Insulating the ceiling in a house with a cold roof: types of effective insulation + installation instructions
High-quality ceiling insulation in a house with a cold roof reduces thermal costs, reduces heating costs and increases living comfort.Thermal insulation is carried out in different ways, using materials of various compositions and forms. How to choose the best option?
We will talk about which methods are most effective in constructing a system that prevents heat loss through the ceiling. We'll tell you what to look for when choosing insulation. In our article you will find valuable recommendations for improving the thermal insulation characteristics of your home.
The content of the article:
The need for ceiling insulation
A cold roof is a budget and practical option for organizing the roof of a house for seasonal living. This design significantly saves construction costs, but does not contribute to heat conservation.
It is advisable to resolve the issue of thermal insulation of the ceiling zone at the stage of building a house. However, insulation is often used in the used premises.
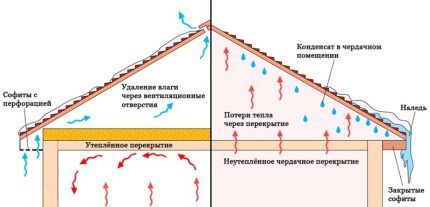
Thermal insulation of the ceiling solves a number of problems:
- Reduces the cooling intensity of heated air, helping to save home heating costs.
- Increases sound insulation in the room, muffling the rumble from the wind or noise from heavy rain.
- In summer, insulating material helps keep the room cool by keeping heated air from outside in.
Insulating the ceiling increases the comfort of a private home and optimizes the microclimate of the room. If the installation technology is followed, thermal insulation prevents the appearance of condensation on structural elements.
Methods of thermal insulation of floors
Thinking about what's right insulate the ceiling of the house Under a cold roof, first of all, you need to decide on the method of thermal insulation.
There are two radically different approaches:
- insulation from the attic side;
- installation of thermal insulation material from inside the room.
The first method is more preferable for a number of reasons. Thus, the installation technology itself is significantly simplified - there is no need to build a suspended frame or fix the insulation with glue to the ceiling.

Also, with this approach, the risks of condensation are minimized. The same cannot be said about thermal insulation from inside the room.
If you choose the wrong insulation and do not exclude contact of warm air with a cold slab, then water vapor from the room will accumulate - this is fraught with the appearance of dampness, fungus and gradual destruction of the ceiling.
However, in some situations, internal ceiling insulation is a necessary measure, for example:
- lack of access to the attic;
- carrying out reconstruction of an old building with a ready-made attic floor;
- thermal insulation of a garage located in the basement.
If internal insulation is necessary, installation technology should be followed to prevent condensation from occurring inside the building. It is important to comply with two requirements: block the flow of water vapor and use insulation of sufficient thickness.
Review of the best insulation for ceilings
The choice of installation method also determines the list of possible heat insulator options. When insulating from the attic side, the range of materials is much larger - from natural compounds to technologically advanced modern solutions. Installation from inside the room imposes a number of restrictions.
Regardless of the placement method, insulation for ceiling system must have low thermal conductivity. The coefficient determines the ability of the insulator to transfer energy from heated elements to cold ones. The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the material retains heat.

Additional requirements include:
- durability;
- environmental friendliness and safety for humans;
- low flammability - it is better to use non-flammable insulators, compositions with minimal smoke generation;
- resistance to rodents - important for materials placed in the attic.
It is important to take into account the vapor permeability of the insulation. But there are nuances here. When thermally insulating a concrete slab from the attic side, it is necessary to use a material that allows steam to pass through. For installation from inside the room, on the contrary, use vapor-tight insulation.
Type #1 - mineral wool insulation
The popular heat insulator maintains its leadership position due to its affordability, ease of installation and good thermal efficiency.

For installation under a cold roof, mineral wool with a synthetic binder, basalt insulation and glass wool are used. The latter option provides maximum thermal efficiency. The thermal conductivity of glass wool is 0.044 W/(m°C).
However, it should be used with caution - the particles cause irritation to the skin and mucous membranes. Glass wool is not acceptable for indoor use. Basalt insulation does not have these disadvantages. Additional advantages of the material: fire safety and plasticity.
General disadvantages of mineral wool materials:
- water absorption;
- low strength;
- tendency to shrink;
- content of unsafe components - abrasive particles or formaldehyde resins.
To place layers of mineral wool, you will need to install wooden logs; it is advisable to waterproof the insulation itself on top.
Type #2 - bulk cellulose insulator
Bulk material produced from paper and pulp waste. To protect against rotting and fire, synthetic components are added to ecowool.

