Septic tank design: operating principle and basic organization diagrams
Country houses and country buildings, as a rule, are located remotely from the centralized sewer network.Therefore, the issue of organizing a local treatment system is very relevant for many homeowners. The optimal solution to the problem is to install a septic tank on the site.
However, it is difficult for an uninformed consumer to navigate the variety of offers. But, you must agree, the uninterrupted operation of equipment and sewage systems as a whole largely depends on the right choice.
To make your task easier, we have prepared a detailed review of autonomous structures. Let's figure out what the structure of a septic tank is and the general principle of operation of the cleaning system. We will also outline the features of the functioning, installation and operation of different septic tanks.
Based on the information provided, photo and video selection, you will be able to determine the optimal modification of the unit to suit your needs.
The content of the article:
Basic elements of a septic tank
A septic tank is a local treatment plant designed to create a sewerage system independent from central networks.
The main tasks of the element are the temporary accumulation of wastewater and their subsequent filtration. Modern septic tanks have become an improved alternative to traditional cesspools.
Understanding the structure and operating mechanism of a septic tank will make it easier to select a treatment plant and its installation.
The designs of different modifications have some common components. The cleaning system is a sealed tank that includes one or more compartments.

The septic tank chambers are separated by partitions. The movement of liquid between them is carried out through overflow pipes.
A drain pipe is connected to the first compartment from the internal sewage system of the house, and from the last chamber purified water is discharged into the ground or semi-purified water is discharged for soil purification.
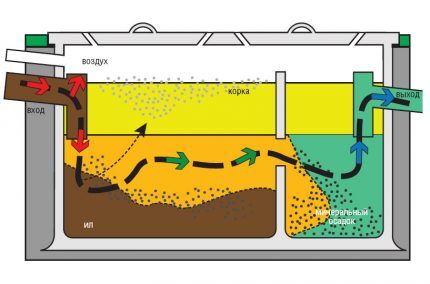
The main components of all treatment units are:
- Tanks for settling wastewater. Storage tanks are made of plastic, metal, concrete or brick. The most preferred models are made of fiberglass and polypropylene - the materials are resistant to abrasion and guarantee the tightness of the tank throughout its entire service life.
- Incoming and outgoing pipeline. Overflow pipes are installed at an angle, ensuring unhindered flow of liquid between the tanks.
- Service elements. Inspection wells and hatches. At least one well is installed on the external route of the sewer pipeline. When the length of the branch increases to more than 25 m, an additional revision is arranged.
- Ventilation system. Regardless of which bacteria (anaerobic or aerobic) are involved in the process of wastewater processing, air exchange is necessary for the normal functioning of microorganisms, methane removal and maintaining the desired temperature.
The simplest scheme for ventilating a local sewerage system includes one riser at the beginning of the system, and a second one at the outermost section of the septic tank. When constructing filtration fields, a ventilation riser is installed on each drainage pipe.
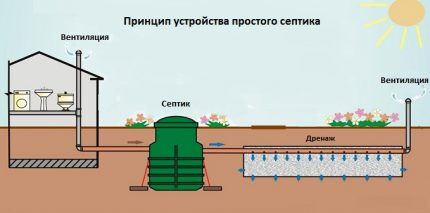
General principle of operation of the treatment plant
The functioning of any septic tank is based on the principles of gravitational settling and biological filtration using a natural or forced method. It is possible to use bioenzyme preparations and biofilters. Conventionally, the sequence of sewage treatment can be divided into several standard stages.
Stage 1. Primary cleaning. The sewer pipe from the house carries wastewater into the first tank or compartment. Here a rough cleaning of suspended large particles occurs. Heavy suspensions (grains of sand and similar insoluble waste inclusions) settle to the bottom of the chamber. Light fractions (fats and oils) rise to the surface and flow into the next compartment.
Stage 2. Decomposition of heavy particles. The waste that has sunk to the bottom of the first chamber begins to ferment and decompose - the process takes about 3 days. As a result, sewage breaks down into a thick mass, carbon dioxide and water.
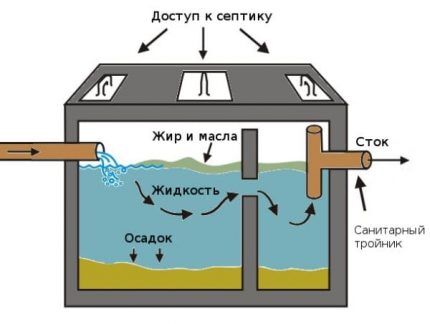
Stage 3. Re-cleaning. In the second chamber, the waste is re-decomposed. In some septic tanks, at this stage, due to the action of special bacteria and preparations, chemical (personal hygiene product waste) and organic compounds break down.
Stage 4. Liquid drainageAnd. The further path of the water depends on the type of treatment system. The purified liquid can flow into the reservoir for subsequent watering of the garden.
If the degree of purification is insufficient, then the water must undergo a further purification process through infiltration, a drainage well, fields for ground filtration, etc.
A schematic description of the traditional operating principle of a septic tank conveys the general features of the process. Each modification of the treatment plant has design and operational nuances.
Features of the operation of different types of septic tanks
All local treatment systems are divided into three categories: storage tanks, settling tank models with soil post-treatment and septic tanks for deep biological processing of wastewater. Let's look at how each septic tank works in more detail.
Storage wastewater system
Essentially, a storage septic tank is an analogue cesspool – a sealed durable single-chamber tank into which sewage enters. In storage-type structures, waste is collected and temporarily stored. As the tank fills, the wastewater is pumped out using vacuum trucks.

