Pressure in the gas pipeline: technical standards + features of gas pressure distribution on the line
The proximity of the gas pipeline network to a populated area does not guarantee the absence of problems with connecting to it.The communications transporting the most popular fuel have different tasks, which is why the pressure in the gas pipeline is also different.
We will tell you how the gas transportation network works and what pressure the fuel supplied to consumers is under in its linear segments. The article we presented describes in detail the principles of organizing gas supply systems at different levels. Mechanisms for shutting off gas are given.
The content of the article:
Natural gas supply
Household and industrial equipment operating on a natural mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons is well known to everyone. Residential buildings are equipped with boilers, gas stoves and water heaters.
Many enterprises have boiler equipment and fenced “houses” of the GRU at their disposal. And on the streets there are gas distribution points that attract attention with their yellow color and bright red inscription “Gas. Flammable."
Everyone knows that gas comes through pipes. But how does it get into these same pipes? The path traveled by natural gas to every apartment, every house is truly enormous. After all, from the deposit to the end consumers, fuel follows branched, sealed channels stretching for thousands of kilometers.
Immediately after production at the field, the mixture of gases is purified from impurities and prepared for pumping.Injected by compressor stations to high pressure values, natural gas is sent through a main pipeline to a gas distribution station.
Its installations lower the pressure and odorize the gas mixture with methane, ethane and pentane with thiols, ethyl mercaptan and similar substances to give it an odor (in its pure form, natural gas has no odor). After undergoing additional purification, gaseous fuel is sent to gas pipelines in populated areas.

Natural gas is then distributed to gas distribution points within city neighborhoods. Before being sent to the gas pipeline network of the block, the pressure of the transported gas is reduced to the required minimum. Finally, the gas flows into the internal gas supply network - to the gas stove, water heating column or a floor boiler.
Each gas processing plant is equipped with a special burner that mixes the main fuel with air before combustion. In its pure form (i.e., without access to oxygen), the flammability of natural gas is zero.

Composition of the gas supply system
The gas transportation complex consists of pipelines and structures, as well as technical devices that supply and distribute the flow between consumers.The intensity of gas supply is determined by the needs of end users - industrial and municipal organizations, private households.
The gas supply network consists of:
- high, medium and low pressure pipelines;
- gas control devices – stations (GDS), points (GRP), installations (GRU);
- automatic control and monitoring systems;
- dispatch and operational service.
Under high pressure, the main gas pipeline delivers natural gas to distribution stations, which reduce the pressure level to the required level using automatic regulator valves.
Further gas networks send fuel to consumers. GDS automatically maintain pressure readings in a given range.
How is the gas supply system organized?
Its hierarchy is determined by the classes of elements of the gas transmission network associated with the pressure of the pumped natural gas.

Principles of gas pipeline network design
The first level gas pipelines include gas communications in which the pressure of natural gas is high or medium. To eliminate dead-end sections, gas pipelines are backed up - duplicating individual segments or ringing. The creation of a dead-end network is allowed only in small settlements.
Natural gas under high pressure passes through several successive stages where its pressure is reduced. The process of reducing pressure at gas control points occurs intermittently, at the outlet of them the pressure is constant.In urban areas, gas communications with medium and high pressure levels form a hydraulically connected common network.

The use of hydraulic fracturing makes it possible to supply consumers with gas of different pressures, even if they are located on the same street - gas pipelines of unequal pressures are placed in parallel.
Second-level gas pipelines provide low-pressure gas fuel supply to the majority of consumers. Such networks are mixed, with a predominance of dead-end segments. Only the main pipelines are subject to ringing.
A low-pressure gas pipeline should not cross large man-made (highways, railway tracks) or natural (lakes, rivers, ravines) barriers. Installation of such communications in industrial areas is not allowed.
Gas networks supplying fuel at low pressure cannot form a hydraulically connected system for a large population center. They are designed exclusively as local complexes fed by several hydraulic fracturing units.
In turn, connected to medium pressure networks, which in turn, by analogy, are connected to high pressure mains.The third level of network gas pipelines is used at consuming facilities - on the territories of enterprises, in residential and public buildings.
The pressure requirement for such networks is determined by their purpose and the performance characteristics of gas-using devices (installations). Redundancy (partial duplication) on gas communications of the third level is usually not performed.
Types and categories of gas pipelines
The division of gas supply pipelines by type is reflected in SNiP 42-01-2002. High pressure gas mains correspond to one type, divided into two categories.
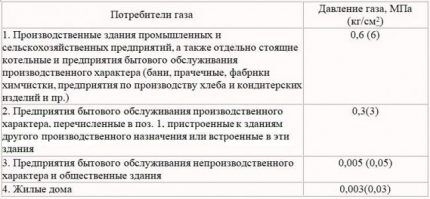
Gas-conducting communications of the first category are located exclusively for consumers in the industrial sector, which consume significant volumes of gaseous fuel under consistently high (0.6-1.2 MPa) pressure.
For example, these are steel smelting plants. Connecting each industrial consumer to a gas pipeline of the first category requires the preparation of a special gas supply project.

