Standard diagrams and rules for drafting a heating system for a one-story private house
The heating system in a one-story house can be installed according to various schemes. When choosing the optimal option, the project budget and the availability of fuels are taken into account.
As well as the features of the structural elements of a private residential building: the area of the facility, the materials used in construction, the presence of a warehouse for the installation of boiler equipment.
Let's figure out what rules should be followed when designing a heating system, and what actions should be avoided in order to avoid heating problems in the future.
The content of the article:
- Requirements for individual heating
- Classification of heat supply systems
- Features of coolant circulation
- Single-pipe heating system
- Two-pipe heating system
- Lower and upper wiring diagram
- Types of two-pipe horizontal layout system
- Rules for drafting a heating system
- What information do craftsmen need?
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Requirements for individual heating
The heating unit must be planned so that it matches the architectural design of the building. The location of all functional elements should be as convenient as possible for operation and carrying out scheduled repairs without compromising the structural integrity of the house.
Basic requirements for modern heating systems:
- energy efficiency;
- easy installation and maintenance;
- high heat transfer rates;
- complete/partial independence from electricity.
Before you begin designing a heat supply, you need to select the most suitable and economical source of thermal energy - stove or fireplace, water, steam, air or electric heating.
And we still have to decide on the basic piping diagram for heating a one-story private house, accurately calculate the power and objectively assess the load on the system, taking into account all the features.

A properly installed heating distribution line makes it possible to organize uniform heating of the air in all rooms of a private house in a minimum amount of time.
Classification of heat supply systems
In one-story buildings, cottages, and houses, autonomous heating systems or those dependent on external power sources are installed. The former operate on liquefied gas, diesel, and solid fuel. The second ones require connection to the electrical network or main gas pipeline.
Another difference between heat supply options is the need for human participation in the operation of the equipment.
Automated systems do not require 24/7 monitoring or manual configuration. Maintaining a comfortable temperature inside the building is ensured by thermostats and temperature sensors.
These devices regularly monitor changes in temperature indicators, which allows the heating system to take into account all factors that directly affect the temperature in the room: solar heat, radiation from household electrical appliances, heating from lighting lamps, etc.
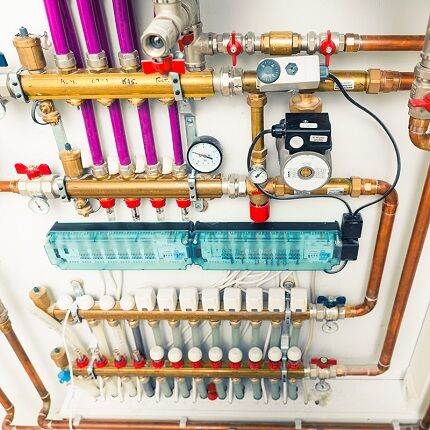

Automation makes it possible to change the temperature in the house at different times of the day.
When classifying heating systems, the following characteristics are taken into account:
- type of coolant - air, water or steam, combined;
- type of fuel used — gas, electric, peat, wood, pellet, coal;
- method of transporting working fluid — with natural and forced circulation;
- coolant movement progress — passing and dead-end;
- method of connecting boiler equipment — one-pipe and two-pipe layout;
- wiring diagram - with a vertical or horizontal distribution line, upper or lower, combined.
In multi-apartment buildings, the vertical wiring pattern dominates, while in single-story buildings, a horizontal layout is found. Combined heat supply methods prevail in high-rise new buildings.
Features of coolant circulation
It is effective to install heating systems in private low-rise buildings with liquid coolant. To do this, the pipes are filled with antifreeze or water.
The movement of the working fluid along the heating circuit can be carried out in natural or forced mode. The water heated by the heat generator enters the distribution pipeline, and then to the radiators. This part of the contour is called the forward stroke.
After entering the batteries, the coolant liquid cools down and is quickly sent to the boiler for heating. This interval is called the return stroke. To speed up the transportation of coolant, a circulation pump is installed inside the system.
Natural fluid movement
In the heating circuit, horizontal pipelines are sloped, thereby creating conditions for the movement of working fluid under the influence of gravity.
An open expansion tank is also installed - a special tank for receiving excess water to ensure proper and safe operation of all components of the utility network.

Heating systems operate with natural circulation due to the different densities of heated and cold coolant. According to the laws of physics, hot water rushes upward.
In a closed circuit, cold flows inevitably displace heated ones, forcing them to move in the opposite direction from the heat source. A moving fluid with kinetic energy potential passes through all batteries, giving off heat. After returning to the boiler equipment, the cycle repeats.
