Converting Amperes to Watts: rules and practical examples of converting voltage and current units
Owners of private houses, apartments, cottages or small utility rooms connected to electricity often need to convert amperes into watts or solve the inverse problem. To carry out conversions of units that determine current characteristics, well-known formulas are used, which are based on Ohm's law.
We will tell you how to correctly translate physical units. In addition, the article we presented provides methods for determining the operating power and starting currents of home appliances. The nuances of calculating the cross-section of electrical wiring components are discussed.
The content of the article:
Determining the power of connected devices
To calculate the value of the maximum possible power in a section of the circuit, it is necessary to sum up the indicators of all connected devices. But not everything is so simple: many of these devices are complex electrodynamic systems, so their parameters must be correctly determined.
Active and apparent power component
Active (or consumed) power of the device (P) determines the irretrievable loss of electricity during its operation. It is this indicator that the electric meter will calculate, and, therefore, it affects the amount of resources (money) spent during the operation of the device.
The active component in watts is indicated for all electricity consumers. However, there is another indicator - power factor (cos(f)), which can be found in the technical documentation, as well as on special plates or labels with the main parameters.
Through it you can calculate the total power (S) devices according to the following formula:
S = P / cos(f)
The physical meaning of these quantities can be described as follows: a current with full power flows from the source (transformer) to the electrical device, which converts its active component, and returns the remaining (reactive) component back to the network. Thus, the load on the circuit components (wiring and circuit breakers) must be calculated taking into account the full power.

For most household appliances, the coefficient is equal to unity, therefore, the active and apparent power are the same. But if the electrical consumer has capacitors (capacitors) or an inductor, a reactive component appears.
You need to pay attention to the following types of equipment:
- refrigerators;
- washing machines;
- air conditioners;
- pumps;
- induction ovens and stoves;
- fluorescent lamps;
- TVs;
- computers and other electronic equipment.
Also often to electrical system of private houses or business facilities connect machines with electric motors, arc welding machines and other equipment whose total power is significantly higher than consumed. Therefore, you need to carefully read the technical characteristics of devices before connecting them to the network.
Starting currents of compressors and motors
If household appliances are equipped with an electric motor, compressor, filament or transformer at the input to the power supply, then when it starts to operate, inrush currents occur for a short time (IP). Their value can be several times higher than the nominal values (In), specified in the device passport.
These quantities are related by the following formula:
IP = k * In
Here k – starting current multiplicity factor.
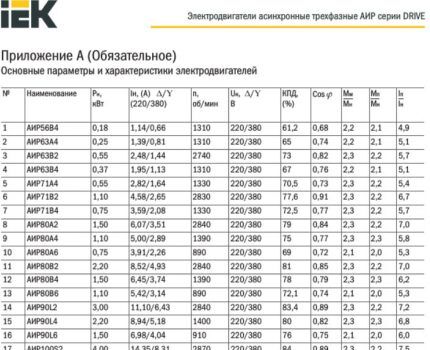
The multiplicity index exceeds the value “2” for the following common household appliances:
- submersible pump;
- refrigerator and freezer;
- powerful vacuum cleaner;
- washing machine;
- split system;
- microwave;
- neon lighting;
- some types of power tools (drill, hammer drill, compressor).
The calculation of the total power in the presence of such devices in the circuit must be carried out taking into account their starting currents. Since the time of increased power consumption is small, and synchronous switching is unlikely, it is enough to take one device that is the most powerful in terms of starting currents.
Current strength and wiring parameters
To determine the required cross-section of electrical wiring conductors and circuit breaker rating convert the total number of watts into amperes and obtain the value of the maximum continuous current.
The correlation between the cross-section of the cores and the maximum permissible current for wiring is carried out using tables provided by cable manufacturers. Depending on the manufacturer, the main indicators may differ slightly, but they must always comply with the current GOST 31996-2012.
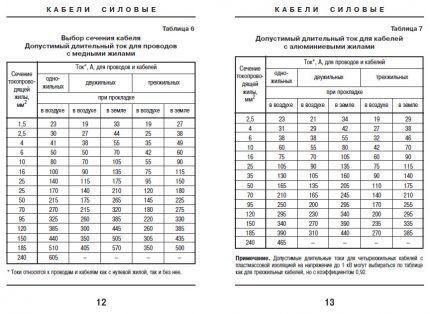
Sometimes they choose wiring not with the minimum allowable cross-section, but with a slightly larger one.This is justified, since the bandwidth reserve allows you to connect new electrical appliances without costly dismantling old ones and laying new cables.
Installable parameters to the electrical panel circuit breakers selected so that it is guaranteed to trip if the current exceeds the value determined as the maximum permissible for the installed wiring.
Rated current of the machine (In) are calculated based on the permissible current for the cable (Ip) according to the following formula:
In <=Ip / 1.45
Usually, a machine with the maximum nominal value among the permitted ones is selected in order to minimize the likelihood of a shutdown when the circuit is heavily, but still permissibly, loaded.
Relationship between basic electrical quantities
Power and current can be related through voltage (U) or circuit resistance (R). However, in practice, apply the formula P = I2 * R is difficult because it is difficult to accurately calculate the resistance in a real area.
Single and three phase connection
Most electrical wiring for residential use is single-phase.
In this case, recalculation of the total power (S) and AC current (I) using a known voltage occurs according to the following formulas resulting from the classical Ohm's law:
S=U*I
I=S/U
Nowadays, the practice of connecting a three-phase network to residential, household and small industrial facilities has become widespread. This is justified from the standpoint of minimizing the costs of cables and transformers, which are borne by the company supplying electricity.

