Calculation of pipe volume: principles of calculations and rules for making calculations in liters and cubic meters
When finding the amount of required liquid in a heating system, it is often necessary to solve a separate problem - to calculate the volume of a pipe with given parameters.The calculation formula itself is simple. However, in practice, to obtain an accurate result, it must be used carefully.
We will talk about how to calculate the internal volume of an important communication system. In the article we presented, the options for carrying out calculations for pipelines and heating devices are discussed in detail. Taking into account our advice, you will quickly solve the problem.
The content of the article:
Geometric parameters of pipes
To determine the volume of a pipe, it is necessary and sufficient to know only two of its indicators: length and internal (actual) diameter. It is important not to confuse the last parameter with the external size, which is given for the correct selection of fittings and connecting elements.
If the wall thickness is unknown, then DN (internal bore diameter) can be used instead of the calculated internal diameter. They are approximately equal, and the DN value is usually indicated on the marking, which is placed on the outside of the product.
Before trying to calculate the volume of any pipe, it is necessary to avoid a common mistake and bring all parameters to a single measurement system. The fact is that the length is usually expressed in meters, and the diameter in millimeters. The relationship of these two units is as follows: 1 m = 1000 mm.
In fact, it is possible to reduce the parameters to intermediate values - centimeters or decimeters. Sometimes this is even convenient, given that in this case the number of decimal places or, conversely, zeros will not be very large.
For pipes not produced in Russia (and not for Russia), the diameter can be expressed in inches. In this case, it is necessary to recalculate, taking into account that 1″ = 25.4 mm.
Formula for a single pipe
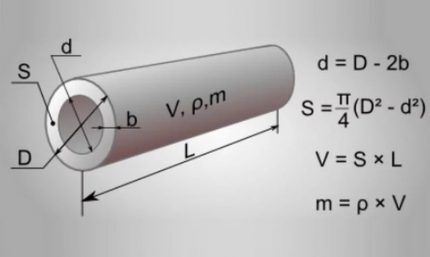
From a geometry standpoint, the pipe is a straight circular cylinder.
The volume of such an object is equal to the cross-sectional area multiplied by the length:
V = l * S
In it:
- V – volume (m3);
- l – length (m);
- S – cross-sectional area (m2).
The cross-sectional area of a pipe shaped like a circle with a known diameter is calculated using the formula:
S = π * d2 / 4
Here:
- π = 3.1415926;
- d – circle diameter (m).
The final formula for the volume of a pipe with a known internal diameter and length will be as follows:
V = π * l * d2 / 4
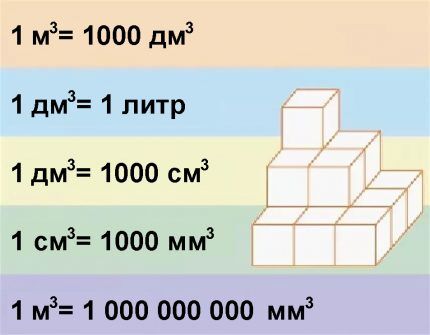
If the unit of measurement for the length and diameter of the pipe is another value (dm, cm or mm), then the volume will be expressed in dm3, cm3 or mm3 respectively.
Also, I wanted to show you a simple way to measure the outer diameter of a pipe (D) without calipers. D = L/π, Where L - circumference:
To correctly calculate the volume of pipes, you need to substitute two parameters into a simple formula: length and internal diameter. The more accurately they are measured or calculated, the more accurate the result will be.
Applied examples of calculations
Specific examples will provide significant assistance in understanding the principles of calculations and the sequence of actions when performing calculations, which interested visitors should familiarize themselves with.
Task #1 - calculating the volume of coolant required
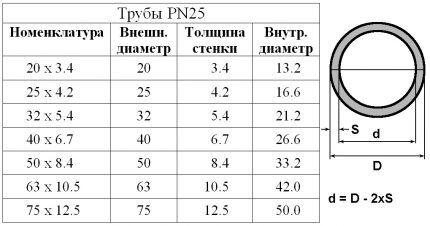
For a country house of temporary residence, you need to calculate the volume of purchased propylene glycol - coolant does not harden at temperatures down to -30°C. The heating system consists of a 60 liter jacketed stove, four aluminum radiators of 8 sections each and 90 meters of PN25 pipe (20 x 3.4).
The volume of liquid in the pipe must be calculated in liters. To do this, you need to take the decimeter as a unit of measurement. The formulas for converting from standard length values are as follows: 1 m = 10 dm and 1 mm = 0.01 dm.
The volume of the boiler jacket is known. V1 = 60 l.
The passport of the aluminum radiator Elegance EL 500 indicates that the volume of one section is 0.36 liters. Then V2 = 4 * 8 * 0.36 = 11.5 l.
Let's calculate the total volume of pipes. Their inner diameter d = 20 – 2 * 3.4 = 13.2 mm = 0.132 dm. Length l = 90 m = 900 dm. Hence:
V3 = π * l * d2 / 4 = 3.1415926 * 900 * 0.132 * 0.132 / 4 = 12.3 dm3 = 12.3 l.
Thus, we can now find the total volume:
V = V1 + V2 + V3 = 60 + 11.5 + 12.3 = 83.8 l.
The percentage of liquid in the pipes relative to the entire system is only 15%.But if the length of communications is large or they use a system "water heated floor", then the contribution of pipes to the total volume increases significantly.

