Calculation of a kitchen hood: how to calculate the power of an exhaust device
The atmosphere of the house is more or less protected from the dusty and polluted street, but is defenseless against air pollutants produced by the kitchen.Agree that an open window when cooking is extremely rare.
You need an exhaust hood over the stove and a ventilation duct with an outlet “outside”, but first, calculate the hood for the kitchen to select equipment with suitable power. But how to do this without involving specialists?
We will try to advise you - this material discusses in detail the procedure for performing the calculation, provides formulas and specific examples of calculations. Also included are visual photos and useful video tips on choosing and installing hoods.
By following the recommendations, you can independently calculate the required power of the exhaust device, which will promptly and completely remove exhaust air.
The content of the article:
How is a hood different from ventilation?
In modern apartments, above the kitchen stove there is a exhaust hood, better known as a hood. Many homeowners are convinced that this air collector is responsible for the ventilation of the kitchen.
Therefore, with a clear conscience, they lead the ventilation duct pipe from the hood into the ventilation hole, designed and built by the designers of the high-rise building.
What happens if the standard ventilation in the kitchen is blocked by an air duct from an exhaust hood? The intensity of air exchange in the apartment will decrease sharply.
Kitchen hood installers and kitchen umbrella sellers usually state the opposite. They will say: this equipment will significantly improve the quality of air supply at home, because it has a powerful ventilation unit.
However, the power of a stove hood has nothing to do with ventilation. The reason is that the air exchange in the apartments of most residential high-rise buildings, especially those built before 2000, was designed with the expectation of supply and exhaust ventilation.
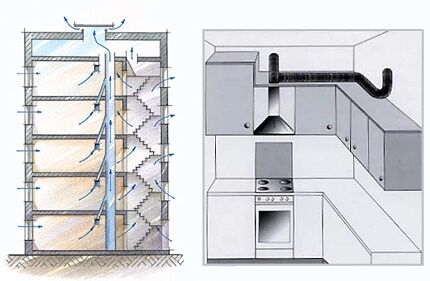
Street air entered through the cracks in the window frames and the front door. And the channels ventilation in the kitchen, in the bathroom and toilet were used to remove “stale” air. It would seem – what’s wrong?
The hood in the kitchen is for extracting air. So why can’t you “stick” an air duct from an exhaust hood into it? It's all about air performance.
Air ducts in residential apartment buildings are designed for a certain load. In general, the throughput of any communications is carefully calculated at the design stage.
And under ideal conditions (clean walls of the ventilation duct, no interference at the entrance or exit, etc.), the performance of natural ventilation in a high-rise apartment will be 160-180 m3/h.
You may also be interested in information about the standard air speed in air ducts, reviewed In this article.
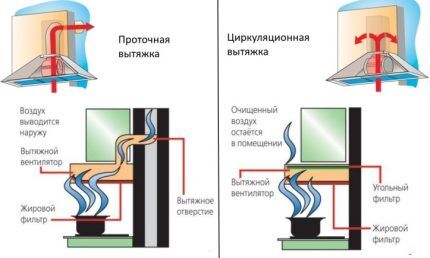
Features of the kitchen hood
Models of exhaust hoods have a significantly higher power - 200-1100 m3/h.This power is necessary to draw volatile pollutants generated during cooking into the air duct.
However, sellers of hoods state a different reason for choosing the power of an exhaust device - the need for frequent air exchange in the kitchen.

Mechanical ventilation standards actually state 10-12 times air changes in the volume of the serviced room (SNiP 41-01-2003).
But the hood located above the kitchen stove does not perform the function of “room ventilation” because it is not capable.
Air in need of renewal (replacement) accumulates near the ceiling. The exhaust hood is not able to suck it into the ventilation duct - its socket is not set high enough. And the air flow during ejection and injection behaves differently.
The electromechanical installation draws air from a distance not exceeding the diameter of the suction socket. Those. with a hood hood width of 400 mm, air located no further than 400 mm from the socket will be drawn into it.
Meanwhile, the air flow is released over a distance exceeding 15 diameters of the exhaust opening.
A simple “home” example: a turned on household fan. On its back side, the air movement is barely noticeable, but on the front side there is a powerful air flow. By the way, the vacuum cleaner only works to suck up dust at a minimum distance from the carpet.

