Corrugation for electrical wiring: how to choose and install a corrugated cable sleeve
Do you want to protect electrical wires by putting a corrugated sleeve on them during installation? The cable must be protected from external damage, right? But you don’t know how to properly install flexible corrugation for electrical wiring?
We will show you how to install the corrugated hose. Here you will find out what types of flexible channels are used for these purposes. The article examines their pros and cons, and highlights the intricacies of installation of existing options for electrical pipes made of different materials.
The article is equipped with thematic photos, tips on choosing corrugated hoses and video recommendations for laying wires on your own. Visual illustrations will greatly simplify installation and dismantling work.
The content of the article:
Why do you need a corrugated hose?
Installing electrical wiring is a responsible matter that does not tolerate mistakes. The safety of staying in electrified premises directly depends on its quality.
The benefits of civilization in the form of glowing light bulbs and numerous household appliances, by definition, cannot work without being connected to the power grid. And any live electrical cable is a source of damaging current that is dangerous to humans.

The first protection against electric shock is the insulating braid of the cable itself. Regardless of the material used, it reliably protects a person from the current flowing through the veins.
However, insulation does not last long. These aluminum or copper wires can last 15–25 years, but the outer braid on them is often damaged within 3–4 years after the wiring is put into operation.
The service life of electrical wire insulation is greatly reduced due to:
- high humidity (outdoor or room);
- overheating under increased loads;
- ultraviolet radiation and other factors.
The result is a breakdown, short circuit, fire and electric shock to a person. To minimize risks, electricians lay wires in rigid cable channels or flexible corrugated hoses. On the one hand, it serves as an additional barrier between electric current and a person, and on the other hand, it serves as protection for the cable.

A cable laid in a corrugated pipe receives protection from:
- compression and other mechanical damage;
- ultraviolet radiation and precipitation (when laying wires outdoors);
- exposure to moisture.
And the last thing is fire safety. This quality is especially important if they are laying wiring in a wooden house. All corrugated hoses for electrical cables are made of non-flammable or self-extinguishing materials.
This reduces the likelihood of exposure to an open flame on the wire inside the corrugation, and also prevents the spread of fire during short circuits and fires of the plastic cable braid.
Types of corrugations for electrical cables
Corrugated hoses for electrical wiring are used when open wiring device, when laying lines on the street or in a channel formed in a wooden wall. Corrugated pipes are produced from various plastics and metals. There are also composite options made of iron wrapped in a layer of PVC.
It is recommended to choose one sleeve for the street, another for installation in a screed or ground, and a third for installation behind interior cladding.

All corrugations based on strength, wall thickness and design are divided into:
- lungs (withstand loads up to 320 N/5 cm2) – thin-walled, flexible and fragile, designed for installation under sheathing on ceilings and walls;
- average (designed for loads up to 750 N/ 5 cm2) – recommended for installation in wall grooves;
- heavy (withstand up to 1250 N/ 5 cm2) – thick-walled and rigid, used when installing wires in screeds on the floor;
- super heavy reinforced (designed for 4000 N/ 5 cm2 and above) - sleeves made of twisted steel wire and a plastic sheath, needed for laying cables underground and on the streets by hanging.
The thinner the walls of the corrugation, the softer and more flexible it is. However, as the flexibility of a corrugated hose increases, its resistance to mechanical damage decreases. At the same time, it is difficult to bend a pipe that is too thick at a right angle; it may simply break.
But such heavy corrugated hoses provide more reliable protection from moisture and dust. This is especially true when laying cables in the ground.
Type #1 - metal hose
When compared to plastics, metal is obviously a more advantageous option in terms of strength. It perfectly protects the cable from chemicals, moisture, ultraviolet radiation, shock and compression. And in the event of a fire, a metal hose will last much longer than its plastic counterpart.

Metal corrugations for laying cables are divided into several types:
- RZ-Ts, RZ-TSH, RZ-CA – made of galvanized steel.
- RZ-SL and RZ-SL-X – from tinned steel tape (tin plated with tin).
- RZ-CP – with PVC insulation.
Letter "X" in the first two options indicates the presence of cotton, and "A" asbestos cement seal. "P" in the latter type, the corrugation indicates the outer layer of PVC.
Also, metal hoses for wires exist with flanges at the ends and welded ends. Plus, there are variations of high pressure hoses in explosion-proof versions and for high pressure.
However, such corrugated pipes are more intended for industrial conditions. They are not used for installing electrical wiring in the house due to their high price and fundamental uselessness.
Conventional metal hoses are made from steel tape by winding it in a spiral. At the same time, the resulting corrugation is not airtight. When pressed firmly, the joints of the tape immediately separate and the sleeve simply falls apart.

