Do-it-yourself garage ventilation: a review of the best options for arranging an air exchange system
Insufficient or ineffective garage ventilation contributes to the formation of condensation on vehicle components.Exhaust gases and evaporation of working fluids make the garage atmosphere unsafe for the car owner.
To avoid these problems, it is necessary to ensure normal air circulation. Moreover, improving the microclimate in a car garage often does not require special engineering and construction skills or significant financial investments.
We'll show you how to calculate and make natural garage ventilation more efficient, as well as suggest alternative methods for inducing air exchange.
The content of the article:
Features of garage ventilation
At the dawn of car enthusiasts, cars needed a fenced shelter to carry out routine repairs. Later, cars became valuable items that required protection from theft - a reliable garage with a perimeter protected from penetration.
The experience of previous generations of car owners requires protecting the car and storing it in a garage.
But a garage is good if it has ventilation. When driving into a parking lot after traveling for many kilometers on rainy and snowy roads, the car brings moisture with it. The room for the car is traditionally small - moisture quickly saturates its atmosphere.
And if the volume of humid air in the garage is not changed 6 times per hour (preferably 10 times), then the car will certainly rust.
SNiP 02/21/99 sets the winter storage temperature of the machine at +5OC, if the box is heated.By the way, this SNiP also allows you not to heat the garage premises.
Comfortable temperature for the car owner (for example, +15OC) in a winter garage it is “uncomfortable” for the car due to the melting of ice and snow stuck to it. It is more rational to adhere to the normative 5OWITH.
The air exchange standard in the garage is established according to ONTP 01-91 in a volume of 150 m3/h for each parking space. Externally, the task is not difficult - determine the diameter of the air ducts, set one for supply, the other for exhaust, and the atmosphere is renewed.
However, in the cold climate of Russia supply and exhaust system indoor parking spaces need to be designed more closely.

Working conditions and calculation of natural ventilation
For self-built ventilation in a garage to work, its design must take into account the volume of air changes, seasonal temperature changes and the wind rose.
Natural ventilation of a car box directly depends on the following parameters:
- Air temperature difference indoors and outdoors. The atmosphere of the garage should be hotter and therefore lighter than the outside air. Then heavy and fresh air will penetrate into the garage through the supply air duct by gravity, trying to replace the less dense volume of the internal atmosphere.
- Pressure differences between the vertical positions of inlet and outlet. A difference of more than 3 m is required between the supply air inlet and the exhaust air outlet.
- Pressure of a moving air mass (wind). On the windward side of the garage, increased pressure is established, and on the leeward side, decreased pressure.It is necessary to place the supply air duct on the side of the prevailing wind direction.
Ignoring these conditions will lead to complete ineffectiveness of natural hood. Therefore, in winter, you should set the car box at a higher temperature relative to the street and reduce air exchange by adjusting the degree of opening of the air ducts.
Required to open in summer supply and exhaust air ducts completely, betting on the compass rose.
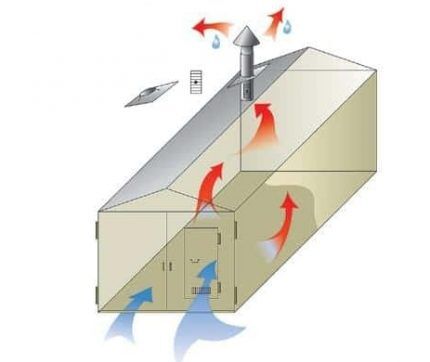
The main parameter of air exchange is its frequency, i.e. the number of complete changes in the volume of atmosphere in the garage with “street” air.
Knowing the normalized frequency of supply and exhaust air exchange (6-10 times) and the internal volume of the car box, it is necessary to calculate the air consumption per hour:
L=n•Vg, Where
- L – air consumption per hour, m3/h;
- n – numerical value of the standard for air exchange rate;
- Vg – garage air volume, m3.
To determine the volume of air a garage can hold, you need to multiply its internal dimensions of width, length and height.
For example, a box 4 m wide, 6 m long and 2.7 m high holds Vg=4•6•2.7=64.8 m3. When choosing, say, seven times air exchange per hour, such a garage will require L=7•64.8=453.6 m3.
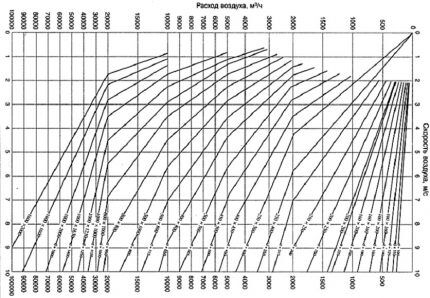
For selection of air duct cross-sections inlets and exhausts, the resulting value of L should be rounded upward, achieving a multiple of 5.