Lines carrying natural gas of the second category are created for other production facilities that require the supply of a gas mixture at high pressure, but less (0.3-0.6 MPa) than consumers of the first category. The same gas pipelines supply fuel to boiler houses that heat industrial buildings.
Pipelines supplying gas at an average (0.005-0.3 MPa) pressure level are supplied to boiler houses that heat domestic and administrative facilities.They are also used to supply public buildings that require an increased volume of fuel.
Low-pressure gas pipelines (up to 0.005 MPa) reach household consumers. All household equipment is designed specifically for these gas supply characteristics.
It is impossible to achieve maximum safety in gas communications for residential buildings otherwise than by reducing the pressure parameters as much as possible. Organization of gas supply to residential buildings medium-pressure and higher lines are strictly prohibited.
Multi-stage gas supply system
The need to create several stages in the local natural gas supply system, incl. caused by the presence of consumers requiring supplies of gaseous fuel at various pressures.
Gradation of gas pipelines by stages
The following gas supply systems differ in the number of pressure stages:
- Two-stage. Formed by networks under low and medium pressure, or low and high pressure;
- Three-stage. Consist of communications with high, medium and low pressures;
- Stepped. They are formed by gas pipelines with pressures of all levels.
Alternating high- and medium-pressure lines is required due to the significant length of network pipelines, as well as several transportation directions. In areas with significant population density laying gas pipelinesconducting gaseous fuel under high pressure is not recommended.

Another common reason is that in older areas, city streets are not wide enough to accommodate high-pressure gas supply lines. After all, the higher the pressure of the gas moving through the pipeline, the greater the distance required between communications and neighboring buildings.
The need for a stepped gas supply scheme is also caused by technological requirements for the connection and installation of gas control units installed on buildings.
Types of urban networks according to purpose
Urban areas are equipped with the most extensive network of gas supply communications.
The urban complex supplying natural gas includes the following types of gas pipelines:
- distribution, conducting gas under different (actually necessary) pressure. Provide transportation throughout the serviced territory;
- subscriber branches supplying gas from distribution mains to specific subscribers;
- intra-house and intra-shop.
The gas distribution communications scheme designed for the city, supplying gas under medium and high pressure, forms a common network. With development specifics project for gasification of a private house our proposed article will introduce you.

Those. Natural gas is supplied to utility consumers, boiler houses and industrial facilities via a common gas distribution network. The construction of separate backbone networks for municipal or industrial consumers is unprofitable from an economic point of view.
When choosing planning solutions for urban gas supply, the layout and size of the city, population and building density, and the needs of power plants and industrial facilities are taken into account. The prospects for the future development of the city and the presence of major obstacles (artificial, natural) to gas pipeline communications are taken into account.
Features of urban gas supply planning
Within the city limits, the ideal natural gas supply scheme must be economically profitable, operationally safe and reliable, convenient and easy to work with.

installed on the gas pipeline when it is discharged through a gas control station, allowing you to switch the gas supply circuits of the system
The gas supply pipeline network must allow accident-free shutdown of individual segments for repairs. A prerequisite is complete uniformity of units, equipment and structures within one system.
When depicted in the diagram, city gas pipelines are shown sequentially. However, it is allowed to lay parallel gas communications along the streets, subject to different pressures in them.
This layout is cost-effective because it reduces pipe consumption:
- low-pressure gas lines are fed by several hydraulic fracturing units;
- Methane is supplied to central hydraulic fracturing stations by parallel laid gas pipelines of medium or high pressure.
Similar communications laying schemes are used to supply boiler houses and enterprises located inside residential areas.
The structure of urban development requires the construction of a low-pressure network in the format of two unconnected zones. To reserve a low pressure stage, hydraulic fracturing of each of the two zones is connected to large-diameter pipelines carrying gas under low pressure.
In cities of small and medium area, a two-stage gas pipeline complex is used, combining low and high pressure communications (no more than 0.6 MPa).
If it is impossible to lay gas pipes in the city center for pumping a high-pressure gas mixture, their design capacities are divided between high-pressure networks (laid in the periphery) and medium-pressure networks (created in the central part).
As a result, a three-stage natural gas supply system is formed, equipped with gas distribution pipelines with a diameter of 50-400 mm.
Before the construction of a separate gas transmission line and before insertion into an existing gas pipe the planned section of the system is being designed, hydraulic calculation, providing the opportunity to select gas pipes and fittings for network arrangement.
Natural gas shut-off mechanisms
Carrying out repairs requires periodically shutting down certain sections of city gas communications that are under high and medium pressure, as well as certain networks under low pressure.
Therefore, gas pipeline systems of network, public and residential pipelines, as well as industrial facilities or several buildings, are equipped with shut-off devices - valves (another name - plug valves).
The assembly of the communication system according to the rules is completed gas pipeline pressure testing, allowing you to identify problem areas.They most often appear at the locations of locking devices.

