RCD for water heater: selection criteria + diagrams and connection rules
Installation of a boiler operating on electricity must be carried out using protective shutdown equipment.The presence of such devices allows you to avoid electric shock and fire of wiring.
But there are many RCD models for water heaters with different characteristics. You need to choose a protection device wisely, without confusing it with other machines and switches.
We will tell you how the RCD works, what the differences are between the protective device and the differential circuit breaker, we will explain, and we will also explain what parameters must be taken into account when choosing a differential switch. In addition, we have prepared a detailed diagram for connecting the RCD to the boiler and identified possible installation errors.
The content of the article:
Why does a water heater need an RCD?
An electric boiler combines water and electric current, and with the slightest malfunction in the water heating element, this is a direct path to fire and electrical injuries. The safety of the water heater power supply must be given special attention.
With proper use, this electrical appliance will fully fulfill its service life, but if errors are made during its installation, problems may arise that lead to repairs.
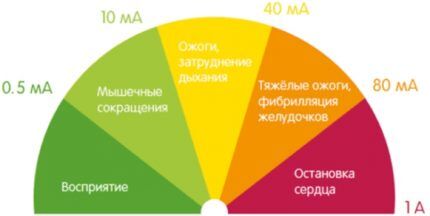
Main purpose RCD – break in the power supply circuit of the electrical installation (its protective disconnection from the network) when a leakage current occurs.On the one hand, this protective switch prevents electric shock to a person, and on the other hand, it prevents overheating of the wire cores.
If the heating element or the cable suitable for it is suddenly damaged, then the condensate outside and the water inside the boiler turn into a natural conductive element, and when it comes into contact with them or the body of the water heater, a person is hit with a leakage current.
The result is discomfort, cardiac arrhythmia and possible death. It all depends on the strength of the applied electric current in amperes.

When a powerful leakage current appears in the circuit, the wires begin to operate at extreme levels. But the cross-section of the cores is simply not designed for such loads. As a result, the wire begins to get very hot, burning through the insulation. And this inevitably leads to an increased risk of fire in the house.
Thus, it is not recommended to connect a water heater to the electrical network without an RCD.
The most common RCD triggering situations are:
- damage to the wire and short circuit of the exposed wire to the boiler body;
- damage to the insulation layer in the tubular electric heating element;
- incorrect selection of parameters of the protective device;
- incorrect connection diagram of the water heater to the power supply;
- malfunction of the leakage current protection device itself.
In all these cases, in the absence of an RCD, human touch to the body of the water heater or the water heated in it is fraught with serious injury.
The difference between a residual current device
It is necessary to clearly separate the RCD (differential switch) and the differential circuit breaker (differential machine, residual current circuit breaker, RCBO). They have slightly different purposes, they work fundamentally differently, and their internal structure is also different.
The RCD reacts exclusively to leakage current. A difavtomat is a more complex device, part of which is a protective shutdown device. The differential circuit breaker is triggered not only by the current leaks described above, but also by short circuits and overloads in the electrical network.
In addition to the RCD, the RCBO additionally contains thermal and electromagnetic releases that respond to those same ultra-high currents and short circuits.

The main unit of the RCD is a differential transformer with three windings (input, outlet and control). The electric current passing through the protective device excites magnetic fluxes with directly opposite poles on them. In the absence of leaks, when the water heater is working properly, the sum of the currents is zero.
But if the heating element breaks down or the insulation breaks down, if a person takes hold of a bare wire (or the metal body of the boiler), then through his body the electric current will begin to flow into the ground - as a result, the sum of the currents will turn from zero to positive.
Then the balance in the transformer is upset and the EMF acting on the internal relay instantly opens the circuit, and the RCD is triggered.
Additional information about the differences between an RCD and a difavtomat, as well as the choice of a load disconnect switching device, is presented in this article.
Types of differential switches
RCDs installed with water heaters and other electrical appliances are divided according to the nature of the leakage current, operating current, number of phases, as well as the presence/absence of a delay and the technology of operation of the protection device.
All RCD models according to the type of leakage current are divided into three types:
- "A" – designed to be triggered by alternating and pulsating electric current;
- "AS" – inexpensive household devices that operate only from alternating current;
- "IN" – industrial options designed to operate in networks with alternating, direct and rectified electric current.
If the RCD marking on the body contains "S", then this is a device with an adjustable selective response delay. It breaks the chain only after a strictly set time, and not immediately. Such devices are used in cascade protection systems with multiple circuits. They are practically not used in everyday life.
According to the principle of circuit breaking, RCDs are:
- electromechanical;
- electronic.
Electromechanical models do not require separate external power and are more reliable. However, they also cost more than the latter. But, despite the high price, it is recommended to install electromechanical devices.
Electronic analogues During voltage surges, the efficiency of the device decreases - in such situations, their response time increases. Plus, if the neutral wire is accidentally damaged, such an RCD will simply stop working without power.
How to choose a protection device
The operating current of the RCD determines the maximum permissible load in the circuit that will pass through it. It must match the power of the water heater.
For example, if a boiler consumes up to 2.3 kW, then the protective device should be rated at 10 A. For heaters of 5.5–7 kW, a 32 A device is needed. But for boilers of 7–8 kW, a 40 A RCD is required.