The design of the sewer system is as simple as possible and consists of a storage tank and an external pipeline.
The septic tank can additionally be equipped with:
- check valve – prevents the movement of sewage in the opposite direction;
- alarm with drain level sensor – notifies the owners about the filling of the tank and the need to pump out sewage.
Popular models of storage septic tanks: Bars-N, Bug, Rodlex, Purges.

Sedimentation tanks with ground treatment systems
Units with ground-based post-treatment are classified as overflow structures.The system consists of two or three sections and a device for additional filtration of wastewater. Once in the storage tank, the wastewater settles and decomposes under the influence of anaerobic bacteria.
Flowing from container to container, wastewater goes through several stages of natural separation. However, the degree of purely mechanical processing reaches a maximum of 65 - 70%. Therefore, for complete treatment, wastewater leaving sedimentation tanks must undergo additional post-treatment before disposal and discharge onto the terrain or into the ground.

Methods for organizing ground wastewater treatment:
- filtration well;
- underground cleaning field;
- filter trench.
Filter well. Installed in sandy soils of varying coarseness and density. Can be used in sandy loams with a minimum plasticity number.
Make filter well can be made from precast concrete elements, stone or brick. The structure has no bottom - the base of the well is filled with crushed stone. The height of the drainage layer is 1 m.

Underground filtration field. A set of perforated pipes located on the filter platform - sand and gravel backfill. The clarified and settled water in the septic tank is supplied to irrigation pipes with holes.
The liquid seeps out and enters the soil filter.The pipes can be connected by a collector jumper to a ventilation outlet or equipped with separate ventilation risers.

Filter trench system. The structure is used on clay soils and in areas with the possibility of discharging treated wastewater into an unused reservoir. In prepared trenches 1.5-1.7 m deep, pipes are placed in two tiers: the upper one is called irrigation, the lower one is called drainage.
The water settled in the septic tank enters the upper pipeline, seeps through the perforations and undergoes further treatment through crushed stone and sand. Then the wastewater passing through the natural soil filter is collected by an underlying drainage pipe - a drain, through which it is discharged to the disposal site.

The main “element” of post-treatment and disposal of wastewater is not the drainage structure, but the multilayer soil filter itself. It is only necessary to assemble an interface for the effective distribution of liquid throughout the earth.
Septic tank with biological treatment
Bioseptic is a deep cleaning station based on microorganisms. The system is a sealed single block, reinforced with stiffening ribs and divided into several chambers. The number of sections determines the cleaning efficiency.
When wastewater enters the septic tank through the sewer pipe, it is subjected to various treatment methods.The output water is purified by 90 - 96% or more, which allows it to be used for watering plants or discharged into a reservoir. Additional filtration in soil systems is not required.
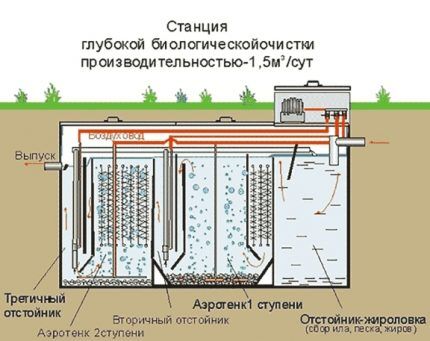
The operating procedure of the “bioseptic”:
- The first chamber acts as a sump. Here, sewage is divided into particles of heavy and light fractions, forming a floating film and sediment, and processed by anaerobes that do not require oxygen supply.
- In the second compartment, organic and inorganic waste decompose under the influence of aerobic microorganisms, which require a regular supply of oxygen for processing and their own life activity.
- In the third chamber, filtered wastewater is disinfected with chemical components or re-exposed to aerobe bacteria.
To activate aerobic microorganisms, oxygen must be supplied to the chambers of the septic tank - the device is equipped with an aerator. Therefore, most biorefinery plants are energy dependent.
Basic diagrams of popular models
In an effort to increase the efficiency of the septic system, manufacturers are constantly improving the design of the units. Some are trying to simplify the design and make the operation scheme more understandable, while others are increasing the number of cycles and the quality of cleaning by introducing innovative technologies.
Tank – comprehensive cleaning with infiltrator
Septic tank Tank – treatment system with ground treatment devices.The one-piece body of the device is reinforced with thick ribs 17 mm thick. Due to its design, the septic tank can be installed on different soils.
Thanks to the block-modular structure, if necessary, it is possible to “increase” the system’s performance.

