Fittings for steel pipes: types, classification, marking and installation examples
The arrangement of utilities with the laying of steel pipelines of various configurations cannot be performed without the use of connection parts.
Before you begin calculating the system and assembling it, you need to understand what fittings for steel pipes the modern market offers and how the parts are installed, don’t you agree?
We have prepared a detailed review of pipe fittings for making detachable connections, provided recommendations for the selection of elements, and also described the specifics of their application. Step-by-step instructions for installing a threaded fitting and a ferrule will help you assemble a pipeline without the involvement of specialists.
The content of the article:
Options for connection parts
End connection steel main pipes carried out in two ways: detachable and permanent. The first involves the use of fittings, the second involves welding parts.
The material for the manufacture of connecting elements is most often stainless steel or ferrous metal. From non-ferrous metals: brass or copper.
The connecting elements can be simply steel or coated with a chrome-plated composition. Chrome-plated products are more preferable in that they have higher anti-corrosion properties.

Although experts do not recommend using fittings made of materials other than those used in the manufacture of pipes, this is still allowed. So, brass fittings great for joining copper pipes. Copper can be used to safely connect pipes made of any type of material. The reliability of the connection will not suffer from this.
The main thing is to avoid combining copper elements with bends made of unalloyed galvanized steel. When these two metals interact, corrosion processes are immediately triggered, which has a detrimental effect on the durability of the products.
The fittings presented on the market come in several versions in terms of shape and purpose:
- Couplings – elements installed on straight sections for joining pipes of equal diameter.
- Tees – structures with three outlets that change the direction of the pipeline and create a branch from the main branch in one direction.
- Crosspieces – designs with four outlets divide the flow into several “beams”, providing a branch from the main highway in perpendicular directions.
- Adapters – designed for joining elements with different diameters.
- Fittings – used when it is necessary to connect a rigid pipe with a flexible hose.
- Stubs – used when it is necessary to seal pipe ends tightly.
To change the direction of the pipeline within 45-90° in both the vertical and horizontal planes, angles are installed.

The range of nominal bore sizes produced by fitting manufacturers is quite wide and varies from 8 to 125 mm.
Specific application of pipe fittings:
- products D 16-63 mm used where the pressure does not reach 16 atmospheres;
- fittings D 75-125 mm used for pipelines where the pressure is 10 atmospheres.
All dimensions of metal pipe products comply with the current GOST 8996-75. According to this regulatory document, custom-made production of couplings with an internal diameter of 150 mm is also allowed.
If the pipe size is indicated in inches, then this indicates the outside diameter.If the other units of measurement are millimeters, then this is an indicator of the internal cross-section of the product.
Important point! Regardless of the design, when purchasing fittings, you should pay attention to the fact that both the outer and inner surfaces do not have any cavities or foreign inclusions. The end planes of the connecting elements must be strictly at right angles to the axes of the passages.
Main types of fittings
Depending on the method of connection to the metal pipe, fittings come in several types: welded, crimped, threaded and flanged. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Weld-type couplings
Welded fittings, referred to as segment fittings, are among the non-separable elements. They cannot be dismantled and reused. Segmental parts are used for pipelines operating at temperatures from -70°C to +450°C with a system operating pressure within 16 MPa.
The main difference between such products is that their ends have a smooth surface. The selection principle is based only on the identity of the characteristics and dimensions of the pipes and connecting elements being joined.

Welding fittings are used when laying communications that are placed inside structures and do not require replacement of structural elements over a long period.
Due to the complexity of installation, welded fittings are used on pipelines in the oil and gas industry. To create tight connections, installation is entrusted to qualified specialists working on special equipment.
Screw threaded elements
Threaded fittings used for joining gas and water supply steel pipes are produced with cylindrical screw threads. They are used in the assembly of pipelines whose temperature regime of the transported liquid does not exceed +175°C. As a rule, this type of connection is chosen for pipelines with a diameter of up to 50 mm.

Stainless alloy steel threaded fittings are widely used in the construction, chemical, oil and gas industries. But they found their main application precisely in the arrangement of water supply networks and heating systems.
Among novice craftsmen and non-professional plumbers, a simple connection method called the “American” connection is widely popular. It received its name in honor of the country in which it was patented. The main elements of such a connection are the body and the union nut.

One of the halves of the “American” is screwed onto the short thread of the first pipe, and the second - onto the counter pipe. Then both halves are twisted using a union nut placed on the fitting. A high degree of sealing is achieved due to the seal. But to improve it, many craftsmen still lay flax fibers “the old fashioned way.”
Features of crimp couplings
Pipes can be securely connected without welding or threading by installing compression fittings.They are available with one or two O-rings made of flexible, elastic materials. They are mainly used when it is necessary to join pipeline elements of the same diameter.
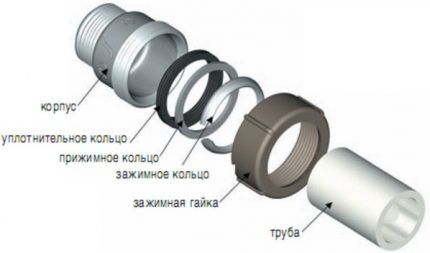
The design of crimping elements for steel pipelines is practically no different from fittings for metal-plastic pipes or “brothers” made of polymers.
It includes three main elements:
- frame;
- clamping ring and clamping nut
- sealing ring.
The principle of connecting pipeline sections using compression fittings is based on the fact that the sealing ring and rubber gasket fit tightly to the surface under pressure from the union nut. The crimp ring is tightened using a manual or automatic press.
When connecting pipes by installing compression fittings, deviation from the axis is allowed within three degrees.