The exhaust hood over the kitchen stove performs the only task - removing the air that comes to it from the surface of the hob.
Of course, in exchange for the pumped air, another portion of it will flow to the stove from a window, an open door to the next room, etc. But a complete change in the air volume in the kitchen will not happen.
If cooking odors rise to the ceiling, they will not participate in the mixing and will be difficult to remove.
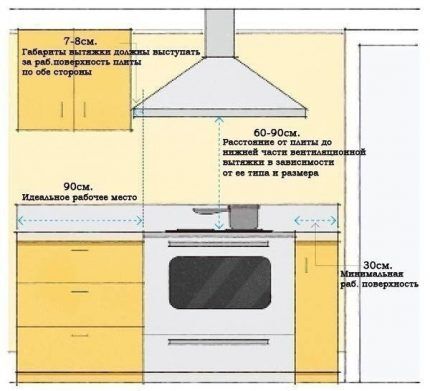
For this reason, the instructions for exhaust hoods contain the following conditions hood placement and work: 600 mm from the electric stove; 750 mm from the gas stove; Do not allow air flows (drafts) when the hood is operating, otherwise odors will spread throughout the room.
A stove hood does not provide air change in the kitchen. When choosing its model, the air volume of the room does not matter. The relationship between the size of the kitchen and the power of the exhaust hood was invented by sellers of kitchen appliances salons.
How to calculate the required exhaust power? Of course, based on the performance of the cooker.
When performing calculations for selecting a kitchen hood, the following factors should be taken into account:
The procedure for calculating the exhaust hood
To calculate the required hood performance, you need to know the parameters of the stove.
In the calculation given below as an example, the characteristics of a gas stove from the Slovenian manufacturer Gorenje (model GI633E35WKB) were used. Please note that the brand and model of the stove were chosen arbitrarily.
You may also find information about how to hang the hood over the gas stove, discussed in our other article.

The calculations below were performed according to the method R NP "ABOK" 7.3-2007. Despite the “industrial” purpose of this method (ventilation of hot catering shops), its formulas can be used to calculate the parameters of a domestic kitchen hood.
When cooking food, the stove generates heat that needs to be recovered (exhausted). The heat generated by the stove creates convection air currents above it, which simplifies the operation of the exhaust hood. But it is impossible to completely eliminate air pollution arising above the stove by relying only on convection.
Stage #1 - calculation of total thermal power
Volatile particles generated during cooking are delivered to the hood or panel by convection air flow. It is the heat developed by the burners that provides the volumes of air for elimination. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate their total thermal power.
To determine it, the formula is used:
QT=q1+q2+q3+q4,
Here q – nameplate thermal power of one burner, kW.
The model of kitchen stove under consideration has four gas burners on the surface; their thermal powers must be summed up.
We count: QT=1.9+1.9+1.0+3.5=8.3 kW. The resulting heat output value is valid when cooking on all burners simultaneously, which is rare.
In principle, it is possible to take into account the heat emission of only three burners with the highest heat output. But let's leave it like that, just in case.
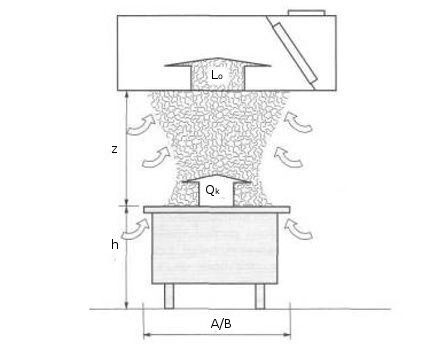
To calculate the hood power, it is necessary to determine the air flow (Lo) according to the parameters of the kitchen stove. However, the air flow formula requires calculating intermediate parameters - the hydraulic diameter of the slab surface (D), air flow in the convective flow (Lki) and volumetric flow rate of combustion products (Lri).
Also in the calculation process, coefficients developed by specialists of NP "ABOC" are used. The coefficient values were selected according to parameters suitable for household stoves.
