Ventilation of industrial premises: rules for organizing air exchange
The main work performed by the ventilation of industrial premises is the removal of used air and the injection of fresh air.With its help, enterprises create a comfortable air environment in workshops and offices that meets regulatory requirements.
It is difficult to overestimate the role of an effective ventilation system. After all, you must agree that only in conditions of clean air, normal temperature and humidity conditions can an increase in labor productivity be achieved.
To understand how to organize sufficient air exchange in a building, it is necessary to understand the types and operating features of different ventilation systems.
We will tell you how natural and mechanical ventilation functions, describe methods for arranging local ventilation of the work area, and also explain the principles of calculating air exchange.
The content of the article:
Classification of ventilation systems
All existing ventilation systems grouped according to 4 characteristics:
- By way of air movement ventilation is called: natural, mechanical or artificial, combined, when both options are present at the same time.
- In the direction of air flow Ventilation systems are divided into supply, exhaust or supply and exhaust.
- By location ventilation systems are divided into 3 groups: general exchange, local, combined.
- By purpose There are working and emergency systems.
The basis for designing ventilation for workplaces in production is the standards prescribed in SNiP 41-01-2003. Natural and mechanical air exchange work according to different schemes.
While the processes occurring during natural ventilation depend on heat and wind pressure and are practically beyond the control of man, forced air exchange is possible only with his active participation.
Scheme of natural air exchange
Ventilation of premises, carried out in the first way, is nothing more than simple ventilation. It occurs without human intervention and is possible when the fences are not tight enough and allow air into the room both from the outside and from the inside.
Direction is influenced by pressure. If its indicators are higher outside, then a path is opened for clean air to enter the room from the street. Otherwise, warm air from the room finds its way out. Often these processes occur in parallel.

Active natural ventilation occurs unorganized due to random circumstances. It is observed in conditions when the air temperature outside and inside the building differs sharply.
This process is also facilitated by the appearance of individual areas with high and low pressure indicators on the side of the hull, intensively blown by the wind, and on its more protected side, respectively. In this situation, infiltration is observed - air enters the room from the windward side, and comes out from the leeward side.
The air exchange coefficient, which characterizes the intensity of the process, with the natural method of ventilation does not exceed 0.5.
Unorganized ventilation cannot provide comfortable conditions for people and operating equipment in the production area.Specially designed systems must be present here.
Organized natural ventilation is realized through aeration or using deflectors. Both the supply and removal of air from the room occurs either through openings in the enclosing structures or through air vents. Duct ventilation must have a deflector.

Natural ventilation using aeration
In workshops where technology provides for the generation of heat in large quantities, aeration involves air exchange carried out through skylights and window openings under the influence of temperature and wind pressure. In cold shops, air assimilation occurs only under wind pressure.
When installing aeration, it is necessary to take into account the wind rose, otherwise harmful emissions from the pipes of neighboring enterprises may enter the production premises. Nothing should interfere with the escape of vapors and harmful gases through the skylights.
The best conditions for ventilation are created by the location of the building on the windward side in relation to hazardous production. The opening and closing of transoms must be automated so that they can be controlled from below.
Their different locations allow you to regulate the supply of fresh air. Aeration is a more suitable option for large-volume workshops in which it is not possible to use mechanical ventilation due to its high cost.

The recommended height of air supply to the room with this type of ventilation is a minimum of 0.3 and a maximum of 1.8 m in the warm period and a minimum of 4 m in the cold season. The best option is specially designed windows on 3 levels. When it’s warm, fresh air passes through the transoms located below, and dirty air leaves through the top.
The middle row of vents provides air flow at subzero temperatures. During the time the air mass reaches the floor level, it has time to warm up.

In production buildings of small volumes, channels or pipes intended for exhaust install deflectors. With their help, exhaust air is removed from workshops where there is a general exhaust hood.
They are also used to remove heated gases from furnaces, presses, and forges. When installing them, they proceed from the trajectory of the prevailing air flow.
Artificial or mechanical ventilation
Being more advanced than natural ventilation, this type of ventilation requires significant financial and operational investments. Such a system may contain devices that not only purify, but also ionize, humidify, and heat the air.
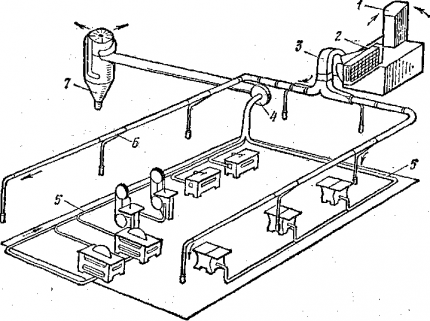
Mechanical ventilation can be either supply or exhaust or combined, that is, supply and exhaust.
Its advantages are obvious:
- ensuring clean air intake and its processing - heating, drying, moistening;
- movement of air masses over considerable distances;
- clean air delivery directly to the workplace;
- removal of dirty air and its cleaning;
- work independence — the efficiency of the system does not depend on environmental conditions.
Basically, exhaust and supply systems work together, but sometimes it is recommended to use only one of these two types.
Task supply ventilation - ensure the supply of air to the work area that has a beneficial effect on people’s health.
It is used where production processes are accompanied by large heat emissions containing a small amount of harmful substances. Clean air flowing through the air ducts is distributed to workplaces through the use of distribution nozzles.
Systems that remove air containing various pollutants from a room are called exhaust systems. This type of air exchange is used in industrial premises where there are no harmful emissions and the minimum value of such a parameter as the air exchange rate cannot be excluded.
These can be storage, auxiliary, and household premises. Air flow is provided by infiltration. They cope well with the task of effectively removing contaminated air and cleaning it aspiration systems.
If there is a need for active and reliable air exchange, use supply and exhaust ventilation. In order to somehow protect slightly polluted premises from neighboring workshops with an increased level of pollution, a slight pressure is created in the system.

