What is needed to design ventilation: the regulatory framework and the procedure for drawing up the project
Ventilation is one of the most important life support systems.After all, comfort and freshness in an apartment or private house directly depend on the correct design, as well as the subsequent installation of an air exchange regulator. Agree, due to constant ventilation, allergens, dust and extraneous noise enter the room.
With the help of ventilation ducts, you can solve the problem of a safe, uninterrupted supply of clean air. The reliability and durability of ventilation equipment largely depends on the preparation of a competent project.
What is needed to design ventilation will be discussed in our article - let's talk about the advantages of drawing up a plan and its main components. Let's consider the main stages and features of the ventilation system design process, supplementing the material with visual photos and useful videos.
The content of the article:
The importance of ventilation system design
Ventilation involves organized air exchange in the room. The system provides both an influx of fresh air and an intake of exhaust air, including odors and gases. Ventilation can also be only supply or exhaust, depending on the purpose of the building. We described in detail the features of the supply and exhaust system in this material.
Natural air exchange is possible through cracks when windows and doors are not tightly closed.But this type of ventilation is not effective enough and, as a rule, is not able to provide proper microclimatic conditions.

It is possible to install equipment without design - this is exactly what new owners of apartments and houses often think, but in the end it turns out that the system does not work at full capacity, does not function correctly, or does not function at all.
Installation without preliminary design can lead to the following violations:
- incorrectly selected diameter of air ducts;
- lack of fresh air supplied to the premises;
- improper installation of ventilation units;
- poor quality installation of equipment.
Poor ventilation promotes formation and spread mold and mildew, and this is fraught with an increase in cases of illness in households. For normal human life, it is important to maintain optimal room temperature and effective air exchange.
Key design benefits
The preparation of the project ends with the issuance of a document to the customer, which presents the concept of a ventilation system for the apartment, private house, office or any other room. The project determines the exact location of air ducts, ventilation grilles, and other equipment.
Using the plan, you can also find out the characteristics of individual components and equipment of the ventilation system, and coordinate the placement of elements taking into account the interior and design of the room.

The project minimizes further conflict situations between the customer and the contractor and allows us to assess the correctness of the future installation. The presence of the document provides an opportunity to evaluate the correctness of the proposed options.
Regulatory framework for design
When planning ventilation systems, a number of domestic and foreign regulations should be taken into account. We will now briefly review the main ones.
Brief overview of domestic regulations
Forced ventilation involves the use of powerful ventilation equipment, so the design is determined taking into account the reserved capacity in terms of power supply.
Ventilation is regulated in conjunction with heating systems SNiP 41-01-2003. This becomes possible due to the extremely significant influence on the heat balance of a capital construction project, both under construction and at the reconstruction stage.

For constructed facilities, the design of ventilation systems involves a large number of technical solutions.
But this is only possible if plans for all systems are drawn up, including heating, construction and power supply. In this case, it is possible to make adjustments to documents being developed in parallel.

The design of the ventilation system must be carried out taking into account regulations.
The list of mandatory building codes and regulations includes the following documents:
- "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning" - SNiP 41-01-2003;
- "Building climatology" - SNiP 23-01-99;
- "Protection from noise" - SNiP 03/23/2003;
- "Public structures and buildings" - SNiP 2.08.02-89;
- "Fire safety" - SNiP 21-01-97;
- “Single-apartment residential houses” - SNiP 02/31/2001;
- "Industrial buildings" - SNiP 31-03-2001;
- "Residential multi-apartment buildings" - SNiP 01/31/2003;
- "Public buildings" - SNiP 05/31/2003;
- "Warehouse buildings" - SNiP 04/31/2001;
- “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements” - SanPiN 2.1.2.1002-00.
You should also take into account some state standards.
Among which:
- "Noise" - GOST 12.1.003-83;
- “General sanitary and hygienic requirements for the air of the working area” - GOST 12.1.005-88;
- "Air equipment" - GOST 24751-81;
- "Residential and public buildings" - GOST 30494-96.
When developing a project, territorial acts can also be taken into account, for example, for the capital it will be the Government Decree and the Moscow Urban Planning Code, Moscow City Building Codes.
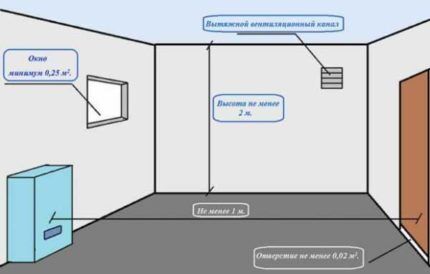
The development of a ventilation system project can be carried out not only according to Russian regulatory documents. As an alternative, foreign standards regulating air quality in a building are also suitable.
Design according to foreign standards
In January 2003, the European Directive on energy efficiency in premises 2002/91/EC came into force. The legislation applies to the countries of the European Union. An action plan adopted in 2006 aims to improve energy efficiency in the construction sector.
To implement the requirements in practice, the following standards have been developed:
- Energy consumption calculation for heating, as well as cooling of premises and other energy characteristics are provided EN ISO 13790.
- Initial values of microclimatic conditions buildings for the design and assessment of energy performance, including thermal comfort, air quality, acoustics and lighting.
- Technical requirements to the ventilation system, prescribed in the standard EN 13779.
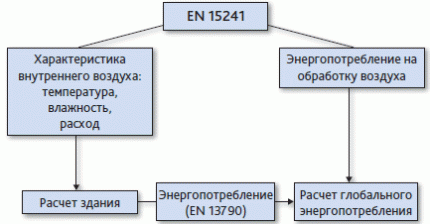
- Description of methods for calculating energy losses in ventilation systems and infiltration - EN 15241.
- Airflow speed calculation indoors reviewed in EN 15242.
Energy consumption for the ventilation system is determined according to the standard EN 13790, the main characteristics of the premises are considered, taking into account the internal environment - the level of infiltration and the ventilation rate.
Air flow calculations for hybrid, mechanical and passive ventilation are described in the standard EN 15242.
Specific requirements and rules for designing ventilation systems are specified in the standard EN 13799, the document also includes design guidelines. Its applications extend to exhaust and supply ventilation mechanical type, but the document is not intended for residential premises.
For private houses and apartments there is a standard CEN/TR 14788, which provides typical ranges of values that are advisory in nature and are used only if other parameters are not available.

