Grounding a gas boiler in a private house: standards, device features and checks
Installation of thermal equipment operating on natural gas is a widespread practice both in industry and in everyday life. But household installations are significantly inferior in power and other technical parameters. At first glance, a home gas water heater (boiler) is a simple piece of equipment that makes minimal demands on the potential owner, isn’t it?
Then why is grounding a gas boiler in a private house a mandatory norm and can it be ignored? We will help you figure it out - this publication discusses the reasons for grounding, features of its implementation, norms and rules for testing. Also provided are device diagrams, visual photos and video recommendations.
The content of the article:
Why do you need to ground a gas boiler?
Modern gas boilers traditionally contain control elements made according to the principle of digital high-tech electronics.
Schemes of such equipment contain:
- digital microcontrollers;
- sensitive electronic sensors,
- field-effect transistors and planar microcircuits.
For electronics of this type, the presence of static electricity is “like death.” At the most unexpected moment, a gas boiler may stop functioning due to failure of electronic components from exposure to static microcurrents.
This is one of the main reasons requiring a mandatory grounding loop in gas boiler diagram.

Another no less significant reason for the introduction of grounding is the obvious danger of uncontrolled gas ignition, which creates a high risk of fire or explosion of a gas boiler. Here, again, the notorious static electricity plays its “negative” role, and only the correct design of the grounding loop can help get rid of it. We reviewed the rules for the safe use of a gas boiler in next article.
Grounding standards and rules
Regulatory requirements and rules describing the geyser grounding scheme are presented in an official document PUE.
According to the established standards for grounding a domestic gas boiler in a house, the equipment must be supplemented with an earth circuit, but it does not specifically indicate which circuit should be used - an industrial design or a home-made one.

Meanwhile, regardless of the method of manufacturing the contour grounding system, the PEU document is quite specific clause 1.7.103 the resistance parameters of the loop loop are specified.
For a system built at home or using a team of specialists, the following requirements are relevant: “The total resistance to spreading of grounding conductors... of all repeated groundings... at any time of the year should be no more than 5, 10 and 20 Ohms, respectively, at line voltages of 660, 380 and 220 V three-phase current source (380, 220 and 127 V for single-phase current source). In this case, the spreading resistance of the grounding conductor of each of the repeated groundings should be no more than 15, 30 and 60 Ohms, respectively, at the same voltages.”
In practice, gas service representatives require that the resistance not exceed 10 ohms.
According to the standards of the PEU document, it is categorically unacceptable to use the following elements for grounding for a domestic gas boiler:
- ground lines of fixed household sockets;
- surfaces of heating pipelines;
- surfaces of sewer pipes;
- pipes of stationary gas lines and other pipelines of flammable or explosive liquids, gases, mixtures.
It is allowed to use metal water pipes laid in the ground, reinforced concrete foundation structures that have reliable waterproofing, metal structures of structures located in the ground, etc. as a natural ground electrode (clause 1.7.109 PUE).
If there is nothing nearby suitable for the role of a grounding conductor, it is imperative to arrange an individual grounding circuit.
Arrangement of the grounding circuit of the geyser
So, if you are still in doubt whether you need to ground a domestic gas boiler in a residential building, the answer is clear - need to. Moreover, immediately after the installation of new gas equipment, followed by checking the correctness of the “ground” device.
[adinserter name=”mobile: insert in text -5″]Therefore, it is worth considering the traditional design of the device, the materials and components required to organize the “contour ground,” as well as the testing features.
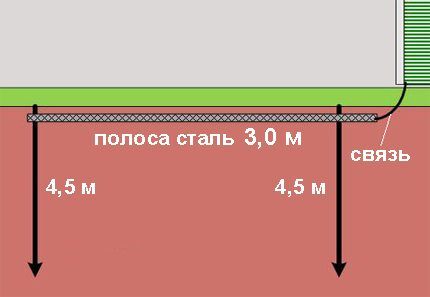
The circuit diagram, as a rule, constitutes the classic version of the mold manufacturing "triangle"immersed in the ground to a depth of at least 0.5 meters. In this case, the corner points of the “triangle” are metal (preferably coated with a layer of copper) electrodes.
The optimal immersion depth of metal electrode pins is 4.5 meters. A metal strip is used as the connecting material between the electrode elements.
Thus, the construction of the “earth triangle” circuit involves the process of driving three metal electrode pins into the ground, followed by making a loading trench between them, where a metal strip is laid and welded to the electrode pins.
According to the same PUE rules, the grounding “triangle” should be installed at least 1 meter from the wall of a residential building. The classic distance between the elements of the circuit electrodes driven into the ground is 2.5 meters.
However, instead of the “triangle” option, it is also quite suitable (PEU is not prohibited) simply a straight metal strip between two electrodes, immersed in the ground, the length of which is at least 3 meters (the circuit design is shown below). The dimensions of grounding conductors and grounding conductors laid in the ground are also indicated in PUE table 1.7.4.
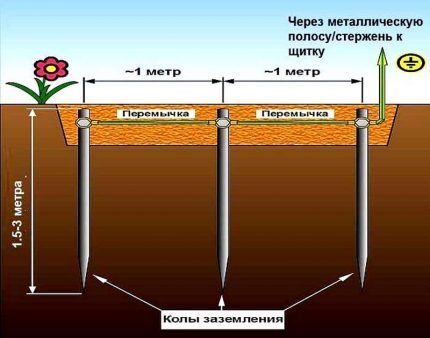

