Ventilation deflector: device, types, installation rules
A well-designed room ventilation system is the key to a healthy microclimate.One of the priority conditions for natural air circulation is the presence of draft. To normalize pressure, a ventilation deflector is often used - the device increases the suction from the ventilation duct due to wind pressure.
Despite the simplicity of the design and affordable price, such a cap significantly increases traction. The only difficulty is choosing the best option among the variety of offers.
We will help you understand this issue. The article provides a detailed overview of the devices and operating principles of various deflectors, and provides practical recommendations for the selection and installation of hoods.
To make it easier for you to decide on the model and understand the sequence of installation of the air “stimulant”, we have prepared a thematic photo and video selection.
The content of the article:
The main tasks of the “ventilation hood”
Efficiency ventilation systems with the natural movement of air largely determined by atmospheric conditions. Air flows circulate due to the lifting force that arises due to the temperature difference between inside and outside the room.
The work of ventilation is also “corrected” by the wind - it can either accelerate or complicate natural air exchange.
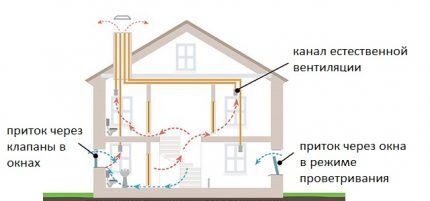
Partially reduce the influence of weather factors, direct them to benefit the functioning of the ventilation system and increase air speed allows installation of a deflector. The module, shaped like a cap, is mounted at the top point of the exhaust duct.
The deflector solves two main problems:
- Protects the mine from being clogged with debris and birds.
- Minimizes the negative impact of precipitation on ventilation equipment.
- Activates and enhances traction, generating and redirecting wind flows - the efficiency of the ventilation system increases by 15-20%. The deflector reduces the likelihood of reverse thrust.
The umbrella design is used to increase draft in the chimney. Besides, chimney deflector additionally acts as a spark arrestor.

Device diagram and operating principle of the deflector
To get an accurate idea of what a deflector is and how it functions, let’s look at a typical diagram of its design.
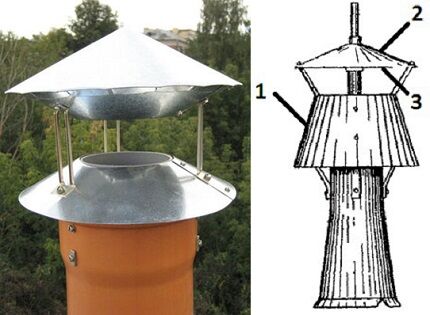
Main parts of the ventilation nozzle:
- Diffuser – base in the form of a truncated cone. The lower part of the cylindrical flask is mounted on the top of the ventilation duct leading through the roof. It is in the diffuser that the air flow slows down and the pressure increases.
- Umbrella – upper protective cap attached to the diffuser with stands. The element prevents debris from entering the ventilation duct.
- Frame - ring or shell.The visible part of the deflector, connected to the diffuser by two or three brackets. The plane of the housing cuts the air flow and creates an area of low pressure inside the cylinder.
Some modifications have a mesh installed to retain small debris. The filter insert somewhat weakens the draft.
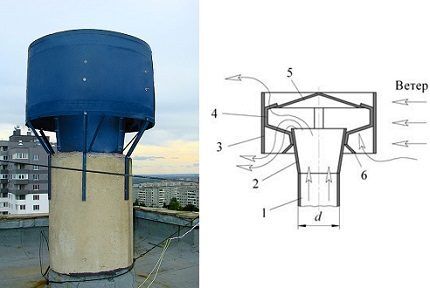
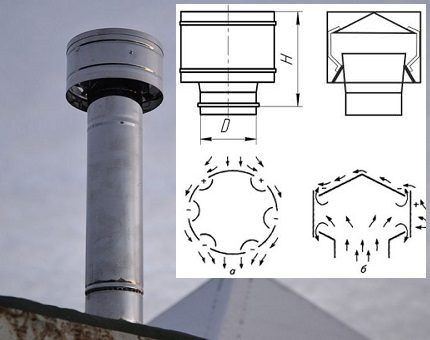
The action of the ventilation nozzle is based on the Bernoulli effect - the relationship between pressure and air flow speed in the channel. During acceleration, caused by a narrowing of the air duct, the pressure in the system drops, forming a vacuum in the pipeline.
Principle of operation:
- The deflector catches the wind.
- Air masses rush into the diffuser, branch and provoke a decrease in pressure at the top of the ventilation duct.
- Exhaust air from the room rushes into the rarefied void.
With the correct selection and installation of the deflector at the end of the exhaust duct, the pressure difference increases, and accordingly, the intensity of air exchange increases.
Classification of wind nozzles
Despite the same purpose, exhaust hoods differ from each other.
When determining the optimal device model, you need to evaluate:
- material of manufacture;
- principle of operation;
- design features.
Material of manufacture. Aluminum, stainless steel, galvanization, copper, plastic and ceramics are used in production.
The optimal solution from the point of view of the cost/quality balance is considered to be steel and aluminum products. Copper deflectors are rarely used due to their high cost.

