Sewerage installation in a private house: drawing up a diagram and project + stages of work
A separate section of engineering communications design is sewer system planning.Owners of cottages and country houses often have to independently draw up diagrams and install equipment, so knowing the nuances of organizing work is simply necessary.
The efficiency of the system largely depends on whether the sewerage installation in a private house is done correctly - the internal pipe system and the equipment connected to them. For competent design, it is important to take into account everything: from the choice of components to the material used to manufacture individual elements. And we will tell you how to do it correctly.
The content of the article:
Sewer system design
Unlike electricity, gas, and water supply systems, which are installed in accordance with documentation certified by certain authorities, sewerage systems on your own land plot and in your house are allowed to be installed without permits.
However, one cannot do without a project, as it will protect against errors associated with violation of generally accepted requirements.
For example, one of the common violations is failure to respect the boundaries of the sanitary zone when installing a drainage pit. The supply and drain systems must not come into contact with each other.
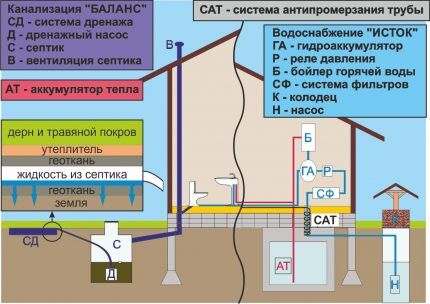
The installation of internal wiring is often associated with errors in the organization of ventilation, incorrect choice of pipe diameter or angle of inclination.
The construction of an axonometric diagram is usually carried out by specialists. They also carry out hydraulic calculations of the internal network and the highway located on the outside of the building. Now there is a more interesting option - creating a sewer model in 3D format.
3D modeling programs allow you to create an accurate and complete project that simplifies the selection of pipes, fittings, fasteners, and installation methods as much as possible.
They turn to specialists for a project when they want to reduce risks. But there is another option - study sanitary and technical standards, familiarize yourself with internal wiring diagrams, learn to understand the quality of plumbing equipment and draw up a project yourself.
Placement of important system components
The peculiarity of an autonomous sewerage system is that the principles of its arrangement depend on each component in the overall system.
For example, the criterion for choosing a wastewater storage tank is not only the number of people living in the cottage, but also the number of connected sources for draining technical and household water - from the house, garage, bathhouse, summer kitchen.
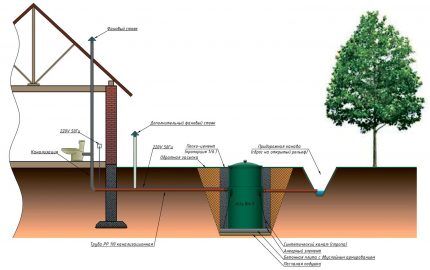
Based on location and main functions, sewerage is divided into 3 categories:
- internal – a network of pipelines from plumbing equipment to the exit outside, beyond the walls of the house;
- external – highway from buildings (houses, bathhouses) to treatment equipment;
- cleaning systems – septic tanks, drives, filter fields, wells, settling tanks, biological treatment stations.
When considering the layout of the internal sewerage wiring in the house, you need to take into account the location of the external main and cleaning (storage) equipment.
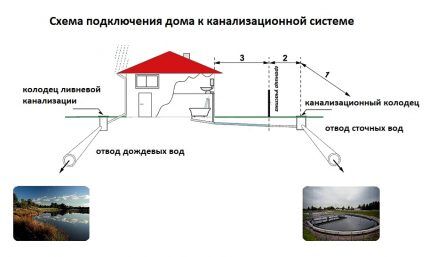
A complete system includes not only drainage of household wastewater, but also storm drain - a complex of storm water inlets, gutters, pipes and connecting elements responsible for the collection and accumulation of rainwater.
Domestic sewerage on diagrams is usually designated K1, storm sewerage - K2. There is a third type - K3, but this is industrial equipment that has nothing to do with private farming.
Source data analysis
Everyone's sewerage conditions are different. Small country houses are characterized by the simplest system: a riser with a pipe outlet to the bathroom, where a toilet and shower are installed.
Multi-room or two-story cottages are equipped with a network of pipelines, which also converge to one riser, less often to two.
Accordingly, projects for different houses will differ. To take into account all the nuances, it is necessary to answer a number of questions before choosing a scheme:
- What method of wastewater treatment is appropriate?
- Is it possible to connect to a centralized sewer?
- How much wastewater should a treatment plant accept per day?
- How often will the drainage system be used? (Year-round, seasonal, weekends).
- Is additional insulation required for pipes?
- What pipe material is optimal for creating a network?
- Will the waste drain by gravity or will a pump be required?
Most of the questions will arise during the design process, when you will need to select a wiring diagram and materials for its assembly.