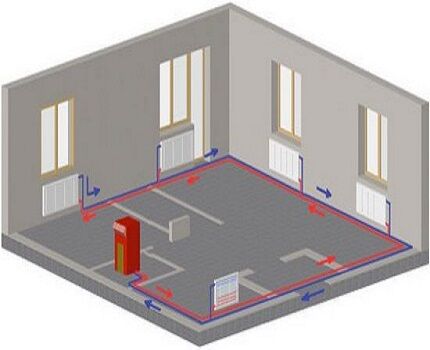
In order for the gravity-flow design to function fully, the boiler is installed below the central axis of the main circuit. Usually the heat generator is mounted in a recess in the floor, but sometimes in basements, with the exception of gas units.
The supply pipeline from the boiler is raised vertically to the highest possible point. This creates additional space in a closed loop for acceleration of the working fluid.
The number of necessary shut-off valves in gravity heating systems is reduced to a minimum. Strict requirements are imposed on the diameter of the installed pipes - it must be at least 32 mm.Since the speed of water movement in the circuit is insignificant, in order to increase the heating efficiency, only large-diameter pipes are installed.
An autonomous heating system, the operating principle of which is based on the natural circulation of the coolant fluid, is the simplest. Such a home heating project is easy to implement in practice. However, this option is only suitable for small private buildings, since the length of the heating circuit is limited to 30 meters.
The main advantage of gravity systems is complete independence from electricity. Read more about heating systems with natural coolant circulation Further.
Forced circulation in the system
For private buildings with a total area of more than 60 square meters. m. they design heating with forced transportation of working fluid. Install in a closed loop circulation pumpto ensure accelerated movement of hot coolant to the radiators, and cooled coolant to the heat generator.
Installation of pipes in the system can be carried out without a slope in the horizontal plane. Water moves due to the difference in pressure that occurs in the section of the line between the forward and reverse flow of the liquid.

A significant drawback of a coercive system is its energy dependence. For constant circulation of water in the circuit, continuous operation of the pump is necessary, and its performance directly depends on the power supply.
In the event of a sudden power outage, the equipment simply will not be able to pump liquid. Therefore, experts recommend additionally installing backup generators that can provide stable, uninterrupted heat supply even in unforeseen situations.
Such schemes can be used when installing heating in buildings of any size. You just need to select a circulation pump with suitable power ratings and provide power supply.
Single-pipe heating system
Only one main line is installed in the house, under or above the floor, with batteries connected in series. In such a heating circuit there is no distribution between the supply pipe and the return pipe.
Along the perimeter of a one-story building, only one round pipe with a diameter of at least 32 mm is installed, which is conventionally divided in half. The half leaving the heat generator is called the supply, and the second part of the line is called the return. Radiators/convectors are mounted into the loop using a welded or seamless pipe of small diameter.
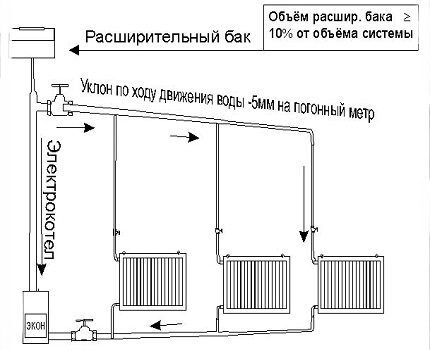
The single-pipe circuit includes the following functional elements:
- heat supply source (boiler);
- heating radiators;
- expansion tank;
- pipe routing elements.
The heated liquid flows alternately into the heating radiators, each time giving off part of its heat. After this, it is already cooled and returned to the boiler for the next heating cycle. Each battery loses heat and the last element in the chain remains the coldest in comparison with the others.
There are several ways to optimize the operation of a single-pipe system.You can additionally install special thermostatic valves for heat exchangers, balancing valves with adjustable hydraulic resistance or compact ball valves. Such equipment helps normalize the heat supply to the batteries.
Another way is to increase the number of sections of each subsequent radiator in the heating circuit. You can also install a circulation pump. The pumping device is connected at the end of the return line - the place where the working fluid has the lowest temperature.
The single-pipe heating option is easy to install and put into operation. Heat loss is minimized, since absolutely all communications are located inside the living rooms of a private house.
Such a scheme can be organized in the form of a system with horizontal wiring and forced movement of the coolant or a vertical heating network with natural, forced or combined movement of the working fluid.
We also recommend reading our other material, where we discussed in detail single pipe heating system for a private home.
Horizontal wiring method
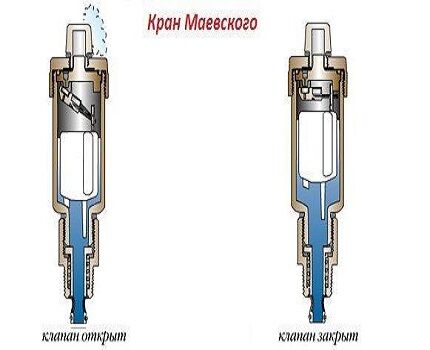
Installation of the supply pipe in a horizontal plane is carried out with the required slope in the direction of movement of the heated water. In this case, all batteries around the perimeter of the house must be installed at the same level. For releasing air from radiators use Mayevsky taps or automatic air vent devices.
