Cast iron pipes for external sewerage: types, features of application and installation
Cast iron pipes used in the construction of sewer networks continue to be a relevant material.Despite the high competition from plastic, reliable pipelines are built from cast iron products, designed for the longest service life. They have both strengths and weaknesses that are worth becoming familiar with. Do you agree?
We will tell you which cast iron pipes are ideal for external sewerage, and which ones are used exclusively for laying the internal system. The article we presented shows the features of marking and describes the types of connections in the assembly of cast iron communications. Alternative options are also listed.
The content of the article:
High Strength Cast Iron Pipe
Design decisions to reduce cast iron in sewer networks are traditionally driven by economic considerations. As for reliability and durability, there are simply no materials equal to a cast iron pipe.
Products made from high-strength cast iron are widely used in mechanical engineering, water supply, wastewater disposal, as well as in gas and oil production.
A significant share of these products are high-strength cast iron pipes.
Their performance properties, compared to conventional pipes, are complemented by the following mechanical characteristics:
- high degree of impact strength;
- low yield strength;
- low temporary resistance;
- low relative elongation coefficient.
Obtaining such characteristics is achieved by introducing spheroidal (or lamellar) graphite into the structure of cast iron.
In other words, the metal structure is saturated with a significant amount of carbon, which in practical terms adds such properties to the final products as:
- wear resistance;
- compressive strength;
- fatigue strength;
- ease of machining;
- good casting qualities.
High-strength cast iron pipes are mentioned for a reason. The implementation of external sewerage projects usually involves the construction of drainage lines from structures and their laying under the soil thickness. This sewage system is classified by the abbreviation TML.
The operation of underground sewer lines is usually characterized by increased physical and temperature loads, which high-strength cast iron pipes can easily cope with. Laying depth of sewer pipes in the ground is regulated by building regulations.
Classification of pipes by design
For sewer cast iron pipes of the TML classification, there is a conditional division according to functional properties into two types:
- Socketless (SML).
- Socket type (SME).
The first are distinguished by the fact that they are structurally designed as extremely smooth elements from start to finish along the entire length. The latter, on the contrary, have a bell slightly wider in diameter at one end.

Socketless cast iron pipes are considered the best option for installing external sewer systems classified as TML systems. Pipes of the SML type provide more convenience during installation and allow easy and quick dismantling if necessary.
Both types of pipes are produced with a nominal internal diameter size of 100 mm, while the external diameter size is 110 mm. As a rule, the nominal and any other diameter size is indicated by markings (for example, DN100).
Often practiced diameter sizes for cast iron pipes (socketed and socketless) are in the range of 100 - 400 mm. In general, this range covers diameter sizes up to 1000 mm. The standard length is 3000 mm.

There are also products that belong to other classification groups. For example, SMU classification products are functionally designed for building drainage and drainage systems.
There are pipes for transporting chemical aggressive media. They are classified according to MLK. And cast iron products classified as MLB are suitable for drainage systems on roads and bridges.
Features of the design and composition used in casting cast iron pipes are indicated in the markings:
How are SML and SME pipes connected?
Socketless sewer pipes made of cast iron are connected one to another using special tightening fixing devices. These connecting elements consist of a steel clamp and an elastic coupling, which is applied to the joint area.
In practice, two modifications of steel clamp ties are used - one screw (CE) or two screws (CV). The material of the elastic coupling ensures a high quality of tightness, and the properties of the steel of the tightening ring prevent the occurrence of corrosion.