The external pipeline is laid in the same way - with slope from the building to the pit or treatment plant.
Important rules for setting up an internal network:
- the cross-section of the pipes is selected taking into account the volume of waste;
- During the installation process, the principle of serial connection is used;
- the number of turns and sudden changes in elevation are kept to a minimum;
- ventilation equipment must be installed;
- think over installation locations for inspection hatches;
- choose thermal insulation for areas located in unheated areas.
If the pipeline is long, it is difficult to maintain the slope along the entire line, so additional equipment is installed - circulation pump.
Work planning and scheme selection
The installation of sewer pipes is usually carried out together with the installation of a water supply system; accordingly, it is better to design these two systems together.
If we summarize all the documents that make up the project and try to act according to the rules, we will get the following list:
- General data - description and conditions for installation of water supply and sanitation systems based on regulatory documents.
- Explication of the premises (explanation of the diagram) indicating wet areas and the method of waterproofing them.
- Calculation of water consumption and wastewater disposal volumes taking into account standards.
- Floor plan for the location of the water supply system and axonometric diagram.
- Floor plan for sewerage location.
- Specification - a listing of all components, indicating the quantity or footage.
The last point is difficult to calculate unless there is an exact diagram (model) of pipelines indicating all turns and connections.
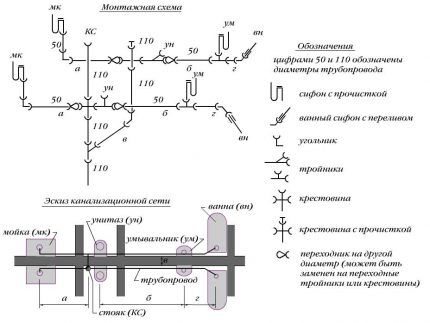
Having diagrams developed for a specific building, wiring becomes much easier, and with the availability of modern materials, almost anyone can do it.
Therefore, owners of new private houses act as follows: they order documentation from designers, and do the installation themselves.
Internal drainage system design
Internal sewerage has long taken on a standard form, which can be called the most rational: horizontal pipes are connected to risers located vertically. The riser is designed for an increased volume of wastewater, so its diameter is larger.

The internal wiring is connected to the external main, which consists of pipes of even larger diameter. The pipeline leads to a septic tank or other storage and treatment facility.
The location of the riser and the lines connected to it is subject to certain rules. For example, all wet areas are usually located in adjacent rooms: the kitchen is across the wall from the bathroom or toilet. Often the rooms are combined, an example of this is a shower room combined with a toilet.
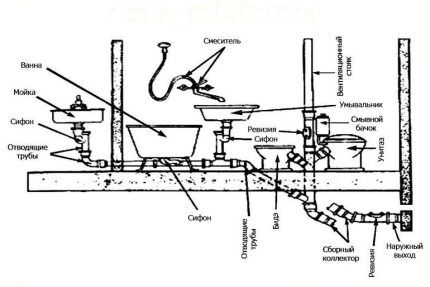
So the sewer pipe has a minimum length to the riser, therefore, the drains move outward by gravity, without additional force. The riser, in turn, is located at the exit of the sewer line and water supply from the house.
The closest plumbing fixture to it is the toilet. If you place a bathtub or kitchen between the toilet and the riser, then with each flush, water will be sucked out of the siphons.
Tilt is a necessary condition for a gravity flow system. The angle of inclination depends on the diameter of the pipe. There are parameters from which it is not recommended to deviate: for pipes 50-80 mm - 25-35 mm/meter of line.
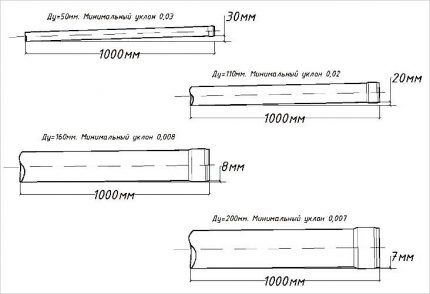
Thus, the wiring in a country house should cover a minimum set of plumbing equipment: toilet, kitchen sink, shower (bath).
Residential buildings usually have more connected appliances, which may include additional sinks and toilets, a Jacuzzi, a dishwasher, grease trap, chopper, etc.
When installing the system, you cannot do without turns, although it is recommended to reduce their number. Every drop and turn is a chronic risk zone that provokes a blockage.
If it is not possible to avoid sharp turns, it is necessary to provide free access to them: either leave them open, or disguise them by equipping an inspection hatch.