If you need a sealed metal sleeve, you should take a product with additional insulation made of polyvinyl chloride. In this case, the top layer of self-extinguishing plastic will definitely prevent moisture and dust from reaching the steel base.
Only such corrugations are recommended for use in bathrooms and outbuildings, where constant changes in humidity and temperature are the norm.
Type #2 - polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Gray electrical corrugations made of PVC are characterized by low price and self-extinguishing. In the event of a fire, they not only do not burn, but thanks to the additives in the plastic, they go out on their own.
The main disadvantage of any polyvinyl chloride products is their poor tolerance to UV rays. Under the influence of the sun, this material begins to simply “deteriorate,” which sharply reduces their actual service life.

Another disadvantage of PVC corrugated sheets is their intolerance to low and too high temperatures, as well as excess humidity. When frozen, this plastic becomes brittle. In the cold it is destroyed even from a slight blow.
And in extreme heat (and even if in the sun), the corrugated polyvinyl chloride sleeve begins to soften slightly and “flow”. This does not lead to its immediate destruction or damage, but its service life is sharply reduced due to such operating conditions.
The situation is similar with water. With constant exposure to moisture, the walls of such corrugations begin to gradually collapse. These PVC pipes for water supply are initially designed for such an impact, but corrugated hoses have slightly different characteristics.
If the wiring needs to be laid in the bathroom or outdoors in direct sunlight, then it is better to look for another cable channel option for it.
Corrugated PVC pipes are ideal for installing wires in dry, heated rooms. They are cheap and flexible, and installation should not be difficult. But their gray appearance frankly does not please with its presentability and aesthetics.
It is best to cover such corrugations on top with finishing (wall panels, plaster with wallpaper on top or clapboard).
Type #3 - polyethylene and polypropylene
Corrugations made from HDPE polyethylene (or LDPE) and PPR polypropylene are approximately equal in cost and characteristics. They are resistant to strong moisture, temperature changes and ultraviolet rays. Such corrugated sleeves are universal.
They can be used both indoors and outdoors. For example, when installing a connection line heating cable, electrical panel when entering the site, branches of external lighting, activation of the irrigation system, etc.

Both versions of these electrical corrugated hoses feel comfortable at air temperatures in the range of -40...+45 degrees Celsius. At the same time, HDPE is famous for its resistance to oils, acids and solvents.
It is recommended to use corrugated products made from it in garages, utility rooms and on the streets - that is, anywhere where aggressive technical liquids can get on the wires.
Nuances of choosing and installing corrugated channels
Plastic corrugations for cables are available in various colors. Gray ones are usually made of PVC, black ones are made of polyethylene, and blue ones are made of polypropylene. But there are no strict rules in terms of color.
Each manufacturer adds dye to the polymer when making corrugated pipes at its own discretion. However, there is an international standard for the coloring of such products and the wires in them, which provides for the choice of color in accordance with the purpose of the cable route.
White wires and corrugations are recommended to be used for computer networks, gray and black for general purposes, green for telephone lines, and red - exclusively for external street installation.
Following these recommendations greatly simplifies the life of electricians when they come to carry out repairs in an unfamiliar place. So the direction of each line is immediately clear.
The following gallery of step-by-step photos will clearly introduce you to the procedure for laying cables in a corrugated pipe:
After pulling the cable into the corrugated channel, we begin attaching the lines to the building structures:
To install a cable with a cross-section of 3×2.5 mm², you usually buy a corrugated pipe with a diameter of 16 mm and mounting clips of the appropriate size.

