Differential circuit breaker: purpose, types, marking + selection tips
The operating algorithm of differential switches is based on providing reliable protection against possible leakage currents.For example, in cases of indirect contact with conductive elements or in moments of short circuit of current-carrying parts to the housing. The choice of protective device should be taken responsibly. Do you agree?
We will tell you how to correctly select a differential circuit breaker equipped with advanced protective functionality. The article we have presented describes in detail the types of devices that can prevent a lot of threatening situations. Valuable recommendations were given to future buyers.
The content of the article:
Operation of the residual current device
Considering the standard design of an RCD (UDT), three main modules should be highlighted:
- Summing current transformer.
- Trip-converter.
- Switching elements blocking device.
The current-carrying conductors of the current circuit are connected to the contacts of the summing transformer. Taking into account Ohm's law, according to which the sum of all currents gives zero, the magnetic effect of the current-carrying conductors of the transformer is mutually compensated.
There is no magnetic field that causes the appearance of voltage in the secondary winding of the transformer due to the induction effect. This state corresponds to normal conditions for the passage of current in the circuit.
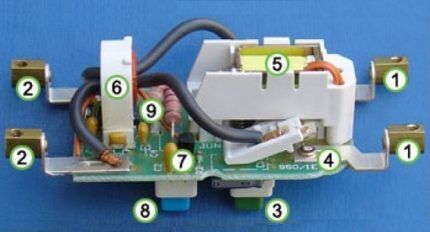
However, the formation of even a small leakage current upsets this balance. The transformer core area is exposed to a residual magnetic field. As a result, the secondary winding produces voltage.
The release is naturally activated, converting the electrical quantity into a mechanical action. Next, the differential current blocking device is activated.
This type of protection technique is characterized as high-level because the circuit is broken regardless of the mains voltage or the voltage of the auxiliary power source. It is this principle of operation that 100% guarantees that the protection will operate in any circumstances.
The design of each residual current switch is usually equipped with a test key. The so-called “control button” is specially displayed on the front panel of the device so that users can check the operational readiness of the protective device.

If the “Test” key is pressed, the device mechanism artificially generates a leakage current. In this case, a working device will definitely work. Typically, the “Test” button is used immediately after installing the machine in the circuit, when connecting electricity for the first time. Subsequently, they are tested according to a schedule, approximately once a quarter.
Types of residual current devices
The variety of automatic differential switches is impressive. This diversity opens up the possibility of organizing effective protection in projects of any purpose. Let's look at several examples of the design of RCDs to evaluate all the existing advantages.
Standard devices
The main purpose of standard devices, for example, the F, FH series, is to protect operating personnel. Direct/indirect contact with live equipment elements, risk of electric shock - such situations are reduced to zero when F, FH series switches are used.

The optimal choice for use in domestic and commercial circuits. The devices also provide fire protection, if there is a risk of cable fire under conditions of long-term exposure to leakage current.
This type of device is designed for implementation in alternating current networks with minimal levels of high harmonics and the absence of direct voltage. Load current 16 – 63A, mechanical cycling reserve – 20,000.
Another example of standard selective devices is the DS series from ABB. They are designed for installation and operation in single-phase network circuits. WITH principle of selectivity will introduce you to the article, which we highly recommend reading.
The purpose of the DS series residual current circuit breakers is to organize protective circuits against overloads and short circuits.The modules ensure precise operation of protective functions against accidental contact with live lines or equipment elements.

A distinctive feature of the serial development of DS is the presence of a visually detectable indication indicating the presence of leakage current. This is one of those protective device designs that makes it possible to prevent fire and signal a violation of electrical insulation. Permissible load 6 – 40A. Cyclicity – 20000.
The “home” differential switch of the AD, BD series is a product of the German company Schneider Electric, and was developed, first of all, for implementation in household electrical networks.
The main purpose is to prevent electric shock from damaging the physical body. Also, this type of protective devices quite effectively and quickly protects electrical equipment, cables, and equipment.
The sensitivity of the machine for direct (indirect) contacts with parts of electrical equipment under voltage complies with the standard (30 mA). Standard sensitivity (100 – 300 mA) is also provided in case of detecting current leakage as a result of fires. A good solution for equipping residential buildings and office premises.
Differential monoblock machines
Monoblock devices function comprehensively, and this is their main difference from standard designs. Cover the entire range of protective functions that modern protection devices should have. True, standard devices also provide users with wide functionality.
A striking example of automatic residual current switches operating in complex functionality are the products of the same company “Schneider Electric”. In particular, the models of the “Multi” series are selective and instantaneous load switches.

The machines, depending on the model, are intended for installation as part of distribution networks of administrative (utility) buildings of industrial production.
These UDTs provide circuit breaking at leakage currents from 10 to 500 mA. A design feature is the ability to be adjusted to exclude accidental triggering (lightning discharges, breakdown through a layer of dust, etc.).
Surge protectors
Perhaps, design developments like circuit breakers, the design of which provides protection against surge voltages, should also be considered a separate type of device.
As a rule, this type of device is endowed with ultra-high performance, a sensitivity level of 10 - 30 mA in case of activation upon touching live surfaces. These same circuit breakers guarantee reliable protection of equipment from overcurrents.

