Requirements for laying a gas pipeline in populated areas: depth and rules for laying above-ground and underground pipelines
Gas makes our life comfortable and convenient. But its improper consumption is fraught with danger, isn’t it? However, negative consequences can be easily avoided. For this reason, you must initially comply with the requirements for laying a gas pipeline, and also do not forget about safety measures.
What are the requirements and what rules for laying gas pipes exist? We will talk about all this in detail in this article. We will provide the material with visual photos and useful video recommendations.
The content of the article:
What to consider when laying a gas pipeline?
The laying of any gas pipeline begins with the initiator having a number of responsibilities. Thus, he must organize the work in such a way that during construction and operation the “blue” fuel transportation system is safe for people, their property, animals, and the environment. You should also follow the control rules gas consumption.
Responsibility for violation of requirements
If you ignore regulatory requirements, then a person becomes a violator and there is a high probability of being punished for his actions. For example, receive a fine for unauthorized connection to a gas pipeline.
Didn't connect? But in order to fall under sanctions for this act, it is not necessary to crash into a pipe, but rather to keep incorrect records of energy consumption.

That is, it is enough to accidentally break or damage the meter or even the seal on it. And according to Art. 7.19 Code of Administrative Offenses for such an offense you will have to transfer a considerable 10-30 thousand rubles to the budget. But even more severe measures of influence are provided for in Criminal Code. So it's Art. 215.3 states that for unauthorized actions the fine can be 80-400 thousand rubles. And, if the actions caused an accident, then the performer of the work may well be imprisoned for an impressive period (up to 8 years).
We talked more about gas fines in this material.
As we can see, the state takes its gas pipeline construction activities seriously. As a result, it is necessary to obtain appropriate permits before carrying out work. And the gasket itself should be entrusted to a company with a special license. The specialists of which will be responsible for the completeness and quality of pipe laying, which will help potential consumers avoid trouble.
Profile regulatory framework
The main document regulating the creation of energy transportation systems is SP 62.13330.2011. This set of rules is the current version of the popular SNiP 42-01-2002. Both documents are called “Gas distribution systems”.

In addition, the necessary requirements are contained in:
Each of the above documents sets out reliability characteristics, limit states, and calculated load values. This information is useful if you need to determine the thickness of pipeline walls or calculate the strength of supports.
How to deal with corrosion caused by soil aggressiveness or stray currents is described in GOST 9.602-2005. If the pipes will be laid above ground, then you should familiarize yourself with the requirements SNiP 2.03.11-85. It describes how to properly protect the gas pipeline structure from corrosion.
Features of choosing the type of gas pipeline
Before constructing a highway, you should decide on the best option suitable for specific conditions and familiarize yourself with the rules for laying it. Since all this affects financial costs, efficiency and labor costs.
Since, first of all, the gas pipeline must be reliable, when choosing an option it is necessary to take into account such points as:
- soil corrosion activity;
- building density;
- the presence of stray currents;
- terrain features;
- the type of road surface if the gas pipeline will cross it;
- entrance width;
- presence of water barriers and many others.
In addition, you need to determine the type of gas that will be supplied. And also its quantity - the volumes should be enough to satisfy the needs of all consumers.

You should also take care of the reliability of supplies. In view of this, it should be remembered that a ring gas pipeline is preferable to a dead-end or mixed one.For example, if gas is supplied to a so-called non-switchable consumer, then the specified option should be chosen.
All of the points listed above cannot be ignored - each of them is indicated in the documents regulating issues related to the laying of gas pipelines. Among which SP 62.13330.2011 and others.
We also must not forget that the construction and modernization of any gas pipelines must be carried out in accordance with gas supply schemes. Which are developed at various levels - from federal to regional.
Therefore, before starting design, the owner of the building or premises must:
- obtain permission for gasification in city, district architectural and design management;
- write to the local city gas (raigaz) in order to receive the so-called technical specifications, which is a set of information necessary to create a gas pipeline.
And only after this is it allowed to proceed design. Which ends with approval in Gorgaz (raygaz).
Only after this will it be possible to begin laying the gas pipeline. Which, when ready, should provide consumers with fuel in the required quantity and be safe.
We described the intricacies of laying a gas pipeline to a private house in next publication.

Laying a highway in a populated area
Today, there are two ways to provide a building (residential, industrial, any other) located in a city, village or holiday village with “blue” fuel: by laying underground (in demand in cities) or aboveground gas pipeline (most often used in small settlements).