Connecting clamps are used not only to connect individual pipes when constructing a pipeline. The same components are used for connections with shaped parts.
Clamps are produced for various mounting diameters and are designed for the entire range of operating pressures. There are modifications of clamps with a sound absorption effect used in the device silent sewer. Their installation does not require the use of additional sound insulation in places where pipelines pass through the ceilings.
Bell-shaped elements are connected by the principle of inserting the straight end of one pipe into the bell-shaped part of another. The softness of the connection and tightness, as a rule, is ensured by a rubber ring, which is pressed into a groove on the inner surface of the socket of a cast iron pipe.
There is also a scheme where the tightness of the connection in the socket (and softness) is achieved by filling the gap between the pipes with sealing material.
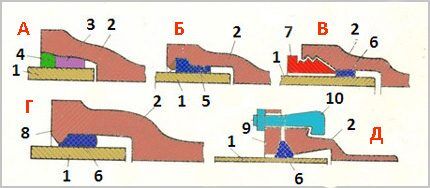
The following types of sealing and fixing of connections are typical for socket elements:
- Embossing with asbestos cement filler.
- Installation of the sealing collar.
- Installing a self-sealing ring.
- Use of a bolt-on slip-on flange.
- Application of a tenon.
The technique of fixing a pipe joint using hot and cold welding is also practiced, but it is used extremely rarely. This is explained by the complexity of cast iron welding technology. In addition, welding work on cast iron requires specialists, professional welding tools and expensive nickel-based electrodes.
With features of the choice of pipes for the construction of an internal sewer system read the article, which sets out all the arguments in detail and examines the characteristics of the various types.
Features of structure and application
The main feature of cast iron pipes from the TML classifier group is that they are intended for installation underground at a depth of 0.8 to 6 meters. Created specifically as elements of TML external systems, the pipes are characterized by an increased degree of strength and anti-corrosion protection.
The operational parameters of compression resistance make it possible to lay sewer lines, for example, under a road surface with large weight loads, without fear of damage. But during installation it is necessary to comply with the standards DIN EN 877, 1610, GOST, which provide for the creation of an appropriate supporting foundation and floors.
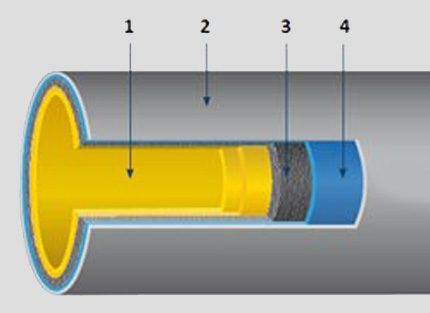
Among the features of high-strength cast iron pipes, the presence of an effective coating (external and internal), including on shaped parts, should also be highlighted. The coating is carried out using zinc and epoxy resins, which ensures high reliability of corrosion protection even in highly aggressive environments.
These pipes can be successfully used for laying in soils with high pH levels (0-10). The internal varnish epoxy coating of cast iron sewer pipes has a smooth (sliding) structure, which minimizes the coefficient of resistance when moving wastewater.
Structure of modern TML cast iron pipe:
- Coating with modified epoxy resin in two layers (layer thickness 120 microns).
- Protective coating with epoxy varnish (layer thickness 60 microns).
- Cast iron base layer with high carbon content.
- Protective coating with zinc powder (spray density 130 g/m2).
The standard pipe length (3000 mm) can be easily shortened to the required size if necessary, for example, with an electric pipe cutter. When cutting a cast iron pipe, you need to ensure an accurate, even cut. This approach guarantees reliable sealing when assembling drain lines.
In addition, the edges of the cut are usually painted with special paint and covered with Pro-Cut insulating tape. For aggressive environments, special seals are used. These measures further increase and eliminate the risk of leaks.