The leakage current is indicated in mA (milliamps). According to electrical rules, its calculation must be made based on 0.4 mA for each Ampere of operating electric current. Plus, 10 µA per meter of wire to the water heater is added.
It is not for nothing that RCDs are recommended to be installed directly next to the boiler in order to exclude the influence of the second parameter in the calculations.
The shape and size of the protective device under consideration can be mounted on a DIN rail in a switchboard or in the form of a block with a plug in a regular socket.
There are models of water heaters on sale that initially come with RCDs built into the cable. All parameters of such protective devices are already pre-calculated for a specific boiler; they just need to be plugged into a power outlet.

One more moment selection of RCD – this is the presence of natural current leaks in almost every electrical appliance. If they exist, they are indicated in the technical data sheet of the water heater.
The nominal parameters of the protection device must exceed these rating data at least three times, otherwise false alarms will constantly occur.
Among the best manufacturers of differential switches are:
- Swedish-Swiss ABB;
- French Legrand And Schneider Electric;
- German Siemens And AEG;
- Russian "KEAZ", IEK And DEKraft.
European manufacturers have slightly higher prices. At the same time, products from Russian companies are often in no way inferior in quality.
Connection diagrams for electric boilers
For a water heater, the current leakage protection device can be installed directly in the apartment (cottage) electrical panel or directly on the wall near the heating device.
The principle of the connection sequence is the same in both cases - boiler, RCD, line circuit breaker, meter and general circuit breaker. In this case, the RCD and the circuit breaker of a specific line with a socket for the water heater can be swapped, both diagrams are correct.
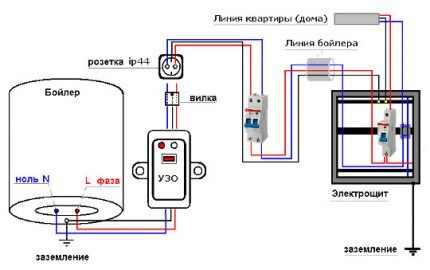
The domestic water heater should be connected to a separate branch from the electrical panel. Moreover, ideally there should be no sockets or other electrical appliances on it.
A boiler is a rather dangerous device.It is best if the protective device only works for him. This will both increase the safety of operating the heater and make it easier to identify problem areas throughout the wiring around the house.
If the RCD is installed next to the water heater, then the wire from the protective device to the machine in the panel will be unattended. If the insulation on it is damaged, the boiler protection device simply will not work. It won't even notice the flowing electric current.
However, boilers are often installed in bathrooms where there is high humidity. It’s also good if there is an additional common RCD in the electrical panel for the whole house, at least it will turn off the network. Otherwise, such a breakdown will inevitably lead to electric shock to a person who decides to take a shower.
Possible installation errors
Mistake #1. In order for the RCD to work correctly, contacts between the “working zero” and “ground” are not allowed in the protected circuit. Each of these wires must have its own bus. At the same time, “grounding” is not present at all in connecting the protection device. This conductor is not connected to it anywhere.
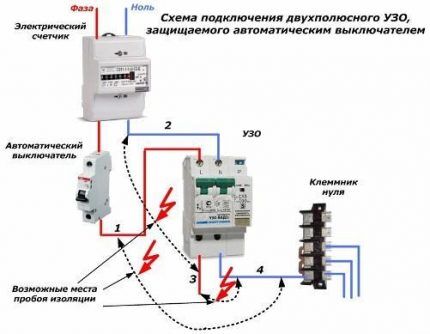
Mistake #2. The operating current of the RCD is selected to be the same or slightly exceed the operating current of the machine in the circuit. The only way circuit breaker will be able to protect the protective device itself from overloads.
Mistake #3. Inexperienced electricians often install sockets and RCDs directly under the water heater. This is strictly not recommended.
Leaks from hot water titanium cannot be completely excluded, and with such a layout of sockets and other electrical appliances with exposed wires under a potential “waterfall”, tragedy is not so far away.
Mistake #4. The water heater cannot be connected only through an RCD or one automatic circuit breaker. These devices complement, but do not duplicate each other. They protect the boiler from fundamentally different problematic situations in the electrical network.
Mistake #5. If you choose an RCD that is too sensitive (with a low leakage current), then it will trigger too often to block the circuit. The water heater will constantly turn off. As a result, the water will not heat up normally and the boiler may fail due to continuous switching on/off.
After completing the electrical installation, you must check the functionality of the RCD. To do this, most water heaters have a “TEST” function, which simulates current leakage. If everything is connected correctly and the protection is working, then the latter will trip and de-energize the boiler.
Otherwise, you need to look at where and what is not working as expected. It is recommended to carry out such checks once a month and thereafter.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
There are few nuances in installing a residual current device, but they exist. To make it easier for you to understand these issues and choose the right device, we have made a selection of relevant videos. They describe in detail the principles of operation and diagrams for connecting an RCD to a network with a water heater.
Connecting protective devices in networks without grounding:
What is an RCD, why is it needed in everyday life (using the example of connecting a washing machine):
It is not recommended to connect the water heater to the network without an RCD.Only a protective device that monitors current leakage can protect users. There are no difficulties in installing such a device; you can connect it to the power circuit yourself by selecting the parameters for the electric current.
Do you have personal experience in selecting and connecting an RCD to a water heater? Do you want to share your accumulated knowledge or ask questions on the topic? Please leave comments and participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.