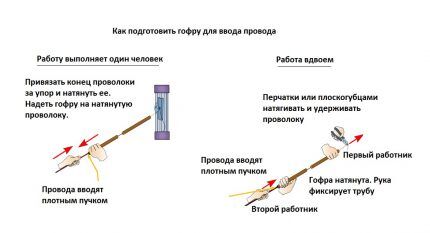
Installation of corrugations and electrical wiring in them is carried out in five stages:
- The corrugated sleeve and cable are cut into pieces of the required length.
- Using a cable stocking, a built-in broach, or a wire simply inserted into the pipe, the wire is pulled into the corrugation.
- Sleeves with a cable inside are fixed in a groove, on the floor or wall.
- The laid and secured corrugations are connected to the inlet holes on the bodies of boxes, panels and socket boxes, or simply inserted into them, and the wires are led out.
- Next is the usual electrical installation of devices connected to the electrical network.
To make it easier for yourself installation of electrical wiring, on sale you should look for a corrugated hose with a special harness (broach) inside. This is ordinary wire that was pre-strung through a corrugated pipe at the factory.
Only when cutting the corrugation you need to be careful so that this broach does not go inside. The cable on it for pulling into the sleeve is secured using ordinary electrical tape.
The metal corrugation must be grounded. And this should be done on both sides of the sleeve. The internal diameter of the corrugated pipe is selected by doubling the total cross-section of all cables laid in it. This is necessary both to simplify installation and to prevent overheating of the wires inside.
The corrugation must fit flush into the body of the socket, switch or panel.Any “peeking out” of the cable or breaks between the end of the pipe and the body of the installation or distribution device are unacceptable.
In this case, you can forget about protecting the wiring with a corrugated sleeve. Such incorrect installation will only take time and money, it will be of zero use.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
So that you can understand in all the nuances the types of corrugations for low-current and electrical cables, we have made for you a selection of video materials on this topic.
After looking at the reviews and installation descriptions below, you definitely won’t have any questions about the need, types and features of performing electrical installation work using corrugated hoses.
Video #1. The importance of installing additional insulation on electrical wiring in the form of a special corrugation:
Video #2. Pulling wires through a corrugated hose in detail:
Video #3. Overview of different types of electrical installation corrugations:
Cable ducts in the form of corrugated sleeves are extremely easy to install. They are inexpensive, and the benefits of such additional protection for wiring are enormous..
The cost of repairs in the event of a fire caused by a short circuit will obviously be higher. Pulling a cable through an electrical installation sleeve looks complicated only at first glance. Everything can be done independently.
Please write comments in the block below. Tell us about how you built or repaired wiring using corrugated wire as a cable duct. Perhaps you have any questions, do you have useful information and photos on the topic of the article?




It is clear that for a long time no one has laid cables into the wall without corrugations.It’s really worth getting rid of metal corrugations, but PVC is great not only for heated rooms. They installed them themselves in basements. At the same time, their service life is quite satisfactory. For outdoor work, you should not take PVC, but polypropylene or polyethylene corrugations precisely because of their resistance to atmospheric influences.
I decided to replace the electrical wiring in the house, since the house construction is from an old housing stock, the wiring is all made of aluminum. I looked for help online - I’m not an electrician myself and don’t understand this well. Well, I read it and understood how to use corrugation correctly, how to choose the appropriate option for arranging the line. It turned out very well. It’s convenient that I have learned all the information on the topic of proper installation: now I can confidently work with corrugation.
Corrugation allows cables to be laid over any building materials that have different thermal resistance, while maintaining the rated current of the cable. However, the cable sheath, compared to a single-insulated wire, reduces the rated current of the cable, even when laid open, by approximately 10%.
When laying a cable in a pipe (and a corrugated pipe is a flexible PVC pipe), the influence of the cable sheath on its rated current is even more pronounced. The rated current of a cable when laid in corrugation is reduced by 22%, and of a single-core wire in single insulation by only 10%.
In general, a corrugated cable has a rated current that is 22% less than a single-core wire in single insulation when the cross-section of the cable and wire cores is equal. That is, the cable sheath and the proximity of the cores in the cable due to the thermal resistance of its sheath lead to a decrease in the useful power transmitted through the cable by approximately 1.3 kilowatts.
In addition, this also increases the cost of wiring by approximately 27%. So the cables must be used for their intended purpose - for open or hidden wiring. And in the corrugation it is necessary to pull single-core copper wires in single insulation. But the cables are also not suitable for grooves under plaster, of course, if you lay them on reinforced concrete, under a layer of sand-cement plaster, then, according to the PUE, such a scheme is allowed, but it is impossible to lay cables in grooves in materials that have high thermal resistance.
In these cases, wiring should be done only in the corrugation. For example, for lightweight aerated concrete or foam concrete in grooves under a layer of gypsum plaster, the rated current of the cable is already reduced by about half compared to laying it in a corrugated cable. And this rated current is approximately 2.7 times less than the current of single-core wires in single insulation of the same cross-section when laying single-core wires in single insulation in corrugation in the same grooves in aerated concrete under a layer of gypsum plaster. Of course, we are talking exclusively about copper conductors of cables and wires, while their rated currents are taken from the PUE tables.
Thanks for the info!
Good afternoon, Anatoly. I'll break your comment down paragraph by paragraph.
First paragraph - let's say the entrance to the house is made through the basement. There it is more expedient to route the route along the cable shelves. They preserve the current-carrying capacity of the cable better than corrugations.
Second paragraph - the pipe has no effect on the cable sheath. Corrugation too. They worsen the heat transfer between cable and environment.
The third paragraph is that it is incorrect to compare a four-core cable with a single wire.
The fourth paragraph - here you, having finished the general reasoning, answer for yourself when to use wires and when to use cables. PUE 2.1.4, of course, allows for laying the cable under the plaster, but in terms of feasibility this option is in fifth place.
The fifth paragraph - the exclusivity of corrugation you proclaimed, contradicts paragraph 2.1.4 of the PUE.
Conclusion - your calculations have no practical value - engineers are guided by the conditions in which the wires and cables will be used.