Separately, it is worth noting the technology of immersing metal electrode pins into the ground, taking into account the immersion depth of 4.5 meters.
To immerse a relatively thin-diameter metal electrode pin to such a depth, several short lengths are used, which are connected to one another as they are immersed. Connections are made using special couplings or by welding. (the second option is preferable).
We recommend that you read detailed instructions on choosing a suitable material and arranging grounding with your own hands.
How to connect the ground loop to the shield?
The manufactured and installed circuit element for a domestic gas boiler must be correctly connected to the gas equipment switching unit (usually a three-pin power socket or control panel).
PEU standards allow the use of different types of conductors as a communication line, but stipulates the diameter of the wire depending on the wire material used: copper, aluminum, steel.

Allowed as part of power switching equipment of a gas boiler install RCD (residual current device), but only strictly in the presence of a loop grounding system.It is also allowed to use RCD sockets. This point is noted by the rules of the PES.
Features of checking the grounding of gas equipment
In a situation where a gas service representative checks the correct installation of the boiler, its connection and operation, the question of checking the correct grounding of the home gas boiler does not arise. However, in practice, technical incidents of some kind often occur.
Indeed, the electrical grounding circuit, in fact, seems to be the prerogative of representatives of the service responsible for power supply. This means that the circuit is checked by the electrical service, which is confirmed by the rules of the PUE.

To perform the test, special electrical equipment (laboratory) is required. Using an electrical measuring laboratory, not only the resistance of current flow in the circuit is measured, but also the degree of lightning protection.
However, this option is usually applicable to industrial equipment. For the domestic sphere, as practice shows, much in terms of verification depends on the local rules of each individual region.
Federal legislation specifically mentions only the standards for periodic inspections ( PTEEP appendix 3, clause 26), and also stipulates the rules for preparation of equipment and commissioning (PTEEP, PUE).
According to regulations, it is required to check the grounding of the boiler at least once a year. Based on the results of the inspection, the owner of the gas equipment is issued a corresponding document (Inspection Certificate).We discussed methods for measuring ground resistance in this material.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below demonstrates the sequence in which the activity to create protection for gas equipment is carried out.
Thanks to the video, you can get a complete picture of the work required, the tools used and other subtleties of the process:
As practice shows, it is possible and necessary to supplement a household boiler with a grounding component. Even if the production of such work requires some financial costs from the potential user, it is worth it.
By equipping a gas water heater with a grounding loop, the user of the equipment not only greatly enhances the reliability of the equipment, but also ensures a high level of personal safety..
Would you like to supplement the above material with useful comments? Or do you still have questions about arrangement of the grounding loop? Feel free to ask our experts and other site visitors for advice, write your comments - there is a feedback form below the article.




When installing the grounding loop, you can use iron (chernukha) or necessarily galvanized, copper-plated, etc. iron!
Based on what standards do gas workers require a grounding resistance of 10 ohms?