Stage #2 - calculation of hydraulic diameter and flow
Let's start calculating the hydraulic diameter and convective air flow. The first parameter is determined by the formula:
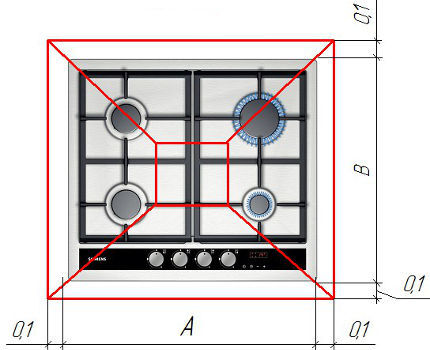
D=2*A*B/(A+B),
Where:
- A – width of the kitchen stove, m;
- B – kitchen stove length, m.
We substitute the width and length of the gas stove model selected for the approximate calculation: D=2*0.6*0.6/(0.6+0.6)=0.6 m.

To determine the volume of convective flow, it is necessary to first find out the share of convective heat release of our slab. It is calculated using the formula:
Qk=QT*KI*KK,
Where:
- QT – plate power determined above, kW;
- KI – the share of sensible heat generated from the thermal power of kitchen equipment. For a domestic stove, the value taken is 250 W/kW;
- KK – the proportion of convective heat release in relation to the sensible heat release of kitchen equipment. The accepted value is 0.5.
We substitute the numerical data into the formula and calculate: Qk=8.3*250*0.5=1037.5 W. Let's move on and start calculating the convective air flow.
The formula is as follows:
Lki=k*Qk1/3*(z+1.7*D)5/3*r,
Where:
- k – coefficient obtained experimentally by specialists of NP “ABOK”. It is taken equal to 5·10-3;
- Qk – the share of convective heat release of the slab calculated above, W;
- z – distance from the surface of the stove to the exhaust hood, m. The minimum vertical distance of the hood from the gas stove is 0.75 m;
- D – hydraulic diameter of the tile surface, m. The formula for its calculation and an example of calculation are presented above;
- r – correction factor, the value of which depends on the conditions of placement of the hood (see the table image above). In our example, the position of the exhaust hood “next to the wall” will be selected, with a coefficient value of 0.75 (due to the conditional “proximity” of cabinet furniture next door, which is usually for kitchens).
We determine the convective flow rate by substituting numerical data into the formula:
Lki=5·10-3*1037,51/3*(0,75+1,7*0,6)5/3*0.75= 0.061 m3/With
As the calculation results show, the air flow as a result of convection over the stove is quite intense. Taking these data into account, you will be able to choose the right power of the exhaust unit.
Stage #3 - calculating the power of the exhaust hood
An electric stove does not emit combustion products during cooking, because The burners are heated without open combustion - thanks to the heaters. But gas burners produce combustion products and the hood will have to remove them.
Formula for calculating volumetric flow rate for methane combustion products:
Lri=3,75*10-7*QT,
Here QT – installed power of the kitchen stove, kW. This parameter was previously found by us.
We enter its data into the formula and get: Lri=3,75*10-7*8,3= 3,1125*10-6.
It is clear from the example that the volumetric flow rate of combustion products of a household gas stove is small. Therefore, when determining the parameters of a kitchen hood, it is permissible to neglect them.
So, it’s time to calculate the air flow for our stove. This is the determining parameter when choosing a hood.
The formula for calculating it:
Lo=Lki+ Lri,
Where:
- Lki – value of air flow from the convective flow rising above the slab, m3/With;
- Lri – data on the volumetric flow rate of natural gas combustion products in the stove burners, m3/With.
All that remains is to enter the data and calculate the required air flow, rounding the result to three decimal places: Lo=0,061+3,1125*10-6=0.061 m3/With. We found the air flow in cubic meters per second, but to select the model of the exhaust hood we need cubic meters per hour (L).
To translate m3/s to m3/h, multiply the resulting air flow (Lo) by the number of seconds in one hour and by the hydraulic diameter of the plate (D)/L=0.061*3600*0.6=131.76 m3/h.
Thus, the sufficient maximum power of the exhaust hood for the Gorenje gas stove model shown in the example, rounded “in reserve”, will be 150 m3/h. Greater power is simply not needed - a waste of electricity.
Why doesn’t a powerful hood “pull”?