In terms of mechanical strength, the crimp method is somewhat inferior to the same welded or threaded connection. To tear the pipe out of the assembly, it is enough to apply a little physical effort.
For this reason, compression fittings are rarely used when arranging pipelines intended for transporting hot water.
The elastic O-ring included with the compression fittings is designed for temperatures up to 100°C.With prolonged exposure to hot temperatures, rubber loses its properties. As a result, the tightness of the connection is broken.
Although compression fittings belong to the group of dismountable systems, if one of the structural elements fails, the entire unit has to be replaced.
Flange Fitting Design
The strength and durability of a flange connection is not inferior. For this reason, it is successfully used in the installation of systems that transport aggressive media under high pressure.
In household communications - water supply and heating systems - it is used quite rarely. This is due to the fact that the increased thickness of the pipeline due to the large diameter of the flange becomes inconvenient in terms of installation and unattractive in terms of aesthetics.

The fittings kit includes:
- paired discs;
- nuts and bolts for tightening planes;
- sealing gasket made of rubber, graphite or paronite.
The number and dimensions of bolt holes for flange connections are determined by the manufacturer in accordance with GOST. The fittings themselves are most often fastened to the pipe by welding or using threads applied to the inner surface of the flange.
If we compare the listed types, the most common are compression and threaded fittings. The secret of such popularity lies in the ability to create airtight connections, as well as to re-dismantle products in order to reuse them over and over again.
In addition, the installation of such removable elements is easier and faster than in welded joints.
Threaded fitting installation technology
There is nothing difficult about installing a steel fitting on a pipe. As an example, let’s look at the technology for installing a threaded type coupling.
Set of tools required for work:
- pipe cutter for steel pipes;
- gas and adjustable wrenches;
- manual clamp equipped with a holder;
- sealing material.
To increase the tightness of the threaded connections of pipelines intended for transporting cold and hot water, use flax strands or FUM tape impregnated with red lead.
For lines with coolant whose temperature is above 100°C, graphite-impregnated flax strands intertwined with asbestos cord are used as a sealant.
The installation process includes a number of main stages:
- The pipe is clamped in a clamp. The ends, pre-treated with drying oil, are threaded.
- A thin layer of sealing material is wound along the thread in the direction of movement.
- A coupling is screwed onto the end of the first pipe, pre-treated with drying oil or oil paint, until it jams at the run-out.
- Dock the end of the second pipe, wrapped in the same way, screwing the second branch of the coupling until it jams at the run-out.
The coupling is first tightened by hand and then strengthened with a pipe wrench. The result is a connection in which the ends of the pipes screwed into the coupling meet, but do not rest against each other.
After completing the repair work, all that remains is to check the quality of the connections. To do this, open the tap and fill the system. If a leak is detected at the connection point, the locknuts must be tightened.If the efforts made do not give the desired result, it is better to re-establish the connection.
Subtleties of installing a crimp coupling
In a situation where the thread on a pipe has rotted and cutting it is impractical, a universal solution would be to install a crimp coupling.

To correctly install the compression fitting, installation is performed in the following order:
- The pipe section to be joined is cleaned of burrs, treating both the outer and inner surfaces of the product.
- The end of the pipe is inserted into the fitting body, positioning it in such a way that the central part of the coupling strictly corresponds to the joint.
- A crimp ring is pulled onto the pipe.
- A crimp nut is placed on the resulting segment. As the nut moves along the thread, it will press the ferrule into the pipe, creating a tight connection.
When tightening the nut, do not use excessive force. Otherwise, the nut will compress the connection or simply burst.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Installation procedure using a threaded coupling:
Threadless joining technology:
We have described the main methods of connecting steel pipes by installing fittings. The best option should be chosen based on the conditions of a particular situation.
Do you have personal experience assembling steel pipeline using fittings? Do you want to share your accumulated knowledge or ask questions on the topic? Please leave comments and participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.




About flax with red lead - this is probably unnecessary. Yes.It’s quite possible to combine it this way, but this is the last century. Like black fabric tape.
Don't touch the sacred!!! Just like the words of the plumber - “I’ll do everything right now”!!! And dissolving into the sunset))).
An 8th grade mechanic himself, I was always amazed at the schedule and stupid #@ism of the “pissed” technicians.
Whether outdated or not, FUM tape and flax strands with red lead are still included in the recommendations of SNiP 3.05.01-85 as a sealant for threaded connections. Although, of course, new sealants have almost replaced all this.