The characteristics of cellulose insulation and the technology of its application have endowed the modern method of thermal insulation with a number of advantages:
- good thermal efficiency - thermal conductivity is about 0.038 W/(m°C);
- the material fills all the voids and cracks, forming a solid fabric - no cold bridges are formed;
- due to its light weight, ecowool of any thickness can be laid;
- durability of service and preservation of original properties;
- environmental friendliness - ecowool does not emit toxic fumes;
- low flammability and self-extinguishing ability;
- vapor permeability.
Despite its many advantages, ecowool has not gained much popularity. The main reasons for low demand: high cost, impossibility of installation by hand.
In addition, ecowool is prone to shrinkage and wrinkles; it is advisable to provide a rigid support on top for movement around the attic.
Type #3 - slab polymer types
This group of insulation materials includes: foam plastic and extruded polystyrene foam (EPPS). Their thermal efficiency exceeds that of mineral wool insulation. The leader is EPPS, the thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.038 W/m°C.

Polystyrene foam is cheaper than polystyrene foam. Among the general advantages are:
- water resistance;
- low biological activity;
- wide choice of geometric sizes and thicknesses.
Both materials are vapor-tight, so they are used to insulate concrete and brick surfaces.

Material suitable for installation from inside the room. Penofol is placed with the foil side facing the inside of the room - the canvas not only retains heat, but also partially reflects it back.
It is advisable to use foamed polyethylene as an independent material in areas with a mild climate.In regions with harsh winters, a combination of penofol and penoplex shows a good effect.
Type #4 - bulk heat insulator
Lightweight porous material in the form of round granules. Contains baked clay. The natural origin of the insulation explains its environmental friendliness.
Additional benefits of expanded clay:
- fire resistance;
- ensuring a good degree of sound insulation;
- durability;
- chemical inertness;
- not of interest to rodents;
- the insulation does not produce dust.
The thermal efficiency of expanded clay depends on the density of the embankment and the size of the granules.

To ensure heat conservation, you will have to use an embankment 20 cm thick or more; in cold regions, the layer is increased to 40-50 cm. This leads to an increase in the cost of the insulation procedure and significantly increases the load on the floor.
Type #5 - liquid polyurethane
Polyurethane foam is supplied to the surface under pressure; special equipment is used for spraying. Polyurethane foam is an excellent solution for attic floors with complex terrain and thermal insulation of hard-to-reach places.
The main advantages of ceiling insulation with foam:
- formation of a seamless sealed coating;
- high adhesion to materials - polyurethane foam fills all cracks and voids;
- low water absorption;
- excellent thermal efficiency due to the porous structure of the hardened foam - thermal conductivity of about 0.027 W/m°C;
- preservation of qualities in humid conditions;
- possibility of multi-layer spraying – relevant for cold regions;
- providing acoustic insulation;
- durability of the coating – service life is about 25 years;
- speed of processing;
- resistance to microorganisms;
- lightness of the material - does not put pressure on the ceiling.
Polyurethane foam is difficult to ignite, the insulation does not propagate combustion.

The total cost includes the price of the insulation itself and the cost of attracting craftsmen with equipment. Spraying foam cannot be carried out if the air temperature in the attic is below +10 ° C.
Type #6 - natural materials
The main advantages of traditional methods: affordable cost and environmental friendliness. The technique of using and the effectiveness of natural materials such as sawdust and algae varies.
Features of sawdust insulation
Bulk woodworking waste is often mixed with shavings and distributed over the ceiling from the attic side.
Insulation methods:
- Dry backfill. Wooden logs are installed on the floor, and the cells are filled with sawdust. The material shrinks over time and requires periodic renewal.
- Wet method. Combine sawdust, cement and water in a ratio of 10:2:1.5, respectively. This thermal layer is more durable.
Weaknesses of sawdust: flammability, rodent hazard and water absorption.

Characteristics and varieties of algae
In coastal areas, algae is widely used; the second name for insulation is damask. The material is distinguished by its naturalness and good thermal insulation characteristics.Rodents do not grow in algae, and the insulation itself is not afraid of moisture and does not rot.
There are three types of damask:
- hanging – bales or loose rolls collected from dried compressed seaweed;
- mats in nets – canvas 10 cm thick, tied with synthetic thread for ease of installation;
- dense slabs – the composition contains up to 85% algae, the rest is a binding component, for example, silicone.
In terms of thermal efficiency, damask is significantly inferior to many insulation materials; the heat capacity coefficient is 0.087 W/(m°C).

