attached a screenshot. By the way, on circuits without a meter, they make do with one input circuit breaker.
Regarding the neutral, which remains energized, there is an opinion among ordinary people that the potential of the “neutral wire” is equal to “zero”. In fact, the voltage of this conductor can reach tens of volts during phase imbalances (there have been cases when the “zero” voltage reached 90 V). When a broken phase wire falls to zero, the phase potential is brought to “zero” (until the protection is triggered).
Not a bad post - everything is written in great detail about the choice of slot machines. Bookmarked it. But this is in theory. In practice, I choose an automatic machine depending on the required power (I roughly calculate the current strength - and that’s all). I use machines, as a rule, from IEK or (shown in the photo in the post) ABB - the best in my opinion. And another note: selectivity must be observed - each machine below the circuit must be lower in current value than the previous one - otherwise it will not work. And this is very important for safety.
Good afternoon, Alexander.
Theory and practice “merge” when developing power supply schemes for workshops and enterprises - apartments, cottages are clicked by designers like seeds. It is impossible to choose an economically feasible option for providing electricity to several hundred machines connected by technological chains, range of parts, and production program, following your advice.
Regarding selectivity, the question is also quite complex. For example, a workshop is supplied with electricity via 10 0.4 kV cable lines. And what kind of machines, one wonders, will you install on TP-10/0.4 kV, implementing your theory of selectivity?
To understand the complexity of the task, I have attached a screenshot of several points of the PUE dedicated to selectivity. There are others too.
If we talk about choosing the rating of the machine based on the total load of consumers, then it is necessary to indicate that the cable for the resulting total load must be appropriate. The rating of the machine is selected solely depending on the cross-section of the cable, since the machine is no longer needed for anything other than to protect the cable itself from overheating.So, if the cable to the kitchen sockets is 3x2.5, even though you plug all the appliances in the house into it, the circuit breaker should be no more than 16A. Otherwise, the cable will overheat, the insulation will melt, and there will be a fire.
Good afternoon, Artem! The principles for choosing a circuit breaker are set out professionally by you, but the 16-amp rating of the circuit breaker is not tied to the material of the cores. If they are aluminum, then everything is fine. True, laying conditions affect. If the conductors are copper, then a permissible current of 21 amperes appears when laid in one pipe - I selected the table column you used. A screenshot of the corresponding lines of the PUE tables is attached.
I don't agree with the last comment. First, the maximum current that will cause wire failure varies greatly. For copper wire made according to GOST standards, it can be 30 amperes. Secondly, the cost of connected equipment can be many times higher than the cost of a piece of wire. And the task is not to protect copper or aluminum liners, but to protect devices, the failure of which can cause catastrophic consequences.
Good afternoon, Uncle Vasya 🙂 Artem outlined the principles of choosing a machine correctly - the branch of the network connected to the machine is protected (attached a screenshot of the PUE point). Regarding the accounting of core material, you are right. Protecting expensive equipment is a different story. Here we must take into account the presence of built-in protections.
Good afternoon, I correctly understand that according to your table, for a VVG 3x2.5 cable, a machine with a nominal value of 25A is suitable, and for a 3x1.5 cable, a nominal value of 16A is suitable.I’m asking because serious disputes are roaming the Internet in connection with this issue... I tried to understand the PUE, but it didn’t work out very well.
Many people advise installing a 16A machine on a 3x2.5 cable, and increase the number of groups, thereby increasing wiring costs. What is the optimal argument in this case, what can you refer to to confirm your table.
Do I understand correctly that the rating of the machine must be higher than the permissible continuous current in table 1.3.4. and if so, why? Thank you in advance for your response.
A 25 A machine continuously passes about 5% more than the nominal value, i.e. 26.25 A - this meets the requirements for open wiring and two single-core wires in a pipe, but exceeds the long-term permissible limit for three single-core wires in a pipe
“A single-pole circuit breaker does not perform the function of an input circuit breaker, since when it is forced to turn off, the phase line is broken, and the neutral is connected to the voltage source, which does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection.” — Author, from what voltage source is the neutral connected!?
firstly the neutral is connected to the midpoint of the transformer
secondly, if the zero between you substation burns out, then all the consumers on your side of the break will land on your zero if it is honestly grounded along TN-C-S