Installation of valves is carried out:
- on gas pipes in hydraulic fracturing (outgoing and incoming);
- on branches of main gas pipelines going to microdistricts and neighborhoods;
- in front of a major obstacle crossed by the pipeline (reservoirs, highways and railway routes).
On external gas pipelines, valves are installed deep into wells. Lens compensators are installed together with them, designed to take readings of voltage (installation, temperature) along the pipeline, as well as to facilitate the procedures for installing and removing shut-off valves.
It is permissible to lay wells at a distance of more than 2 m from the nearest building or fence.
Shut-off valves at gas inlets into buildings it is placed on the wall. Gas taps, the replacement of which will be introduced next article, placed maintaining a meter distance from the nearest openings.
Regardless of the pressure level, branching and length of the pipeline carrying the gas mixture, the number of shutdown devices should be the minimum necessary, with a justification for each location.
An important issue for owners is the price of connecting to the main gas, the details of which are determined are given here. We recommend that you read the useful material.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video #1. How is gas supplied to an apartment building:
Video #2. How ball valves for gas pipelines are designed and manufactured:
The gas pipeline system ensures an efficient supply of natural gas only if it is balanced. Any work with gas transportation equipment can be performed exclusively by gas service employees. Outside interference in the operation of the gas network is unacceptable and extremely dangerous - remember this!
Please write comments in the block below. Share valuable recommendations and information that will be useful to site visitors. Leave posts, post photos on the topic, ask questions.




My daughter is a 3rd year college student majoring in “Installation and operation of equipment and gas supply systems.” Recently she was writing her first term paper, and I saw her drawing on the computer in a computer-aided design program. I am once again convinced that this is a complex and responsible profession. Almost only boys study in their group, but they treat their studies with coldness. Our safety is in the hands of these students, and much will depend on their knowledge.
Yla, I didn’t see the conclusion in your comment. And in general, how does this relate to the material here? Nowadays, wherever you look, a serious approach is needed everywhere. Maybe your daughter doesn’t take it seriously either, how do you know, you never know what she was drawing there. And the guys are still young, everything has its time. Knowing our education system and the attitude of educational institutions towards employment, most of them will not work in their specialty, and there are differences between groups.
Explain to me, “dense”, I haven’t been able to figure out this question for many years using the Internet... everything seems to be clear: 1 bar = 1 atmosphere, well, so roughly, = 0.1 Mpascal.High pressure network 0.6-1.2mp = 6-12 bar, medium 0.3-0.6mp = 3-6 bar, low pressure 0.005-0.3 = attention 0.05 bar = 0.05 atmospheres, i.e. what happens, how will the gas come out if its pressure is 20 times lower than atmospheric????
Excess pressure is used in calculations. Read about absolute and gauge pressure. There are a lot of online calculations of gas pipelines on the Internet, go to any form of support there and they will tell you. I won’t write links, otherwise the comment won’t be missed. To Yandex ->
Sergey! You forgot that natural gas is not a liquid. Natural gas is compressed under pressure, and the higher the gas pressure in the pipelines, the more concentrated and energy-intensive it is, i.e., the better its quality and calorific value. Therefore, for the suckers, the pressure in the low-pressure lines is artificially reduced so that consumers receive less fuel, but pay as for high-quality gas! Professional banditry on behalf of “NATIONAL PROPERTY”.
I'll correct you:
-0.6- 0.3 MPa is high pressure category 2;
— 0.3-0.005 MPa is the average pressure;
— up to 0.005 MPa — low pressure.
Household consumers are allowed to supply natural gas with a pressure of no more than 0.003 MPa, which is 300 mm. Water column.
All pressure is measured as gauge.
This year there is a warm winter. Temperatures are around zero. Gas consumption is the same as at 30 degrees below zero.
Could this be due to low gas pressure in the line? Thank you