The first type of energy transportation systems is traditionally considered more expensive. But horizontal drilling is becoming increasingly popular, making the construction of underground gas pipelines more accessible.
The laying of their above-ground analogues is irreplaceable if there is no permission to carry out work on other people's land plots and in a number of other cases.
Method #1 - rules for constructing underground networks
Although the creation of such a system is expensive, in some cases its use is mandatory. For example, this happens if there are high-voltage transmission lines near the installation site. Or when you need to cross a road (road, railway).
The depth of the underground gas pipeline under construction is indicated in the above-mentioned joint venture. Where does it say that the distance from the pipe or protective case to the surface should be not less than 80 cm.
This means that the specified value is relevant only for cases when the same is freezing depth for a specific region. That is, if it is more than 80 cm (for example, equal to a meter), then it should be laid at a depth of at least 100 cm.

And also when preparing for laying, the following features should be taken into account:
- Laying the pipe is possible at a depth of 60 cm, but only in cases where there is no traffic over the place where the gas pipeline will be located.
- The presence of rocky soil in the place where the construction of an underground pipeline is planned is the reason for creating a sand cushion. The thickness should be at least 20 cm. Therefore, the trench should become deeper by the specified number of centimeters.
It is allowed to intersect existing underground gas pipelines with any other utilities. But at the same time it is necessary to maintain the established vertical distance.
Which, when crossed, should be:
- no less than half a meter for electrical cables, any armored telephone cables;
- 1 meter for oil-filled electrical cables, the voltage in which is in the range of 110-220 kilovolts;
- from 20 cm - for water pipes, sewer drains, drains, unarmored telephone cables, heating network channels.
The distance between any electrical cables and other utilities can be reduced if they are laid in a protective case. The ends of which extend at least a meter out on both sides of the pipeline being crossed.
But there should still not be less than 20 cm between the gas pipeline and other communications with which the intersection occurs.

If there are collectors, heating network channels, or any tunnels in the path of the gas pipe, and the transition will be carried out above or below them, then the laying of any type of gas pipeline must be carried out in a case. In addition, additional inspection of welds will be required.
In this case, the protective case must be a pipe, the distance from the inner surface of which to the nearest point on the surface of the gas pipe should not be less than 50 mm. That is, the diameter of the specified device must exceed the same parameter of the gas pipeline by no less than 100 mm. And when crossing the external walls of buildings, the difference can be 200 mm. In this case, the void between the casing and the gas pipeline pipe is filled with bitumen.
The case serves to protect the gas pipe from mechanical damage and corrosion, both as a result of exposure to aggressive soils and from stray currents. Therefore, these devices are in demand, and their use in some cases is mandatory. For example, when a gas pipeline intersects with any utilities.

It should also be remembered that any shut-off valves, as well as condensate collectors, must be placed no closer than 2 m from the intersection of the gas pipeline with utilities.
It is allowed to lay two different gas pipelines in populated areas and place them in one trench.Moreover, they can be placed: near or on top of each other. In this case, the exact distance between the pipes is not indicated, but the available clearance should allow all necessary work to be performed, for example, dismantling, installation, etc.

The laying of underground gas pipelines in canals, tunnels, and sewers is prohibited. But there is an exception - permafrost soils. For them, it is permissible to lay pipes under roads (roads, railways), the pressure in which will not exceed 0.6 MPa. Places where pipes enter/exit from the ground must be enclosed in cases.
Method #2 - subtleties of laying pipes above ground
In the case of the above-ground installation method, the energy carrier is transported through pipes placed above the ground surface. Namely on height up to 2.2 m.
What are they used for:
- supports, and exclusively from non-combustible materials;
- building structures of various buildings and structures.
Moreover, the following can be used as supports for placing gas pipelines: columns, shelves, overpasses, walls of industrial and other buildings, and other structures.

The specialized joint venture regulates the question of which buildings can accommodate gas pipelines and with what operating pressure.
So, it says that:
- pipes for transporting gas, the pressure of which is no more than 0.005 MPa, are placed on structures of residential, administrative, as well as domestic (non-industrial) real estate;
- on the walls and roofs of industrial buildings, as well as boiler rooms of 1 and 2 degrees of fire resistance, as well as related to fire hazard class C0 it is possible to place gas pipelines with a gas pressure of 1.2 MPa;
- along the walls of most other buildings it is allowed to place gas pipelines with a working pressure not exceeding 0.3 MPa.
We talked more about pressure in high, medium and low gas networks in our other article.
The above-ground laying of any transit gas pipeline on the construction of administrative, public, household (non-industrial) buildings is prohibited.