A symbiosis of strength and decorativeness - combined metal caps coated with plastic.
Principle of operation. Based on their functional features, ventilation devices are divided into 4 groups.
Deflector types:
- static nozzles;
- rotary deflectors;
- static installations with an ejecting fan;
- models with a rotating body.
The first group includes models of the traditional type. Static deflectors are characterized by their simplicity of design and the possibility of self-assembly. The valves are mounted on exhaust shafts of residential and industrial aeration air ducts.
The second group (rotational deflectors) are equipped with a system of rotating blades. The complex mechanism consists of an active head and a static base.

Static exhaust deflector with ejecting fan – modern technology. A fixed cap is installed at the end of the ventilation duct; a low-pressure axial fan is mounted directly below it inside the shaft.
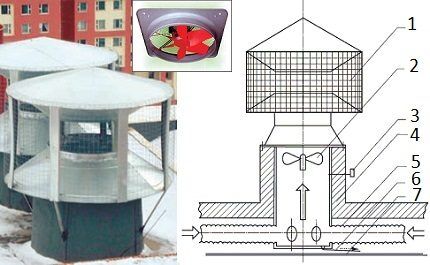
Under normal external conditions, the system functions like a traditional static deflector. As the wind and thermal pressure decreases, the sensor is triggered - the axial fan is switched on and the draft is normalized.
An interesting development that deserves attention is an ejection-type deflector with a rotating body. A rotating hood is installed above the shaft.
The model consists of a horizontal and vertical pipe, which are connected to each other by a hinge mechanism. On top of the deflector there is a partition - a weather vane.
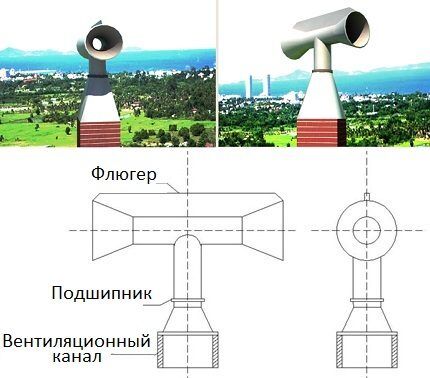
Design features. Models with the same principle of inducing natural ventilation have some differences in design.
Deflectors are of open or closed type, square or round, with one hood or several conical umbrellas. The characteristics of the most popular and effective modifications are described below.
Review of popular models
In practice, the following types have proven themselves well: Grigorovich, Volpera, TsAGI, double and H-shaped deflector, rotary weather vane of the “Net” or “Hood” type.

View #1 - classic Grigorovich cap
The most common option used in ventilation and smoke removal systems. Due to its simplicity and accessibility, the Grigorovich deflector holds a leading position among analogues.
The device is represented by a pair of umbrellas connected into a single “plate”.
The cap is installed on round pipelines or mounted through an adapter plate on rectangular and square shafts.
Thanks to the design, double air ejection is carried out - in the direction of the expanded part of the diffuser and in the direction of the return hood.
The flow velocity under the lower cone increases due to the narrowing of the channel cross-section, as a result, the pressure difference increases.
Type #2 - TsAGI universal nozzle
The ventilation hood, designed by the Aerohydrodynamic Institute, enhances traction due to wind pressure and pressure differences at different altitudes.
The nozzle is complemented by a cylindrical screen, inside of which a prototype of a traditional deflector is placed.
Distinctive features:
- bandage, rack, flange and nipple connections to the air duct are acceptable, depending on the shape of the shaft neck;
- the ability to transport air, a chemically non-aggressive environment (steel models can withstand temperatures up to +800 ° C);
- In winter, ice may form on the inner walls of the cylinder, which can block the flow area.
The deflector is susceptible to wind currents - in calm weather it creates traction resistance.
View #3 - Astato static-dynamic hood
Stato-mechanical deflector - developed by a French company Astato. The device increases the draft of the exhaust flow of the natural ventilation system due to the wind and the fan.
The nozzle is mounted on houses of any number of floors, reconstructed and new buildings.