At the design stage of creating a supply and exhaust ventilation system, air flow is calculated using the formula:
Lots = 3600FWо, Where
F — total area of openings in m², Wo - the average value of the speed at which air is drawn in. This parameter depends on the toxicity of the emissions and the type of operations performed.
Receiving exhaust devices can be at different heights. The main thing is that polluted air flows do not change their natural trajectory. Emissions that have a higher specific gravity than air are always located in the lower zone, so devices for their intake must be placed there as well.
In the autumn-winter period, the air supplied to the room must be heated. To reduce costs use recycling, which involves heating part of the purified air and returning it to the room.
For PVU operation with recovery 2 rules must be followed:
- At least 10% of fresh air is supplied from outside, and in the return air the content of contaminated impurities does not exceed 30% of the maximum permissible capacity.
- It is prohibited to use recirculation in production where the air mass contains explosive dust, microorganisms that can cause various diseases, emissions belonging to hazard classes 1-3.
The choice of type of ventilation at the scene depends on the weight of emissions, their concentration, and temperature. Generalized ventilation allows you to remove the entire volume of dirty air, regardless of where it comes from.
The most widespread is the channel version. Here, to move air through special air ducts, an ejector unit or turn on the fan - axial or centrifugal type.
If there are no air ducts, the system is called ductless. In this case, ventilation equipment is mounted directly in the wall or ceiling. The main condition is the presence of natural ventilation.
The possibility of emissions with a high degree of explosion hazard appearing in the room does not allow the installation of ventilation equipment on air ducts, so in these cases ejectors are used.
A forced-air, general-exchange artificial ventilation system is often connected to central heating. Outside the building, air intakes are installed to supply fresh air.
The shafts are located above the roof and above the ground. The main thing is that there are no industries with harmful emissions near the receivers.
The air intake openings themselves must be at least 2 m from the ground, and if the production is located in a green zone, the minimum permissible distance from the ground level to the bottom point of the opening should be 1 m.
The principle of operation of general exchange supply ventilation is simple:
- the fan sucks air masses through the heater;
- the air is heated and humidified;
- air flows enter the building through special ventilation ducts.
The volume of incoming air is coordinated by valves or dampers designed for this purpose.

General supply and exhaust artificial ventilation can be open or closed. In the first case, these are 2 independent systems, one of which pumps air, and the second, in parallel, removes previously neutralized waste.
These systems are suitable for workshops where substances of 1-2 hazard classes are released, and the production itself belongs to categories A, B, C.
In addition to working ventilation in potentially hazardous industrial premises, there must also be an emergency version. They make it mostly exhaust. For premises belonging to categories A, B, E, the system is equipped with a mechanical drive.
All elements of the system must comply with the requirements of the PUE. In workshops of categories B, D, D, the presence of natural ventilation is acceptable if productivity is ensured under the most unfavorable weather conditions.
The grilles and pipes of the emergency ventilation system are located in areas of the highest concentration of hazardous substances.
There is no need to install umbrellas on emergency ventilation pipes and shafts. The holes themselves should not be placed where people are constantly present. This will worsen the local microclimate.