Task #2 - calculating the volume of a homemade radiator
Let's look at how to calculate a classic homemade heating radiator made from four horizontal pipes 2 m long. First you need to find the cross-sectional area. You can measure the outer diameter from the end of the product.
Let it be 114 mm. Using the standard parameters table steel pipes, let’s find the wall thickness characteristic of this size – 4.5 mm.
Let's calculate the internal diameter:
d = 114 – 2 * 4.5 = 105 mm.
Let's determine the cross-sectional area:
S = π * d2 / 4 = 8659 mm2.
The total length of all fragments is 8 m (8000 mm). Let's find the volume:
V = l * S = 8000 * 8659 = 69272000 mm3.
The volume of vertical connecting tubes can be calculated in a similar way. But this value can be neglected, since it will be less than 0.1% of the total volume heating radiator.
The resulting value is not informative, so let’s convert it to liters. Since 1 dm = 100 mm, then 1 dm3 = 100 * 100 * 100 = 1000000 = 106 mm3.
That's why V = 69272000 / 106 = 69.3 dm3 = 69.3 l.
Large radiators or heating systems (which are installed, for example, on farms) require significant volumes of coolant.
Therefore, since it will be necessary to calculate the volume of pipes in m3, then all dimensions will need to be immediately converted into meters before substituting them into the formula.
Task #3 - calculation of the required length of PP pipes
You can get the fragment length using an ordinary ruler or tape measure.Minor bends and sagging of polymer pipes can be neglected, since they will not lead to a serious final error.

To maintain accuracy, it is much more important to correctly determine the beginning and end of the fragment:
- When connecting a pipe to a riser, the length must be measured from the beginning of the horizontal fragment. There is no need to grab the adjacent part of the riser, as this will lead to double counting of the same volume.
- At the entrance to the battery, you need to measure the length up to its tubes by grabbing the taps. They are not taken into account when determining the volume of the radiator according to its passport data.
- At the entrance to the boiler, you need to measure from the jacket, taking into account the length of the exiting pipes.
Curves can be measured in a simplified way - consider that they run at right angles. This method is acceptable, since their total contribution to the length of the pipes is insignificant.
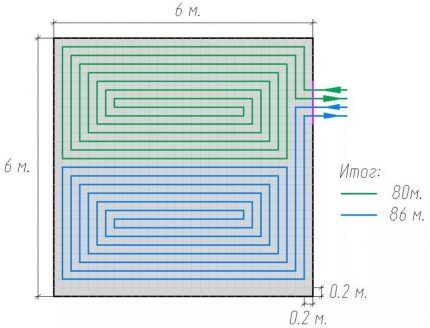
The volume of a warm floor is calculated by the footage of installed pipes.
If there is no length data or diagram, but the pitch between the tubes is known, then the calculation can be carried out using the following approximate formula (regardless of the installation method):
l = (n – k) * (m – k)/k
Here:
- n – length of the heated floor section;
- m – width of the heated floor area;
- k – pitch between tubes;
- l – final length of the tubes.
Despite the small cross-section of pipes that are used for water heated floor, their total length leads to a significant volume of contained coolant.
So, to provide a system similar to the figure above (length - 160 m, outer diameter - 20 mm), 26 liters of liquid will be required.
Obtaining the result using the experimental method
In practice, problematic situations arise when the hydraulic system has a complex structure or some of its fragments are laid in a secret way. In this case, it becomes impossible to determine the geometry of its parts and calculate the total volume. Then the only way out is to conduct an experiment.

It is necessary to drain all the liquid, take some kind of measuring container (for example, a bucket) and fill the system to the desired level. Filling occurs through the highest point: open type expansion tank or top release valve. At the same time, all other valves must be open to avoid the formation of air locks.
If the water movement along the circuit is carried out by a pump, then you need to let it run for an hour or two without heating the coolant. This will help expel residual air pockets. After this, you need to add liquid to the circuit again.
This method can also be used for individual parts of the heating circuit, for example, a heated floor. To do this, you need to disconnect it from the system and “spill” it in the same way.
conclusions
Despite the fact that the network offers us a huge selection of software products for calculating the coolant volume, there are GOST tables for determining the internal volume of pipes, you need to know the principles of “manual” calculations.
They are necessary for those who independently construct and repair communications, and for those who use the services of design and construction organizations. Useful information will help you determine the material consumption before installing the system, accurately calculate the estimate and get an idea of upcoming operating payments.
Would you like to talk about how you calculated the volume of coolant for an autonomous heating system in a country house or country house? Do you have information that might be useful to site visitors? Please write comments, post photos related to the topic of the article, and ask questions in the block below.