The range of rated currents here is usually 6 - 63A at voltages of 230 - 440 volts. The switching capacity reaches 4500A. Structurally, they are produced for power supply via 2 or 4 poles.
Switches with characteristic “A” appear to be from the same series, but slightly modified. A good example is the AD12M series, where the expansion of protective functionality is noted. Among the additions is a shutdown function in case the mains voltage rises above 265 volts for 0.3 seconds.
It should also be noted that devices endowed with characteristic “A” have significant differences from the design of differential automatic machines with characteristic “AC”. The first option is capable of responding to a constantly pulsating differential current and a sinusoidal current.
Mobile residual current devices
Industry (foreign and domestic) produces another type of automatic differential switches in a mobile type design. That is, we are talking about portable devices controlled by differential current.
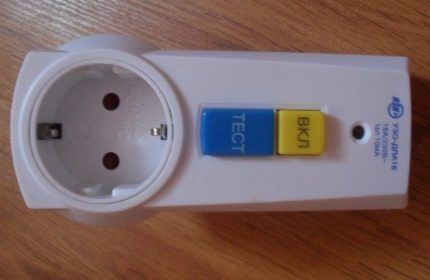
Such mobile modules are made in the form of a miniature block that is simply inserted into a household outlet. Meanwhile, this type of device is intended for use indoors, included in the group of especially dangerous (highly dangerous) premises.
These devices are often installed as additional modules to existing ones residual current devices.
The same type of device, a portable configuration, is recommended for use in domestic conditions to protect children and the elderly. As is known, the resistance of the body of young and old organisms is somewhat different from the same value of the body of a middle-aged person.
Therefore, portable RCDs are designed structurally as devices that have an increased level of response setting. This setting value usually does not exceed 10 mA for mobile type devices.
Portable machines, for example, the UZO-DP series, are considered optimal protection for private urban and country real estate - cottages, country buildings, garages, etc.
RCD (UDT) marking on the device body
It should be noted that the case characteristics (designations on the case) of modern devices show almost complete information regarding the electromechanical and temperature parameters of the devices.
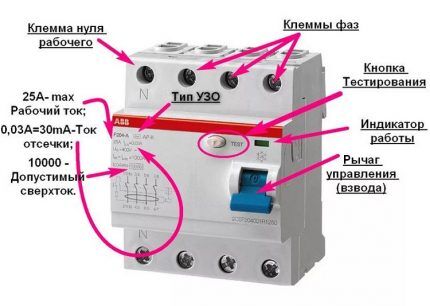
In fact, the user does not even need to refer to the accompanying documentation, since, knowing the designations, all information can be obtained by reading the information from the front of the case.
Among the designations, it is recommended to study the graphics showing the characteristics of the machines regarding the operating conditions: “A”, “B”, “AC”, “F”, which determines the sensitivity of the device to alternating and direct current of various forms.
The abbreviation of devices often reflects their typical and serial affiliation. For example, “AD12M” is a differential automatic machine, serial number – 12, modernized. Or this: “VD63” - differential switch, 63 series.
True, there are models (usually imported) that have a somewhat confusing abbreviation, say, FH200. Here: symbol F is the device series, H is the housing version, 200 is the serial number.
Or another example: a device designated by the abbreviation DS. The first symbol is understandable without “translation” - differential. The second indicates that the device belongs to the category of selective devices.
A question of choosing between differential circuit breaker and RCD requires detailed study. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material that explains their differences, specifics of use, as well as advantages and disadvantages.
How to choose a differential current device?
Residual current devices are selected in the same way as they do, for example, with circuit breakers.

That is, the choice is made based on traditional criteria for selecting electrical equipment of this type:
- Purpose of application.
- Compliance with load current.
- Response sensitivity criterion.
- Case design.
For use in everyday life, the choice usually falls on single-phase devices with characteristics “AC” or “A”. For use on household networks of residential buildings, it is better to take devices with a sensitivity of 10-30 mA (to touch) and 100 mA (fire protection and short circuit).The case design is as convenient as possible for installation and operation.
It should be noted: the differential current device is always mounted in series with the circuit breaker. Therefore, the current characteristics of both devices must be the same, or the rated current of the UDT must be higher.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Even more interesting information about the design, types and operating principle of diffautomats can be found in the following video:
Residual current protective devices are actually circuit breakers supplemented with a sensitive leakage current detection system.
It is mandatory to equip electrical networks with such devices, the implementation of which involves the risk of contact between people and live parts of the equipment. Modern design schemes by default assume the introduction of UDT.
Would you like to talk about how you selected a differential switch to protect your home or country network? Do you have useful information on a topic that is worth sharing with site visitors? Please write comments in the block form below, post photos and ask questions.