First, you should check the condition of the ventilation channel in the exhaust device itself, remove and wash (or replace) the filters - fatty and, perhaps coal, which depends on the hood model. The best methods for cleaning grease from a kitchen hood are reviewed In this article.
You also need to make sure that the ventilation unit is in working order and that there is power supply to it.
The operation of the hood can also be hampered by drafts that interfere with the vertical movement of convection air flow from the stove. If the problem of a “weak” hood is not detected, its source is located outside the kitchen.
The performance of the exhaust hood depends on the cross-section of the ventilation duct where the fumes from the stove go. And homeowners often install an overly powerful hood, or assign it an exaggerated operating mode.
Residential property owners follow a simple logic - the stronger the fan pulls, the better the removal of volatile contaminants from the stove.
This is not true. The performance and operability of the kitchen hood system directly depend on the throughput characteristics of the ventilation duct.
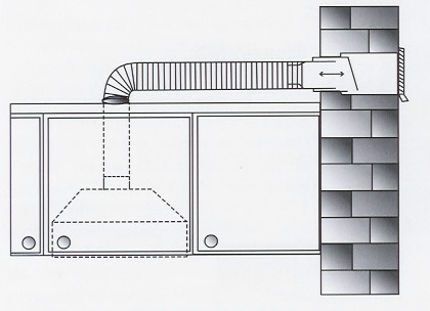
For example, a ventilation duct for supply and exhaust air exchange located in the wall of a house is more than 150 m3/h of air it is not able to remove.
Firstly, the cross-section of such ventilation ducts does not exceed 130-140 mm, which is not enough for mechanical ventilation. Secondly, standard duct ventilation in high-rise buildings is long and contains multiple irregularities.
The instructions for the ventilation unit usually contain a diagram showing the relationship between pressure in the ventilation duct and performance. An increase in pressure causes a decrease in hood performance.
Ventilation ducts in houses are assembled clumsily: uneven walls; solution drips; narrowing due to displaced blocks; lots of turns. Or even completely - the ventilation shaft may be clogged. In such a situation, without cleaning is indispensable.
Attempts to increase the performance of a ventilation hood connected to the house ventilation duct have the opposite effect.
The stronger the air flow, the more intensely it is hampered by defects in the cross-section of the ventilation duct. And if the actively pumped air cannot move forward, it moves backward.
A simple example is a soccer ball. The more air you pump into such a ball, the more difficult it is to operate the pump. The obstacle becomes pressure - there is a lot of air, it tends to come back through the tube, pushing out the pump handle.
The situation is similar with a high-power hood - the more intense the air is supplied, the more its operation is blocked.
The ideal ventilation duct for a kitchen hood is short, with a minimum of bends. Therefore, it is necessary to remove air from the stove not through the supply and exhaust duct, but through one made specifically for the exhaust hood.
A hole in the façade wall, a rigid or flexible air duct (ideally round), check valve and a lattice air intake at the outlet of the channel. This is how you should equip a kitchen hood.
More details about the arrangement exhaust valve through the wall we looked at the street in our other article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Power, brand, design and principle of placement of the hood hood – sellers of kitchen appliances showrooms colorfully talk about all this.
From the video below, you will learn about the nuances of choice that are not mentioned by the sales staff. Hood models are distinguished not by their design, but by the quality of assembly and configuration:
In the following video, craftsmen drill a wall in a high-rise building for an exhaust hood air duct.The work is carried out with professional tools quickly and accurately.
A ventilation duct is mounted to the prepared opening, which will be connected to the hood after finishing the kitchen:
Most videos about range hoods for household use contain either promotional or simplified information of their choice. Moreover, the procedure for calculating power is not given anywhere - it’s all about “kitchen volumes” and “10-fold updates of the atmosphere.”
We are sure that There is only one way to balance the home atmosphere - with the correct calculation of air purification equipment.
Does your kitchen hood do a great job of removing waste air? Share your experience in calculating power. Or maybe you used a simpler method instead of formulas and complex calculations? Tell us about it - leave your comments in the block below.




Sellers of kitchen hoods, in my experience, say anything to sell a hood. They will list a bunch of advantages and benefits, but they will never say anything to the contrary, any negative consequences, so yes, this is a problem. Especially in Khrushchev buildings. True, I was lucky; when installing the hood, I turned to a specialist who knew a lot about all this and successfully selected the best option for me, but this is an exception, as a rule, people install what sellers sell to them.