The horizontal line can be installed in the floor structure itself or mounted above it. To avoid heat loss, in the first case it is necessary to insulate the pipes.
Vertical wiring option
In such a system, the transportation of the coolant liquid is ensured by a natural circulation mode, and therefore there is no need to install an additional pump. Energy independence is the main advantage of a single-pipe vertical home heating system.
With this method of wiring, the working fluid, heated to a given temperature, moves up the riser, after which it enters the batteries through distribution pipes. The operating efficiency of a vertically located single-pipe system is achieved by installing the main line at a slope, as well as by installing large-diameter pipes.
Of course, a massive pipeline will not decorate the interior of living rooms. But this obvious drawback can be avoided by installing circulation equipment in the system.
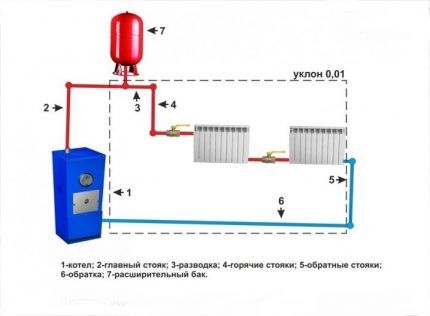
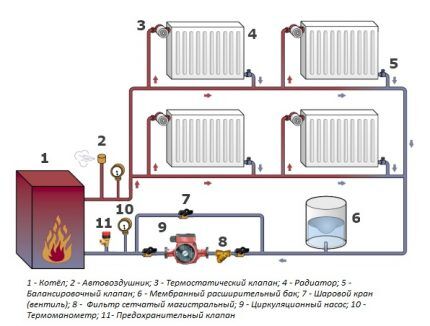
Two-pipe heating system
The main difference between a two-pipe house heating scheme is the presence of one pipe for supplying water and another for returning it. Moreover, the first one receives hot liquid, while the second one sends the already cooled coolant to the boiler.
Each battery is served by both a supply and a return riser. This makes it possible to regulate the amount of heat received by individual radiators. If we do not take into account the cooling of the coolant in the pipes, it turns out that all heating elements receive liquid at the same temperature.
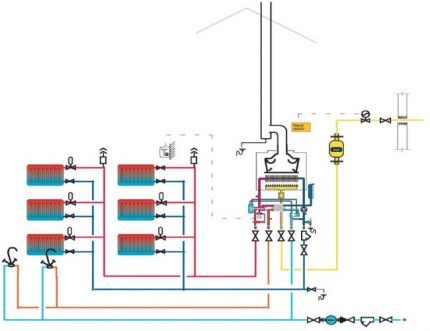
The two-pipe heating circuit includes:
- heat generator;
- batteries;
- expansion tank;
- pipes;
- shut-off valves and special devices for air release.
A pipe with hot water runs from the boiler to the expansion tank. Then it is connected to the distribution line in the heating circuit. In addition, an overflow pipe is cut into the tank to promptly drain excess coolant into the sewer system.
Pipes emerge from the bottom of the heat exchangers, combined into one return line. Through it, the cooled coolant returns back to the boiler. The return pipeline is laid strictly parallel to the upper pipes. It must pass through all rooms where the hot water supply line is installed.
Two-pipe forced systems are considered the most efficient for one-story houses and cottages, but they can also provide heat for two-story large buildings.
And these allow you to evenly and very quickly warm up the room and maintain different temperature conditions in the rooms. In addition, dual-circuit design makes it possible to organize not only heating of the house, but also hot water supply.
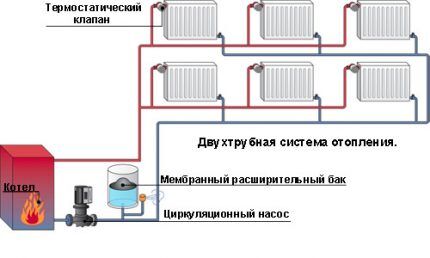
Closed heating systems with forced circulation are installed in two versions - with horizontal and vertical wiring.
The first method is implemented in one-story houses with a long pipeline. In such situations, connecting water radiators to a heating circuit with horizontal wiring is the optimal solution.
With the second wiring option, the riser is located vertically, which makes it possible to use the scheme even in multi-story buildings. In such systems, air does not accumulate, since the resulting bubbles instantly rise in a vertical direction, directly into the expansion tank.