Therefore, the air flow value obtained in our calculation must be increased to 455 m3, because this number is divisible by 5 without a remainder – 455:5=91.
Next, look at the image of the diagram of the diameter of the air ducts and select the appropriate parameter.
Considering that air speed in natural ventilation channels is about 0.5-1 m/s; for the “approximate” garage calculated above, round air ducts with a diameter of 500 mm are required. Or profiled, with an internal section of 450x500 mm.
To improve air flow, you can install not an air duct pipe, but a grated air intake at a height of up to half a meter from the garage floor. Moreover, its cross-section should be two to three times larger than that of the exhaust pipe. Ventilation will improve, but in winter the car box will freeze.
It is necessary to equip the supply grille and exhaust with sliding or removable covers, allowing the cross-section of the air intake to be reduced if necessary.
We pay attention to the sequence of partial overlap of the exhaust and supply openings - first the supply, then the exhaust.
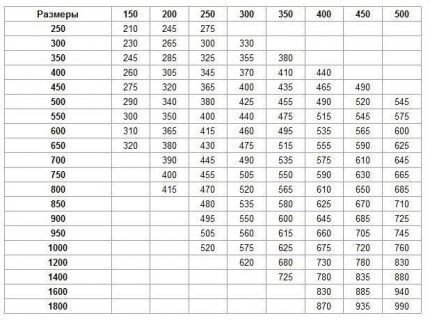
In this case, it is important that the cross-section of the exhaust pipe is not larger than the cross-section of the supply air intake - the draft will overturn. Therefore, when partially closing the supply air duct, it is necessary to reduce the cross-section of the exhaust pipe.
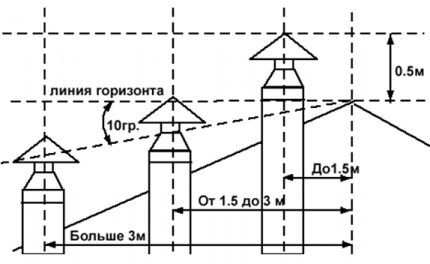
The exhaust air duct must be routed strictly vertically and at least 500 mm above the plane of the garage roof.
Above a gable roof, the hood must be raised to a height corresponding to the proximity of the roof ridge to it (see diagram in the image).
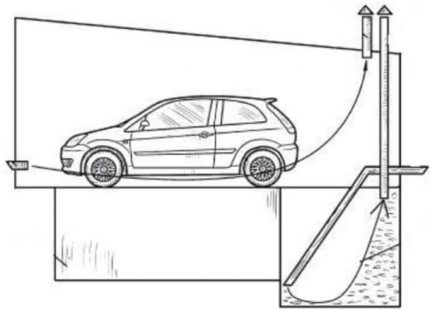
If an inspection pit is installed in the garage for repairs and a cellar for storing food, then for ventilation of the underground rooms it will be necessary to install separate supply and exhaust air ducts.
Thus, an independent pipe is needed to supply air to the cellar and a second, vertical pipe for exhaust.

Ways to improve natural ventilation
Without using mechanical tools to enhance air exchange, you can achieve a stable renewal of the atmosphere in the garage in two ways - by heating the exhaust pipe and installing a deflector on it.
Warming up the exhaust duct
Warmed air is lighter than cold air masses entering through the supply air intake. Striving for the highest point, he exits through exhaust ventilation duct, being replaced by fresh air from outside - the pressure of the internal (in the garage) and external (on the street) atmospheres should be equal.
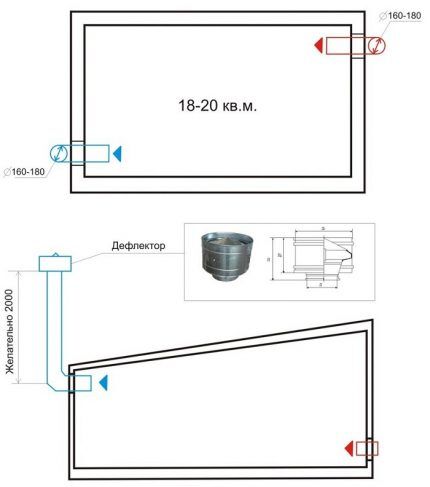
To improve the heating of air in the upper layer of the atmosphere inside a cold garage, you need to paint the exhaust duct black. As a result, the walls of the duct will absorb the maximum amount of solar energy and will heat the air inside the duct, causing it to move upward more intensely.
When planning natural ventilation taking into account the black color, you should not insulate the ventilation duct. However, for the “heating with an incandescent lamp” method, it is extremely necessary to thermally insulate the exhaust duct.