It is allowed to place one pipeline, intended for transporting gas to other consumers, on the walls of a residential building. This rule applies exclusively to low-pressure gas pipelines. Moreover, its diameter should not exceed a moderate 100 mm, and the distance to the roof should be less than 20 cm.
It is permitted to lay overhead gas pipelines over bridges made of non-combustible materials.
It is allowed to use for energy transportation mixed systems. That is, part of the gas pipeline may be in a trench, and if necessary, bypass the obstacle, the pipes are taken out of the ground and placed on supports. If you need to cross a highway, the pipes are again buried in the ground.
We recommend that you read more about device underground and above-ground gas pipelines.
What pipes can be used?
Modern gas pipelines can be made from various materials, but only two of them are in demand: steel and polyethylene. Moreover, the repeatedly mentioned joint venture recommends giving preference to pipes made from the latest type of material.

The reason for the demand for polyethylene pipes is that they are not susceptible to stray currents and are more resistant to corrosion. Due to this, they retain their performance characteristics throughout their entire service life.
The listed features are important - they reduce operating costs and make the gas pipeline safer.
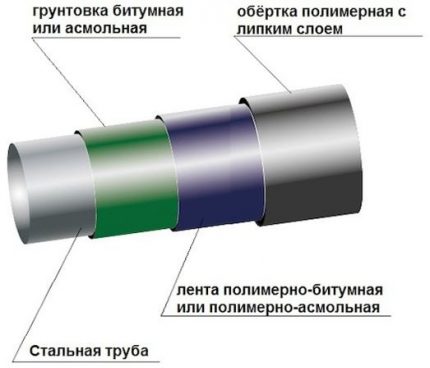
For comparison, steel pipes, according to the requirements of the profile joint venture, must be protected from:
- underground (ground, soil) corrosion — this provision is relevant for all underground gas pipelines;
- corrosion caused by so-called stray currents — this rule applies to underground gas pipelines;
- atmospheric corrosion — the requirement applies to above-ground gas pipelines.
Protection of pipes and other elements made of steel is a mandatory procedure.
This is stated in SP 62.13330.2011which links to:
- GOST 9.602-2005, which sets out the requirements for combating corrosion in the case of underground gas pipelines.
- SNiP 2.03.11-85 — this document specifies rules for the protection of above-ground steel pipelines.
Each of the listed documents repeats the requirement that measures to prevent corrosion are mandatory.

So in GOST 9.602. 2005 it is written that laying steel pipes of any gas pipeline is impossible if they are not covered with a protective layer, for the creation of which the following are used:
- bitumen mastics;
- coal mastics;
- polymer roll materials;
- polyethylene spraying.
We discussed the issue of insulating steel gas pipelines in more detail in our article: Insulation of steel gas pipelines: materials for insulation and methods of their application.
To protect against stray currents use cathodic polarization. It must be completed no later than 1 month from the moment the steel structural element was laid in the trench.
For above-ground gas pipelines, the fight against corrosion should begin at the design stage. So in SNiP 2.03.11-85 it is said that even the design of the supports should be designed in such a way as to reduce the impact of moisture and its accumulation. It is also necessary to exclude the accumulation and stagnation of aggressive gases.
And without all of the above, the gas pipeline will not be allowed to operate. That is, corrosion protection is no less important in creating a gas pipeline than the depth of the trenches for the gas pipeline when laying the pipe into a private house or any other building.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The first video will help you understand how gas pipelines are laid along the streets of populated areas. And also understand what horizontal drilling is:
This video provides an opportunity to learn about the problems encountered when creating gas pipelines in cities and any other populated areas:
Gasification of buildings in a populated area or repair of an existing gas pipeline will make life more comfortable and safe. But such a result can only be achieved in cases where all the work (design, selection of components, laying, intersection with other communications, etc.) is done correctly. That is, taking into account the requirements of relevant guidance documents. Otherwise, you can expect trouble, including sanctions from gas services.
Would you like to supplement the above material with useful information? Or do you still have questions about gasification of populated areas? Ask them in the discussion of this publication - our experts and other site visitors will try to help you.




Hello. We live in a private house. The owner to our right has changed and is accusing us that snow from the roof of our house could damage the gas pipe. Our house was built in 1998, and the gas pipeline was built in 2014. Shouldn't the old owner have taken this into account for his own safety?
Hello! The dacha cooperative laid a gas pipeline underground in a trench to a depth of approximately 2 meters. But the fact is that the road is narrow and the gas pipeline passed right under the wheel track under the unpaved road. At both ends of the street, some conclusions were made to the surface with small hatches.Trucks periodically move along the street, the wheels of which have already broken off all these hatches. We have a question with concerns: is it permissible to lay a gas pipeline under a traffic circle on a dirt road? There is a sand cushion under the gas pipeline, but on top it is simply covered with earth.