Here I completely agree with the comment above. There should be a hood in the kitchen not only so that the rooms don’t smell like food! I wouldn’t even think of connecting a hood with a ventilation outlet, that’s not what it’s designed for. And it’s not for equipment sellers to live in this apartment later. You need to know the standards and be guided by them, and not by information that has not been verified.
The article is excellent, but unfortunately, it has an offensive error that is confusing. The illustrations are mixed up: the 1st illustration in the section “Stage #2—calculation of hydraulic diameter and flow rate” should be instead of the 1st in the section “Features of a kitchen hood,” which shows parameters “A” and “B” from the calculation formula. And it so happened that the section for calculating the performance of the hood contains a formula that is refuted at the beginning of the article.
Yes, you are right, thank you. Corrected.
I praised you early for the article. In it you refer to your other article “Installation height of the hood...” where you provide a table with recommendations for selecting performance depending on the kitchen area... We’ve arrived... It seems that you want to please everyone.
Lki=5·10-3*1037.51/3*(0.75+1.7*0.6)5/3*0.75=0.061 m3/s - recalculated several times - always comes out to 0.0983 . How did you get 0.061? Teach.
Yes, that is right.
How, when converting from cubic meters per second, did we multiply by a meter and get a cubic meter per hour? Why in the formula D/L? It is written that r is from the table above, but I don’t see the table and the answer doesn’t agree with me either.
Hello, I need advice on selecting the cross-section of a rectangular plastic channel for a kitchen hood with a capacity of 400 m3 (output round D = 120 mm). Channel length 4.5m and 4 rotation angles. Is a cross-section of 120x60 mm suitable or do I need 204x60 mm?
Good afternoon, Vladimir Viktorovich.
The equivalent diameter of a rectangular duct, denoted De in calculations, is determined as follows:
De = (1.3×(a×b)×0.625)/(a+b)×0.25.
Here “a” and “b” are the sides of a rectangular duct. All values are taken in millimeters.
For a channel of 120x60 millimeters we get:
De = (1.3×(120×60)×0.625)/(120+60)×0.25 = 130 (mm).
This ventilation duct runs along an equivalent diameter, and 204×60 will be redundant.
There is an article on the site “Calculation of the area of air ducts and fittings”, which will be useful for you to take into account other features of your exhaust system.
Our dear, the area of the outlet is approximately 11310, and the veterinary channel is 120x60-7200. So, with your calculations, you will get a blockage (the throughput diameter of the channel is lower than the outlet diameter). But 204x60 approximately corresponds to the nominal value of the hood outlet, so don’t fool people.
204x60 is fine, the arithmetic is simple
There are errors in calculations in article 2 (hello and goodbye).
Firstly, Lki=0.098322 according to your data and your formula. I calculated it manually, entered it into Excel... And apparently I’m not the only one.
Secondly, to convert m3/sec to m3/h you simply multiply by 3600 (twice the number of seconds in an hour by 60). Why did you have to multiply by D to convert cubic meters per second to cubic meters per hour??? And how will you then get the necessary units of measurement? You multiplied the flow in m3/s by the diameter in meters (and by the number of seconds in an hour - a dimensionless quantity). Your output is meters to the fourth power per hour. Wonderful miracle.
Total, instead of 131.76 m3/h, according to your formulas and data, it comes out to 353.96 m3/h.
Let's either get serious: either correct the arithmetic, or correct the mistakes in the formulas...
I have a big question about the release from a kitchen umbrella onto the facade of a building.Isn’t it necessary to run a ventilation duct along the façade above the canopy of the house? Otherwise, all your pleasant smells from cooking will go directly to your neighbor through his slightly open window (necessary for the air exchange process in his apartment), which he will not be happy about, and the not very pleasant process of finding out through the authorities will begin whether this can be done using snips and so on... And here the management company or other supervisory authorities can issue an order to eliminate such an arbitrary solution to the issue. (and stretching a channel over the canopy is, firstly, expensive and secondly, it spoils the appearance of the facade) That is. drill hole in the wall at your own risk?