The list of features of cast iron sewer pipes is impressive. Compared to the same polymer products, quickly gaining popularity due to their low cost, cast iron products have many advantages.
Cast iron is not afraid of fire and high temperatures, while plastic pipes soften already at T = 100º, and at higher temperatures they begin to deform and can melt.
Cast iron pipelines are characterized by a low noise level during system operation and do not require the installation of expansion joints. They can be laid in the thickness of concrete without fear of rupture due to compression/expansion of materials.
Thus, the acquisition costs are very quickly offset by the economical operation of cast iron pipes. Their use does not require the creation of fire and noise insulation; the overhaul period is several times longer than the same period for plastic communications. The service life is not even limited to 100 years.
Pre-insulated products
The cast iron products of the TML classifier group are complemented by products that are pre-insulated cast iron pipes. Such modifications are successfully used in environmental conditions with low temperature values.
Essentially, these are the same high-strength socketless or socketed pipes (1), additionally coated with technological layers (2, 3, 4) of thermal insulation.
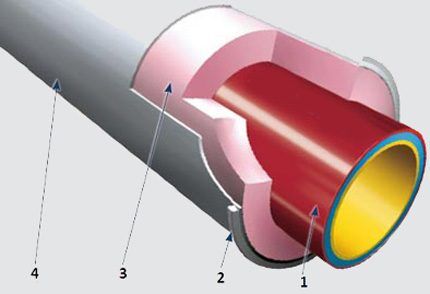
As effective heat insulator Thermosetting foam (3) or a similar material is used that has a dense structure and non-flammable properties according to class “A2”. The heat insulator is covered with a casing made of galvanized steel sheet (4). The thickness of the casing sheet is at least 1 mm. The casing is fixed with clamps (2), also made of galvanized steel.
Pre-insulated cast iron pipes are designed to withstand humidity conditions up to 75%. Insulation eliminates the formation of condensation at low and critically low temperatures. There are modifications with the introduction of a heating cable directly into the structure of the heat insulator.
Reasons for replacing cast iron with polymers
What is the reason for the increasing popularity? polymer productswith which they are trying to replace cast iron?
As it turns out, the main reasons are:
- risks of cast iron corrosion from damage by stray currents of electromagnetic fields;
- lack of additional protection of the internal walls of pipes from aggressive environments;
- rigidity of products, which has a positive effect on an individual pipe, but provokes a displacement of the total soil loads at the joint points on a pipeline assembled from a dozen or more pipes;
- technical difficulties that inevitably arise during the repair process or in the event of creating new communication connections.
Polymer pipes are much more often used than cast iron pipes when creating autonomous systems. sewerage in private houses.
You can learn about which pipes are best used in the construction of the external part of the sewer system in a suburban area from next articlededicated to this difficult issue.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Some useful tips on choosing pipes will be useful for creating sewage systems with your own hands:
Meanwhile, polymer products are inferior in technical and operational indicators to products made from cast iron. They have significantly more disadvantages compared to cast iron sewer pipes.
Polymers are convenient and rational to use in internal sewage systems, but for serious external communications it is reasonable from any point of view to use cast iron.
Do you have useful information on the issue of installing external sewage systems from cast iron pipes? Would you like to tell us about how you built the system on your site? Please write comments in the block below, post photos related to the topic of the article, and ask questions.




Undoubtedly, in the field of sewerage installations, cast iron pipes are the best, they are unrivaled. Of course, purchasing material for laying the pipeline will cost more, but there is still something to spend money on. When choosing pipes for the construction of my sewer system, I didn’t even consider plastic, but immediately decided that I would take cast iron. The advantages of cast iron pipes: fire resistance, resistance to aggressive environments and, perhaps, low noise levels. True, quite high demands are placed on installation and installation, but the service life is many times higher than that of competing plastics.
What's the point of cast iron's fire resistance rating if it's a sewer? And the resistance to aggressive environments is not the same as that of PP pipes! Or am I wrong? I’m already silent about corrosion in the future and the price of the issue!
I partially agree with you about the fire resistance of cast iron.There are, for example, areas in factories where the sewer pipeline will run, then cast iron will be relevant. And for household purposes, it is quite possible to get by with plastic pipes: cheaper and more practical.
Regarding resistance to aggressive environments, plastic pipes have a better indicator here too, only cast iron tolerates mechanical stress better. As for corrosion, this is not a problem for sewer PP pipes; moreover, due to their smooth internal structure, they allow flows to pass better. The latter eliminates the possibility of constant blockages, which are a constant problem for cast iron pipes.