The location of wet areas and the treatment plant or main line leading to the central pipe should be planned in advance. Ideally, they should be located next door, literally behind the wall.
The closer the sewerage elements are located to each other, the fewer problems its operation will cause.
To avoid gross mistakes during installation and to be on the safe side, we recommend that you study SNiP 02.04.01-85, which sets out in detail the norms and rules for installing water supply and sewerage systems.
Main stages of work
Installation work is carried out in stages. Sometimes the order of events changes - much depends on the readiness of the premises and the specific layout.
But you still need to strive for the generally accepted order:
- Release laying - pipes connecting the internal and external systems. It passes through the wall, so it must be placed in a sleeve - a heat-insulated safety casing. There should be no connections or joints in the wall crossing area.
- Riser installation - a vertical pipe running through all floors and ceilings. Usually, 1 riser is installed, but if the length of the internal pipeline exceeds 10 m, then it is better to install a second one.
- Pipe routing — branches leading to plumbing equipment. The diameter of the pipe leading from the toilet is the largest - 100-110 mm, the rest are 50 mm each.
And only after the installation of sewer pipes, the devices are connected, followed by testing of the system.
Recommendations for performing installation work:
Metal pipes and fitting have not been used for a long time. Cast iron was replaced by lightweight and practical polymers: PVC (gray), PP (light gray or white).
Plastic pipes have a perfectly smooth inner surface, excellent resistance to heat and aggressive substances. They are easy to handle and install due to their low weight.
Ventilation system equipment
In order to comply with sanitary standards and make living in the house as comfortable as possible, the sewage system must be equipped with ventilation.
To prevent stagnation of gases in pipes and their penetration into living quarters, install fan pipe.

You can refuse to install additional ventilation equipment, but provided that the private house is no higher than 2 floors and the load on the sewer network is minimal.
If many people live in the building, there are more than 2 bathrooms, and wastewater is discharged to a treatment facility, then the installation of a waste pipe is required. Thanks to it, the atmosphere in the house will be healthy, and the water from the water seals will not disappear anywhere due to the pressure difference in the network.
Features of wiring in a multi-storey building
The number of risers does not increase due to the presence of the 2nd or 3rd floors, but the connection diagram becomes more complicated, since branches are present on all floors. For multi-storey buildings there is a “code” set out in SNiP documents.
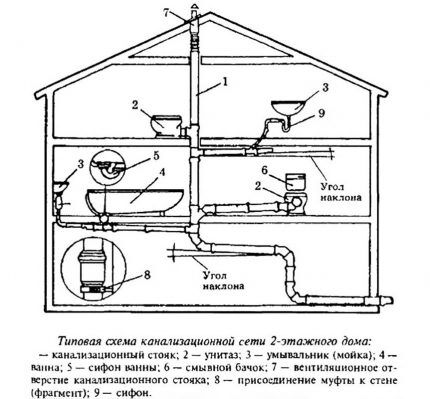
The length of the risers increases and the presence of a drain pipe becomes mandatory. It extends above the roof approximately 1.2-1.5 m in height. Instead of a fan pipe, a vacuum valve is sometimes used.
The protection of the riser in the ceilings is carried out using compensators necessary to suppress linear expansion. The rest of the installation principles, as well as connecting the taps, remain the same.

There are rules for basements and ground floors equipped with toilets. If the toilet is located below the level of the treatment plant, a fecal pump will be required to move the wastewater.
The pumping system is more expensive than the gravity one and is energy dependent, which has its disadvantages, especially with frequent power outages.
Conclusion and useful video on the topic
Tips for installing plastic pipes:
More information about wiring in the bathroom:
Ventilation device and drain pipe outlet to the roof:
Drawing up diagrams and designing sewerage wiring in a private house should be done by specialists or, at a minimum, people with an engineering education.
Independent planning from A to Z is possible only after a thorough study of building codes and regulations. But assembling a sewer system is a completely different matter. Even an amateur can do it if you strictly follow the instructions and carry out installation according to the diagrams.
Do you have any questions, found any shortcomings, or have valuable information that can supplement this material? Please leave your comments in the block below.




When I was making my own sewer system, I had to suffer because of the design of the shower tray. I did everything according to the rules, but the slope doesn’t work. The tray of the selected shower cabin is too low. But it was no longer possible to turn it back. In general, I made the maximum possible slope for this height, and was dissatisfied. The water is bad, in the sense that it drains slowly. It seems like a small problem, but it’s unpleasant that this happened.
Wouldn’t it be better to divide the drains into two categories - “black” drains from the toilet and “gray” drains from the sink, shower, washing machine, dishwasher and other household needs? Will allow you to save significantly on sewer trucks.
Good afternoon, Ruslan. Most modern sewage systems in the private sector are self-contained and require calling sewer men no more than once a year. If we talk about arranging filtration wells, then arranging several different volumes also does not make sense, since the total volume of wastewater remains unchanged. Siltation that requires calling sewer trucks occurs no more than once a year.
If we talk about the high level of groundwater, which does not allow installing a filtration well and the inability to discharge treated wastewater after a septic tank into a ditch or onto a filtration field, then dividing it into two categories “black” and “gray” will not lead to savings. The filling of two cesspools will be exactly the same in volume.Moreover, costs will increase due to the different filling times of the two containers. The “gray” containers will fill up faster and require calling the sewer trucks, at the same moment the “black” container will be conditionally 25% full. You won’t wait for two containers to be filled at the same time and stop using the conditional shower?
Draining into one common system will always remain a more rational solution.