It gets cold in the garage in the fall. This is not a problem for a car, but for supply and exhaust ventilation it is very bad.
If the hot engine for the first hour after entering the box still serves as a source of heat for the air, then after a couple of hours in the unheated garage the temperature will be almost equal to the street temperature. And natural ventilation will stop working.
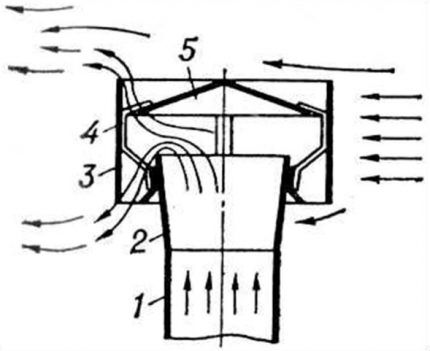
A regular 40-watt incandescent lamp will allow you to maintain air exchange and prevent icing of the exhaust duct (condensation will accumulate in it).
It is enough to hang its cartridge under the opening of the vertical exhaust duct and leave it on. The heat generated by the lamp is enough to move air at a speed of 0.2-0.4 m/s.
Moreover, the air duct must be wrapped in thermal insulation material and make sure that no moisture enters the insulation. There is little heat from the incandescent lamp; it may not be enough for the full length of the exhaust pipe and the air will quickly cool down.
Note that the use of fluorescent or LED lamps does not improve air exchange - they generate significantly less thermal energy. Only incandescent lamps are suitable.
Installing a ventilation deflector
This device helps to increase the exhaust draft by up to 20% without the use of any mechanical devices - due to the formation of a low pressure zone at the head of the air duct.
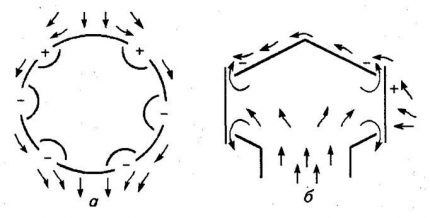
Based on Bernoulli's law, deflectors change the movement of air flows due to their design (section).
The wind is forced around the curved body of the deflector, which leads to the formation of miniature zones of relative vacuum, causing the mass of air in the pipe to move upward.
Structurally ventilation deflector (using the example of the TsAGI project) consists of the following elements:
- Diffuser (glass), having the shape of a truncated conical pipe. The narrow side fits onto the exhaust pipe. Helps establish air pressure differences and increase traction.
- Cap (umbrella) protecting the air duct from the penetration of flying debris and precipitation.
- External housing, having a cylindrical shape. Creates low pressure zones by cutting wind flow.
The TsAGI deflector type is widely used to enhance the natural draft of ventilation pipes in Russia. Along with it, disc-shaped, weathervane, H-shaped and rotary deflectors.
By the way, domestic natural ventilation hoods are especially often equipped with a Grigorovich deflector.
The efficiency of exhaust deflectors of any design is directly related to atmospheric conditions, namely the presence of wind.
That is, in strong winds this device develops maximum thrust in the natural ventilation system, but in calm conditions it does not work at all.
The deflector can not only improve draft, but also prevent “clogging” of the exhaust pipe during strong winds, which low-current natural ventilation cannot overcome.
In addition, the ventilation complex equipped with a deflector device is most protected from draft overturning.
We draw attention to the need to raise the headband of a hood equipped with a deflector above the roof plane by half a meter or more. The location conditions regarding the proximity of the roof ridge, discussed in the diagram above, also apply.
Combined ventilation of the car box
The advantage of combining natural ventilation with a low-power mechanical system is the guaranteed renewal of the garage atmosphere in any weather.
Neither calmness nor summer heat weaken the performance of such a supply and exhaust complex.
The combined ventilation scheme is completely similar to the design of the natural air exchange system. The same arrangement of supply and exhaust air ducts, the same cross-section of air pipes and a deflector at the upper end of the exhaust duct are used.
One difference is the installation of an axial or centrifugal fan.
The power of the ventilation unit should not exceed 100 W, this is enough. The fan must be built into an insulated segment of the air duct, otherwise condensation will enter it.
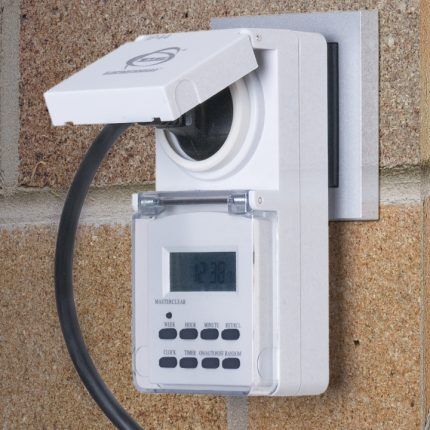
To control the operation of such a fan, an electronic timer built into the adapter between the electrical outlet and the power plug of the exhaust device is useful.