Supply emergency ventilation is installed in workshops where, in the event of an emergency, vapors or gases that are lighter than air will be released. Switching to emergency ventilation should occur automatically as soon as the normal system fails.
Local ventilation of premises
Local exhaust eliminates exhaust air in places where it is polluted. The set of industrial hoods includes exhaust fans, pipelines, and ventilation grilles.
Local ventilation, designed to remove substances belonging to hazard classes 1 and 2 from the equipment, is arranged so that when the ventilation system is turned off, starting the equipment becomes impossible.
In some cases, backup fans are provided and local exhaust systems are equipped with automation. Such ventilation is divided into 2 types - supply and exhaust. The supply type of ventilation is performed in the form of thermal curtains and air showers.
Thermal curtains from the air
Openings that remain open for a long time (more than 40 m per shift) or open quite often (more than 5 times) contribute to hypothermia of people in the room. The operation of drying plants that emit pollution also leads to negative consequences.
In these cases, air curtains are installed. They act as a barrier against cold or very overheated air.
Air and air-thermal screens are designed so that in cold weather, when the openings are opened, the temperature in the workshops does not drop below the mark:
- 14°С - while performing work that does not require much physical effort;
- 12°C - when the work is classified as moderate;
- 8°C - when doing heavy work.
If workplaces are located close to gates and technological openings, screens or partitions are installed. The air-thermal curtain near doors facing outside should consist of air with a maximum temperature of 50°C, and at the gate - no more than 70°C.
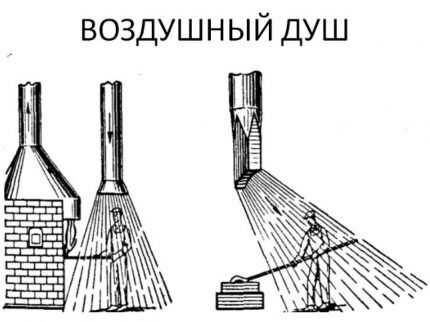
Local exhaust using special suction
The local exhaust system, using special suction, first captures and then removes harmful impurities in the form of gases, smoke and dust.
This is a kind of air shower, the task of which is to pump fresh air into a fixed place and lower the temperature in the inflow area. It is used in production, where workers are exposed to high temperatures and radiant energy with an intensity of more than 300 kcal/m² per hour, emitted by heating and melting furnaces.
There are such installations both stationary and mobile. They must provide a blowing speed from 1 to 3.5 m/s.
There is also such a thing as an air oasis, which is the same device included in the local ventilation system. It creates a microclimate with specified parameters in a certain part of the production room.
Purified air supplied to a given exclusion zone is usually subjected to special heat and humidity treatment.
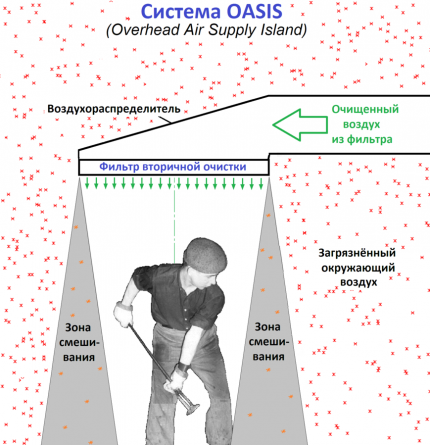
If the local suction device is brought directly to the place of release of substances polluting the space, it will be possible to remove air containing a higher percentage of them than with general-exchange ventilation. Local ventilation can significantly reduce air exchange.
Air exchange calculation
If no harmful substances are released as a result of production activities, then the amount of air required for ventilation is calculated using the formula:
L = N x Lн, Where
N is the number of people usually present in the room, Lн — the volume of air required for 1 person, measured in mᶾ/h. According to the norm, this is from 20 to 60 mᶾ/h.
Using a parameter such as air exchange rate, the calculation is performed using the formula:
L = n x S x H, Where
n — air exchange rate in the room (for production premises n=2), S - room area in m², and H — its height in m.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Here is all about the intricacies of various ventilation systems:
System installation details:
Whatever ventilation system is chosen, it must have two main properties: competent design and functionality. Only if these conditions are met will an optimal microclimate for health be maintained in production.
Do you have anything to add, or do you have any questions about organizing the ventilation of industrial buildings? Please leave comments on the post. The contact form is located in the lower block.





Regarding emergency ventilation installed in rooms of class B, D, D. As the author advises, natural ventilation is acceptable.However, in this case, the main problem of emergency ventilation will be the constant contamination of blowers, grilles, as well as some electrical elements of the ventilation circuit. At the same time, the information presented here speaks of the need to comply with (PUE) “Rules for the operation of electrical installations,” which directly prohibit the risks of any ingress of water and precipitation onto electrical wiring. This means that it is necessary to mention additional insulation of electrical circuits in this case.
Any ventilation gets dirty, Vasily. There is a PPR schedule that includes cleaning. The classes of electrical wiring and electric drive are laid down during the design. If necessary, designers install sealed pipe wiring and a similar electric drive. The author listed all the factors, reminded about the PUE, and did not miss anything. Re-read the text in the screenshot (attached to the comment) again.
It is often observed that the exhaust ventilation of industrial premises does not work effectively. Many mistakes and miscalculations are made even at the installation stage: dust collectors, for example, are installed in the wrong place, the diameter of the pipes and the total length of the ventilation pipe channel are calculated incorrectly. Traction is insufficient where it is needed, and excessive where it is not necessary.
Ventilation installation, Nikolay, is being carried out according to the project. The customer is obliged to supervise the work of the contractor. If its engineering services are not sufficiently qualified, experts are invited. The total length of the ventilation ducts is determined by the design and not calculated.After completion of installation work, testing is carried out - design flaws are eliminated by designers, and then adjustments are made by installers.