Lower and upper wiring diagram
When distributing the system at the bottom, the main line is laid in the basement or basement. It is also possible to install pipes under the floor. The coolant enters the heating equipment from the bottom up.
The mixture of gases is removed through a special air line connected to the risers. In case of unforeseen emergency situations, the return and supply risers are equipped with special shut-off valves.
To implement a scheme with an upper distribution line, the expansion tank is mounted at the highest point of the pipeline. The network is branched in the same place.
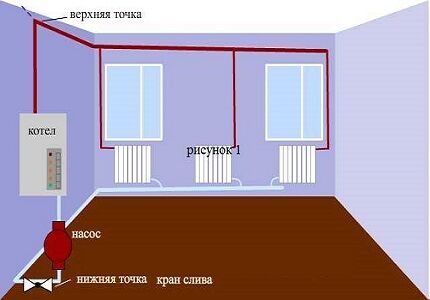
Types of two-pipe horizontal layout system
The most common option for heating a single-story residential building is a two-pipe heating system with horizontal wiring.
To organize such a heating circuit, the following schemes are used:
- tee or otherwise perimeter;
- collector, otherwise radial.
According to the tee scheme, the pipes are connected by tees, the pipelines are laid around the perimeter of the room, and connected in series to the devices. The coolant in the perimeter system flows from one battery to another, cooling somewhat along the way.
Based on the movement of the heated and cooled coolant, tee options are divided into associated and counter. In a dead-end circuit, hot and cooled water move in different directions. In the associated heated and waste coolant flows in one direction.
IN collector circuit From the central organ of the system, the collector, pipes are led to each of the radiators, due to which the coolant enters all devices simultaneously.
The principle of the device resembles the sun's rays emanating from a heat flow distributor usually located in the center. In radial types of wiring, the coolant moves only in different directions.
Rules for drafting a heating system
A well-designed project allows you to launch the most efficient and multifunctional heat supply system.
It must operate smoothly in the climatic conditions characteristic of the specific area where the one-story house is located, and be easy to operate.
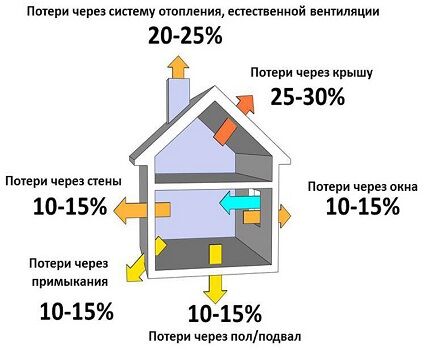
Drawing up a high-quality project for heating a one-story house and accurately calculating the system parameters are carried out according to a specific plan:
- At the first stage, it is necessary to formulate a technical task taking into account all the requirements and details for the heating system.
- The second step is collecting information on a private property. Specialists must take all the indicators to draw up a diagram of the heating circuit.
- The next stage is the calculation of thermal transfer. To do this, you need to carry out calculations and select the optimal heating scheme that will meet basic building standards and the individual requirements of the customer.
- When all calculations are completed, drawings are made.
- The last stage is the design and delivery of the finished heating system project to the customer.
The main design task is to calculate the correct area of heating equipment and select suitable pipeline diameters. And also determine the performance of pumping devices, calculate the insertion points of valves and system components. Therefore, it is advisable to entrust the process to professionals.
If you really want to carry out the calculations yourself, we recommend reading the material where we carried out an example heating system calculation for a private home.
What information do craftsmen need?
Before installation work begins, you should discuss all the nuances with specialists and show your vision of the heating system.
Masters must provide:
- complete information about the materials from which the building’s roof, wall coverings, and window structures are made;
- one-story house plan;
- drawings where the locations of plumbing units are marked.
The service life of a heat supply system is influenced not only by the quality of engineering design and skillful installation, but also by the selected materials, installed boiler equipment, as well as the rational use of heating elements.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video shows a 3-D diagram, design and installation of a single-pipe heating system in a one-story private house:
A schematic representation of a two-pipe polypropylene heating system, the correct connection of boiler equipment and the installation of heating radiators are demonstrated in the video:
The video describes in detail a typical heating project and calculation of heat losses:
Modern heat supply systems are integral attributes of the functioning of private houses, cottages and other construction projects. Professionally executed design is the key to efficient, reliable and long-term trouble-free operation of an individual heating network.
If after reading the material you have questions about the topic of the article, you can ask them in the block below. There you can leave your comment or share your own experience with other site visitors.




Hello.I have a one-story private house. I want to install two-pipe heating from a wood boiler. The upper pipe (supply) will pass under the ceiling.
What are the installation nuances and where should a membrane-type expansion tank be installed? Are unloader and check valves needed and where are they installed? Is there also a need for a valve to bleed air at the V.M. point? Thank you in advance.