Keeping the exhaust fan on for a long time is unprofitable due to its energy consumption, and there is no need for it. In addition, in winter, the combined ventilation of the garage will be too effective and will make the box very cold.
An adapter with a timer will allow you to set the frequency and duration of fan operation for 24 hours and for several days in advance.

Note that when choosing a sufficiently powerful centrifugal ventilation unit, a larger cross-section for the exhaust air duct may be required. We remind you that the choice of cross-section of the air-conducting pipe depends on the speed of the air flow.
If the internal diameter is insufficient, the hood will make loud noise and draw air poorly.
Installation of a mechanical ventilation system
Its main advantage is its independence from natural factors. There are two main disadvantages: dependence on electricity; quite high cost. Centrifugal fans provide air inflow and exhaust air volume removal.
The following mechanical ventilation systems are installed in car boxes:
- Modular. The supply and exhaust complex is assembled from several independent blocks that ensure the injection and preparation of supply air, as well as the removal of polluted atmosphere. Such modules operate independently; control sensors are required for their joint operation.
- Monoblock. Each such block is a complete mechanical ventilation device; it is responsible for supply and exhaust simultaneously. Among monoblock ventilation devices, models equipped with recovery plates are considered economical. Recuperation allows minimizing energy consumption for heating the supply air.
Monoblock mechanical ventilation is easier to install by preparing a single hole in the garage wall. However, an air supply complex equipped with the necessary modules is more productive.
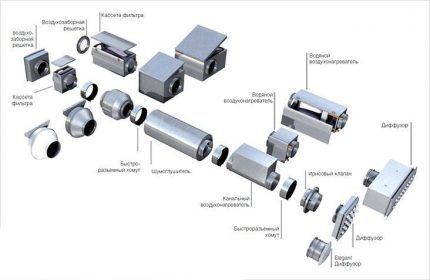
Fresh air is filtered before entering the air ducts and, in the cold season, heated. It is supplied to the garage through air ducts through holes covered with gratings made in the floor or walls almost flush with the floor, as well as in the walls of the inspection pit.
The exhaust air is taken in through an exhaust pipe, in the channel of which a fan of sufficient power is installed.
In large car boxes designed for several cars, it is more efficient to exhaust through air ducts and using a duct ventilation unit.
Organization of temporary ventilation
If repair work is to be carried out in the garage, including welding and painting of metal parts, a serious exhaust hood is required, which does not need to be used all the time.
How to build a system for temporary use? Let's look at one very interesting option:
The following photo selection will help you evaluate the technical essence of the original engineering idea:
The solution presented for consideration allows you to repair a car in winter without opening the gate wide open.
The master will be able to work in temperature conditions that are normal for him, without putting on a warm robe that impedes movement. The hood will release harmful toxins into the vent when the doors are closed.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Effective natural ventilation system in a real garage with a basement:
How to insulate an exhaust pipe above a garage to stop condensation accumulation and freezing:
Mechanical supply and exhaust systems are used in heated garages. For unheated car boxes, a natural ventilation complex is better suited. It is permissible to ventilate underground garages only by means of mechanical ventilation, connecting carbon monoxide controllers.
Looking for a way to improve air circulation in your garage? Or do you have experience using mechanical ventilation units? Please leave comments on the article and ask questions. The communication block is located below.




I am one of the supporters of the idea that good ventilation should be provided in the garage, but heating should not be installed. It is with this option that the car will thaw in winter and the moisture will evaporate. When heating in garages (except for garages in the far north), the car simply rots faster. And ventilation can be done through two pipes - one at the lowest point (for inflow), and the other at the highest point (for exhaust). With this arrangement, you don’t even need to install fans.
Good afternoon If I calculated everything correctly, then with my dimensions (4*11, height 2.5) I need a hole of 66 cm?! Isn't it too much?
Hello. The area of your room is not small, but you did not get an exact figure for the diameter of the ventilation duct opening. Here you need to take into account the air flow that will be transported. Also, you did not indicate what type of ventilation you plan to use: natural or forced?
Without such input data, it is difficult to advise anything, much less make calculations and write specific numbers for different options for ventilating a garage space.
Take advantage this article if you are unable to calculate the correct data. In particular, this is the formula for calculating the cross-section of the air duct: Sc = (L x 2.778) : V.
Thanks for the article and video! I didn’t know how to properly ventilate the garage and insulate the pipe.
Hello!!! Garage 4 width, 6 length, 2.5 height, with a pit. Can you please tell me what pipe diameter is desired??? The garage is not heated.