The use of foreign experience in design is natural, since in this case more stringent requirements for quality of life are taken into account.
Stages of designing a ventilation system
The scope and content of the project will vary depending on its complexity, but the main components will be approximately the same. So, at the preliminary stage a technical project is drawn up, which is essentially Feasibility study (feasibility study). At this stage, specialists visit the site to record initial information, including the purpose and functions of the structure or premises, its area, and the number of residents/employees.
The initial stage ends selection of equipment, consideration of the main characteristics and properties.Optimization decisions are made for interaction with other engineering systems. A calculation of air exchange for each specific room carried out in accordance with technical conditions, construction and sanitary standards.
Further development calculation diagram diameter and area of air ducts and the noise level is determined. Drawings are sent to coordination. The project designer or direct customer can make changes.
At the next stage, after agreement, prepare a package of documents on plumbing, construction work and electrical supply.
Only after completing all the listed stages is the ventilation installation and its launch.

Equally important in design is the rational distribution of funds intended for the purchase of equipment and materials. The modern market offers a huge range of equipment and devices from various manufacturers in different price categories.
To purchase equipment you will need special calculations:
- Using the area and purpose of the room indicated in the floor plan of the structure, the required productivity is determined. The indicator is calculated in m3/h.
- Taking into account the performance, the air temperature at the outlet of the ventilation system and the minimum ambient temperature determine the heater power. The duct heater is used exclusively in the cold season as a building heater.
- Fan characteristics depend on the length and complexity of the route.To calculate the required power, the type and diameter of the air duct, diameter transitions, and the number of bends are used.
- Calculation air flow speed in air ducts.
- Air speed affects noise levels.
The project budget is calculated after all calculations are completed and the proposed ventilation ducts are drawn on the building plan. The drawn up technical specification must be approved by the customer and departmental structures.

Features of project documentation
Project documentation can be divided into three parts:
- explanatory note;
- set of drawings;
- additional information.
IN explanatory note contains a brief description of ventilation, technical specifications for the arrangement of ventilation routes, power and heat consumption, and the value of air exchange in the context of premises.

IN set of drawings includes a distribution diagram of ventilation equipment with detailed components and a structural diagram, drawings of components, layout plans for routes and air ducts. This part of the project also includes rules for maintaining communications and additional information for installing a ventilation system.
A complete package of project documentation is impossible without additional information - certificates, licenses, integration tables, axonometric diagrams and equipment specifications.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Design errors in ventilation are discussed in detail in the following video:
The basics of designing a ventilation system in a private house or cottage can be learned from the video:
Everything you need to know about ventilation in just 3 minutes:
Indoor air quality is determined by the air exchange rate. And microclimatic conditions largely depend on a properly designed ventilation system design. The information described above will allow you to easily select the right expert firm and evaluate the proposed options.
If you encountered difficulties at the design stage, please share your experience with other users. You can also ask your questions regarding the development and calculation of a ventilation system plan in the block located below under this publication.