The water purification cycle in a septic tank tank is divided into the following stages:
- Heavy inorganic substances are deposited in the receiver. The clarified water flows into the second compartment.
- The liquid undergoes anaerobic processing and, during the fermentation process, is broken down into simple compounds. The second chamber contains membranes that retain fat fractions.
- In two-compartment settling tanks, the cleaning cycle ends in the infiltrator. In three-chamber tanks, water undergoes biological treatment. The last compartment is filled with a colony of bacteria that can utilize impurities.
At the outlet, the water is 75-80% purified (depending on the number of chambers). For complete clarification, the system is supplemented with an infiltrator - a tank without a bottom, installed in a trench on a “cushion” of sand and crushed stone.

Topas – multi-stage biofiltration
Septic tank Topas – sewer system for deep bio-cleaning. The design of the unit is fundamentally different from the design of “horizontal” septic tanks. The vertically oriented body is divided into 4 sections, circulating between which, sewage is purified by 98%.
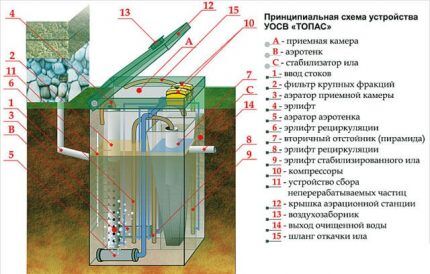
The diagram of the aerobic septic tank structure shows that all sections of the treatment plant are connected to each other by hoses. An airlift is a type of pipe pump that transports purified water, sludge and other impurities from one compartment to another.

Compartment 1. Primary sewage enters the chamber and, under the influence of aerobic bacteria, is broken down into light components, water and sludge.
Compartment 2. The chamber receives wastewater that is 45-50% purified. In an aeration tank, the air flow lifts small particles to the surface of the water. The compartment has a pyramidal shape, which promotes rapid sedimentation of sludge. Through the airlift, the liquid flows into the next chamber.
Compartment 3. In the secondary settling tank, the wastewater is re-converted into water and sludge.
Compartment 4. Purified water accumulates in the chamber. As the tank fills, the liquid level sensor rises, transmitting a signal to the drainage pump that the tank is full.
Triton – non-volatile cleaning system
Septic tanks Triton performs mechanical and biological filtration with ground purification. Important advantages of Triton models: compactness and simplicity of design. For a summer cottage, a small country estate or an allotment with a bathhouse, the Triton-Mini septic tank is often chosen.
The two tanks are connected to each other at the top pipes and at the bottom.This solution increased the space for the accumulation of sludge on the common bottom, and allowed semi-purified water to flow freely into the adjacent compartment.
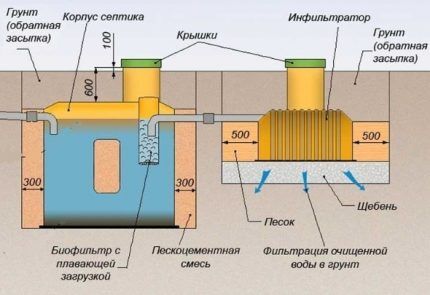
For post-treatment of wastewater in a local treatment system Triton-Mini infiltration is provided Triton-400.
Ecopan - six-stage wastewater filtration
Septic tank Ecopan – local station with a full cycle of biological sewage treatment. The design is designed for difficult operating conditions: heaving, clayey soil, high groundwater levels, large depth of installation of the supply pipeline.
The tank is cylindrical in shape with a reinforced bottom. The rigidity of the container is increased by transverse partitions. Inside, the septic tank is divided into six chambers.
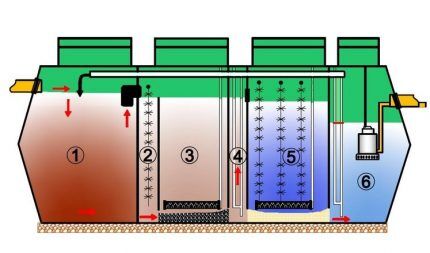
Operating principle:
- In the septic chamber, wastewater settles and solid fractions settle.
- In the anaerobic compartment, microorganisms process wastewater, purifying and clarifying it.
- In the aeration tank, aerobic bacteria come into action. The aerator saturates waste with oxygen, activating the action of microorganisms and accelerating the breakdown of organic and inorganic substances.
- The secondary settling tank accumulates sludge residues, which are pumped into the first chamber for repeated cleaning using an airlift.
- The post-treatment bioreactor contains dolomite. The mineral promotes better filtration of wastewater.
- The third settling tank also contains an airlift, which removes sediment into the first chamber.
After treatment, purified water is discharged into natural soil or discharged into a storage tank for use for technical purposes.
Rodlex - storage type septic tank
Storage tank Rodlex made of polymer using rotational molding. The one-piece container is equipped with elongated necks and lids (hatch diameter – 80 cm). The septic tank is used as a cesspool.