The cross-section of the wiring cores and the rated power when using three-phase consumers are also determined by the current strength, which is calculated as follows:
Il = S / (1.73 * Ul)
Here the index "l" means the linear nature of the quantities.
During planning and subsequent implementation indoor wiring It is better to separate three-phase consumers into separate circuits. Devices operating from standard 220 V try to be distributed more or less evenly across phases, so that there is no significant imbalance in power.
Sometimes mixed connection of devices operating from both one and three phases is allowed. This situation is not the simplest, so it is better to consider it with a specific example.
Let a three-phase induction furnace with an active power of 7.0 kW and a power factor of 0.9 be included in the circuit. A 0.8 kW microwave oven with a starting current factor of “2” is connected to phase “A”, and a 2.2 kW electric kettle is connected to phase “B”. It is necessary to calculate the electrical network parameters for this area.
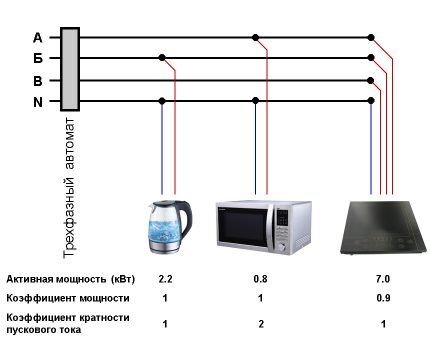
Let's determine the total power of all devices:
Si = Pi / cos(f) = 7000 / 0.9 = 7800 VA;
Sm =Pm * 2 = 800 * 2 = 1600 VA;
SWith = Pc = 2200 VA*A.
Let's determine the current strength of each device:
Ii = Si / (1.73 * Ul) = 7800 / (1.73 * 380) = 11.9 A;
Im = Sm /uf = 1600 / 220 = 7.2 A;
Ic = Sc /uf = 2200 / 220 = 10 A.
Let's determine the current strength by phase:
IA = Ii +Im = 11.9 + 7.2 = 19.1 A;
IB = Ii +Ic = 11.9 + 10 = 21.9 A;
IWITH = Ii = 11.9 A.
The maximum current with all electrical appliances turned on flows through phase “B” and will be equal to 21.9 A. A sufficient combination for the trouble-free operation of all devices in this circuit is a cross-section of copper conductors of 4.0 mm2 and a 20 or 25 A circuit breaker.
Typical household voltage
Since power and current are related through voltage, it is necessary to accurately determine this value. Before the introduction of GOST 29322-2014 in October 2015, the value for an ordinary network was 220 V, and for a three-phase network - 380 V.
According to the new document, these indicators are brought into line with European requirements - 230 / 400 V, but most household power supply systems still operate according to the old parameters.

A deviation of 5% of the real value from the reference value is acceptable for any period, and 10% - for no more than one hour. When the voltage drops, some consumers, such as an electric kettle, incandescent lamp or microwave oven, lose power.
But if the device is equipped with an integrated stabilizer (for example, a gas boiler) or has a separate switching power supply, then the power consumption will remain constant.
In this case, given that I = S / U, a drop in voltage will lead to an increase in current. Therefore, it is not recommended to select the cross-section of the cable cores “butt-to-peak” to the maximum calculated values, but it is advisable to have a margin of 15-20%.
Useful video on the topic
Measuring current with a multimeter and then calculating power:
Electronic device for detecting voltage, current and automatic power calculation:
Determining the current strength, knowing the network voltage and the total power of the devices in the circuit section, is quite simple. The difficulty lies in measuring or calculating the initial parameters.
If you have doubts about the correctness of the solution found, it is better to contact electricians, since errors in calculations can lead to serious problems.
Would you like to share your own experience in converting amps to watts? Do you have an original method in your arsenal that may be useful to site visitors? Please write comments in the block below, post photos and ask questions about the topic of the article.




I myself work as a commissioning engineer, but only in underground electrical installations. It is often necessary to calculate settings and other parameters. Sometimes on power supply diagrams they simply indicate the value of the short-circuit current. And here it is very difficult to understand whether this is a two or three phase current. Therefore, you have to recalculate everything yourself and make logical conclusions.
Good afternoon, Vladimir.
Usually the number of phases on diagrams of, for example, a distribution network is indicated by dashes - I have attached a screenshot. Short-circuit currents are calculated for the most severe cases of short circuits. For a three-phase network, this is a metal three-phase circuit, similarly for two, single-phase ones. The person who puts the I short circuit on the diagram already knows which option he has considered. How are the types of short circuits designated? look at the second screenshot. Train your colleagues to be orderly.