After turning on the electric motor, the aerodynamics of the ventilation duct are maintained, the degree of vacuum is the total value of the fan pressure and pressure.
Deflector characteristics:
- Installation methods. Nipple connection for round ventilation ducts, through an adapter - for a group of air ducts or rectangular shafts.
- Control Modes. Manual regulation and automatic regulation are permissible - via a pressure sensor or time relay.
- Material of manufacture – aluminum.
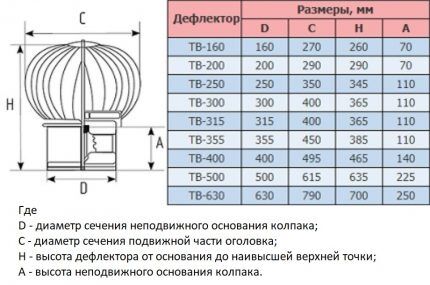
- The lineup. The Astato deflector is available in six positions, with a nominal diameter of 16-50 cm.
Series modifications DYN-Astato equipped with a two-speed fan, the cost of the products is 1300-4000 USD. depending on the dimensions of the deflector.
View #4 - DS series deflector
The open-type static nozzle DS looks like the Astato deflector. But, unlike the French cap, the DS series models do not have moving parts.The cap contains three conical disks.

The highest speed of wind swirl is observed in the truncated channel of the hood - above the ventilation pipe. The pressure difference inside the deflector and remotely from it causes additional vacuum, which increases thrust.
Features of the DS series model:
- the deflector is compatible with forced means of inducing air exchange - fans;
- a wind flow speed of 5-10 m/s increases thrust by 10-40 Pa - the data is valid at a relative humidity of 50°, air temperature +25 °C and a wind flow deviation of up to 30° from the horizontal plane.
Deflectors are available in 13 standard sizes. Designation of ventilation hoods: DS-***, Where *** — internal diameter in mm. The DS-100 model has the minimum dimensions, the DS-900 has the maximum dimensions.
Type #5 - rotary turbine or turbo deflector
The dynamic deflector consists of a fixed base and a rotating turbine head.
The elements of the spherical cap are made of light, thin metal, which allows the drum with blades to start working in light winds - from 0.5 m/s.

Advantages of a turbo deflector:
- efficiency work is 2-4 times higher than that of static models;
- premises protection from overheating in summer and reducing air conditioning costs in hot weather;
- aesthetic appearance – the deflector head is made in the form of an elegant spherical cap;
- preventing condensation inside the roof by lowering the temperature in hot weather;
- economical operation – the active deflector operates without electricity.
The turbo deflector removes excess heat, moisture, dust, vapors and harmful gases from the shaft from the building and under-roof space, thereby increasing the service life of the structural elements of the house.
The disadvantage of an active deflector is zero performance in calm weather.
Dynamic attachments are available wide range. The following companies' products are in demand: Aerotek (Russia), Turbovent (Ukraine), Rotovent (Poland) and Turbomax (Belarus).
View #6 - rotating weather vane of the “hood” type
A rotary cap of the “hood” or “net” type is a semicircular rotating air flow catcher mounted on a rod.
Its curved visors are attached to a bearing assembly. There is a weather vane at the top of the hull, allowing the structure to follow the direction of the wind.
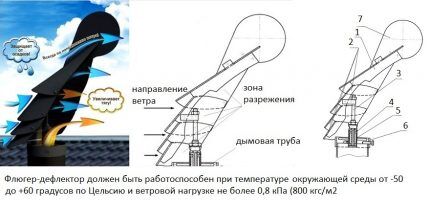
Operating principle of the ventilation “hood”:
- Under the pressure of the wind, the weather vane rotates, positioning itself along the line of the air flow.
- Jets of air pass through the space between the curved visors.
- The flows change vector and rush upward.
- In this zone, according to the postulates of aerodynamics, the speed of air movement increases, and the pressure drops - a deep vacuum is formed.
- The draft from the ventilation shaft increases, providing additional exhaust air suction.
A weather vane deflector is more difficult to make yourself than static models. The nozzle is operational under wind loads of up to 0.8 kPa (no more than 800 kgf/sq.m).
View #7 - H-type module
The H-shaped deflector is preferably installed on manufacturing enterprises. Its purpose is to increase draft in the ventilation and chimney.