Calculation of the thickness of the thermal insulation layer
From the accuracy of determining the thickness of the insulation, which is part of thermotechnical calculationdepends on the effectiveness of thermal insulation. In addition, the indicator allows you to calculate the loads placed on the ceiling structure. When calculating, the values of the permissible weight and the required thermal protection are compared.
The thickness of the insulation is determined by the formula
q = R * k,
Where:
- q – thickness of heat-insulating material, m;
- R – thermal resistance, m2°C/W;
- k – thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation, W/(m°C).
The R value is determined from tabular data - the indicator is calculated for each region, taking into account the climate characteristics.
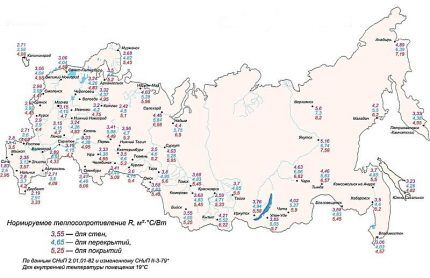
To calculate, it is enough to multiply the indicators 4.26 and 0.038. The last value is the thermal conductivity coefficient of extruded polystyrene foam.The weight of the ceiling is calculated based on the volume of insulation and its density. The first indicator is determined by the product of the area and thickness of the thermal insulation, the second - the tabular value.
The minimum load on the ceiling is exerted by polyurethane foam and ecowool, their density is in the range of 25-60 kg/cu. m. One of the heaviest insulation materials is expanded clay - 180-330 kg/cu.m. m.
Features of installation of different materials
The tactics of action depend on the chosen material and the location of its placement - from inside the room or from the attic.
Laying mineral wool
Installation of insulation is carried out along the attic floor.
When constructing a thermal insulation cake, it is important to meet two conditions:
- ensure protection of mineral wool from water vapor coming from inside a warm room;
- arrange ventilation of the outer surface to ventilate moisture from the insulation.
Mineral wool slabs are laid between beams or strips of prepared sheathing. Can be mounted on the ceiling surface.

The surface is cleared of debris, and if necessary, a wooden frame is constructed.
Further actions:
- Install a vapor barrier membrane.
- Roll out rolls or place mats between beams.
- Install a wooden base, maintaining a ventilation gap between the insulation and the hard floor.
The last step can be missed. However, it will not be possible to walk in the attic or store things there, since mineral wool cannot be pressed.
Internal lining with expanded polystyrene
This thermal insulation option is suitable for concrete ceilings. Expanded polystyrene slabs are fixed to the surface with glue and secured with “fungi”.

Before installing the insulation, the ceiling is treated with an antifungal compound and primer.
The procedure for attaching polystyrene foam boards:
- Apply glue to the insulation, apply and press it to the ceiling.
- Cover the entire area with slabs, leaving no gaps between the elements.
- Use a hammer drill to drill holes for fasteners.
- Kill the fungi.
- Foam the joints and gaps between the plates.
- Cut off the remaining foam and fix the reinforcing mesh with adhesive.
- The surface should be primed and plastered.
After the layer has dried, clean the ceiling and apply the final decorative coating.
Filling the attic with expanded clay
The minimum layer of bulk insulation is 20 cm. To adjust the height of the backfill, you need to prepare a beacon - make the necessary mark on a piece of reinforcement, securing a piece of electrical tape.

There is no need to lay a water barrier on a concrete base.
Sequence of work:
- Pour in expanded clay and distribute the granules evenly.
- Check the thickness of the insulating layer. Its height should be 3-4 cm below the level of the flooring. If this norm is neglected, then when walking through the attic the sound of granules rubbing will be heard.
- Lay a layer of vapor barrier membrane and seal the joints of the panels with tape.
- Install a rigid base. Boards, fiberboard or OSB panels are suitable.
The floor on top of expanded clay makes it easier to move around the attic and increases the effectiveness of the insulation cake.
Application of Spray Insulation
It will not be possible to carry out the work yourself, since spraying will require expensive equipment - a high-pressure apparatus. In addition, skills in working with equipment are required to evenly distribute polyurethane foam.
To start the device, a voltage of 380 V is required. If there is a two-phase network in the house, a generator is connected that produces the required value of the electric field.

Recommended work order:
- Install wooden joists on the attic floor. They will be needed for subsequent fastening of the flooring.
- Fill the device with components in the required proportions.
- Set the gun to the minimum foam supply force.
- Apply polyurethane foam between the joists in an even layer.
- Wait for the composition to dry. If the thickness of one layer is not enough, then the treatment must be repeated.
- Level the cured coating by cutting off the excess to the level of the joist.
- Mount on boards on a rigid base.
To insulate a small ceiling yourself, you can use a disposable foam spray kit.

Assembly and preparation takes a couple of minutes, no power supplies are needed - the device operates autonomously.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Technology of floor insulation with mineral wool:
Thermal insulation of the ceiling of a private house with sawdust:
Insulating the ceiling with a cold roof is one of the conditions for comfortable and economical operation of the house. When arranging a thermal insulation layer, it is important to choose the right material.The installation method is important, as well as the mandatory formation of a reliable condensate shutoff.
Would you like to share your own experience in arranging a thermal insulation ceiling system? Do you have information that will be useful to site visitors? Please write comments in the block below, ask questions and post photos on the topic of the article.




In my house I used two types of ceiling insulation - glass wool and expanded clay. In the early 90s I laid glass wool. After 20 years, I had to change the insulation, I brought gas masks from work (I had to throw out the filters after work). While my father and I were cleaning out the attic, everyone was cursed. My whole body itched. The ceiling is covered with reinforced concrete slabs, so I chose expanded clay for insulation. 15 cm thickness is enough in our region, I hope this is the most durable option of all existing ones.