If it is necessary to expand the working volume, several tanks are connected in series to form an integral storage system.
Fast – aerobic recycling technology
Septic tank Fast – an innovative solution for the treatment of household wastewater. The unit is designed in such a way that the wastewater processing work is carried out as quickly as possible.
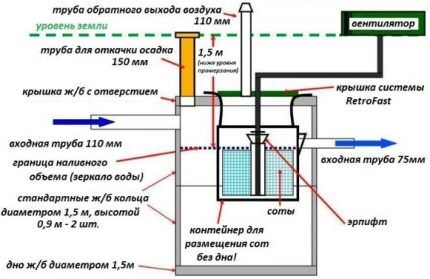
Sewage entering the receiving compartment is immediately treated with aerobic microorganisms. With the help of a compressor and a fan, air is supplied to the septic tank - the biomass is activated and breaks down the waste. In the cellular structure of the module, sewage, air and active microorganisms are mixed - the wastewater is converted into water and sediment.
At the same time, the airlift is switched on, ensuring the movement of liquid into the second compartment.Here the water settles and clarifies naturally - the silt falls to the bottom. Anaerobic bacteria continue to work on the decomposition of sewage.
The clarified liquid is discharged through the outlet. In parallel with the drainage, a new portion of sewage is received.
The Fast septic tank is a self-regulating system that adapts to wastewater with large fractions or sewage with chemical components. Thanks to the cellular structure of the module, bacteria are capable of self-healing.
The action of aggressive chemicals kills microorganisms deposited on the walls of the septic tank and the surface of the wastewater. The bacteria inside the cells survive and continue to actively reproduce.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Visual videos will help you get a complete understanding of the structure and operating principle of treatment plants.
The main components of a local sewer system based on a septic tank Tank and its principle of operation:
The principle of fluid movement in an autonomous sewer system Topas:
The procedure for deep processing of wastewater using the example of a Unilos Astra septic tank:
Understanding the structure and principle of organizing the cleaning process, you will be able to choose the most optimal septic tank model. Despite the external similarity, each modification has its own technical and operational features that must be taken into account during installation and maintenance of the system.
Are you looking for a septic tank for a country house or cottage? Or do you have experience using such installations? Please leave comments on the article and share your impressions about the use of autonomous wastewater treatment plants.




Oh, that's the system. I’m going to install a septic tank in the summer, so I’m looking for various kinds of information.In principle, the device is clear, I wonder how much it will all cost, and where to order installation. I figured that Topas is more suitable for me, because the plot is small and a vertical unit is the most reasonable option. There would be a bigger picture of his device, otherwise I can’t see where and what.
PM me. At one time I designed them as part of various cleaning complexes and carried out commissioning work. I will explain to you all the installation details.
Hello. Perhaps it will be seen better this way.
Here you need to decide: either you need to build a cesspool, or build a septic tank. If you have a shower or bath, a toilet and a washing machine, in my opinion, it is easier to make a septic tank. There are no particular difficulties in this. First of all, it is a tank consisting of several compartments or several sequentially located chambers. The compartments/chambers are connected by pipes through which water flows from one compartment to another. From the sewerage system from the house, the pipe goes to the first compartment, the treated wastewater goes into a filtration field or into a storage tank for watering the soil. Nowadays, plastic tanks are popular; they are durable and affordable.
We have a high groundwater level in our area. We chose between old Tver and modern Eurolos GRUNT. In the end, we ordered the second one, because... this is essentially the same Tver, only modified and brought to mind. We are very pleased with the septic tank. According to the manufacturer, the degree of purification is 99%, there are not even competitors yet!
My opinion is that the degree of purification tending to 100% is nothing more than an advertising gimmick. This doesn't happen.
The supply ventilation opening should be 2-4 meters lower than the exhaust opening (according to the text), and drawn in reverse. How to understand this?