The design does not require the use of a canopy, since the top of the air duct is protected by a horizontal element.
The main advantage of the H-shaped hood is its performance in strong gusts of wind. To operate, the deflector is able to use the force of wind flows directed from the bottom up.
The nuances of installing wind hoods
When installing the deflector, you should be guided by SNiP standards.
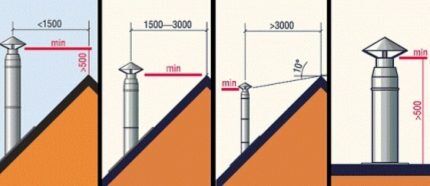
The main attention is paid to the height of the ventilation pipe and hood:
- from 500 mm above the parapet/ridge of the roof, if the air duct is 1.5 m or less from the top of the roof;
- level with the ridge or higher, if the distance from the ventilation duct to the parapet is 1.5-3 m;
- not lower than the deviation line drawn at an angle of 10° from the ridge downwards, provided that the pipe is more than 3 m away.
On a flat roof, the deflector is installed at a height of 50 cm or higher.
Additional installation details:
- installation in the area of the aerodynamic shadow of neighboring buildings is unacceptable;
- the deflector is placed in the free airflow zone, optimally if the cap is the highest part of the roof.
Installation of a round nozzle on a square air duct is carried out through an adapter pipe.
The requirements and methods for installing the deflector on the boiler chimney are described in this article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparison of the characteristics of the rotary turbine and the TsAGI model:
Operating principle of the rotary weather vane deflector:
Technology for installing a turbo deflector on a flat roof:
Such a simple device as a deflector can solve a common problem of natural ventilation - insufficient exhaust draft.
In addition to increasing the efficiency of air circulation, the cap plays a protective role, preventing the ventilation duct from clogging with debris.
Do you have experience in installing and operating a ventilation deflector? Or still have questions on the topic? Please share your opinion and leave comments. The feedback block is located below.




A good ventilation deflector does not guarantee a good hood. However, a budget option does not mean that it will work poorly. We installed an Aerotek turbo deflector because the house area is large, etc. It was already installed when we moved into our new house. It survived the fall and winter and worked without any complaints, completely fulfilling its purpose. In the spring, after the snow melted during heavy rains, the wall began to leak.
For a long time we tried to independently determine the cause of the leak. But it turned out that everything was banally simple. The roofers did not connect the roof to the pipes correctly.This applied to both the deflector pipe and the chimney pipe, which had not yet leaked. However, for preventive purposes it was also redone. Good luck to all installers!
Nowadays, most roofers do not know how to make a passage through the roof. They learn how to twist screws with a screwdriver and think that they can safely tackle roofs. A real tinsmith will do everything for you without using sealants. There will be no leak.
I would like to share a little experience in installing a deflector in the production of dry mixes. I made a choice for a very long time, first at the construction market (Melnitsa) in Moscow, on the recommendation of a ventilation equipment seller, I purchased a deflector from the Cheboksary company Turbodeflector.
He brought it to production, prepared a seat instead of the old chain and began installation. People, I have never seen such disgusting quality of products! The turbo deflector is not centered - I tried to spin it, but it didn’t rotate for a long time, but it was no use, apparently a bad bearing! I packed it back and returned it to the seller...!
Because I have the seat ready, started a thorough search for another deflector, and came across the Moscow company “VentDeflector”. I checked the warehouse in advance, everything seemed to be fine, and started installation. I want to note the quality in comparison with the Turbo deflector - perfect, perfectly centered, rotates constantly even in the slightest wind! Because the production is quite dusty, after installation it was noticeable that there was less dust, especially in windy weather you can notice how the cloud rises and pulls towards the street from the deflector! I was very worried that it would not work for a long time and would become clogged with dust, but now a year has passed and everything is working well.
Hello, Igor. Thank you for sharing your personal experience regarding vent deflectors. Yes, manufacturers have different quality of materials and workmanship, so ordering such equipment through online stores is quite risky. Poor quality assembly can only be detected during the installation process.
In fact, the optimal solution is to order the production of a ventilation deflector from specialists in your city. This way, you will be able to pre-agreed on all the details and technical specifications in order to adjust the equipment for installation as accurately as possible.
Personally, I very rarely buy factory-made deflectors; for installation, clients receive equipment manufactured by trusted private owners. And as practice shows, it is much more reliable than the factory one. I am attaching a photo of the deflector still in the manufacturing process.
Good afternoon! Help with advice, please! We assembled natural ventilation from twisted galvanized pipes with a diameter of 125 mm each. The pipes reach the roof through a shaft and end at the same level as the shaft. The shaft (2600x540) is covered with a fungus at a height of 300 mm from the shaft. The problem is that
the lips sometimes howl like an organ. How can you get rid of this effect? Thank you!